-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2018; 8(1): 341-347
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20180811.09

A Comparative Study: The Effect of Ghrelin on Blood Pressure in Normotensive and Induced Hypertensive Rats
Mohamad Y. R. Yosof1, Husam M. Edrees1, 2
1Physiology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, Egypt
2College of Public Health and Health Informatics, Qassim University, Saudi Arabia
Correspondence to: Husam M. Edrees, Physiology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Ghrelin receptors in the heart, kidney, and blood vessels provide proof of ghrelin effect on blood pressure. Aim: This research was conducted to compare the effect of ghrelin on blood pressure in normotensive and hypertensive rats with other common antihypertensive drugs. Methods: 72 male albino rats were distributed into 9 groups; 1st group: control, 2nd group: Ghrelin treated, 3rd group: Uninephrectomized (UNX) rats, 4th group: UNX + Ghrelin treated (UNX+Gh) rats, 5th group: DOCA-salt Hypertensive, 6th group: DOCA-salt Hypertensive + Ghrelin (DOCA+Gh), 7th group: DOCA-salt Hypertensive + Ca channel Blocker, 8th group: DOCA-salt Hypertensive + Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitor, 9th group: DOCA-salt Hypertensive + Selective Beta 1 receptor Blocker. Results: blood pressures (diastolic and systolic) were decreased insignificantly (P>0.05) in ghrelin treated group in comparison with control group and significantly (P < 0.05) in (UNX+Gh) group in comparison with UNX group. In (DOCA+Gh) group, ghrelin decreased systolic blood pressure significantly (P<0.05 compared with UNX group and highly significantly (P<0.0001) compared with DOCA group in all weeks. DOCA+Gh group was Significantly different (p<0.05) from DOCA+ Nifidipine, DOCA+ ACEI and DOCA+ B Blocker groups. Conclusion: ghrelin produced a significant inhibitory effect on systolic and diastolic blood pressure, this effect is comparable to that produced by calcium channel blockers and less than that produced by ACEI and B blockers. Indication of ghrelin as a new antihypertensive line for treatment of hypertension in chronic use needs further studies on human for longer periods.
Keywords: Blood pressure, DOCA, Ghrelin, Uninephrectomy
Cite this paper: Mohamad Y. R. Yosof, Husam M. Edrees, A Comparative Study: The Effect of Ghrelin on Blood Pressure in Normotensive and Induced Hypertensive Rats, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 8 No. 1, 2018, pp. 341-347. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20180811.09.
1. Introduction
- Ghrelin is a hormone synthesized by gastric mucosal cells in humans and was purified from rat stomach [1-3]. Ghrelin regulates appetite, food and calories intake as it has orexigenic effect, it also has regulatory effect on various organs and systems. Ghrelin is stated to be manager of obesity, insulin resistance and diabetes independent of its effect on food intake. In addition, ghrelin stimulates secretion of growth hormone, modulates gastric acid secretion, motility and pancreatic secretions [4].Ghrelin is isolated from human cardiomyocytes. Ghrelin has been proofed to affect the vagal fibers preventing the increase of cardiac sympathetic nerve activity (CSNA) and arrhythmia accompanying Myocardial infarction (MI), improving the survival prognosis [5]. Moreover, it prevents severe sympathetic stimulation by decreasing epinephrine and norepinephrine during the recovery period after MI [6].Serum ghrelin consists of deacyl ghrelin (90%) and acyl ghrelin (10%). The acyl part is mandatory for ghrelin to bind to secretagogue receptor of growth hormone (GHS-R) and motivation of the pathway of inositol triphosphates/calcium [7]. Ghrelin is presented in multiple tissues in addition to stomach like cardiomyocytes, lung cells, pituitary and hypothalamus [8, 9]. Moreover, ghrelin receptors are expressed in pre-ganglionic sympathetic fibers [10], so, microinjection of ghrelin into Nucleus of the Tractus Solitarius (NTS) created hypotensive effects [11].Mao et al. [12] proofed that ghrelin regulates blood pressure by reporting highly expressed growth hormone secretagogue receptor in heart, kidney and blood vessels. He reported that serum ghrelin level correlates inversely with blood pressure. The same results obtained by Zhao et al. [13] who stated that ghrelin significantly reduced systolic blood pressure and increased insulin sensitivity by decreasing oxidative stress in fructose-induced rat. In addition, studies of Nagaya et al. [14] showed a hypotensive response including reductions in BP and HR in healthy subjects and patients with congestive heart failure elicited by ghrelin. Matsumura et al. [15] discovered that acute intra-cerebro-ventricular (ICV) injection of ghrelin in conscious rabbits elicited a dose-dependent decrease in blood pressure, heart rate and renal sympathetic nerve activity. These results indicated the effect of ghrelin as a regulator of cardiovascular function.However, You et al. [16] found that mutations in the GHRL gene did not confer risk for Metabolic Syndrome. Moreover, Prior et al. [17] found that children from mothers fed an non-fat diet exhibited no alteration in renal sympathetic nerve activity (RSNA), whereas increased RSNA response was shown in m-HFD (maternal- High Fat Diet) rabbits received low dose of ghrelin that provoked little change in Mean Arterial Pressure or HR.For this controversy, this study was conducted to elucidate the effect of ghrelin on blood pressure in normotensive and hypertensive rats and comparing this effect (if present) with other common antihypertensive drugs.
2. Material
- Ghrelin: was purchased from sigma trade company, Cairo, Egypt. It was dissolved in saline to a stock solution of 100 µM/L [18]. It is injected intravenously (10 μg/kg) 30 minutes before induction of hypertension [13].DOCA: Sigma Chemical Co., dissolved in Di-Methyle-Sulf-Oxide (DMSO). 25 mg/kg, twice/week injected subcutaneously [19].Captopril: (10 mg/kg b.w.) was injected intraperitoneally to block angiotensin-converting enzyme [20].Nifedipine: was dissolved in 50% ethanol (1 mg/ml) and injected intravenously in volumes up to 0.4 ml/kg b.w. This vehicle had no significant lasting BP effects [20].Bisoprolol: 10 mg/ kg/ day administered orally [21].
3. Methods
- 72 male albino rats obtained from laboratory animal research unit of college of agriculture, Zagazig University, Egypt. All animal experiments were done consisting with national ethical guidelines.Experimental protocol: Animals were divided into 9 groups (8 rats/group):1st group; control group.2nd group: Ghrelin treated group.3rd group: Uninephrectomized, UNX-group.4th group: UNX+ Ghrelin group.5th group: DOCA-salt Hypertensive group.6th group: DOCA-salt Hypertensive + Ghrelin group.7th group: DOCA-salt Hypertensive + Ca channel Blocker group (Nifidipine).8th group: DOCA-salt Hypertensive + Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitor (ACEI) treated group (Captopril).9th group: DOCA-salt Hypertensive + Selective Beta 1 receptor Blocker group (Concor).Induction of Hypertension:Uninephrectomy (UNX) hypertensive rats:Left nephrectomy was performed onrats of group 3 to group 9. Rats were anaesthetized with ketamine (75 mg/kg) injected intraperitoneally. Left kidney was exposed by a left lateral abdominal incision (1 cm long), ligation of left renal artery and ureter by silk thread, dissection of the left kidney and the muscles and skin over the incision was sutured. Rats were allowed to drink tap water ad libitum after operation without treatment [19].DOCA-salt hypertensive rats:In DOCA-salt hypertensive groups (from group 5 to group 9), rats were injected subcutaneously with DOCA (25 mg/kg, twice/week) and received NaCl 1% in the drinking water for six consecutive weeks [22].Measurement of blood pressure:Blood pressures (Systolic and diastolic) were recorded weekly using tail-cuff method (IITC, model 31, Woodland Hills, CA, USA). For 15 min, the rats were sited in heated chamber at a temperature of (30–34°C). We recorded 1–9 values for each animal and the mean blood pressure was calculated by the sum of lowest three records [23].Statistical analysis:All data were presented as mean ± standard deviation. Statistical significance of the differences was calculated by unpaired Student’s t-test using Graph Pad Software Quick Calcs. A p value ≤ 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
4. Results
- Table 1 demonstrates that systolic blood pressure was decreased insignificantly (p>0.05) in 2nd group (ghrelin treated group) in comparison with 1st group (control group) in all weeks. However, Systolic blood pressure was decreased significantly in 4th group (UNX+ Ghrelin group) compared with 3rd group (UNX group) throughout the experiment period.
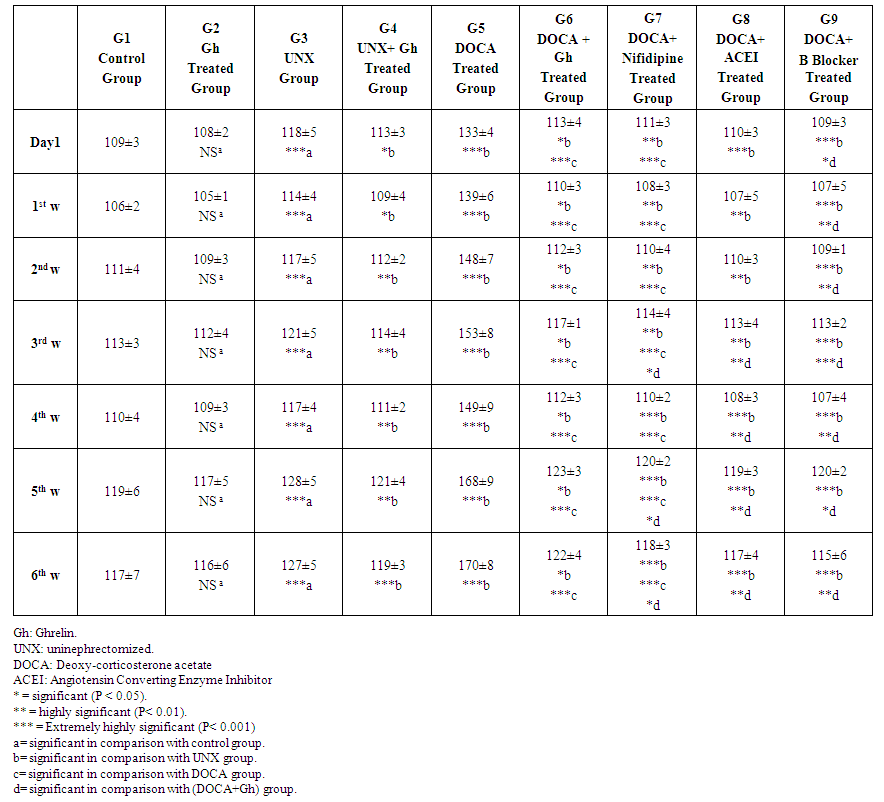 | Table 1. Effect of Ghrelin on systolic blood pressure (mmHg) in comparison with other antihypertensive Drugs |
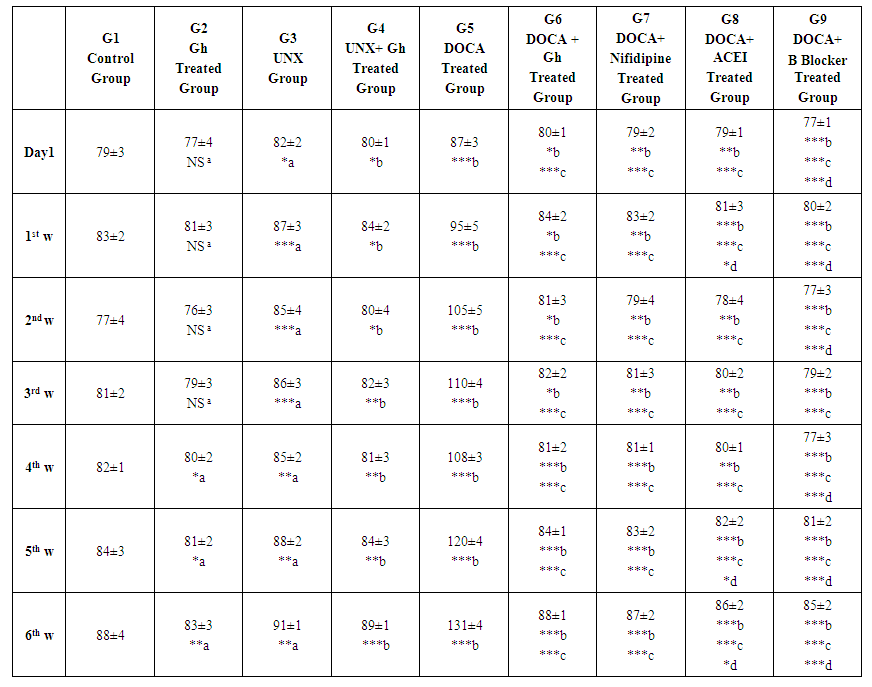 | Table 2. Effect of Ghrelin on diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) in comparison with other antihypertensive Drugs |
5. Discussion
- Ghrelin is a hormone synthesized by gastric mucosal cells in humans, regulates obesity and insulin resistance and proofed that ghrelin regulates blood pressure. Moreover, ghrelin receptors are expressed in pre-ganglionic sympathetic fibers [10], so, microinjection of ghrelin into Nucleus of the Tractus Solitarius (NTS) created hypotensive effects [11].Zhao et al. [13] found that ghrelin decreased systolic blood pressure significantly and they concluded that ghrelin might lower blood pressure. Other studies have shown that ghrelin reduced blood pressure and heart rate in congestive heart failure and in healthy subjects [14]. Acute intra-cerebro-ventricular (ICV) injection of ghrelin in conscious rabbits elicited a dose-dependent decrease in blood pressure, heart rate and renal sympathetic nerve activity. These results indicated the effect of ghrelin as a regulator of cardiovascular function [15]. However, You et al. [16] found that mutations in the GHRL gene did not confer risk for Metabolic Syndrome.For this controversy, we designed this study to examine the effect of ghrelin on blood pressure in normotensive and hypertensive rats and comparing this effect (if present) with some common antihypertensive drugs.In the present study, systolic blood pressure (SBP) was decreased insignificantly (P>0.05) in ghrelin group compared with normal control group throughout experimental period. However, ghrelin decreased systolic blood pressure significantly (P < 0.05) in (UNX+G) group compared with UNX group in (first day, 1st week and 2nd week) and highly significantly in 3rd, 4th, 5th and 6th weeks. Our findings are in agreement with [24] who found that chronic intra-cerebro-ventricular (ICV) ghrelin infusion decreased blood pressure slightly, decreased HR by ~26 bpm and reduced sympathetic tone by 50%. They concluded that ghrelin reduced HR in a sustained manner with moderate reduction of blood pressure animals with normal and high blood pressure in spite of elevated appetite and body weight.Our results revealed that in uninephrectomized (UNX) rats, SBP was significantly higher compared with control group (p< 0.001) and significantly lower than in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. In this study, Ghrelin decreased systolic blood pressure significantly (P<0.05) in (DOCA+Gh) group compared with UNX group (P= 0.04, 0.04, 0.02, 0.04, 0.01, 0.02 and 0.04) in Day 1, 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th and 6th weeks respectively. Ghrelin also decreased systolic blood pressure highly significantly (P<0.0001) in (DOCA+Gh) group compared with DOCA group in all weeks. Our findings are in agreement with [13] who found that the systolic blood pressure decreased significantly (P <0.05) to the steady state in the 5th week.The mechanism of action of ghrelin is suggested to be due to inhibited sympathetic activity as well as inhibited myocardial contractility. Our suggestion is supported by [15, 17, 23]. Matsumura et al. [15] reported that decreases in cardiac output and HR with ghrelin treatment reduced BP. Prior et al. [17] postulated that higher doses of ghrelin reduced mean arterial blood pressure and heart rate centrally by decreasing sympathetic stimulation of the heart or to non-renal vasculature and not due to increased renal sympathetic discharge. Soeki et al. [25] found that acute ghrelin administration in conscious rats with myocardial infarction reduced high plasma norepinephrine levels. They suggested that decreased heart rate after ghrelin administration may be due to stimulation of parasympathetic nervous system beside inhibited sympathetic activity.In the present study, we found highly significant (P= 0.004) and extremely highly significant reduction (P< 0.0001) in systolic blood pressure in DOCA+Nifidipine group compared with UNX and DOCA groups respectively. Also, ACEI produced highly significant decrease in systolic blood pressure in comparison with UNX group in Day 1, 1st, 2nd and 3rd weeks (P= 0.001, 0.008, 0.004 and 0.003 respectively) and extremely significant reductions in 4th, 5th and 6th weeks (P= 0.0002, 0.0006 and 0.0006 respectively). Beta Blocker produced highly significant decrease in systolic blood pressure in comparison with UNX group in Day 1 (P= 0.001) and extremely significant reductions throughout experimental period (P= 0.0006, 0.0006, 0.0009, 0.0002, 0.0009 and 0.0007 respectively).In this study, insignificant differences were found between DOCA+Gh group and DOCA+ Nifidipine group in first day, 1st and 2nd weeks respectively. However, significant differences were found between DOCA+Gh group and DOCA+ Nifidipine group (p=0.05, 0.03, 0.04) in 3rd, 5th and 6th weeks respectively. Significant differences were also found between DOCA+Gh group and DOCA+ ACEI group (p=0.01, 0.01, 0.01 and 0.02) in 3rd, 4th, 5th and 6th weeks respectively. Significant differences were also found between DOCA+Gh group and DOCA+ B Blocker group (p=0.04, 0.01, 0.0002, 0.01, 0.03 and 0.01) throughout experimental period. The findings of this study are in accordance with [17] who found that ICV ghrelin infusion created dose-dependant decrease in mean arterial pressure (7%–10% at the highest dose of 5 nmol) and HR (21% to 24%) in m-NFD (maternal Non-Fat Diet) and m-HFD (maternal High-Fat Diet) rabbits (P<0.05). Our findings suggested that the effect of ghrelin on blood pressure is lesser than that produced by common antihypertensive drugs and this can be explained by the mechanism of action of ghrelin which is not mediated by direct effect on blood vessels. Our suggestion is supported by [26] who found that ghrelin decreased blood pressure by inhibiting sympathetic discharge and not due to direct effect on blood vessels.However, our suggestion is in controversy with [12] who suggested that ghrelin affect blood pressure through modifying activity of autonomic nervous system, direct vasodilatation effect and renal diuresis. However, this controversy might be due to species differences where studies reporting direct vasodilator effect are conducted in human volunteers. Also, this difference can be attributed to method of administration of ghrelin where chronic ghrelin administration here differs from acute administration in other studies reporting direct action [27, 28]. Our suggestion is also supported by [29] who reported that ghrelin does not affect unique vascular receptor reducing BP when activated by low MW GHSR1a agonists.In this study, Ghrelin also produced insignificant inhibitory effect on diastolic blood pressure in day 1, 1st, 2nd and 3rd weeks however significant inhibitory effect was found in 4th, 5th and 6th weeks (p=0.02, 0.03 and 0.01 respectively). In the current study, Ghrelin also produced significant reduction in diastolic pressure (1st day; p=0.02), (1st week; p=0.03), (2nd week; p=0.02), (3rd week; p=0.01) and highly significant reductions (in 4th week; p=0.007), (5th week; p=0.007) and (5th week; p=0.001). Diastolic pressure was increased significantly in DOCA group in comparison with UNX group (P= day 1; 0.001 and 1st week; 0.001) and (P< 0.0001 in 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th and 6th weeks). Ghrelin also produced extremely significant (P< 0.0001 in all weeks) reduction in diastolic pressure in DOCA+G group compared with DOCA group throughout experiment period. Effect of Ghrelin was also significant if compared with UNX group (1st day, P= 0.02), (1st week, P= 0.03), (2nd week, P= 0.04), and highly significant in (3rd week, P= 0.007), (4th week, P= 0.001), (5th week, P= 0.0002) and (6th week, P= 0.0001). Our findings are in agreement with [29] who found that acyl ghrelin (AG) and combined AG + desacyl ghrelin (DAG) infusions decreased systolic BP, diastolic BP, mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) and Heart Rate in comparison with the control. They suggested that the effects of AG are mediated through the autonomic nervous system which needs stimulation of the ghrelin receptor.In the present study, insignificant differences (p>0.05) were found between DOCA+Gh group and DOCA+ Nifidipine group in all weeks which suggest that the effect of Ghrelin on diastolic pressure is comparable to that produced by calcium channel blocker (Nifidipine). However, significant differences were found between DOCA+Gh group and DOCA+ ACEI group (p=0.03, 0.02 and 0.02) in 1st, 5th and 6th weeks respectively and highly Significant differences were also found between DOCA+Gh group and DOCA+ B Blocker group (p=0.0001, 0.001, 0.01, 0.001, 0.002 and 0.002) in first day, 1st, 2nd, 4th, 5th and 6th weeks respectively. These findings suggest that the action of ghrelin on blood pressure is mediated by its inhibitory effect on cardiac contractility as well as sympathetic activity and this explains why ghrelin effect is lesser than B blocker effect. This suggestion is in agreement with [29] who showed that ghrelin inhibits cardiac sympathetic activity and stops early left ventricular remodeling in rats with myocardial infarction.They also found that an intravenous administration of a bolus of human synthetic ghrelin (10μg/kg) to 10 healthy men reduced both heart rate and blood pressure. They suggested that ghrelin could inhibit sympathetic activity and stimulate parasympathetic activity to the heart.Our suggestion is also supported by [29] who reported that ghrelin does not affect a unique vascular receptor or receptors whose activation by ulimorelin, capromorelin and CP464709 reduced BP when activated by low MW GHSR1a agonists.In conclusion, ghrelin produced a significant inhibitory effect on systolic and diastolic blood pressure and this effect is comparable to that produced by calcium channel blockers and less than that produced by ACEI and B blockers. Indication of ghrelin as a new antihypertensive line for treatment of hypertension in chronic use needs further studies on human for longer periods.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML