-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2015; 5(1): 53-57
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20150501.10
Curbing Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Challenges and Options in Drug Therapy
Anas Rashid 1, Aiman Rashid 2, Hamza Rashid 3, 4, Usamah Rashid Qureshi 5, 6
1Hamdard Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences (HIPS), Hamdard University Islamabad Campus (HUIC), Islamabad, Pakistan
2Department of Design and Manufacturing Engineering, School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering (SMME), National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), NUST Campus, Islamabad, Pakistan
3Department of Computer Sciences, Faculty of Natural Sciences, Quaid-i-Azam University (QAU), Islamabad, Pakistan
4Faculty of Computer Science, Preston University Islamabad Campus, Islamabad, Pakistan
5Department of Business Studies, Faculty of Economics and Business Studies, Pakistan Institute of Development Economics (PIDE), Quaid-i-Azam University Campus, Islamabad, Pakistan
6Department of Electrical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering Sciences, Army Public College of Management and Sciences (APCOMS), Rawalpindi, Pakistan
Correspondence to: Anas Rashid , Hamdard Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences (HIPS), Hamdard University Islamabad Campus (HUIC), Islamabad, Pakistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Clinical physicians and microbiologist are consistently challenged to find way to a cure Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). When selected drugs are tested on human; unique resistance were shown by this bacterial infection known as Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). If holistic approach is disregarded less options are left for medication to overcome this lethal toxicity. If solo range of drug treatment are applied only, the allied complications and consequences of infections may proliferate beyond critical levels. The research article is centred on primary microbial data collection (from urine and blood) in hospital. The emphasis of experimentation is to scrutinize the highest risk susceptible hospital area including sampled fluid. The precautionary and therapeutic measures are discussed along with alternative means of medication with judicious selection to achieve targeted and optimum outcome.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA, ATCC 29213, Drug Therapy
Cite this paper: Anas Rashid , Aiman Rashid , Hamza Rashid , Usamah Rashid Qureshi , Curbing Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Challenges and Options in Drug Therapy, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 5 No. 1, 2015, pp. 53-57. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20150501.10.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Microbiologists are witnessing an exponential growth in infectious human diseases through Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), which is exactly known as Methicillin Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) [1]. In this case, bacterial skin infections are due to the strains (i.e. invasive) of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) [2]. The microbe has latency to severely resist antibiotics as observed in the last decade. The human race is facing significant morbidity caused by these lethal infections. These are also cause of constant worry (including both economic and financial) on health care system. The focus of this empirical study is to propose an ingenious approach to find out optimal solution by applying preventive measures to control epidemic. It also focuses on using localized treatment and alternative medicines to cure and treat the menace of infections produced by MRSA in human [3].
1.1. Perspectives
- Controlling MRSA is a clinical challenge faced by clinicians across the world [4]. The objective of the study is to figure out optimal and convenient methods to treat infections caused by MRSA in human. The focus of research is to consider alternative medicine including natural, herbal, ayurvedic, homeopathic, and Chinese medicine. Modern therapeutic methods like radio waves, laser therapy, and nuclear and radioactive radiations are essential as well as effective. These not only boost natural physiological immune system but also efficiently reduce the infectious effects and therapeutic side effects on human body [5].People not involved in health care settings are often less aware of this silent and lethal epidemic. This lack of awareness lies in significance of risk, perils of hospital acquired MRSA infection, and potential threat to overall health care system. A significant public behavioural change is needed in order to control this global menace as well as a well-informed public.
1.2. Environment
- S. aureus is a highly contagious bacterial species found throughout the ecosystem [5]. The microorganism invades the skin and enters deeper tissues. As in septicaemia, it multiplies to cause a localized or systemic response. The patient gets infected with the growth of its population.It is found abundantly in damp healthcare environment. People who are weaker, older and sicker have weaker immune system and may get infected easily. Many individuals either living or functioning closely together provide congenial setting for transmission of infectious diseases. It is also reported that people may carry this infection without having any visible indications.
1.3. Sources
- Production of β – lactamase enzyme in the affected area is the main cause of microbial resistance. Some strain of MRSA are labelled as epidemic strains (EMRSA) [6]. Seventeen variants of EMRSA strain have been explored in the globe [7]. Recently, common strain variant to affect hospitals is EMRSA sixteen [8, 9]. The choice of antibiotics as efficient and effective treatment is reduced after the maturity of infection. Such methods are expensive and possibly show harmful side effects to the patient. Recent evidence supports that domestic pets like cat, dog and hen can transmit MRSA to their owners [10].
2. Material and Methods
- District Head Quarters (DHQ) Hospital is an eight hundred bed tertiary teaching hospital located in the city Rawalpindi, Pakistan. An empirical study on MRSA was conducted here from November to December 2014. The patients were clinically spotted. Later on, the data was gathered using the information and support system from the targeted hospital. For this purpose, collection of samples was gathered in containers which were pre-sterile using aseptic technique by healthcare team and transported to the laboratory by brain – heart infusion broth (BHIB) medium in controlled environment without delay for immediate processing.Mannitol Salt agar and Chocolate agar were used for the identification and isolation of S. aureus [11]. The collected samples were inoculated onto Chocolate agar as well as on Mannitol Salt agar [12]. Two tests were used to identify the type of bacteria namely; coagulase and catalase [13]. The identification of S. aureus suspicious grown colonies was based on gram staining and standard biochemical reactions, including catalase and coagulase [14].The Chocolate agar plates were incubated in a ten percent (10%) carbon dioxide incubator at 37oC for 24 hours. The Mannitol Salt agar (MSA) plates were incubated for 18-72 hours at 30-35oC [15]. Standard microbiological techniques are applied to identify particular bacterial characteristics [16].Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus was identified by using Vancomycin (30µg) and Oxacillin (1µg) disks as recommended by Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute (CLSI) [17]. Inducible resistance was identified in S. aureus by disk approximation test [18]. The data was documented and analysed for the completion of this study. A reference strain S. aureus ATCC 29213 was used for the standardization of antibiotic susceptibility testing [19, 20].
3. Results
- A total of 679 samples were processed from in-patients; which comprises 361 samples of Blood and remaining were Urine (Table 1). The sample contained 36% MRSA identified in ICU (both Blood and Urine processed samples) which depicted as clinically high risk. Whereas Neonatal Unit contains 29% MRSA Positive samples (both Blood and Urine processed samples) which depicted as moderate risk. Children (not neonates) Unit contains 21% MRSA Positive samples (both Blood and Urine processed samples) which depicted as low risk. Psychogeriatric Unit contains 12% MRSA identified samples (both Blood and Urine processed samples) which depicted as clinically minimal risk. Sampled data tabulated in Table 1 is graphically depicted in Figure 1 and Figure 2. To conclude, overall the study showed high prevalence of MRSA (31%) among in-door hospitalized human patients in their processed blood and urine samples.
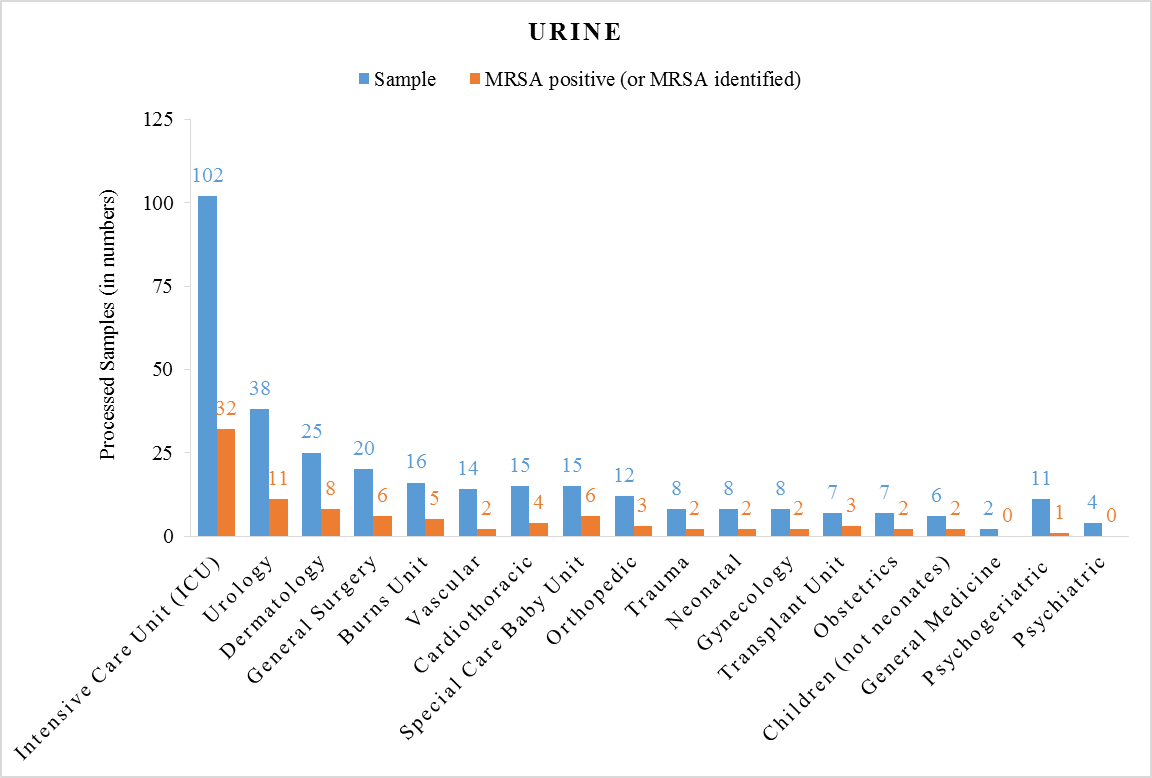 | Figure 1. Processed Samples of Urine |
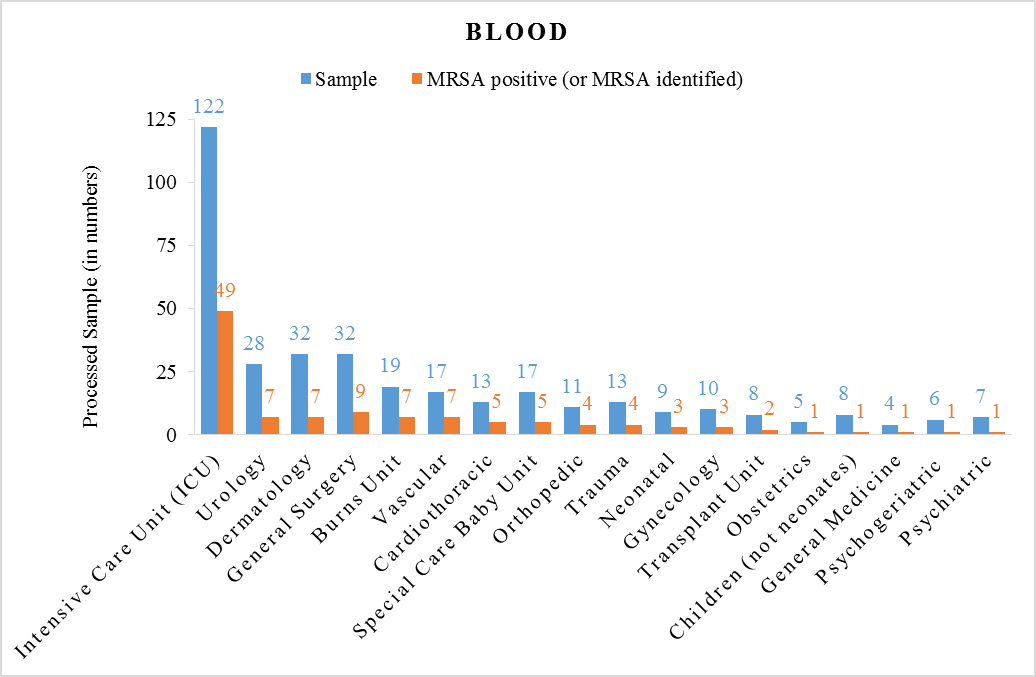 | Figure 2. Processed Samples of Blood |
4. Discussion
4.1. Precautionary Measures (Cost Effective and Convenient)
- Following measures are essentially taken to prevent early spread of infectious diseases. These measures must be taken by each and every individual especially persons dealing with them in healthcare systems.Appropriate hand washing (including areas between fingers and nails) is generally accepted to be the first necessary action used for decreasing the infection risk. Alternatively, alcohol-hand-rub can be applied for decontamination. Maintain cleanliness of hands when contact with patients, replacing bed linen as well as bedding, careful handling of anything contaminated with body fluids, removing protective clothing and gloves, prior to aseptic technique, handling invasive devices and also before handling food. MRSA is both airborne and waterborne disease so maintain cleanliness of general environment including atmosphere. Also maintain an appropriate ratio of staff to patient. Keep nails clean, short as well as polish free, avoid wearing finger-ring and wristwatch, are considered among the best preventive measure [5, 16].
4.2. Remedial Measures
- The use of oral antibiotics and topical Mupirocin directed towards common skin flora is the first line of treatment for mild skin infections [21]. Topical antibiotics are useful for less severe infectious cases. MRSA strains are highly resistant to various antibiotics including Cephalosporins, Macrolides and Quinolones.The use of systemic antibiotic should be reserved for mild to moderate or severe infections that cover a large surface area. The use of an antimicrobial agent is highly recommended for the purpose of treatment. Antibiotics like Ciprofloxacin, Sulfamethoxazole, Trimethoprim, Linezolid, Rifampin or Vancomycin are right options for treatment [22]. It is noticed that most of the infections with appropriate treatment resolved within ten days. If symptoms do not resolve then the right mix of antibiotics and medicine may be recommended. It can simultaneously defend and destroy the bacterial invasion in the body and boost the self-immune system with least side effects.
4.3. Substitute Medicines
- Herbal drug treatment may be adapted such as turmeric (dried rhizome of Curcuma longa belonging to family Zingiberaceae) [23], olive leaves extract, and essential oils such as tea tree oil or lavender oil, black drawing salve, bentonite clay ichthammol ointment may be applied. Specialists also suggest washing the infected area with hydrogen peroxide before applying the bentonite clay [24].Selective range of electromagnetic waves and radio-nuclear therapy may be adopted as localized modern clinical treatment. MRSA was detected sensitive towards both solar (Ultraviolet A & B) as well as germicidal (Ultraviolet C) ultraviolet radiation. Ultraviolet-C radiation is substantially more lethal. The calculated exposure of both solar and germicidal ultraviolet radiation increases the concentration of Sodium Chloride (NaCl) medium where cells exhibit increase in sensitivity.The most common homeopathic treatment for MRSA may include Pulsatilla and Aconitum (genera in the family of Ranunculaceae) and also belladonna (species in the family of Solanaceae) [25]. Pulsatilla is a homeopathic remedy especially recommended in women and children. Aconitum is proven to be helpful in all kinds of infection including MRSA. In homeopathic doses, belladonna remedy (extremely small doses) is also used to cure the red skin, often associated with the infections [26].
5. Conclusions
- The study showed high prevalence of MRSA (36%) among sampled in-door hospitalized human patients’ fluid; who belong to Intensive Care Unit (ICU). To minimize the extent of infection, healthcare staff should make sure that they wash their hands with sterile liquid thoroughly between patient’s clinical examinations. Hand washing is advised for attendants and visitors too. Healthcare associated infection should be highlighted prominently on the media at national and international level for public awareness. However, the affected patients can socialize as usual but proper decontamination of hands and use of face mask need to be incorporated.An integrated drug therapy approach should be adopted to deplete the cause and effect, and simultaneously boost the natural physiological immune system for optimum outcome.
References
| [1] | Kim, H. K., Missiakas, D. and Schneewind, O. 2014. Mouse models for infectious diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Journal of Immunological Methods; 410:88-99. |
| [2] | Luna, C. M., Rodríguez-Noriega, E., Bavestrello, L. and Gotuzzo, E. 2010. Treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Latin America. Brazilian Journal of Infectious Diseases; 14(Suppl 2):S119-S127. |
| [3] | Rashid, A., Qureshi, U. R., Rashid, A. and Rashid, H. 2015. Combating MRSA in Pakistan: An Integrated Drug Therapy Approach. American Journal of Life Sciences; 3(2):71-75. |
| [4] | Planet, P. J., LaRussa, S. J., Dana, A., Smith, H., Xu, A., Ryan, C., Uhlemann, A.-C., Boundy, S., Goldberg, J., Narechania, A., Kulkarni, R., Ratner, A. J., Geoghegan, J. A., Kolokotronis, S.-O. and Prince, A. 2013. Emergence of the Epidemic Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strain USA300 Coincides with Horizontal Transfer of the Arginine Catabolic Mobile Element and speG-mediated Adaptations for Survival on Skin. mBio; 4(6): e00889-13. |
| [5] | Chang, H. R. and Chang, D. H. 2006. MRSA and Staphylococcal Infections, Large Print Ed., Lulu Press, Inc., Raleigh, NC, United States. |
| [6] | Stapleton, P. D. and Taylor, P. W. 2007. Methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: mechanisms and modulation. Science Progress; 85(Pt. 1):57-72. |
| [7] | Simor, A., Boyd, D., Louie, L., McGeer, A., Mulvey, M. and Willey, B. 1999. Characterization and proposed nomenclature of epidemic strains of MRSA in Canada. The Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases; 10(5):333–336. |
| [8] | Miller, R. R., Price, J. R., Batty, E. M., Didelot, X., Wyllie, D., Golubchik, T., Crook, D. W., Paul, J., Peto, T. E. A., Wilson, D. J., Cule, M., Ip, C. L. C., Day, N. P. J., Moore, C. E., Bowden, R. and Llewelync, M. J. 2014. Healthcare-associated outbreak of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia: role of a cryptic variant of an epidemic clone. The Journal of Hospital Infection; 86(2):83–89. |
| [9] | Kumari, H. B. V., Nagaraja, D., Nagarathna, S., Kulkarni, G. B., Praveen, C. S., Nadig, S. and Arakere, G. 2010. A variant epidemic methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus-15 cavernous sinus thrombosis and meningitis: A rare occurrence with unusual presentation. Indian Journal of Medical Microbiology; 28(3):255-257. |
| [10] | Bramble, M., Morris, D., Tolomeo, P. and Lautenbach, E. 2011. Potential Role of Pet Animals in Household Transmission of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A Narrative Review. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases; 11(6):617–620. |
| [11] | Perry, J. D., Rennison, C., Butterworth, L. A., Hopley, A. L. J. and Gould, F. K. 2003. Evaluation of S. aureus ID, a New Chromogenic Agar Medium for Detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Journal of Clinical Microbiology; 41(12):5695-5698. |
| [12] | Flayhart, D., Lema, C., Borek, A. and Carroll, K. C. 2004. Comparison of the BBL CHROMagar Staph aureus Agar Medium to Conventional Media for Detection of Staphylococcus aureus in Respiratory Samples. Journal of Clinical Microbiology; 42(8):3566–3569. |
| [13] | Siegrist, J. Media for detection of Staphylococcus Aureus: a Spreading Bacteria. AnalytiX; 10(Article 2):1-4. |
| [14] | Pournajaf, A., Ardebili, A., Goudarzi, L., Khodabandeh, M., Narimani, T. and Abbaszadeh, H. 2014. PCR-based identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains and their antibiotic resistance profiles Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine; 4(Suppl 1):S293-S297. |
| [15] | Cappuccino, J. and Sherman, N. 2013. Microbiology: A Laboratory Manual, 10th Ed., Pearson - Benjamin Cummings, Boston, MA, United Sates. |
| [16] | Engelkirk, P. G. and Duben-Engelkirk, J. 2015. Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences, 10th Ed., Wolters Kluwer Health, Philadelphia, PA, United States. |
| [17] | Mimica, M. J., Berezin, E. N., Carvalho, R. L. B., Mimica, I. M., Mimica, L. M. J., Sáfadi, M. A. P., Schneider, E. and Caiaffa-Filho, H. H. 2007. Detection of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus isolated from pediatric patients: is the cefoxitin disk diffusion test accurate enough? Brazilian Journal of Infectious Diseases; 11(4):415-417. |
| [18] | Ajantha, G. S., Kulkarni, R. D., Shetty, J., Shubhada, C. and Jain, P. 2008. Phenotypic detection of inducible clindamycin resistance among Staphylococcus aureus isolates by using the lower limit of recommended inter-disk distance. Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology; 51(3):376-378. |
| [19] | Rennie, R. P., Koeth, L., Jones, R. N., Fritsche, T. R., Knapp, C. C., Killian, S. B. and Goldstein, a. B. P. 2007. Factors Influencing Broth Microdilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test Results for Dalbavancin, a New Glycopeptide Agent. Journal of Clinical Microbiology; 45(10):3151–3154. |
| [20] | Hombach, M., Zbinden, R. and Böttger, E. C. 2013. Standardisation of disk diffusion results for antibiotic susceptibility testing using the sirscan automated zone reader. BMC Microbiology; 13(225):1-8. |
| [21] | Grindstaff, T. L., Saliba, S. A., Mistry, D. J. and MacKnight, J. M. 2007. Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. North American Journal of Sports Physical Therapy; 2(3):138–146. |
| [22] | Cosgrove, S. E. and Auwaerter, P. G. 2013. Staphylococcus aureus. Johns Hopkins Antibiotic (ABX) Guide. http://www.hopkinsguides.com/hopkins/ub/view/Johns_Hopkins_ABX_Guide. Accessed on February 10, 2015. |
| [23] | Gupta, A., Mahajan, S. and Sharma, R. 2015. Evaluation of antimicrobial activity of Curcuma longa rhizome extract against Staphylococcus aureus. Biotechnology Reports. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2015.02.001. Available online: February 18, 2015. |
| [24] | Kavanaugh, N. L. and Ribbeck, K. 2012. Selected Antimicrobial Essential Oils Eradicate Pseudomonas spp. and Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms. Applied and Environmental Microbiology; 78(11):4057-4061. |
| [25] | Halcón, L. and Milkus, K. Staphylococcus aureus and wounds: A review of tea tree oil as a promising antimicrobial. American Journal of Infection Control; 32(7):402-408. |
| [26] | Edwards-Jones, V., Buck, R., Shawcross, S. G., Dawson, M. M. and Dunn, K. The effect of essential oils on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus using a dressing model. Burns; 30(8):772-777. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML