Sh. I. Navruzova1, Sh. T. Muxamedova2
1Department of Pediatrics (Head.- Prof.), Bukhara State Medical Institute Named after Abu Ali Ibn Sina Ministry of Health of Uzbekistan
2Department of Pediatrics Bukhara State Medical Institute Named after Abu Ali Ibn Sina Ministry of Health of Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
The authors conducted a study on the cytokine status of newborns with perinatal infections in the neonatal period of adaptation. IL-8 acts as one of the criteria for the severity of systemic inflammatory response in newborns. The authors argue that the level of IL-8 in urine can predict the outcome of both early and late neonatal period in newborns with infections. The criterion of severity of both early and late neonatal period in newborns with infections is the concentration of IL-8 in the urine. Prognostic criteria for the severity of CIRS in newborns with non-communicable diseases are: In the early neonatal period: - TNF-α > 20.3 PG / ml in urine; - INF-γ > 9.2 PG / ml in urine; In the late neonatal period: - IL-6 > 56.9 PG / ml in blood; - TNF-α >39.0 PG/ml in blood; - IL-8 >1.1 PG / ml in urine.
Keywords:
Adaptation period, Cytokines, Systemic inflammatory response syndrome
Cite this paper: Sh. I. Navruzova, Sh. T. Muxamedova, Prognostic Criteria of Severity of Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome in Newborns, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 10 No. 2, 2020, pp. 81-85. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20201002.03.
1. Introduction
The systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) is a systemic inflammatory reaction in response to various severe damaging effects of infectious and noninfectious nature, i.e. it "model, multisensory, fazospecificnam pathological process that develops in system damage and characterized by the total inflammatory reactivity of endothelial cells, plasma and cellular blood factors, connective tissue, and in the final stages of microcirculatory disorders in vital organs and tissues" (academician V. A. Chernyshev). I. N. Leiderman is convinced that the systemic inflammatory response (SVO) is a symptom complex that characterizes the severity of the inflammatory reaction in the endothelial cell system. Thus, SVO is the response of organs and systems to inflammation, and SIRS is the symptom complex of the main pathological conditions (respiratory failure, cardiovascular failure, acute renal failure, etc.). It follows that the syndrome of endogenous intoxication (SEI) and CIRS are identical. Both concepts are based on systemic inflammation [2].It is known that generalized production of proinflammatory cytokines (mainly tumor necrosis factor - TNF-α, IL-16, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10) is the basis of CIRS pathogenesis. TNF-α and IL-6 play a leading role in epithelial dysfunction syndrome (SDE). At the heart of the imbalance of pro - and anti-inflammatory cytokines, triggered by a number of trigger factors, a very significant role probably belongs to genetic determinism. With a small aggressiveness of the initiating agent (physiological pregnancy), the activity of cytokines is balanced by their antagonists, and the process stops at this phase. With the predominance of cytokine activity, the situation progresses, the content of proteins of the inflammatory cytokines increases in the bloodstream, the level of TNF-α and endotoxin steadily increases [5]. Among the various methods of research at the present stage, fetal assessment and prediction of pregnancy outcome are possible based on the results of the study of anti-inflammatory cytokines, which play an important role in the development of the immune response of cellular and humoral type and provide processes of intercellular cooperation, growth and differentiation of lymphoid cells, hematopoiesis, angiogenesis, neuroimmunoendocrine interactions [1]. The clinical criterion for CIRS (according to the conciliation conference) is the presence of at least two of the following features:1) body temperature above 38°C or below 35.5°C;2) heart rate more than 165 in 1 min;3) respiratory rate more than 60 in 1 min;4) the number of leukocytes in peripheral blood more than 14 • 109 / l or less than 5 • 109 / l (or at least 10% of immature cells);5) thrombocytopenia less than 120 thousand [2]. The term SIRS and its criteria have been widely accepted, but discussions in the medical community have suggested that SIRS criteria are not specific and do not adequately characterize this clinical condition. Determination of the level of proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, which is now widely used for research and practical purposes. However, despite the significant physiological role and diagnostic value of these studies, it is impossible to carry out an unambiguous interpretation of the state of the cytokine system. Perhaps, only a one-stage assessment of the level of several oppositional subgroups can more correctly reflect the shift in the cytokine balance [3]. In addition, the amount of cytokines in the blood is individual for each microorganism. Therefore, only dynamic monitoring of cytokine levels is of diagnostic value [4].In order to introduce minimally invasive and non-invasive manipulations in neonatology practice and improve methods of non-invasive diagnosis of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) in newborns, correlation analysis of blood and urine cytokine parameters was performed.Correlation analysis helps to predict the possible values of one indicator, knowing the value of the other, which is very important when performing non-invasive diagnostic manipulations with high accuracy and significance. There was an average positive relationship between the concentrations of TNF-α in urine and blood (r=0.30), an average negative relationship between TNF-α in urine and IL-8 in blood (r=-0.32) and between IL-6 and INF-γ in blood (r= -0.37) in newborns with infectious pathologies in the early neonatal period. The results obtained allow us to state the prognosis of the pathological process in such a way that with a favorable course of infectious diseases in newborns in the early neonatal period, there is an increase in INF-γ and a decrease in the level of IL-6 and TNF-α in the blood. Established also weak positive relationship IL-6 blood IL -8 urine (r=0.22) and TNF-α blood (r=0.29) is the basis for considering IL-8 urine indicator of inflammation in newborns with infections in the early neonatal period (table.1.)Table 1. Correlation of blood and urine cytokines in newborns with infections in the early neonatal period
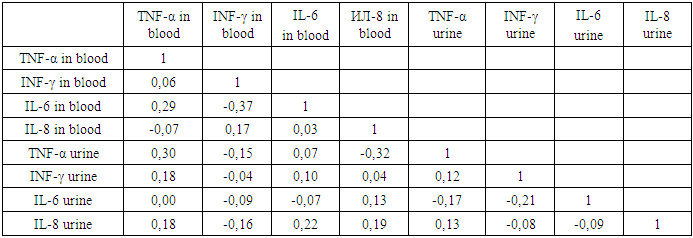 |
| |
|
There was also a weak positive relationship between TNF-α and IL-6 in the blood. The identified positive relationship provides an opportunity to predict their dynamics according to the initial state of one of them in the blood and the reduction of blood volume for analysis, as well as financial costs in this case.Thus, the study of the concentration of cytokines in the urine can determine the prognostic direction of the pathological process. Due to the positive relationship between IL-8 in the urine and IL-6 in the blood, it is possible to predict the level of IFN-γ and TNF-α in the blood. Consequently, the prognostic criterion for the severity of the early neonatal period in infants with infections is an increase in the concentration of IL-8 in the urine.In the late neonatal period of adaptation in infants of the infected group, a moderate positive relationship was established between the concentration of TNF-α urine and INF - γ urine (r=0.43) and IL-8 blood (r=0.31). And between TNF-α blood and IL-6 in urine (r=0.29) and TNF-α blood and IL-8 blood (r=0.24) (table.2.)Table 2. Correlation of blood and urine cytokines in newborns with infections in the late neonatal period
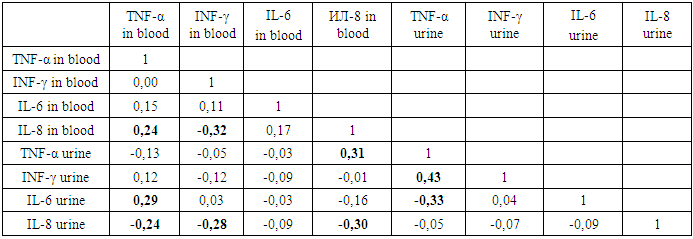 |
| |
|
A moderate negative correlation between the cytokines have:- IL-6 and TNF-α urine (r=-0.33);- IL-8 and INF-γ blood (r=-0,32);- IL-8 in blood and urine (r=-0.30);- IL-8 and TNF-α blood (r=-0,24).- IL-8 in urine and INF-γ in blood (r=-0,28).Analysis of the relationship of the studied cytokines showed the value of determining IL-8 in urine. Since INF-γ in the blood has a negative relationship with Il-8 blood r=-0,32 and IL-8 urine r=-0,28, the level of IL-8 in the urine can predict the activity and severity of the pathological process in the late neonatal period. And TNF-α urine has a positive relationship with IL - 8 blood, that is, increased activity of the inflammatory process (IL-8 in the blood) is accompanied by an increase in the concentration of TNF-α in urine and a decrease in IL-8 in urine. It follows that the increase in the concentration of TNF-α and IL-8 in urine are prognostic criteria for the severity of the infectious process in newborns during late neonatal adaptation.Thus, the correlation analysis of cytokine parameters of blood and urine of newborns with infectious diseases depending on the period of adaptation showed prognostic significance (at the level of 5%) and the advantage of determining the studied cytokines in urine. In CIRS in newborns with infections, the severity criteria are:- In the early neonatal period: IL-8> 1,1 PG / ml in urine;- Late neonatal period: - TNF-α> 20.3 PG / ml in urine; - IL-8> 1,1 PG / ml in urine.In the early neonatal period in newborns with noninfectious diseases, in the genesis of CIRS, the linear correlation coefficient showed a moderate positive relationship between the concentrations of INF-γ and TNF-α in urine (r=0.46), as well as between IL-8 and INF-γ in urine (r=0.30). The established relationship predicts a simultaneous increase in INF-γ and IL-8 in urine with an increase in TNF-α in urine. This phenomenon indicates the compensatory mechanisms of the body's defense system in response to non-infectious damaging factors in the early neonatal period of life (table.3). Table 3. Correlation of blood and urine cytokines in neonates with noninfectious diseases in the early neonatal period
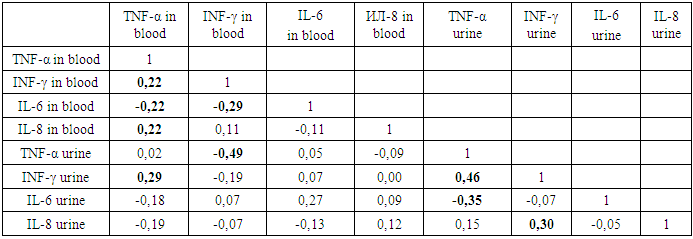 |
| |
|
As can be seen from table 3, the relationship come all studied cytokines: TNF-α blood and urine, IL - 6 blood and urine, blood and urine INF-γ, IL-8 blood and urine. The sample studied by parametric indicators show the relationship thus, the increase in urine concentrations of TNF-α is accompanied by increased IFN-γ in the urine, the latter contributes to IL-8 in urine and blood, IFN-γ and TNF-α in blood and decrease of IL-6 in blood.It follows that by determining the level of TNF-α in urine, it is possible to predict and/or predict blood and urine INF-γ concentrations. There was an inverse negative moderate relationship between TNF-α urine and blood INF-γ and (r=-0.49) and TNF-α urine and IL-6 urine (r= -0.35). Hence, the increase in TNF-α in urine is accompanied by a decrease in the level of INF-γ in the blood and IL-6 in the urine. The revealed weak positive relationship between INF-γ and TNF-α in blood (r=0.22), IL-8 and TNF-α in blood (r=0.22), INF-γ in urine and TNF-α in blood (r=0.29) allowed us to consider urine INF-γ as an indicator of the severity of the pathological process. The basis of this conclusion is its positive relationship with TNF-α blood -r=0,29 and urine-r=0,46, also reverse negative relationship exists between IL-6 and TNF-α in the blood (r=-0,22) and IL-6 with INF-γ in the blood (r=-0,29).At the same time, a negative moderate relationship between IL-6 blood and INF-γ blood (r=-0.37) and TNF-α blood (r=-0.29), which helps to assess the degree of influence of IL-6 - on many organs and systems of the body: blood, liver, immune and endocrine systems, as well as metabolism. Given that the increase in IL-6 levels in the blood is observed not only in infections, but also in injuries and non-infectious conditions, when the secretion of vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) can be disturbed, its concentration in the blood can predict the condition of newborns during adaptation. Therefore, due to the relationship of the studied cytokines, the level of TNF-α in urine can be predicted and the level of INF-γ in blood and urine and IL-6 in urine.The presence of a negative average association of TNF-α urine with IL-6 urine (r= -0.35) allows the diagnosis of the activity and severity of the inflammatory process. Thus, in the early neonatal period of adaptation of newborns with non-communicable diseases, the prognostic criteria for the severity of CIRS is an increase in TNF-α and INF-γ in urine.In the late neonatal period of adaptation of newborns with non-infectious pathologies in the genesis of SIRS, a noticeable positive association of TNF-α blood with IL-8 blood (r=0.63) and its moderate relationship with IL-8 urine (r=0.35) was established (table.4). Table 4. Correlation of blood and urine cytokines in newborns with noninfectious diseases in the late neonatal period
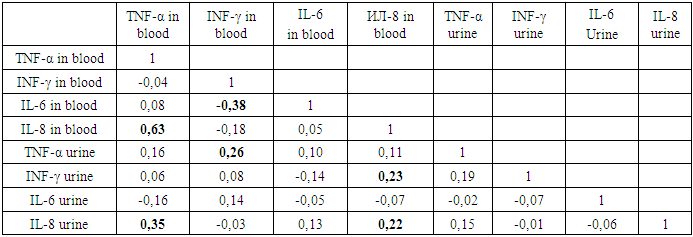 |
| |
|
In turn, IL-8 blood has a weak positive relationship with IL-8 urine (r=0.22) and INF-γ urine (r=0.23), therefore, in newborns with non-infectious pathological conditions in the late period of adaptation to the level of IL-8 in the urine can predict the level of IL-8 in the blood and TNF-α in the blood. Increasing the level of IL-8 in the blood increases the level of IL-8 and INF-γ in the urine.IL-6 blood had a moderate negative relationship with the INF-γ in the blood (r=-0.38), which determines the body's response to the banal non-infectious process, its growth predicts the severity of the condition.At the same time, blood INF-γ has a weak positive relationship with urine TNF-α (r=0.26), the level of urine TNF-α can predict the content and dynamics of blood INF-γ, which has a moderate negative relationship with IL-6 blood. It follows that an indicator of the severity of the pathological process in newborns with non-communicable diseases in the late period of adaptation is an increase in IL-6 and TNF-α in the blood.The correlation analysis made it possible to predict the possible values of IL-8 in blood and TNF-α in blood by the level of IL-8 in urine, which is very important for the introduction and implementation of non-invasive diagnostic manipulations with high accuracy and significance for newborns with non-communicable diseases in the late period of adaptation.Thus, cytokine indicators of blood and urine are of high importance for the early diagnosis and prognosis of SIRS in newborns with non-infectious perinatal diseases. Predictors of the severity of SIRS in newborns during adaptation are prognostic criteria that determine the activity of inflammatory mediators and the response of the body's defense system to damaging factors. Prognostic criteria for the severity of CIRS in newborns with noninfectious diseases are: in the early neonatal period- TNF-α > 20.3 PG / ml in urine; - INF-γ > 9.2 PG / ml in urine; In the late neonatal period:- IL-6 > 56.9 PG / ml in blood;- TNF-α >39.0 PG / ml in blood; - IL-8 >1,1 PG / ml in urine.
2. Conclusions
In CIRS in infants with infections, the severity criteria are: - in the early neonatal period: IL-8> 1.1 PG / ml in urine; -in the late neonatal period: - TNF-α> 20.3 PG / ml in urine; - IL-8> 1.1 PG / ml in urine. Prognostic criteria for the severity of CIRS in newborns with non-communicable diseases are: In the early neonatal period: - TNF-α > 20.3 PG / ml in urine; - INF-γ > 9.2 PG / ml in urine; In the late neonatal period: - IL-6 > 56.9 PG / ml in blood; - TNF-α >39.0 PG/ml in blood; - IL-8 >1.1 PG / ml in urine.
References
| [1] | Veropotvelyan P. N., Veropotvelyan N. P. Gajewski, I. V. cytokines in the system mother-placenta-fetus in physiological and pathological pregnancy//women's HEALTH No. 1 (77)/2013 ISSN 1992-5921/C/126-129. |
| [2] | Danilova V. V. Modern views on the diagnosis of sepsis in newborns/ / Medicine of emergency conditions №7 (78), -2016. P. 120-123. |
| [3] | Savelyev V. S., Gelfand B. R. Sepsis at the beginning of the XXI century. - M.: Litterra, 2006. |
| [4] | Tselina S. V., Govorova N. V., Dolgikh V. T. et al. Clinical significance of indicators of SSVO, leukocyte intoxication index and procalcitonin test in the diagnosis of purulent-destructive pyelonephritis in pregnant women / / Anesthesiology and resuscitation. — 2008. — No. 3. — P. 29-31. |
| [5] | Jorgensen I, Rayamajhi M, Miao EA. Programmed cell death as a defence against infection. Nature reviews immunology. 2017; 17:3: 151-164. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2016.147. |
| [6] | Makarova V. I., Makarov A. I. the Role of cytokines in the inflammatory response / / human Ecology 2008.05. P. 31-35. |
| [7] | Mayansky A. N. NADPH oxidase of neutrophils: activation and regulation / A. N. mayansky / / Ibid. – 2007.- Vol. 6, No. 3. - Pp. 3-13. |
| [8] | Spiders V. S. the Role of macrophages in the pathogenesis of limited inflammation / V. S. Spiders, S. A. Daabul, N. Yu. Belyaeva / / Archive of pathology. – 2005. – Vol. 67, No. 4. – P. 3-10.16. |
| [9] | Khaitov R. M. Basic principles of immunomodulatory therapy / R. M. Khaitov, B. V. Pinegin / / Allergy, asthma and clinical immunology. – 2000. – No. 1. – P. 9-16. |
| [10] | Becker T. C. Bone marrow is a preferred site for homeostatic proliferation of memory CD8 T cells / T. C. Becker, S. M. Coley, E. J. Wherry, R. Ahmed // J. Immunol. – 2005. – Vol. 174. – P. 1269–1273. |


 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML


