-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2019; 9(6): 213-216
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20190906.08

Efficacy of Photodynamic Therapy and Traumeel S in the Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis
Khaydar Kamilov, Kamolakhon Takhirova
Hospital Therapeutic Dentistry Department, Tashkent State Dental Institute, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Kamolakhon Takhirova, Hospital Therapeutic Dentistry Department, Tashkent State Dental Institute, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Despite the existing large number of drugs, currently there are no optimal methods for influencing on the mechanisms of the pathogenesis of inflammatory periodontal diseases, and the problem of treating active inflammatory-destructive processes in the periodontium continues to be relevant. This study was conducted to investigate the efficacy of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy and Traumeel S. The purpose was to evaluate of the effectiveness of homeopathic and photodynamic therapy in the treatment of chronic periodontitis. 120 patients with generalized periodontitis were examined at the Department of Hospital Therapeutic Dentistry, Tashkent State Dental Institute clinics. After the treatment concluded Traumeel S the highest results were achieved, where the value of PMA decreased from 45.60 ± 3.09 to 2.67 ± 0.05%, PI was 1.26 ± 0.09, CPI was 0.63 ± 0.04. So the effectiveness of topical use of PDT and Traumeel S was confirmed by the results of clinical, instrumental and laboratory studies.
Keywords: Periodontitis, Laser Doppler Flowmetry (LDF), Polymerase Chain reaction (PCR), Photodynamic Therapy (PDT), Traumeel S
Cite this paper: Khaydar Kamilov, Kamolakhon Takhirova, Efficacy of Photodynamic Therapy and Traumeel S in the Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 9 No. 6, 2019, pp. 213-216. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20190906.08.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Inflammatory periodontal diseases occupy the second place among dental diseases after dental caries. This level has been maintained for a long time, however in recent years there has been a tendency to increase the incidence of diseases among younger people. According to the world health Organization, a high frequency of periodontal diseases is noted at the age of 20 – 44 years (65 – 95%), severe forms of periodontal diseases are detected in 5-25% of the adult population, moderate forms are 30-45%, and only 2-8% of people have healthy periodontal tissue at the age of 35-45 years. [1, 2, 3, 5]. Periodontal disease dramatically reduces the quality of life of patients. Thus, periodontal disease is a problem that has not only medical but also social significance. The solution of these issues is of particular relevance for modern society. In 2014 the prevalence of periodontal disease was 72.9% in Uzbekistan [J. A. Rizayev, 2015]. Considering that pathological processes in periodontal disease develop against the background of many common diseases, as well as the influence of periodontal diseases on many body functions, including natural defense mechanisms, treatment of patients should be directed not only at eliminating the pathological process in periodontal tissues, restoring their functio, but also for the rehabilitation of the general condition, the restoration of normal homeostasis, the stimulation of the body's defences [4, 7, 8].Despite the existing large number of drugs, currently there are no optimal methods for influencing on the mechanisms of the pathogenesis of inflammatory periodontal diseases, and the problem of treating active inflammatory-destructive processes in the periodontium continues to be relevant [6, 9, 10].
2. Object of Research
- Increase the effectiveness of complex treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases by improving the system of diagnosis and treatment. Evaluation of the effectiveness of homeopathic and photodynamic therapy in the treatment of chronic periodontitis.
3. Material and Methods of Research
- The study was performed for the period from 2017 to 2018 at the Department of Hospital Therapeutic Dentistry, Tashkent State Dental Institute. Studies were conducted in 120 patients. All the patients have signed the written consent to studies carried out at the department. 90 patients with generalized periodontitis of moderate severity (MGP) were the main group. The control group consisted of 30 patients without periodontal disease. The age group of patients is from 20 to 65 years.Depending on the applied complex therapy, 3 groups of patients with MGP were identified: 1 group, concluded 30 patients, received traditional treatment and local antimicrobial therapy using fixing bandage with metronidazole (Metrogyl-denta gel) in an amount of 10 g during 5-7 days. The 2nd group, concluded 30 patients, received traditional treatment and antimicrobial therapy using photodynamic therapy with the help of "UFD-1" device (Uzbekistan) for 2 minutes during 5 days. The 3rd group, concluded 30 patients, received Traumeel S drugs in the form of an injection along the transitional fold in addition to therapeutic measures for 5 days.
4. The Results of the Study
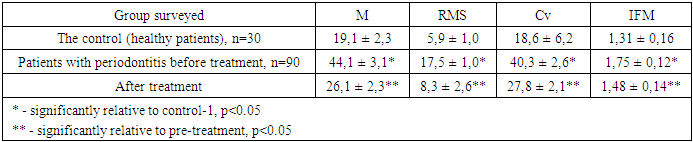
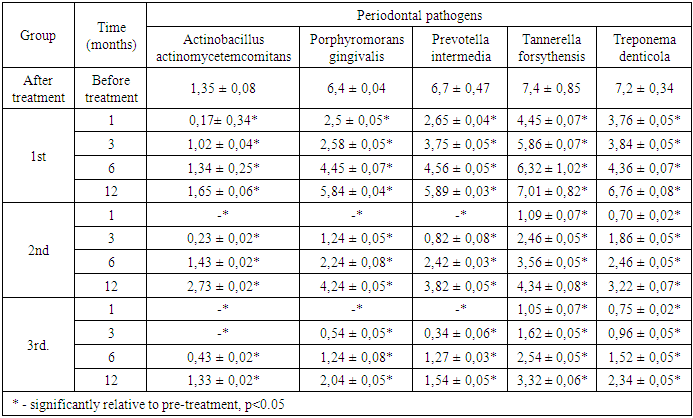
- Before the treatment patients complained of pain and gum bleeding, bad breath, hypersensitivity to cold and hot stimuli, mobility of teeth. During the examination, there were stagnant hyperemia of the interdental, marginal and part of the alveolar gums, abundant gray-yellow plaque on the gums, mobility of teeth of I – II degree, periodontal pockets up to 5.0 mm in depth with abundant serous purulent discharge determined (Figure 1). PI (3.95 ± 0.04) reflected the presence of inflammation in the gums. The value of PMA (45.60 ± 3.09) indicated the localization of the inflammatory process in the marginal gingival margin. The average CPI value was 2.79 ± 0.17, which corresponds to the diagnosis. To make a more accurate diagnosis, the quantitative and qualitative composition of periodontal pathogens was investigated by molecular genetic method (PCR in real time). The contents of periodontal pockets were taken with the help of sterile excavators, probes. The instrument was inserted into a periodontal pocket (in patients diagnosed with "generalized periodontitis of moderate severity") or a furrow (in the case of control). The tool was placed in a polypropylene vial with a lid with a volume of 1.5 ml containing "Sample-rapid" solution. A comparative study of the composition of periodontal microflora in the content of periodontal pocket (PP) found that the frequency of occurrence of periodontal microflora was high enough. At the same time, the frequency of detection of all periodontal pathogenic bacteria studied by us in patients with periodontitis and in the control group was statistically significantly different from each other (P<0.05). In general, in the control group contents of the PC periodontopathogenic microorganisms (total bacterial mass) was varied in the range of 3.5 to 6.5 Lg., in patients with MGP it was 8.5-9.7 Lg. When examining patients in the MGP of 73.33% of cases in detachable PC there were B. forsynthus; the corresponding dynamics of T. denticola to 46.7% detected; P. gingivales made up of 66.67%; P. intermedia was 61,11%; A. actinomycetencomitans was 13,33%. The concentration of Porphyromonas gingivalis, Tannerella forsythensis and Prevotella Intermedia, Treponema denticola and the amount of total bacterial mass was higher in patients with moderate-severe periodontitis compared to the control group. (P<0.05).
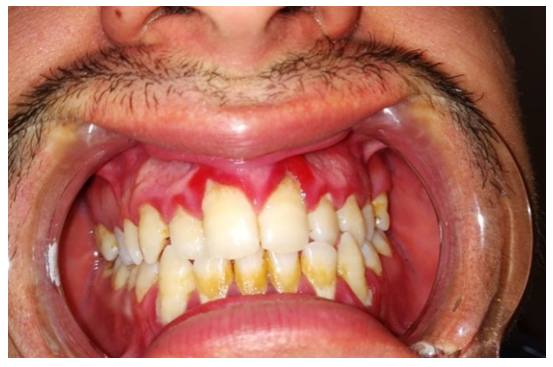 | Figure 1. Patient X. The state of periodontium before treatment |
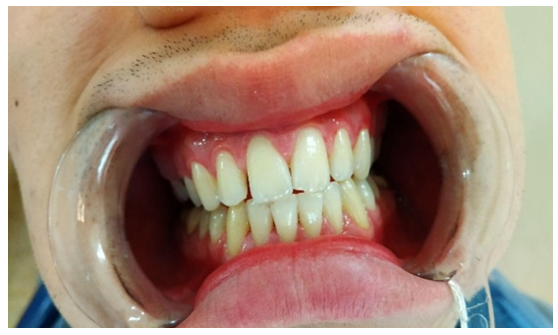 | Figure 2. Patient X. The state of periodontium before treatment after treatment |
|
|
5. Conclusions
- After the treatment concluded Traumeel S and PDT the highest results were achieved, where the value of PMA decreased from 45.60 ± 3.09 to 2.67 ± 0.05%, PI was 1.26 ± 0.09, CPI was 0.63 ± 0.04. The effectiveness of topical use of PDT and the drug "Traumeel S" was confirmed by the results of clinical, instrumental and laboratory studies. The results of treatment proved the high efficiency of this complex for the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis of moderate severity, which allows us to recommend this drug for use in periodontal practice.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML