-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2018; 8(2): 377-381
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20180812.05

The Use of Cyclopheron for Immunocorrection in Patients with Ovarian Cancer
Tillyashaykhov Mirzagaleb Nigmatovich, Kamishov Sergey Viktorovich
Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center of Oncology and Radiology, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The aim of the research was to study the main cytokines ofimmune system in the patients with ovarian cancer in the complex of polychemotherapy using extracorporeal immunopharmacotherapy with Cyclopheron. The groups of patients with the use of various immunotherapy options – extracorporeal immunopharmacotherapy with cyclopheron were examined. Carrying out of extracorporeal immunopharmacotherapy with cyclopheron has promoted the increase of immunomodulating cytokines content in the blood. It is obvious that the use of immunotherapy in combination with chemotherapy in our opinion is a justified and effective method which leads to the normalization of the immune system immunological indices, allows to improve immediate treatment results, to reduce the intoxication of the disease and promotes a decrease of the disease clinical manifestations.
Keywords: Ovarian cancer, Immunotherapy, Extracorporeal immunopharmacotherapy, Cycloferon, Polychemotherapy
Cite this paper: Tillyashaykhov Mirzagaleb Nigmatovich, Kamishov Sergey Viktorovich, The Use of Cyclopheron for Immunocorrection in Patients with Ovarian Cancer, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 8 No. 2, 2018, pp. 377-381. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20180812.05.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- A mortality from ovarian cancer (OC) exceeds the mortality from cervical cancer and uterine body taken togetherin spite of the achieved successes in the diagnostics and treatment. A rough index of OC morbidity in 2016 in Uzbekistan made up 2.2 and a mortality – 1.3 for 100000 of population. Meanwhile, a general oncological morbidity all over the country made up 66.8 and mortality – 43.8 for 100000 of population [the State Committee of Statistics of Uzbekistan]. Ovarian cancer occupies a stable third place in the structure of oncogynecological pathology [4, 8]. It has been proved that the course of timorous process itself forms immunodeficiency state reducing antitumoral immune response. Besides, the tumorous process is followed by endotoxicosis. It should be noted that endotoxicosis is a complicated, multicomponent process which is caused by the accumulation of endotoxic substances in the tissues and biological fluids in the conditions of a decrease of physiological processes detoxification. Performing of chemotherapy promotes further growth of endogenous intoxication, suppression of the body's immunocompetence which complicates the course of the main oncological disease and sometimes with the development of organ and systemic disorders, limits the possibilities for an adequate course of antitumor treatment [1-4]. It is known that polychemotherapy suppresses not only cellular parameters but also humoral factors up to cytokines which are very important in the realization of antitumor immunity. A small quantity of immunologic drugs which have an evident immunotropic activity are used in the oncology for stimulation of immunity. Cyclopheron being interferon inducer is an immunotropic drug of broad action spectrum. It helps to overcome an oncological endotoxicosis and a secondary immunologic deficiency. It is necessary to mention that reasonable approaches to the use of immunotropic drugs for achieving the aim are being developed currently. The aim in this situation is a reduce of endotoxicosis and an increase of antitumor and anti-infectious immunity. In connection with all mentioned above, the goal of the research is to study the Cyclopheron effect to the condition of patients with ovarian cancer.
2. Material and Methods
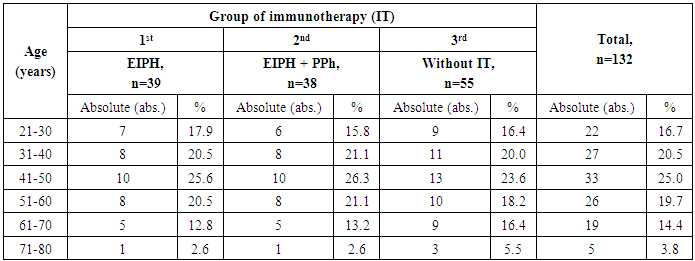
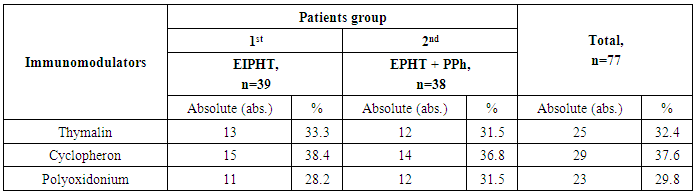
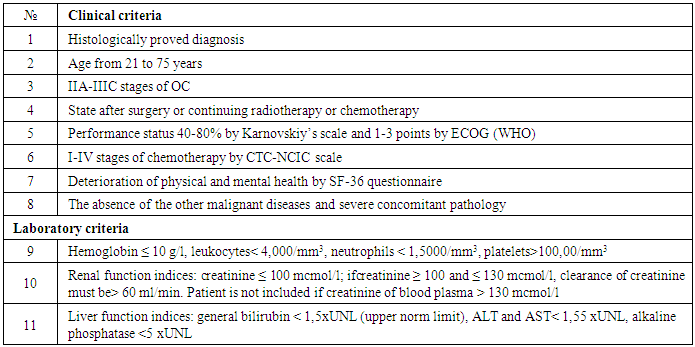
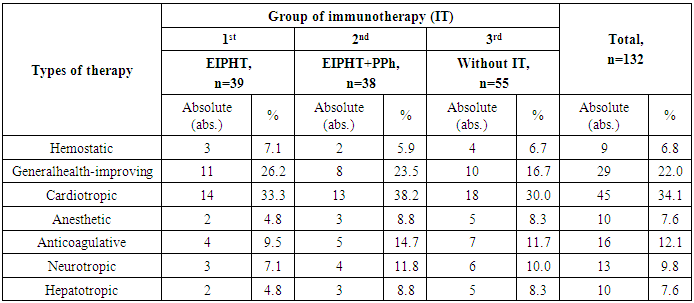
- 132 women with ovarian cancer of T2-3N0-1M0 stages (II-III clinical stages) who were on treatment at oncogynecology and chemotherapy departments of the Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center of Oncology and Radiology between 2004 and 2014 were included into the research. The age of the patients varied from 23 to 75 years (mean age made up 42.6±6.5 years) (Tab.1). In accordance with the objectives of the study patients with OC were randomized to the following groups: the 1st group – 39 (29.5%) patients performed extracorporeal immunopharmacotherapy (EIPHT), the 2nd group – 38(28.8%) patients performed EIPHT with plasmapheresis (PPh) and the 3rd one (control group) – 55 (41.7%) patients without performing immunotherapy (IT).All patients received a combined therapy in adjuvant or neoadjuvant regimens including chemotherapy by standard treatment schemes. EIPHT in the patients with immunomodulators was used in the period of radiotherapy, chemotherapy and also after operative intervention. EIPHT was performed by exfusion of 200-250 ml of autoblood in sterile "Gemakon" or "Terumo" containers and incubation with immunomodulators: thymic drug (Thymalin) in a total dose of 60 mg (3 procedures); Cyclopheron in a total dose of 750 mg (3 procedures); Polyoxidonium in a total dose of 36 mg (3 procedures) at 37°C for 60-100 minutes with the subsequent return of the conjugate to the circulatory system of the patients (Fig.1, 2, Tab.2).
|
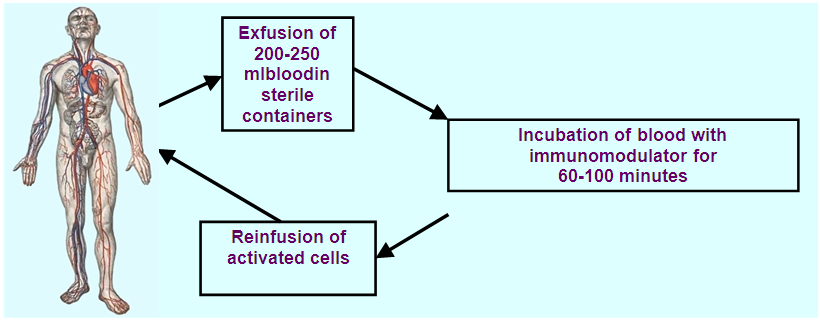 | Figure 1. Method of EIPHT |
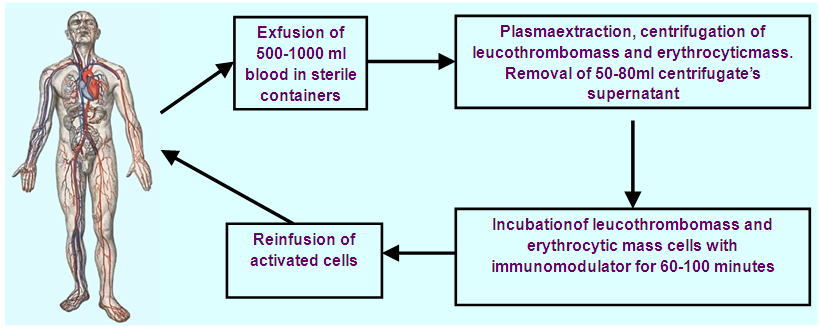 | Figure 2. Method of EIPHT+Plasmapheresis |
|
|
|
|
|
3. Results
- The obtained analysis result showed that a mean content of leucocytes in peripheral blood in all patients groups was reduced in compare with the value of practically healthy persons. Significant reduce of leucocytes content was revealed in the patients groups before and after treatment without the use of IT in compare with the data of healthy persons group and the patients in the groups with the use of EIPHT and EIPHT+PPh. The extreme content of leucocytes was revealed in the group with EIPHT+PPh and made up 6280.9±280.7 kl/mkl and the lowest one – in the group without IT. The study of relative content of lymphocytes general pool between investigated groups showed that the lymphocytes quantity was significantly suppressed in all patients groups in compare with the value of practically healthy group except the value of the patients after using EIPHT+PPh who had a significant increase of lymphocytes general quantity. It was revealed that the most significantly low value of lymphocytes had been observed in patient groups before the treatment and without IT in the complex treatment. The level of lymphocytes in the patients of the 3rd group made up 29.3±1.2%, in the patients with EIPHT – 36.8±1.44% and in the patients with EIPHT+PPh – 41.5±1.2%. The conducted investigations showed that the use of immunotherapy (EIPHT, EIPHT+PPh) in the complex of chemotherapy allows to improve cellular indices of the immune system and to approximate them to the normative values of practically healthy persons.
4. Discussion
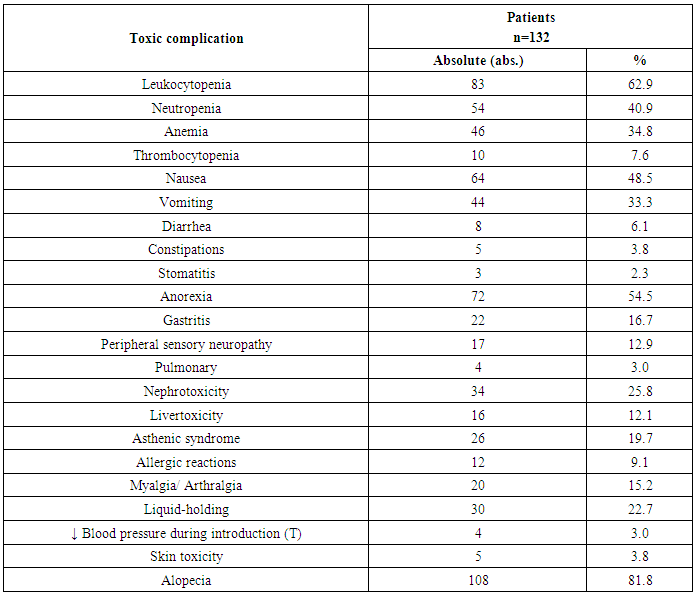
- The peculiarity of patients with OC on the background of PCT was the progressive suppression of the mechanisms of cytokine regulation during chemotherapy. Consequently, an increase in proinflammatory cytokines in the serum of peripheral blood of patients with OC was observed. Thus, cytokines in OC were characterized by an increased content of the main pro-inflammatory cytokines. Inclusion in the complex of accompanying treatment of EIPHT and EIPHT + PPh, is one of the ways to reduce endogenous intoxication during antitumor drug therapy. Application of the abovementioned immunotherapy methods, according to modern literature, can serve as a modifier of chemotherapy treatment, since its tolerance directly depends on the functional state of the organs and systems of physiological detoxification of the organism. The estimation of interferons system functional state is a study of their content [6-7]. The study of immune system mediators condition at malignant processes undergoes particular difficulties which are manifested by instable course of oncologic process, occurrence of different forms and morphologic types of the disease. We detected the increase of proinflammatory cytokines in the serum of peripheral blood in the patients with OC. Cytokine spectrum at OC was characterized by a high content of main proinflammatory cytokines and IL-6 which can be referred to proinflammatory cytokines. It has been shown that proinflammatory cytokines predominated over IL-6 content against the background of interferon’s decrease especially during immunotherapy. Inclusion in the complex of accompanying treatment of EIPHT and EIPHT + PPh is one of the ways to reduce endogenous intoxication during antitumor drug therapy. The use of above mentioned methods of immunotherapy, by literary data, can serve as a modifier of chemotherapeutical treatment because its tolerance directly depends on the organs functional state and the systems of the organism physiological detoxification [8] and also it depends on the state of the immune system. So, the study of cytokines in the patients with OC has not only a scientific but practical value for the estimation of the immune system and prediction of the disease. IFN-γ has antiviral and tumorigenic activity, activates monocytes and macrophages, natural killers (cytotoxicity), proliferation and differentiation of T-lymphocytes, suppresses tumor growth, proliferation of B-lymphocytes [4-5]. The highest level of IFN-γ in the serum of peripheral blood was detected in the group after polychemotherapy in the complex of EIPHT with Cyclopheron. Moreover, Cyclopheron possesses a pronounced ability to induce the main interferons of the body which play an important role in the formation of an adequate immune response. Therefore, the conducted studies showed that the most effective in reducing the side effects of chemotherapy in the complex treatment of patients with OC II-III stages, as well as in improving the subjective state of patients and their quality of life, immunotherapy schemes including the use of EIPHT and EIPHT + PPh which reduce the main clinical manifestations of the toxicity of chemotherapy, improves the subjective state of the patient.
5. Conclusions
- The EIPHT method developed by us has great prospects in oncological practice due to the possibility of removing the cancer consequences and chemoradiation intoxication and also for activation our own system of antitumor protection of the body which should positively affect the outcome of the disease and lead to an increase of the quality and life span of the patients.
Abbreviations
- PPh– plasmapheresis EIPHT – extracorporeal immunopharmacotherapyOC – ovarian cancersIT – immunotherapyPCT – polychemotherapy
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML