-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2018; 8(9): 230-234
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20180809.03

Comparative Evaluation of the Influence of the Solution for Infusion Therapy "Rheoambrasol" on the Functional Metabolic Parameters of Erythrocytes in Acute Intoxication Caused by a Heliotrope
Khamid Yakubovich Karimov, Abdumannon Abdupattahovich Isroilov, Larisa Ivanovna Shevchenko, Timur Raufovich Alimov
Department of Molecular Medicine and Cell Technologies, Scientific Research Institute of Hematology and Blood Transfusion of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Uzbekistan, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Timur Raufovich Alimov, Department of Molecular Medicine and Cell Technologies, Scientific Research Institute of Hematology and Blood Transfusion of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Uzbekistan, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Comparatively, the effectiveness of the new solution for infusions Rheoambrasol on the structural and functional parameters of erythrocytes in liver damage by heliotrope was evaluated. The model of liver damage by heliotrope was reproduced in non-native (non-linear) rats. Detoxification therapy was carried out with preparations of Rheosorbilact or Rheoambrasol. The activity of synthase of aminolevulenic acid (ALA synthase) and gemsynthesis in bone marrow cells, the content of uroporphyrin, coproporphyrin and protoporphyrin in erythrocytes was determined by the intensity of lipid peroxidation (LPO), the activity of antioxidant system (AOS) enzymes. A new detoxification drug improves the liver function of rats with liver damage caused by heliotrope.
Keywords: Liver damage, Heliotrope, "Rheosorbilact", "Rheoambrasol", Bone marrow, Erythrocytes
Cite this paper: Khamid Yakubovich Karimov, Abdumannon Abdupattahovich Isroilov, Larisa Ivanovna Shevchenko, Timur Raufovich Alimov, Comparative Evaluation of the Influence of the Solution for Infusion Therapy "Rheoambrasol" on the Functional Metabolic Parameters of Erythrocytes in Acute Intoxication Caused by a Heliotrope, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 8 No. 9, 2018, pp. 230-234. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20180809.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- In recent years, despite the great successes achieved in the field of hepatology, the problem of liver damage and its pharmacotherapy remains one of the urgent problems of experimental and clinical medicine. Disclosure of many aspects of the pathogenesis of this disease allowed for the treatment of various forms of hepatitis pathogenetically justified use of membrane stabilizers, immunomodulators, antioxidants. However, a significant suppression of the activity of enzymes detoxifying the function of the liver and, as a consequence, the development of endogenous intoxication of the body, dictates the need for detoxification therapy using colloidal solutions for intravenous infusions. The most commonly used in modern clinical practice are medium molecular weight hydroxyethyl starches and solutions of succinylated or modified liquid gelatin [7, 13]. The main side effects of synthetic colloids are the effect on hemostasis and renal function, their dose-dependent effect [4]. In this regard, great importance is given to research on the search for new non-toxic agents that would have a hemodynamic effect inherent in colloidal drugs. Of particular importance are the work with the use of polysaccharides, which in addition to minimal toxicity have cytoprotective properties [13, 16]. Polysaccharides are able to protect cells from mechanical damage, in particular, during extracorporeal circulation, autotransfusion using "CellSaver" devices, etc.. Similar properties are due to the fact that polysaccharides are reversibly attached to erythrocyte membranes, preventing mechanical damage like plasma proteins [13].The effectiveness of the means of infusion therapy is determined both by the specificity of the action performed by them and by the polyfunctionality of this specificity, which, taking into account the above-mentioned circumstances, determines the importance of developing preparations of complex action. Recently, much attention has been paid to bioactive polymer complexes capable of restoring metabolism in cells and affecting the vital activity of the organism as a whole. Scientists of the Scientific Research Institute of Hematology and Blood Transfusion and the Institute of Plant Substance Chemistry of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Uzbekistan have developed a large number of biologically active substances from plant materials capable of regulating the vital functions of cells, restoring the disturbed functions of organs and possessing antibiotic, antiviral, anti-tumor, antioxidant, detoxification, immunostimulating activity [13, 16].The economic value of this class of substances is associated with their low cost and high efficiency.As a model for investigating the effectiveness of the new domestic blood substitute in intoxication, a model of toxic liver damage was chosen, namely, an experimental model of heliotrope damage. As is known, heliotrorin is a toxicant of natural origin, containing a mixture of alkaloids and derived from the plant Heliotropium dasycarpum Ledeb (Heliotrope is pubescent), distributed in Central Asia, the Caucasus, the southeast and the European part of Russia and located in the same region states. It grows in steppes and semi-deserts, often as a field and ruderal weed. The cause of people poisoning, as a rule, is clogging of cereal seeds with heliotrope seeds, especially in the years with late spring, when the maturation of breads and heliotrope coincides (due to prolongation) [17]. Since the poisoning with heliotrin is typical for the Central Asian and other regions, it is possible to consider intoxication with heliotrone the most natural in the experimental reproduction of liver damage, which is supported by such researchers as N. Kh. Abdullaev (1966), Fesenko, L.M. (1984), Varganova, E.I. (1984), Dombrovskaya N.V. (1993) [1, 2, 11, 14] and other authors using heliotrone intoxication as an experimental model in their studies [10].
2. Main Body
2.1. Purpose of the Study
- Comparatively evaluate the effectiveness of the new solution for infusions "Rheoambrasol" on the structural and functional parameters of erythrocytes with liver damage by heliotrope.
2.2. Material and Methods of Investigation
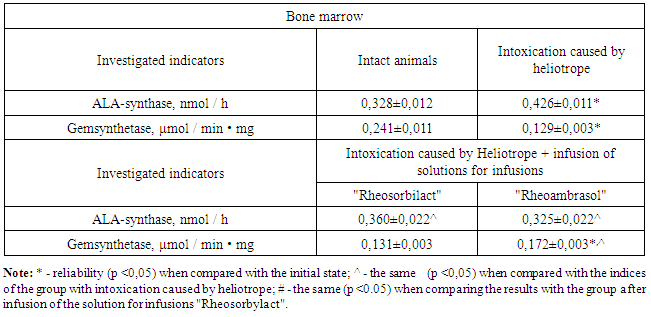
- The model of liver damage by heliotrope in 30 non-native male rats was reproduced by a single administration of heliotrone in a dose of 40 mg / kg subcutaneously. 48 hours after administration of the toxicant (heliotrin), the animals were divided into groups: I - (control) rats with heliotrone hepatitis (n = 10), II - rats with heliotrope hepatitis after infusion of the drug "Rheosorbilact" (n = 10), III - rats with heliotrope hepatitis after infusion of the drug "Rheoambrasol" (n = 10). Infusion therapy was performed by introducing solutions for infusions into the tail vein to rats at a dose of 5 ml / kg body weight for 5 days. An intact group consisted of 8 rats on an ordinary laboratory diet. To determine the status of the liver monooxygenase system, after 24 hours after the final administration of drugs in the rats, etaminal sleep was performed, according to a conventional technique that reflects the detoxifying function of the liver. 24 hours after the ethanol sleep, the animals were sacrificed under light ether anesthesia. In the blood serum, biochemical indices were determined. The measurements were carried out on a BA88A semiautomatic biochemical analyzer (Mindray, China). Synthase activity of aminolevulenic acid (ALA-synthase) and gemseintetase in bone marrow cells was determined by the method of P.A. Kaliman et al. and expressed in nmol ALA/h per 1 mg protein and μM protoporphyrin / min. mg of protein [6]. The content of uroporphyrin, coproporphyrin and protoporphyrin in erythrocytes was determined by the method of E. A. Shwartz in the modification of V. I. Music and expressed in nmol / l. The intensity of lipid peroxidation (LPO) in erythrocyte hemolysates was determined by the level of malonic dialdehyde (MDA) [3]. The activity of the antioxidant system (AOS) enzymes was determined: superoxide dismutase (SOD) [12], glutathione peroxidase (GPO) [5] and catalase [9]. All measurements were performed on a UNICO2800 spectrophotometer (United Products and Instruments, Inc., USA). The digital material is processed by the method of variational statistics. Statistical processing was carried out using the programs "Excel" and "Biostat". The criterion of statistical significance was the value p <0.05.
2.3. Results and Discussion
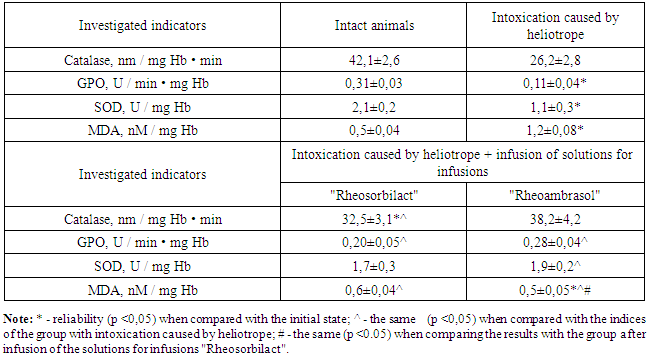
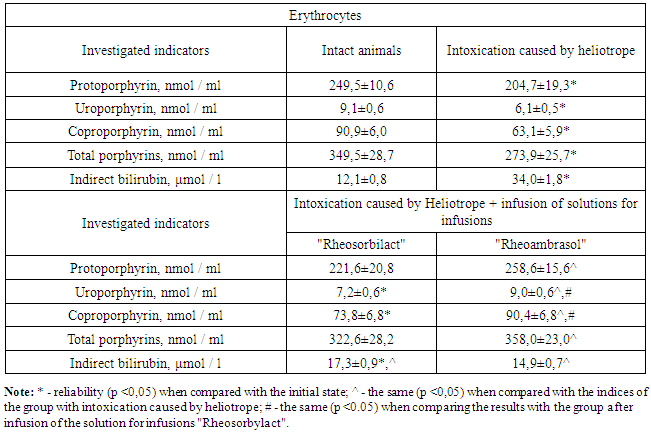
- The results of the conducted studies showed that after the introduction of the heliotrope the condition of animals in group I was severe, they were sluggish, they refused to eat. The duration of etaminal anesthesia was prolonged from 72.8 ± 8.3 min in intact rats to 304.6 ± 16.8 min (P <0.001) in the experimental, cytolysis and cholestasis syndromes developed, which was confirmed by exertion of ALT and AST in the blood plasma by 351.7 (P <0.001) and 456.3% (P <0.001), the level of total and direct bilirubin by 193.4 (P <0.001) and 255.9% (P <0.001), respectively. There was a slight increase in urea levels, and the creatinine concentration increased by 16.9%.One of the main causes of cell death in the case of the action of the hepatotropic agent is the depletion of the system of energy production and detoxification of xenobiotics. In this regard, a very promising direction in medicine is the creation of tools that restore the metabolism of hepatocytes in various pathological conditions [8, 15]. Carrying out detoxification therapy with "Rheosorbilact" or "Rheoambrasol" preparations, the animals' condition improved, tearing, salivation ceased, animals became active. The activity of ALT significantly decreased in 3 and 3.97 times, AST - in 2.9 and 3.5 times, total bilirubin - in 2.14 and 2.52 times, direct bilirubin – in 2.88 and 3.56 times, respectively. The results of these studies correlated with the parameters of etaminal sleep, which, after the application of solutions for infusions, was shortened by 2 and 3.1 times, respectively, to the groups receiving "Rheosorbilact" and "Rheoambrasol". As can be seen from the data presented, the use of the new domestic preparation "Rheoambrasol" accelerates the excretion of toxins from the body, reducing the cytolytic manifestations of heliotrines, and in its detoxification activity it is not inferior to the widely used "Rheosorbilact".Along with this, we observed the intensification of LPO, which was manifested by an increase in the level of MDA in the erythrocyte hemolysates by 2.4 times (P <0.001) (Table 1).
|
|
|
3. Conclusions
- Based on the data obtained, the following conclusions can be drawn:1. A new detoxification drug improves the liver function of rats with heliotrone liver damage, especially its pharmaco-metabolizing function.2. "Rheoambrasol" has an antioxidant effect, increases the low activity of SOD, GKO and catalase enzymes in erythrocytes, and protects them from hyperlipoperoxidation. 3. "Rheoambrasol" stabilizes the functional metabolic parameters of bone marrow cells, which is manifested by the restoration of hemoglobin-synthesizing activity, an increase in the content of porphyrins.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML