-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2017; 7(4): 202-209
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20170704.08

Serum Lipid Profile and Its Relationship with Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Hypertensive Adults Attending a Tertiary Hospital in Southern Nigeria
Unamba Norbert N.1, Unamba Blessing C.2, Akpa Maclean R.3
1Department of Medicine, University of Portharcourt Teaching Hospital, Portharcourt, Nigeria
2Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, University of Portharcourt Teaching Hospital, Portharcourt, Nigeria
3Department of Medicine, Faculty of Clinical Sciences, University of Portharcourt & University of Portharcourt Teaching Hospital, Portharcourt, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Unamba Norbert N., Department of Medicine, University of Portharcourt Teaching Hospital, Portharcourt, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

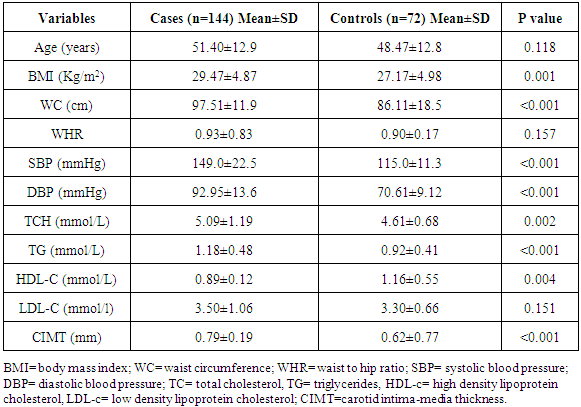
Background: Atherosclerosis is a primary cause of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Dyslipidemia is a key risk factor for the development of atherosclerosis. Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) is an established tool for the detection and assessment of progression of atherosclerosis. The aim was to determine the relationship of serum lipid profile with atherosclerosis determined by Carotid Intima Media Thickness in hypertensive patients attending the cardiology clinic of the UPTH. Methods: 144 Hypertensive subjects and 72 age- and sex- matched controls were recruited. Their waist circumference, body mass indices and fasting lipid profile were determined. Diabetics and patients receiving lipid-lowering drugs were excluded. Carotid intima media thickness was measured in all study subjects using standard protocol. Results were subjected to linear, multiple, and logistic regression analyses. Results: Age range amongst hypertensives was 20 and 86 years, mean was 51.4±12.9 years and controls was 24 – 82years and mean of 47.9±14.7 years p=0.083). Mean waist circumference of the hypertensives was 97.51±11.9cm and controls was 86.11±18.5cm (p<0.001). 50% of the study population were obese, males 20.6% and females 74.4% (X2=61.264, p<0.001).Mean TCH, TG, HDL-C, and LDL-C of hypertensive subjects and controls were (5.09±1.19mmol/L vs. 4.63±0.70mmol/L, P=0.003), (1.18±0.48mmol/L vs. 0.93±0.41mmol/L, p<0.001), (0.90±0.19mmol/L vs. 1.07±0.51mmol/L, p=0.004), and (3.50±1.06mmol/L vs. 3.31±0.66mmol/L, p=0.151). Twenty-seven percent of the study population had elevated total cholesterol, 7.5% had hypertriglyceridemia, 69% had reduced HDL-C and 68.3% had elevated LDL-C. Amongst the hypertensives 52(37.4%), while 5(7.0%) of controls had elevated total cholesterol (X2=21.916, p<0.001), and 87 (62.6%) had reduced HDL-C levels vs. 58 (81.7%) among the hypertensives and controls respectively, (X2=8.022, p=0.005). Mean CIMT in the hypertensives and controls were (0.79± 0.19mm vs. 0.62± 0.78mm, p<0.001). Mean CIMT of untreated and treated hypertensive subjects were 0.83±0.22mm and 0.75±0.14mm respectively, P <0.001). Nine (31%) of the drug-experienced hypertensive patients had increased CIMT while twenty (69%) of the drug-naïve subjects had increased CIMT (X2= 23.729; p<0.001). Conclusion: Triglyceride, LDL-C, age and systolic blood pressure were closely associated with carotid atherosclerosis assessed by carotid intima thickness, while hypertension was most predictive of carotid atherosclerosis.
Keywords: Carotid intima-media, Hypertension, Lipid profile
Cite this paper: Unamba Norbert N., Unamba Blessing C., Akpa Maclean R., Serum Lipid Profile and Its Relationship with Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Hypertensive Adults Attending a Tertiary Hospital in Southern Nigeria, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 7 No. 4, 2017, pp. 202-209. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20170704.08.
1. Introduction
- Atherosclerosis is a primary cause of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Atherosclerosis is a slowly progressive disease with multiple risk modifiable and non modifiable factors. Modifiable risk factors include diabetes mellitus, hypertension, smoking and dyslipidemia. Dyslipidemia is the key risk factor for the development of atherosclerosis and therefore contributes significantly to the development of cardiovascular disease (CVD) [1]. One of the primary factors responsible for atherosclerosis is an increase in serum level of pro-atherogenic lipoproteins especially low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and triglyceride [2]. In addition to increase in LDL-C as an etiology in atherosclerosis, a reduction in the anti atherogenic lipoprotein high density lipoprotein (HDL-C) increases the atherosclerotic risk [3]. Also, Castelli Risk Index (CRI-I) calculated as (TC/HDL-C) and (CRI-II) as (LDL-C/HDL-C) are fractions which have been known to be independent risk factors for atherosclerosis [4].Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) is an established tool for the detection and assessment of progression of atherosclerosis. CIMT increases with the development of atherosclerosis in other body regions making it possible to make inferences about other unexamined and perhaps hard to reach blood vessels such as the coronary arteries [5]. Carotid ultrasonography can therefore be used to non-invasively identify early-stage atherosclerotic changes in the arterial vasculature.Aim: To determine the relationship of serum lipid profile with atherosclerosis determined by Carotid Intima Media Thickness in hypertensive patients attending the cardiology clinic of the UPTH.
2. Methods
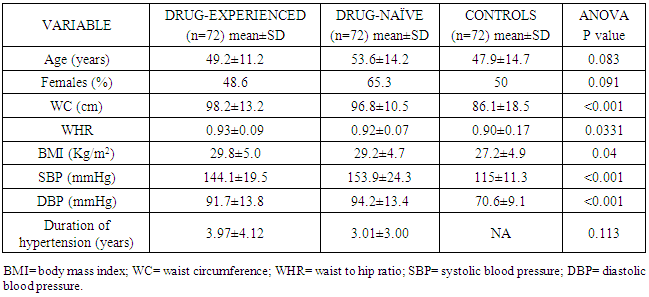
- Study populationStudy subjects were randomly recruited from hypertensive patients attending the general out-patients, and the cardiology out-patients clinics of the University of Port-Harcourt Teaching Hospital from January 2016 to August 2016. Subjects who were on treatment with lipid-lowering drugs and contraceptive pills were excluded from the study. Diabetics were also excluded from the study. All participants underwent a routine clinical examination, blood biochemical examination for lipid profile and carotid ultrasonography. Finally, 144 subjects who met the inclusion criteria were recruited as cases. These were further stratified into two groups of 72 persons with one group consisting of hypertensive patients already on anti-hypertensive drugs (drug-experienced) and the other group were newly-diagnosed, untreated hypertensive patients (drug-naïve). 72 healthy age and sex-matched individuals were randomly selected from hospital staff and patients’ relatives and were classified as controls. Written informed consent was obtained from participants and the ethical committee of the hospital.Demographic and clinical characteristicsDemographic and clinical characteristics such as age, gender, duration of hypertension and current anti-hypertension therapy were obtained by a structured questionnaire. Blood pressure was measured with a standard mercury sphygmomanometer using standard protocol [6]. Height, weight, waist circumference, hip circumference were measured manually. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as weight (kilograms) divided by height (meters) squared. Waist-to-hip ratio was also calculated.Laboratory examinationFasting venous blood were collected after an overnight fast and analyzed in the chemical pathology laboratory of the University of Port Harcourt Teaching Hospital for lipid profile and blood glucose. Fasting cholesterol and triglyceride levels were measured using the enzymatic method [7]. Fasting HDL-C was measured with the precipitation method. LDL-C values were calculated using the Friedewald equation when triglyceride level was less than 4.0mmol/L: LDL-C= TCH- (HDL-C+TG/2.2) [8].Carotid UltrasonographyThe study was performed by the one operator based on agreed protocol by all authors using Aloka Prosound SSD 4000 echocardiography machine equipped with a 7.5 MHz imaging transducer. Both the left and right carotid arteries were evaluated. The common carotid artery was carefully scanned utilizing standard protocol to identify the thickest CIMT. Intima-media thickness was defined as the distance between the leading edge of the lumen-intima and the leading edge of the media-adventitia. Mean value of the three determinations was calculated and the final values of IMT were averaged by the left and right mean IMT values [9]. A normal CIMT was defined as values between 0.5-1.0mm [10]. The radiologists who performed the ultrasound had no data on the patient. Statistical analysisData was expressed as mean± standard deviations and frequencies as a percentage. Continuous variables were compared with the Students t-test or one-way analysis of variance as considered appropriate. Proportions or categorical variables were compared with the Chi-square test. Relations among continuous variables were assessed using Pearson correlation coefficient and linear regression analysis. Multiple logistic models were constructed to elucidate the independent determinants of CIMT. The odds ratio and 95% confidence intervals were calculated. All analyses were performed by SPSS statistical software (version 19.0, SPSS Inc). P values of <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3. Results
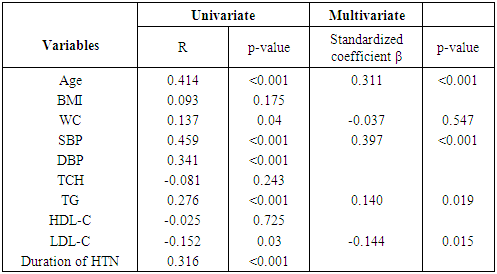
- Clinical characteristicsBaseline clinical characteristics and biochemical parameters of total subjects are shown in Table 1. The age of the study participants with hypertension ranged between 20 and 86 years with a mean age of 51.4±12.9 years. The mean age of the control population was 47.9±14.7 years with a range of 24 – 82 years. The case and controls were matched for age.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. Discussion
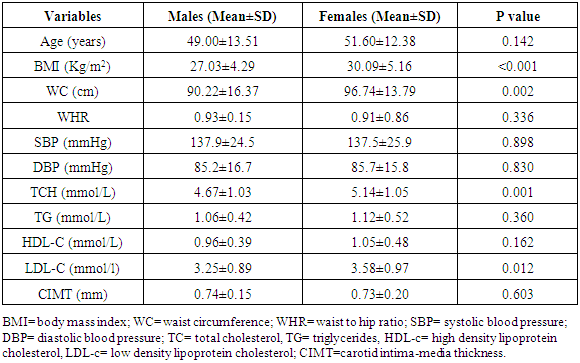
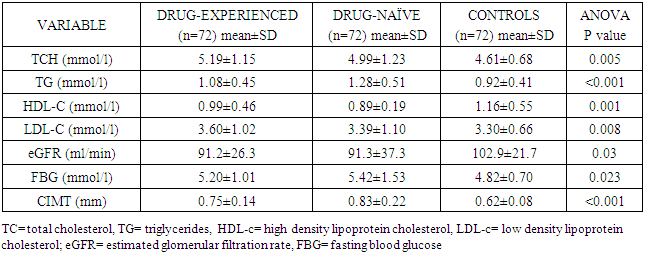
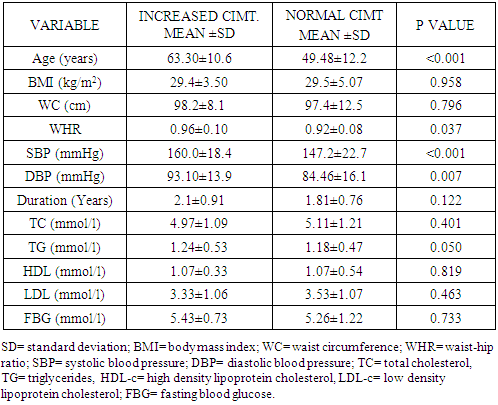
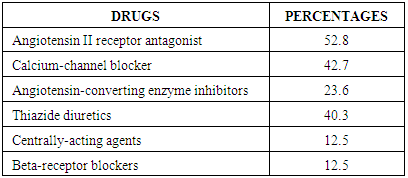
- The measurement of CIMT has emerged as a useful adjunct to cardiovascular disease risk stratification [11]. CIMT is a marker of early atherosclerosis, and CIMT is increased in subjects with several risk factors for atherosclerosis and is a predictor of cardiovascular events and end-organ damage [12]. This study reports a 29.0% prevalence of increased CIMT in patients with essential hypertension. This is lower than the 49.8% reported by Okeahialam et al from the Northern part of Nigeria [13] and postulated that the prevalence rate of increased CIMT in their study population might have been due to the heavy consumption of potato chips which is the staple in their environment. Potato chips are high on acrylamide which is known to induce a proinflammatory state thus contributing to the process of atherosclerosis [13]. In comparison, the staple in Port Harcourt, Southern Nigeria is sea-food which has been proven to be rich in omega-3 fatty acid which is known to retard the progression of atherosclerosis [14]. This study also showed that gender did not have a significant effect on the prevalence of increased CIMT. This was in contrast to the finding by Rahimic-Catic et.al who reported a statistically significant difference in the prevalence of increased CIMT between genders [15]. This can be explained by the fact that there study population comprised of diabetics as well as hypertensives. High glucose levels act directly or indirectly on cells of the artery wall, including endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, and macrophages via the generation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) or reactive oxygen species leading to endothelial dysfunction and accelerated atherosclerosis.This study reported the mean CIMT of the hypertensive subjects were significantly higher than that of the controls. Interestingly, however, was the observation that the mean CIMT value for the newly-diagnosed hypertensives was significantly higher than the mean CIMT values for the drug-treated hypertensives. We found in this study that large proportions of the drug-experienced hypertensives were on treatment with calcium-channel blockers. It is noteworthy to point out that since the turn of the century, a number of clinical trials have sought to show the atherosclerotic attenuating effect of anti-hypertensive drugs. The Prospective Randomized Evaluation of the Vascular Effects of Norvasc Trial (PREVENT) was able show that amlodipine compared with placebo had the ability to significantly slow down carotid atherosclerosis [16]. Furthermore, the disparity in CIMT between the drug-experienced and drug-naïve hypertensive populations could be explained by the fact that a whole lot of hypertensive individuals are actually unaware of their blood pressure situation until their attention is drawn to it by the occurrence of overt cardiovascular complications, or it is discovered incidentally. This was supported by some investigators who found that pre-hypertensive participants (individuals who have not been diagnosed hypertensive or taken anti-hypertensive drugs and having a SBP between 120 to 139mmHg and/or DBP between 80 to 89mmHg) had significantly higher CIMT than normotensives [17, 18]. Two of the major determinants of CVD, hypertension and dyslipidemia commonly co-exist. In fact, a large proportion of the cardiovascular risk in patients with hypertension can be attributable to dyslipidemia [19]. This is also confirmed in this study as dyslipidemia was observed in over 60% of the hypertensive patients and controls, with the majority showing reduced HDL-C levels a vital component of the metabolic syndrome and atherosclerosis promoting pattern [20]. The prevalence of this syndrome is increasing in tandem with the increase in numbers of obese individuals, and is projected to contribute substantially to the burden of atherosclerotic vascular disease in the coming decades [21]. This increase in prevalence of the metabolic syndrome is also borne out in this study where 50% of the study population had visceral obesity (assessed by waist circumference). Visceral obesity is known to cause insulin resistance leading to increased levels of inflammatory cytokines, causing endothelial dysfunction and resulting ultimately in atherosclerotic changes in the vasculature [22].We also found that both the healthy and hypertensive subjects had lower levels of lipids and lipoproteins compared to values found in Caucasians [23, 24] but similar to values reported by other African investigators [25, 26]. The reported differences might be due to the different characteristics of the population studied. Factors such as diet and consumption habits, living standards, stage of epidemiological transition, and life-style ultimately influence these lipid parameters and by association CIMT.In this study, there was statistically significant difference in the level of HDL-C across the three groups, with the drug-naïve hypertensive patients having the lowest values. The low concentration of HDL-C in the drug-naïve patients is not unexpected as low HDL-C values represent a component of the metabolic syndrome, with its attendant risk of cardiovascular events. There was also statistically significant difference in the mean levels of TG and LDL-C across the three groups with the higher values found among the drug-naïve subjects and regression analysis showed that LDL-C and TG were closely associated with CIMT in the study population. Our results are consistent with previous studies which also found a significant association between increased CIMT and high LDL-C levels and hypertriglyceridemia [27, 28]. Studies have shown that TG concentrations are often associated with decreased HDL-C and increased small dense LDL-C levels but the mechanism are not quite clear and this combination appears to promote thrombogenesis, intimal proliferations and atherosclerosis [29, 30]. The use of multiple logistic regression analysis showed that only age and SBP contributed significantly to increase in CIMT. This co-existence of hypertension and dyslipidemia has been reported to have multiplicative rather than additive effects on cardiovascular disease risk through oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction [31, 32]. This was similar to the findings by Chien et al. who reported that changes in blood pressure seems to have a stronger effect on CIMT than change in LDL cholesterol. The stronger association between changes in blood pressure and IMT may be because the hemodynamic change of blood pressure has a stronger impact on carotid intima media thickness, while injuries caused by LDL changes affected the carotid IMT slowly and may not manifest during the study period [33].
5. Conclusions
- In conclusion, we found that TG, LDL-C, age and SBP were closely associated with carotid atherosclerosis. In analyses of the different cardiovascular risk factors, hypertension showed the most consistent positive association with carotid atherosclerosis. The results may indicate that hypertension rather than dyslipidemia may be the principal driver of the atherosclerotic process.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML