-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2015; 5(2): 73-81
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20150502.03
Protective Influence of Zinc on Reproductive Parameters in Male Rat Treated with Cadmium
Nawal Khairy Al-Ani, Ula Al-Kawaz, Ban T. Saeed
High Institute of Infertility Diagnosis and Assisted Reproductive Technology, Al-Nahrain University, Baghdad, Iraq
Correspondence to: Nawal Khairy Al-Ani, High Institute of Infertility Diagnosis and Assisted Reproductive Technology, Al-Nahrain University, Baghdad, Iraq.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The toxic effect of drugs and environmental chemicals on the human reproductive system has become a major health concern. Cadmium (Cd) is a heavy metal toxicant, present widely in our environment and workplaces. A very significant source of Cd is in the production of nickel-cadmium batteries. It is well known that cadmium causes adverse effects on male reproductive organs and reproductive functions in experimental animals. The objective of the present study is to detect the effect of the antioxidant (zinc)) on the toxicity of low dose of Cadmium chloride on some histological and hormonal parameters of the reproductive system of adult male rats.forty five mature albino male rat were used (Rattus rattus norvegicus albinus), as a mammalian model. The statistical analysis shows a highly significant (P< 0.001) decrease in the weight of the testes and the seminal vesicles in treated group when compared with control group and there was a significant (p≤0.05) difference in the group treated with (Cd+zinc) as compared to control. The results of the sperm parameters show a high significant (P< 0.001) decreasein sperm concentration anda highly significant (p≤0.001) decrease in sperm motility mean in treated groups as compared to control. Moreover, administration of (zinc) with Cd in showed a highly significant (p≤0.001) increase in percentage of progressively motile sperms as compared to the group received Cd only. The Levels of serum hormones shows a significant decrease (P<0.05) in the level of testosterone hormone after cadmium administration with non significant deference in testosterone level after cadmium plus zinc administration when compared with control, while highly significant (p≤0.01) increase in the follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) after cadmium administration with significant increase in FSH level after cadmium plus zinc administration when compared with control. Also the results showed significant decrease in LH level after cadmium administration with non significant deference in LH level after cadmium plus zinc administration when compared with control. In conclusion, these findings suggest that cadmium, like all other heavy metals, could induce oxidative stress and the concomitant administration of antioxidants like (zinc) can ameliorate the toxic effect of Cadmium on spermatogenesis.
Keywords: Cadmium, Zinc, Rats, Reproductive organs, Testis
Cite this paper: Nawal Khairy Al-Ani, Ula Al-Kawaz, Ban T. Saeed, Protective Influence of Zinc on Reproductive Parameters in Male Rat Treated with Cadmium, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 5 No. 2, 2015, pp. 73-81. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20150502.03.
1. Introduction
- The toxic effect of drugs and environmental chemicals on the human reproductive system has become a major health concern [1]. Incidence of chemically induced germ cell damage and sterility appears to be on the increase [2]. Cadmium (Cd) is a very toxic heavy metal and an important environmental pollutant which is present in the soil, water, air, food and in cigarette smoke. Cadmium has been released into the environment through human activities and is routinely found as a contaminant in tissues collected from the human population throughout the world [3]. It is a toxicant that has a long biological half-life (15–20 years) and accumulates over time within the blood, kidneys, liver, and reproductive organs [4]. It caused a poisoning in various tissues of humans and animals. Acute administration of Cd often induces lethal toxicity in mice and rats [5]. Cd, like other endocrine disruptors, is able to modify the basal activity of the testes [6]. The gonad is considered the main target for environmental toxins and rodent testes are especially sensitive to the toxic effects of Cd exposure. Cd impairs reproductive capacity by causing severe testicular degeneration, seminiferous tubule damage and necrosis in rats [6] [7]. Different studies have shown that Cd affects plasma gonadotropin levels [8]. The study of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis in animals exposed to the metal is of great interest since the levels of cadmium in air, water, soil, and foods have increased several-fold in many parts of the world as a result of emissions from industrial activities [9]. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) is the free radicals that resulted from O2 metabolism. They have short half live but the high production of them is harmful to the cell. Most common types of ROS are superoxid anion radicals, hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radical and nitric oxide [10]. Antioxidants are the main defense mechanism against oxidative stress induced by free radicals. In general, they are free radical scavengers that suppress the formation of ROS and /or oppose their actions [11] [12]. They can deal with ROS but excessive amounts of ROS or impaired antioxidant defense mechanism oxidative stress will occur which is harmful to the cell. These antioxidant include enzymes such as superoxide dismutase , catalase, glutathione peroxidase and reductase [13] [14], besides non enzymatic antioxidant such as vitamin C, zinc, vitamin E, taurine, hypotaurine, and micronutrients [15]. Zinc is second to iron as the most abundant trace element in the body [16]. High zinc content has been noted in ocular tissues, seminal vesicles, epididymes and prostate [17]. It has been shown that the majority of zinc present in seminal plasma comes from prostate. It is an integral component of nearly 300 enzymes in different species. Zinc plays an important role in the physiology of spermatozoa. It may also have a role in sperm production and /or viability and in the prevention of spermatozoa degradation and in sperm membrane stabilization [18].
2. Aim of the Study
- This study aims to detect the effect of antioxidant (zinc) on the toxicity of low dose of cadmium on the reproductive organs of mature male rats, as a model for human representative.
3. Materials and Methods
- The study was performed on the albino rat (Rattus rattus norvegicus albinus), as a mammalian model. These animals were divided into three groups (15 rat / group) after labeling them with ear or tail marking and weighting them using an electrical balance, as follows:1.Control group (G1): This group was orally administrated with distilled water during the 4 weeks period of the experiment.2. Experimental group (G2): This group was orally administrated with 20 ml cadmium chloride (200 mg/1L body weight) during the 4 weeks period of the experiment.3. Experimental group (G3): This group was orally administrated with zinc sulphate (0.5mg/kg body weight/day) with 20 ml cadmium chloride (200 mg/1L body weight) during the 4 weeks period of the experiment.All treatments were given by intragastric tube daily, separately and continued for 4 weeks. First of all, body weights were recorded then the rats were anesthetized using diethylether. After that blood aspiration using cardiac anesthetic puncture and blood was left in a sterile plastic tube for 20 minutes at room temperature before spin in a centrifuge at 2500 rpm for 5 minutes, the serum was separated using automatic pipette and store at -20ºC until assessment of FSH, LH and testosterone hormones [8]. After that each rat was killed by cervical dislocation; incision of rat was done. The weight of all organs was recorded, reproductive organs (testis, epididymes and seminal vesicle) were quickly excised and immersed in few drops of normal saline which was placed in Petri dish to be cleared from surrounding adipose tissue under dissecting microscope using fine surgical scissors. The organs were blotted dry from normal saline using filter paper and then weighted with electrical balance, while both right and left testes and seminal vesicle were fixed with 10% formal saline for a subsequent histological study. The right and left epididymes were put in a small Petri dish contained 1ml of global culture media then the epididymes were minced by microsurgical scissor about 200 times until we got a homogenized solution which contained the spermatozoa.
4. Results
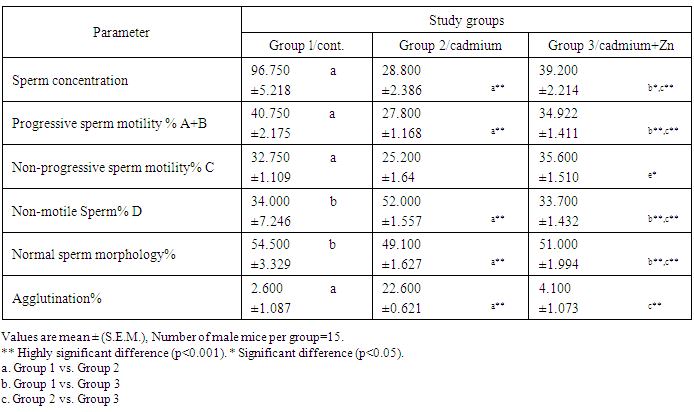
- Daily administration of cadmium chloride (Cd) and antioxidants (zinc) for 4 weeks to the male rats causes some changes including:A - reproductive organs weights: Testicular weights decreased with a highly significant (p≤0.001) difference in Cd treated animals (G2) in comparison to control group (G1) for both the right and left side. There was a significant (p≤0.05) difference in G3 (Cd+zinc) as compared to G1 (control). Testicular weight increased with a highly significant (p≤0.001) difference in animals receiving zinc with Cd ( G3) as compared to Cd only group (G2) (figure 1-a). Similar results were noted in the seminal vesicles weight in comparison with that of the control group (figure 1-b).
|
 | Figure 2. a: Normal sperms concentration from control group, b: Abnormal sperms concentration from treated with Cd, c: Normal sperms concentration from treated with Cd +Zinc (EX40) |
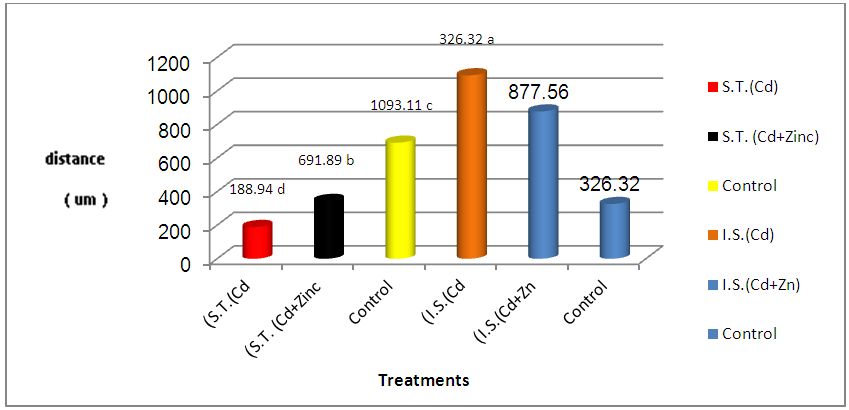 | Figure 4. Diameters of seminiferous tubules (um) (S.T.) and interstitial space (um) (I.S.) in treated and control groups |
5. Discussion
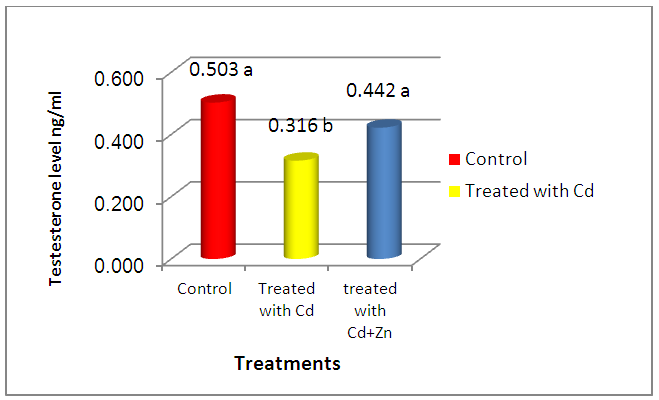
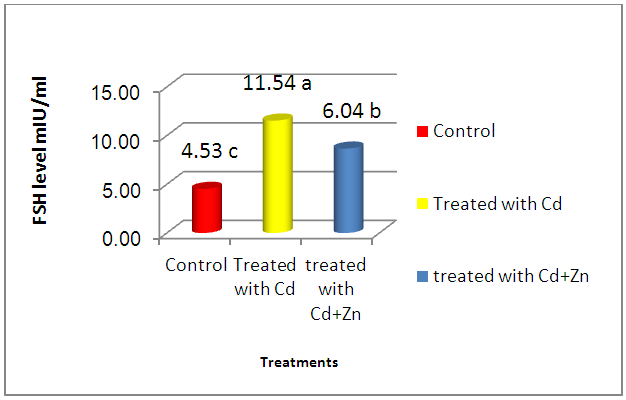
- The present study showed the efficacy of zinc sulphate in preventing the toxic effects of Cadmium chloride in the rat testes. In this study, after Cd administration, we noted weight reductions of accessory sex organs: testes and seminal vesicle after 4 weeks of administration. Probably, this is the natural defenses of this organ required more than 7 days to recover its usual weight after Cd toxicity, as was observed after the longer period [19] [20]. Studies of the consequences of Cd contamination have demonstrated that the testis is more sensitive to Cd than other important organs, in addition, Cd can interfere with testis function [21]. The highly significant reduction in testicular and seminal vesicle weights recorded in animals receiving Cd only may also be related to decrease feeding as even mild food restriction resulted in reduction in serum testosterone concentration, in the weight of androgen dependant organs, and in serum LH concentration [22]. And these observations agree with our results. The results of this study revealed that cadmium administration decreased sperm count, sperm motility, and sperm morphology of the rats, as in previous reports, which demonstrated that cadmium impairs testicular function [23] [24] which agrees with the data reported by Laskey Jw et al and Foote RH [25] [26] and also showed decrease in progressive motility, sperm normality and testicular structure, this may be attributed to testicular germ cell destruction caused either by membrane damage or macromolecular degradation incurred by reactive oxygen species (ROS) leading to a significant decline in spermatogenesis or perhaps due to the low production of sperm in testes and that could be related to the low levels of gonadotrophins and/or serum testosterone level and may be due to testicular necrosis [27]. Zinc has been shown to protect animals and cell cultures from the acute toxicity of heavy metals [28], and zinc containing enzymes are known to be involved in the synthesis and/or degradation of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids [29]. Thus, it plays an important role in body metabolism which is reflected by an increase in body weight and reproductive organs weight in the present study. A highly improvement of sperm parameters in animals treated with zinc and Cd as compared to the group treated with Cd only confirms the importance of zinc as a potent antioxidant and free radicals scavenger which ameliorated the potential increase in free radicals generation from Cd toxicity[30]. The highly significant increase in sperm count in the zinc / Cd group as compared to Cd only group could be linked with the fact that several trace elements have been shown to be essential for testicular development and spermatogenesis [31]. Zinc is vital to human growth and maturation and plays an important role in the reductase enzyme that is necessary for the conversion of testosterone into the biological active form α-dihydrotestosterone (DHT). The co-administration of zinc in the present study resulted in a highly significant increase in normal sperm morphology. These results also give evidence that zinc supports fertility. This finding is in agreement with the study of Namaa (2008) [32], who suggested that seminal plasma has a high content of zinc; which exerts protective antioxidant-like activity that is sufficient to cope with the presence of excessive amount of reactive oxygen radicals in the plasma. Moreover, it is known that zinc is one of the essential components of the body’s most important natural antioxidant [33]. In addition, zinc has been reported to have a membrane stabilizing antioxidant activity and maintains sperm viability by inhibiting DNAase [18]. It is also an integral part of many metalloenzymes, that is believed to stabilize membranes and protect them against free radical injury. Therefore, it appears to be a potent scavenger of excessive superoxide anion produced by defective spermatozoa [34] [35]. Authors described a marked reduction of seminiferous tubular diameter after the higher dose of cadmium, along with the conspicuous decrease of the tubular volume density, which means that cadmium caused a significant reduction in the relative seminiferous tubule length [36]. These data confirm that the severity of cadmium-induced damage at the testicular tissue and the seminal vesicles [37], which lead to decrease in reproductive organ weight and cause changes in the diameter of seminal vesicle and interstial space [38].It has been demonstrated that Cd stimulates free radical production, resulting in oxidative deterioration of lipids, proteins and DNA, and initiating various pathological conditions in humans and animals [39]. Cadmium act on the testes, causing problems in spermatogenesis and spermiogenesis [40]. The damage is due to capillary stasis followed by massive thrombosis, and is highly specific to the testes [41]. The primary insult seems to be an increase in capillary permeability and a breakdown of the blood testes barrier [42]. Our result show increased in plasma levels of FSH after cadmium administration for 4 weeks of life. This finding could be due to the accumulation of cadmium in the testis. In this context, it was shown that cadmium affects Sertoli cell activity by decreasing inhibin synthesis and release. Thus, the increased plasma levels of FSH could be explained, as this peptide is the main inhibitory signal for FSH secretion [43]. Our observations were in line with changes observed by De Souza Predes et al. [44]. The decrease in plasma testosterone levels observed after both prepubertal and postpubertal cadmium exposure may reflect direct effects of the metal at the testis as this metal accumulates in this tissue [45]. Cd has been considered as an important environmental endocrine disruptor [46], this may lead to variations in plasma LH levels, thus indicating that the metal may act at the hypothalamic level, modifying the activity of the endogenous clock, changing the mean concentration of LH secreted daily by the pituitary gland [47]. Zinc is necessary to maintain normal serum testosterone. Inadequate zinc levels prevent the pituitary gland from releasing luteinizing and follicle stimulating hormones, which stimulate testosterone production. Zinc also inhibits the aromatase enzyme that converts testosterone into excess estrogen. In conclusion, these findings concluded that zinc sulphate plays a significant role in the improvement of testicular damage along with reduces oxidative stress and protect from reproductive organs injury during cadmium toxicity.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML