-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2019; 9(2): 523-526
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20190912.16

Morphometric Assessment of Functional Immunomorphology of White Rat Spleen in the Age Aspect
M. R. Turdiyev1, Sh. J. Teshayev2
1Department of Pathological Anatomy Medicine Bukhara State Medical Institute Named after Abu Ali Ibn Sino, Uzbekistan
2Professor of the Department of Anatomy and Clinical Anatomy, Bukhara State Medical Institute Named after Abu Ali Ibn Sino, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This article is devoted to the actual problem-the development of the spleen as an organ of the immune system at the stages of postnatal ontogenesis. In an experiment on 45 white mongrel male rats of 5 age groups using histological and morphometric methods followed by statistical analysis, data on the morphometric parameters of the spleen of white rats in postnatal ontogenesis are presented. It was found that significant changes in the structure of the white pulp of the spleen of white rats in the postnatal period occur against the background of involutive processes.
Keywords: Rats, Spleen, White pulp, Age-related changes, Morphometric parameters
Cite this paper: M. R. Turdiyev, Sh. J. Teshayev, Morphometric Assessment of Functional Immunomorphology of White Rat Spleen in the Age Aspect, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 9 No. 2, 2019, pp. 523-526. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20190912.16.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The immune system of humans and animals is one of the most sensitive systems of the body, which quickly reacts to external influences [4].The largest peripheral organ of the immune system is the spleen [1,7].The rat spleen has a histostructure similar to that of a human organ [10]. The study of structural and functional features of the spleen is an urgent problem, since the spleen, as the largest organ of immunogenesis, is responsible for the effectiveness of cellular and humoral immune response of both innate and acquired immunity [2,6].The immunocompetent compartment of the spleen parenchyma is represented by its white pulp (BP), where two main B - and T-dependent zones are formed, that is, the areas of localization mainly of B - and T-lymphocytes. These are respectively lymphoid follicles (LF) and periarterial lymphoid couplings (PALM) [1;3]. The study of reactive changes of the spleen, in particular the structural elements of PD, devoted a large number of scientific studies based on the study of this body as a person [3], and various agricultural and laboratory animals [3;5]. Despite the presence of numerous modern studies on the structure of the spleen under the influence of external factors [4], the morphofunctional changes of lymphoid formations of the spleen in the age aspect remain insufficiently studied. For an accurate representation of the reactions of the lymphoid structures of the spleen on some external stimuli or alien elements, it is necessary to know the morphology lipofilnykh structures of the spleen were normal.The aim of the work was to study the regularities of the age dynamics of the histological structure of the white pulp of the spleen of white mongrel rats in postnatal ontogenesis from birth to 12 months of age.
2. Materials and Methods
- The study was conducted on 45 white male mongrel rats, weighing from 20 to 280 Gy., which were kept in a vivarium with a standard diet, free access to water, the usual mode of purification. The slaughter of rats was carried out under ether anesthesia at the age of newborns, 90, 180, 270 and 360 days from the beginning of the experiment. The rats were divided into five age groups, 9 individuals each: group 1-newborns, group 2 - 90 day rats, group 3-180 day rats, group 4 - 270 day rats, group 5 - 360 day rats. The studies were carried out in compliance with the rules of humane treatment of animals, which are regulated by the "Rules of work with experimental animals" approved by the ethical Committee of the Bukhara state medical Institute. Abu Ali Ibn Sino (No. 18 of 16.01.2018), and were based on the provisions of the Declaration of Helsinki Of the world Medical Association of 1964, supplemented in 1975, 1983, 1989, 1996, 2000, 2002, 2004, 2008, 2013 gg. To conduct a morphological study, fragments of the spleen were fixed in 10% formalin solution, carried out through a battery of alcohols and poured into paraffin blocks according to generally accepted methods. Paraffin sections 5-8 µm thick were stained with hematoxylin-eosin. Histological and morphometric studies were performed using a microscope Leica CME, with a digital camera Leica Microsistems CH-9435. The relative area of the white pulp (in%), diameters of lymphoid nodules (in microns), germinative centers (in microns), width of the mantle zone (in microns), marginal zone (in microns) of lymph nodes were determined on the sections of the tear. The mathematical treatment is produced directly from the total data matrix "Excel 7,0" involvement opportunities "program STTGRAPH 5.1" determined the indicators of the standard deviation and the margin of error.
3. Research Result
- In newborn white rats, the spleen outside is covered with a thin connective tissue capsule, from which trabeculae extend deep into the organ. The white pulp of the spleen in newborn white rats is just beginning to form. To differentiate periarterial lymphatic clutches and lymphoid nodules is difficult, the generated nodules is possible to define the mantle and marginal zones. In histological preparations, the relative area of the white pulp of the spleen of newborn white rats was 17.16±1.06%, the diameter of the lymph nodes was 242.76±15.22 microns. In lymph nodules visually determined: mantle zone, marginal zone, periarterial area. The width of the mantle, marginal and periarterial zones was 35.28±1.89 microns, 64.32±2.07 microns, 44.16±2.46 microns, respectively. Germinative centers of lymph nodes in newborn white rats with histological sections undetected.The study of histological preparations of other age groups of the spleen of white rats allowed to establish certain relationships of its structural and functional zones. The spleen of white rats has a well-defined connective tissue capsule and trabeculae containing blood vessels. The spleen parenchyma of white rats is represented by red and white pulp. The composition of the red pulp includes sinusoidal capillaries and splenic cords. The white pulp consists of numerous lymph nodes and periarterial lymphoid couplings (Fig. 1).
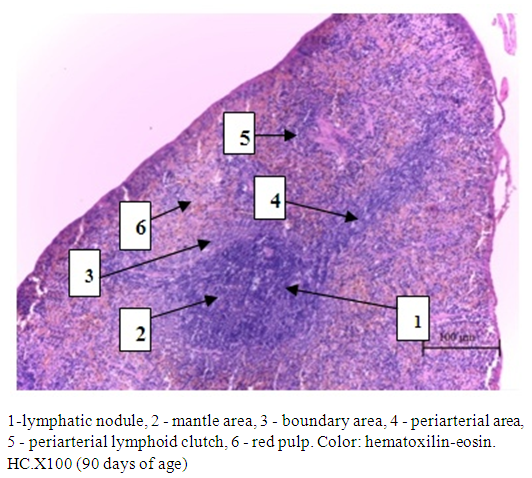 | Figure 1. Rat spleen structure |
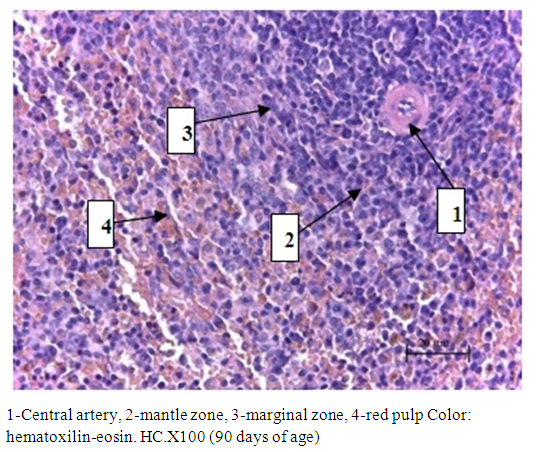 | Figure 2. Lymph node of white pulp of rat spleen |
|
4. Discussion of the Data
- The immune apparatus of the spleen, according to researchers, has a more complex structure than other peripheral organs of the immune system. In the spleen this unit should include areas of white pulp, namely the periarterial lymphatic vagina that envelops everything Polyarnye artery, lymphatic nodules, and venous sinuses [8].The percentage of white pulp in newborn white rats is quite low. This is due to the fact that in the first month of life, lymphocytes only populate the pulp of the spleen, lymph nodes are small, it is difficult to distinguish zones in them [9]. According to our data, in the following age groups, the proportion of white pulp increased markedly. The highest values of the white pulp area were observed in the spleen of white rats at 3 months of age, in other age groups the size of the white pulp steadily decreased, confirming the fact of age involution of the organ.Area of white pulp, the diameter of lymph nodules and the diameter of the germ centers the greatest growth is observed at 3 month of age, the width of the mantle zone, marginal zone width and the width of the periarterial zone the greatest growth observed at 180 days of age.With age, all studied morphometric parameters gradually decreases and the lowest rate is observed at 12 months of age. The obtained data on the main morphometric parameters of the white pulp of the spleen of white rats by age aspects correspond to and Supplement the literature data on the structure of the organ in intact animals.
5. Conclusions
- 1. The relative area of the white pulp of the spleen of newborn white rats was 17.16±1.06%, the largest increase in this indicator is observed in 3 months of age (22.2 ± 1.72%), and the largest in 12 months of age (12.32±1.08%.). After 3 months of age, there is a decrease in this indicator.2. The diameter of lymph nodes up to 3 months of age increases by 1.92 times compared to newborn rats. After 3 months of age, this indicator also gradually decreases and at 12 months of age is equal to 407.98±8.18 microns. 3. Germinative centers of lymph nodes in newborn white rats with histological sections undetected. The greatest growth of this indicator is observed in 3 months of age (147.8±7.66 microns), and the highest in 12 months (120.02±5.36 microns). 4. The width of the mantle zone up to 6 months of age increases by 1.32 times compared to the period of newborn. After 6 months of age, this indicator also gradually decreases and at 12 months of age is equal to 41.32±1.12 microns. The width of the marginal and periarterial zone the period from newborn to 6 months of age increases, and from 6 months to 12 months of age decreases slightly.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML