-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2019; 9(2): 493-498
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20190912.10

Effect of Chronic Gout on Hearing: A Prospective Study
Noha M. Abdelkader 1, Amal El-Sebaie 1, Eman F. Mohamed 2
1ENT Department, Faculty of medicine for girls Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
2Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine for Girls, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
Correspondence to: Eman F. Mohamed , Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine for Girls, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Background: Recent reports showed significant associations between chronic gout and progressive hearing impairment, especially among elderly. Aim: To assess the associating between chronic gout and hearing loss and the correlation between uric acid levels and different degrees of hearing impairments. Subjects and Methods: A prospective, comparative, study was conducted from January 2014 to January 2016 at the Audiology unit of the ENT department, Al-Zahraa University hospital. Patients with chronic gout and age and sex-matched healthy controls were recruited. We used pure tone and speech audiometry and immitancemetry in order to evaluate the hearing impairment among all participants. Results: The present study included 20 patients with chronic gout and a similar number of healthy controls. The analysis showed that patients with gout had statistically significant higher pure tone audiometry threshold of the left (p <0.001) and right ears (p <0.001). The threshold was higher in both ear at the level of 1000 to 8000 Hz. The percentage of patients with bilateral failed Transient evoked otoacoustic emissions (TEOAEs) was significantly higher in gout group (50% versus 0%, p <0.001). The band response of TEOAE from 1500Hz to 4000Hz was significantly higher in gouty patients as well (p <0.001). There was statistically significant positive correlations between pure tone, speech audiometry, and TEOAE with gout duration and uric acid levels (p <0.05). Conclusions: In conclusion, patients with chronic gout had significantly higher risks of high frequency sensorineural hearing loss, as evident by pure tone audiometry and TEOAEs, than age and sex-matched healthy population.
Keywords: Gout, Hearing loss, Uric acid
Cite this paper: Noha M. Abdelkader , Amal El-Sebaie , Eman F. Mohamed , Effect of Chronic Gout on Hearing: A Prospective Study, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 9 No. 2, 2019, pp. 493-498. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20190912.10.
1. Introduction
- Hearing loss is a prevalent medical condition in the elderly population. It reportedly affects half to two thirds of the worldwide population [1,2]. This sensory dysfunction causes communication difficulties, impaired daily of life activities, and worsened quality of life [3–5]. Observational studies showed significant associations between hearing loss and the incidence of stroke and dementia [6,7]. Several risk factors have been implicated in this condition, including non-modifiable (as older age, male sex, and white race), and modifiable (as loud noise, smoking, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes mellitus) [1,8].Another disease that shares the same risk factors and prevalence distribution is hyperuricemia or gout [9]. Therefore, some investigators hypothesized that gout may be a risk factor for hearing loss in the elderly. However, the evidence on the association between serum uric acid and hearing loss has so far been inadequate and controversial. On one hand, Singh and Cleveland analyzed the data of 89409 elderly subjects (> 65 years old) with incident hearing impairment between 2006 and 2012 from the US Medicare claims database. They found a higher hazard ratio of hearing impairment in gouty subjects, which was confirmed by multivariate analysis [10]. This me be because oxidative stress and inflammation (hallmarks in gout pathogenesis) may induce cell death pathways in the cochlear inner cell mass and potentiate noise-induced or age-related hearing loss [11–13].On the other hand, Yang and colleagues analyzed the data of 44084 subjects from the US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey to examine the relationship between serum uric acid levels and hearing thresholds. They reported an inverse association between uric acid serum levels and hearing thresholds for pure tone audiometry [14]. To explain this finding, they relied on observational studies that showed potential anti- oxidative and neuroprotective effects for uric acid against multiple sclerosis and neurodegenerative diseases [15–17]. Therefore, uric acid may scavenge reactive oxygen species in the cochlea, ameliorating their toxic effects and delaying the progression of hearing loss [18].Based on the conflicting evidence mentioned above, we performed this study to examine the association between gout and hearing loss and study the effects of increased uric acid levels and duration of gout on hearing thresholds.
2. Materials and Methods
- The study’s protocol gained the approval of the local ethics and research committee of Al-Zahraa University hospital.Study Design and Patients selection:The present study was a prospective, comparative, study that was conducted through the period from 2014 to January 2016 at the Audiology unit of the ENT department, Al-Zahraa University hospital. Patients with established diagnosis of chronic gout were included. In addition, an age and sex-matched healthy volunteers were included as control group. We excluded patients with any other major systemic illness at time of presentation except for chronic gout, hearing loss before onset of gout, sudden onset of hearing loss, history of ear discharge or any other middle ear problems, family history of head trauma, and/or history of radiotherapy. A written informed consent was obtained from the parents of every eligible fetus prior to study enrollment.Data collection:We collected the following data from every participating patient: age, gender, occupation, marital state, history of hearing loss or hearing- related symptoms, history of gout symptoms and recurrent urinary stone formation, and history of intake of ototoxic drugs. In addition, we collected the findings of routine laboratory investigations and uric acid level from every patient. Then, every patient underwent detail otoscopic and audiological examinations as the following:1) Otoscopic examination of both ears.The ear examination was started by performed otoscopic evaluation of to ensure clear external auditory meatus and examination of any abnormalities of the ear drum.2) Audiological evaluation:a- Pure tone audiometry: The audiological examination included air conduction for octave frequencies (250-500, 1000, 2000, 4000, 8000 Hz) and bone conduction for frequencies (500, 1000, 2000, and 4000 Hz) using ascending descending techniques. Audiometer value (average of 500, 1000, 2000, 4000 HZ) was used in the present study for classification of degree of hearing loss. The hearing threshold grading according to WHO old and new definitions was as following: 0-25 db normal hearing, 26-40 db mild hearing loss, 41-60 db moderate hearing loss, and 61-80 db severe hearing loss. More than 81 db profound hearing loss [20].b- Speech audiometry: which included1- Speech recognition threshold (SRT) using Arabic spondic words.2- Word discrimination score (D.S) using Arabic phonetically balanced words.c- Immitancemettry: The 226HZ probe Tone tympanometry was conducted at varying pressure ranging from +20 to -400mm H2O. Automated acoustic reflex threshold measurement of 500, 1000, 2000, 4000 HZ elicited ipsilateral and contralateral.d- Transient Evoked Otoacoustic Emission (TEOAEs): A probe, which was composed of a loudspeaker and a microphone, was introduced to the ear canal, the loudspeaker produced repetitive waves of sounds and the microphone recorded the OAES, which was generated by the cochlea. The transmitted OAEs was processed to evaluate five (1, 1.5, 2, 3, 4) frequencies. The final report of the TEOAEs examined whether there was an increase in the signal/noise ratio above 3 in at least three frequencies. If so, the ear was categorized as failed, otherwise, the ear was categorized as passed.Study’s outcomes:The primary outcome of the present study was the difference in the frequency of sensorineural hearing loss between chronic gouty patients and healthy controls. The secondary outcomes were the correlation between the degrees of hearing impairment with the duration of gout and uric acid levels.Statistical Analysis:The SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Science; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) version 22 for Microsoft Windows was used for data processing and analysis. The mean ±standard deviation (±SD) or median with interquartile range (IQR) were used to describe numerical variables according to the normality of the data. Frequencies with percentage were used to present while categorical variables. The association between quantitative variables was done using unpaired Student’s t-test for normally-distributed data or Mann-Whitney Rank Sum test for normally-distributed data. Chi-square test was performed to detect the level of significance for categorical variables. The level of significance was set at a probability value (p-value) of less than 0.05.
3. Results
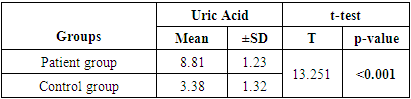
- The present study included 20 patients with chronic gout and a similar number of healthy controls. The mean age of the patients was 56.7 ±8.3 years compared to 54.2 ±10.6 years in control group (p =0.402). The majority of patients were females (60% versus 50% in the control group, p =0.52). The mean uric acid level was significantly higher in patients group (p <0.001) (Table 1).
|
|
|
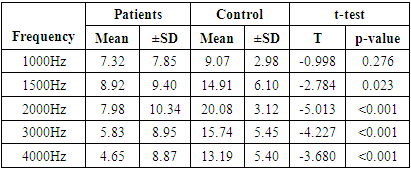
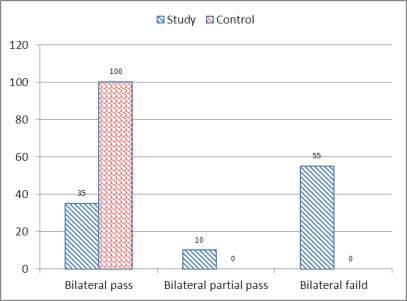 | Figure (1). Bar chart between both groups as regard TEOAE |
|
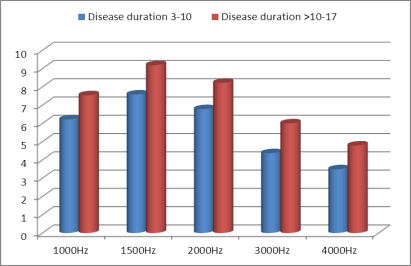 | Figure (2). Relation between transient evoked otoacoustic emission and gout duration |
4. Discussion
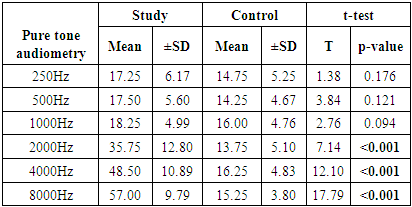
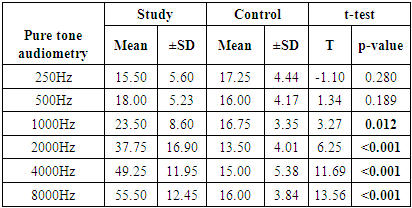
- This study showed that patients with chronic gout have significantly higher serum levels of uric acid in comparison to normal controls. Moreover, we recorded significant differences in the association between uric acid and TEOAEs among the study and control groups. We also found a significant association between pure tone audiometry threshold and gout duration at 2000 to 8000HZ. These results hint at the possible involvement of uric acid crystals in the pathogenesis of age-related hearing impairment.The findings of this study are in line with other published studies in this regard [21–23]. Singh and Cleveland showed in a retrospective cohort study that gout was associated with increased prevalence of hearing impairments in older adults [10]. Another Korean study reported a significant association between serum uric acid and development of hearing loss in older adults > 40 years old [24]. Hamed and El-Attar showed in an otoacoustic emission analysis that asymptomatic patients with hyperuricemia had reduced response levels of TEOAEs, especially at higher frequencies. In compliance with our analysis, the reduced TEOAEs were significantly associated with the duration since gout diagnosis [25].However, our findings are in discordance with those of another large observational study by Yang et al. The research team in that study concluded that higher serum uric levels were associated with lower hearing thresholds [14]. To explain that controversy, the authors relied on the dual role of uric acid; its ability to serve as pro-oxidant and anti-oxidant under different circumstances. On one hand, uric acid has been shown to induce oxidative stress in vascular, adipose, liver and renal cells in animal models and cell cultures [26, 27]. On the other hand, administration of uric acid has been shown to scavenge free radicals and alleviate oxidative stress in animal experiments and a randomized clinical trial [28–30]. This dual function may be regulated by the micro-environmental conditions within the human body.Back to our findings, it remains unclear how elevated uric acid levels may cause hearing impairment. Some theories have been proposed. The most progressive theory is the induction of oxidative stress and inflammation in the cochlea by urate crystals. Several studies have implicated the latter two mechanisms in age-related hearing loss, showing higher cochlear levels of malondialdehyde (lipid peroxidation marker) and tumor necrosis factor-α, as well as alterations in energy-sensing pathways (mTOR and PTEN) [11–13]. Further, treatment with antioxidants as coenzyme Q analogue reduced oxidative stress and associated hearing loss [13]. Another theory was proposed by few published case reports in the literature. These reports revealed urate deposits (tophaceous gout) in the middle ear [31–34]. Gouty tophi are characterized by foreign body granulomas of macrophages surrounding the deposits of urate crystals [35] and may serve as risk factors for conductive hearing loss.The vascular model is another promising theory. Elevated uric acid levels serve as a risk factor for vascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, and ischemic stroke [36–38]. The cochlea is vulnerable to small impairments in blood flow because its blood supply has no collateral vessels, as well as the higher metabolic demands of the inner ear [39]. This was further confirmed by the findings of Hamed and El-Attar that showed that in patients with asymptomatic hyperuricemia, reduced TEOAEs were correlated to the common carotid artery intima-media thickness, as well as the mean flow velocities in the middle cerebral and vertebral arteries. They concluded that hyperuricemia may compromise the blood flow of outer hair cells, disturbing their electro-motile response [25].Our study, along with other evidence, shows that hearing loss in association with high uric acid levels usually occurs at high frequencies. In context, hearing loss in general occurs at higher frequencies [40,41]. A former study hypothesized that the associated impairment in higher frequency hearing may indicate that hyperuricemia compromises outer hair cells along the basal cochlear regions [42]. High-frequency sensori-neural hearing loss was observed after exposure to ototoxic drugs and in patients with metabolic diseases as diabetes mellitus and hypercholesterolemia [43–45].Before discussing the implications of our findings, we have to acknowledge some limitations. First, the observational study design opens the door for potential confounders as noise exposure and use of ototoxic drugs on the hearing loss side, as well as purine food consumption and uric acid excretion rates on the gout side. Further, the cross sectional design precludes our ability to assess the longitudinal relationship between serum uric acid and hearing sensitivity. In addition, the enrolled sample size in our study is relatively small, which did not power multivariate analysis to exclude potential confounders.Our findings have implications for the prevention and management of hearing loss, provided they are confirmed in large-scale interventional studies. Unlike the global economic impact of hearing loss (estimated at 750 billion US dollars annually), the screening for hearing aid is often inexpensive [46] and it should be prioritized in patients with chronic gout. It remains unclear whether treatment of chronic gout or even asymptomatic hyperuricemia may improve hearing sensitivity in these patients, but this point should be investigated in future research. Hearing aids in gouty patients with established hearing loss can not only improve the quality of life, but also protect against the risk of cognitive deterioration.In conclusion, our study showed that chronic gout is associated with sensori-neural hearing impairment, especially at higher frequencies. This impairment was in direct association with the duration since gout diagnosis. Future studies should confirm these findings and develop preventive and management strategies against hearing loss in patients with chronic gout.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML