-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2019; 9(3): 76-80
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20190903.02

The Profile of Immune System Basic Cytokines in Oncogynecologic Patients against the Background of Accompanying Immunotherapy
S. V. Kamishov, M. N. Tillyashaykhov
Republican Specialized Scientific-Practical Medical Center of Oncology and Radiology of Ministry of Health of the Republic of Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The profile of immune system main cytokines (IL-1β, TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-6) in the blood serum of the patients with ovarian cancer has been studied. A comparative estimation of treatment results showed that the use of immunotherapy with further neoadjuvant polychemotherapy allows to transfer patients from inoperable condition to operable one, to improve life quality of patients and to perform surgeries of “full” volume without severe general toxic reactions. Accompanying immunotherapy allowed to keep dosage intensity of chemopreparations, not to increase hospital staying, to improve a tolerance of polychemotherapy courses. The inclusion of immunotherapy in the complex of polychemotherapy in patients with ovarian cancer has detoxification and immunomodulatory effects, as evidenced by a decrease in the content of pro-inflammatory cytokines and an increase of interferon which is a powerful immunomodulatory cytokine.
Keywords: Ovarian cancer, Immunotherapy, Extracorporeal immunopharmacotherapy, Adaptive cellular immunity, Humoral immunity, Polychemotherapy
Cite this paper: S. V. Kamishov, M. N. Tillyashaykhov, The Profile of Immune System Basic Cytokines in Oncogynecologic Patients against the Background of Accompanying Immunotherapy, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 9 No. 3, 2019, pp. 76-80. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20190903.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- As it is known, imbalance in the cytokine system is considered as one of the important mechanisms for the development of many pathological processes, including oncological ones. It has been established that in a malignant process, two systems interact with different cytokines; these are neoplasm – cytokines and the immune system – cytokines [4, 9]. According to various literature sources, it is clear that the tumor cells themselves can produce cytokines, and express the corresponding cytokine receptors, thereby maintaining their vital activity. In addition, all components of modern complex treatment of patients with malignant processes, in particular ovarian cancer, are factors that initiate immunosuppression mainly in cell type, which is extremely dangerous, since the tumor, in turn, also uses suppression mechanisms to reduce the body’s response to its availability.And thus, the process of neogenesis which occurs with an imbalance between the production of the neuroplastic, antineoplastic and other regulatory cytokines is developed [7, 11, 14]. Most clinicians are attracted by the asymptomatic course of the disease in the early stages which leads to a late visit to the doctor, and, consequently, to detectability already with common stages of the disease (up to 70%) [1, 4, 8, 14].As it is known, the course of the tumor process, in particular, in the case of ovarian cancer (OC) is accompanied by the formation of endotoxicosis and secondary immunological failure [1-2]. Thus, endotoxicosis is a complex, multicomponent process which is caused by the accumulation of endotoxic substances in tissues and biological fluids under conditions of a decrease in the physiological processes of detoxification. At the same time, chemotherapy contributes to a further increase of endogenous intoxication, inhibition of the body’s immunocompetence which complicates the course of the main cancer, and sometimes, with the development of organ and systemic disorders limits the ability of conducting an adequate course of antitumor treatment [6, 13]. Despite the high sensitivity of the tumor in case of OC to the effects of modern cytostatic drugs, often the possibilities of antitumor treatment are limited due to their high toxicity and severity of metabolic disorders at the level of the whole organism [3].As for the method of extracorporeal immunopharmacotherapy, it can be noted that this method may be promising in the treatment of oncological processes in connection with the ability to remove the effects of cancer and chemoradiation intoxication, as well as activate the body’s own antitumor defense system [5, 10].Consequently, the main task of our research is to study the immune system status of patients with OC, in particular, the main serum cytokines of the immune system against the background of the use of extracorporeal immunopharmacotherapy and plasmapheresis in the complex treatment of patients with OC in order to ensure the possibility of endogenous intoxication and suppression of immunoresistance.In connection with the foregoing, immunotherapy of OC is a relatively new direction with new approaches to its implementation, along with the possibility of combining with other methods of treatment.
2. Aim of the Research
- To study the profile of the main cytokines of the immune system in patients with ovarian cancer of II-III stages against the background of accompanying immunotherapy. In this regard, we set the following tasks: to assess the effect of chemotherapy on the state of the main cytokines before and after polychemotherapy (PCT); to assess the state of the main cytokines after extracorporeal immunopharmacotherapy using an immunotropic drug - thymalin in a complex of chemotherapy; to assess the values of cytokines after extracorporeal immunopharmacotherapy with thymalin combined with plasma exchange in the chemotherapy complex.
3. Materials and Methods
- The examination included 270 women with stages of T2-3N0-1M0 (II-III clinical stages) who were examined and treated in the gynecological and chemotherapy departments of the Republican Specialized Scientific-Practical Medical Center of Oncology and Radiology (RSSPMCOR) from mid-2000 to 2014.Patients with OC are randomized to groups in order to assess the effect of immunotherapy on the spectrum of the main cytokines in the complex treatment: Group 1 - 42 practically healthy individuals; Group 2 - 46 patients with OC before PCT; Group 3 - 64 patients with OC after PCT without immunotherapy; Group 4 - 62 patients with OC after PCT combined with extracorporeal immunopharmacotherapy (EIFT); Group 5 - 56 patients with OC after PCT in combination with extracorporeal immunopharmacotherapy and plasmapheresis (EIFT + PF).Patients with OC were given combination therapy in an adjuvant or neoadjuvant regimen, including PCT using the cisplatin 75 mg / m2 + cyclophosphamide 1000 mg / m2 for 1 day for 4-6 courses once per 3 weeks and surgical treatment in the amount of radical surgery.Chemotherapy was carried out both in the adjuvant and in the neoadjuvant mode. EIFT and EIFT + PF in patients with OC using immunomodulators were performed during the period of radiotherapy and chemotherapy in the hospital. The method of extracorporal immunopharmacotherapy (EIFT) was carried out with the aim of reducing toxic manifestations after polychemotherapy and improving the immunoresistance of the organism.EIFT was carried out by exfusion of 500-1000 ml of autologous blood into "Gemakon" or "Terumo" sterile containers and centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 30 minutes. 50-80 ml of blood plasma supernatant were removed. Then the obtained leukotrombomass and erythrocyte mass were incubated with an immunotropic preparation in a total dose of 30 mg at 37°C for 60-100 minutes, followed by the return of the conjugate to the circulatory system of patients.To stimulate the cellular immunity immunotropic drug of thymus origin - thymalin was used [6]. Immunotherapy was carried out in the hospital, with admission of patients for chemotherapy and radiation therapy. In total, patients received 2 EIFT sessions at the beginning of admission to the hospital and before discharge from the hospital. Patients of the 5th group underwent accompanying treatment prior to PCT according to generally accepted standard schemes of detoxification drug therapy in the hospital.Groups of patients by age, stages of cancer, concomitant somatic pathology were comparable. Thymalin - thymus extract, obtained from the organ of cattle, has properties to regulate the number and ratio of B- and T-lymphocytes; activates phagocytosis; stimulates hematopoietic processes; stimulates regenerative processes; improves metabolism.Immunological studies included serum evaluation of the main cytokines of the immune system. Serum levels of cytokines (IL-1, IL-6, IFN-γ, TNF-α) were determined by ELISA using test systems of the “Human” company (Germany) in the dynamics of complex treatment.When conducting a statistical analysis of the data presented in the work, the results of the research were entered into databases prepared in the Microsoft Excel XP program. Numerical (continuous) values were presented as arithmetic means and mean error (M ± m). A p <0.05 was taken as the boundary comparative criterion of statistical significance of reliability.
4. Results
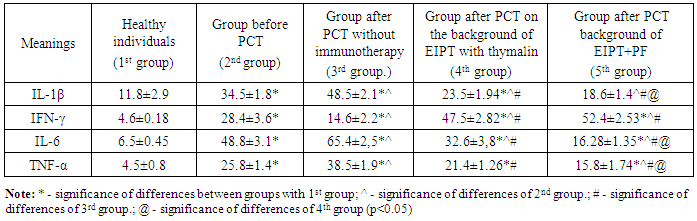
- As a result of the conducted research, a significant increase in the level of all studied cytokines was established compared with the values of a healthy people group.The results are presented in Tab. 1.
|
5. Discussion
- It can be seen that the highest level of IL-6 in the serum of peripheral blood was detected in the group of patients after PCT without the use of immunotherapy options. It has been shown that after PCT without use in the immunotherapy complex, it is manifested by elevated IL-6 values. IL-6 is known to be an important diagnostic indicator of the malignancy of the oncological process [10, 12].Moreover, the best effect from the complex treatment is observed in the group of patients who were applied immunotherapy. Clinically these patients have improved health, no signs of intoxication, the dose intensity of chemotherapy drugs was preserved and the hospital staying did not increase.An imbalance in the content of major cytokines was revealed which manifested itself in significant production of IL-1β and IL-6 and which can be attributed to intermediate cytokines between pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines which in turn indicates the dominance of TX2-type cytokine production.IL-6 is a pleiotropic cytokine with a wide range of biological activity, which is produced by both lymphoid and non-lymphoid cells of the body [7].It should be noted that PCT exacerbated the existing deviations from the average cytokine level of the group of practically healthy individuals and patients before PCT. A special feature of patients with OC on the background of PCT was the progressive inhibition of the mechanisms of cytokine regulation in the course of chemotherapy.Further, the level of TNF-α has been studied which according to the literature is an immunological marker of malignancy and progression of the oncological process, which correlates with the clinical manifestations of malignant processes [12].The study of TNF-α revealed a significant increase in its values in all studied groups of patients with OC compared with the 1st group of healthy individuals. The analysis showed that serum levels of TNF-α were statistically increased in all groups of patients when compared with each other.The exception was the absence of a significant difference in the content of TNF-α between the 2nd and 4th groups of patients with OC.Comparative analysis of TNF-α levels with the 1st group of healthy individuals showed that the level of TNF-α was increased in the 2nd group of patients before PCT in 5.7 times, in the 3rd group after PCT without immunotherapy – in 8.6 times , in the 4th group after PCT in the complex of EIFT – in 4.8 times and in the 5th group of patients after PCT in the complex of EIFT + PF – in 3.5 times.Therefore, the highest level of TNF-α in the serum of peripheral blood was detected in the 3rd group of patients after PCT without the use of immunotherapy options.It was shown that by the end of treatment in the 5th group of patients a significant decrease in the level of TNF-α was observed which was associated with an improvement in the general condition of the patients. Thus, an increase in proinflammatory cytokines in the serum of peripheral blood of patients with OC was found.
6. Conclusions
- The cytokine profile in OC was characterized by a high content of major pro-inflammatory cytokines and IL-6, which can also be attributed to anti-inflammatory cytokines. It was shown that pro-inflammatory cytokines prevailed over the IL-6 content against the background of an increase of interferon, especially during immunotherapy.Inclusion of EIFT and EIFT + PF into the complex of accompanying treatment is one of the ways to reduce endogenous intoxication during antitumor drug therapy. The use of the above-mentioned methods of immunotherapy, according to modern literature, can serve as a modifier of chemotherapeutic treatment, since its tolerance directly depends on the functional state of the organs and physiological detoxification systems of the body [9], as well as, not least, the immune system.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML