-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2014; 4(3): 92-95
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20140403.02
D-Dimer Levels in Sudanese Hypertensive Patients
Hager M. A. Ibrahim1, Mahdi H. A. Abdalla2
1Department of haematology, Faculty of Medical Laboratory Sciences, Alneelain University, Sudan
2Department of Haematology, Faculty of Medical Laboratory Sciences, Omdurman Ahlia University, Sudan
Correspondence to: Mahdi H. A. Abdalla, Department of Haematology, Faculty of Medical Laboratory Sciences, Omdurman Ahlia University, Sudan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Hypertension is the most important modifiable risk factor for coronary heart disease, stroke, congestive heart failure, end-stage renal disease and peripheral vascular disease. The haemostatic system is directly involved in the atherosclerotic process and may affect the impact of hypertension on the development of target-organ damage. The aim of this study was to determine the level of D-dimer among Sudanese hypertensive patients. The study included 60 Sudanese hypertensive patients, their D-dimer levels, PT and APTT were measured and compared with 60 age and sex matched normal subjects as control. The male: female ratio was 1.1 and the median age was 52 year, with minimum age of 29 and maximum of 70 years, mean duration of hypertension among the study group was 5.13±3.8 years. We observed higher D-dimer levels among the hypertensive patients, when compared with the normal healthy controls (p value 0.000). Our study showed no differences in the PT and APTT values between hypertensive patients and normal subjects. This study concluded that D-Dimer levels were higher among Sudanese hypertensive patients than in controls and confirmed the hypercoagulable state among hypertensive patients.
Keywords: D-dimer levels, Hypertension, Sudan
Cite this paper: Hager M. A. Ibrahim, Mahdi H. A. Abdalla, D-Dimer Levels in Sudanese Hypertensive Patients, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 4 No. 3, 2014, pp. 92-95. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20140403.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Hypertension or high blood pressure (BP) is a medical condition in which the blood pressure is chronically elevated. It is the most important modifiable risk factor for coronary heart disease (CHD), stroke, congestive heart failure (CHF), end-stage renal disease and peripheral vascular disease [1]. The proportion of the global burden of disease attributable to hypertension has significantly increased from about 4.5 percent (nearly1 billion adults) in 2000 [2], to 7 percent in 2010 [3]. This makes hypertension the single most important cause of morbidity and mortality globally, and highlights the urgent need of action to address the problem [4]. Propensity of hypertensive patients to develop target-organ damage (TOD) is markedly influenced by coexisting risk factors such as age, gender, smoking, obesity, diabetes, and dyslipidemia. In addition to these factors, the haemostatic system is directly involved in the atherosclerotic process [5] and may affect the impact of hypertension on the development of TOD and thereby on cardiovascular morbidity [6].Many haemostatic factors have been investigated for their potential role in atherogenesis and/or thrombosis, including fibrinogen, D-dimer, prothrombin fragment 1 + 2, factor VII, von Willebrand factor and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 [8].D-dimer is the major breakdown fragment of fibrin and a good biochemical marker of thrombogenesis and fibrin turnover, it is reportedly independent risk marker for myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular events and peripheral arterial disease in the general population [9-11]. Many studies have reported an elevation in the D-dimer levels among hypertensive patients [12-15], but this observation was not confirmed in other studies [16-18]. The aim of this study was to determine the levels of D-dimer among Sudanese hypertensive patients.
2. Materials and Methods
- Following informed consent, one hundred and twenty subjects were enrolled: 60 known hypertensive patients treated with anti-hypertensive drugs for not less than one year, attending Ibrahim Malik Hospital, Khartoum state in Sudan; and age and sex matched 60 non hypertensive healthy subjects as controls. Subjects with recent surgery, trauma, known history of diabetes mellitus, cardiopulmonary disease, autoimmune disease and malignancy were excluded from this study. Two ml of venous blood was collected, from each subject, in 3.8% trisodium citrate (9:1 vol/vol), kept on ice until centrifugation at 2500g for 30 minutes at 4°C, plasma samples were immediately frozen and stored at - 80°C for subsequent coagulation analysis. Laboratory analysis was performed at the Department of Haematology, Faculty of Medical Laboratory Sciences, Alneelain University. D-dimer was measured using i-CHROMATM system (Boditech – Korea). The test uses the sandwich immunodetection method. D-Dimer is bound with an antibody in buffer and the antigen-antibody complexes are captured by antibodies that have been immobilized on the test strip as sample mixture migrates through nitrocellulose matrix. Signal intensity of fluorescence on detection antibody reflects the amount of the antigen captured and is processed by i-CHROMATM Reader to show D-Dimer concentration in the specimen. The working range of i-CHROMATM D-Dimer test is 50 – 10,000 ng/ml. A one-stage procedure was employed in the Prothrombin time (PT) determination. 0.2 mL of thromboplastin-calcium reagent (Diagnostic Reagents Ltd, Thame, UK) was placed in the clotting tube in a water bath at 37°C and left for 2 or 3 minutes until it reached 37°C. 0.1 mL of plasma was then added and a stop watch was started to determine the plasma clotting time. The test was carried out in duplicate, for each sample, and the plasma clotting time was taken as the mean of the duplicated results. Activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) was measure as follows; 0.2 mL of Kaolin platelet substitute (Diagnostic Reagents Ltd) was placed in a clotting tube and 0.1 mL of plasma was added; the tube was incubated at 37°C for exactly 2 minutes. 0.1 mL of 0.025 mol calcium chloride was then added and a stopwatch was started to determine the plasma clotting time. The test was carried out in duplicate, for each sample, and the plasma clotting time was taken as the mean of the duplicated results.Statistical analysis was performed using statistical package for social science (SPSS) software. Evaluation of patient’s data was performed using the t-test and Pearson correlation test. Results with p value < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.Your goal is to adhere to this paper in appearance as closely as possible.
3. Results
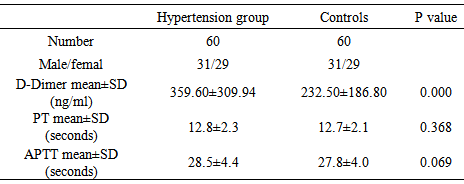
- The male: female ratio was 1.1 and the median age was 52 year, with minimum age of 29 and maximum of 70 years. Mean duration of hypertension among the study group was 5.13±3.8 years. All patients were tested for the D-Dimer level, prothrombin time and partial thromboplastin time. The results of D-Dimer levels, PT and APTT were showed in table 1. D-Dimer level was significantly higher among the hypertensive patients, when compared with the controls (p value 0.000). Mean PT and APTT showed no significant differences between the cases and the controls (p values 0.368 and 0.069) respectively. There was no significant association between the duration of hypertension and the D-dimer level (p value 0.661).
|
4. Discussion
- Many studies have been conducted to assess the function of the haemostatic system in patients with hypertension. Abnormalities within platelet function, coagulation system and fibrinolytic system have been consistently reported in comparison to normotensive subjects [19-21]. In this study we utilized a quantitative approach for the determination of D-dimer level. The study included 60 Sudanese hypertensive patients, their D-dimer levels, PT and APTT were measured and compared with 60 age and sex matched normal subjects as controls. We observed higher D-dimer levels among the hypertensive patients, when compared with the normal healthy controls. Similar findings, with higher D-Dimer level, had previously been reported [19, 21, 22, 23, 24], but conflicting results were reported in other studies [25, 26, 27]. This difference may probably be related to a difference in blood pressure values of patients included in these studies or interference of antihypertensive treatments. Sechi LA et al reported that higher D-dimer levels were independently associated with advanced TOD in hypertensive patients [19]. Further studies with more laboratory investigations and clinical data are needed for logical interpretation and accurate conclusion of the association of an elevated D-Dimer level and TOD in hypertensive patients, which may reveal an important finding with a benefit for the management of such patients.PT and APTT were measured as to assess the overall efficiency of the coagulation system. Our study reported no differences in the PT and APTT values between the hypertensive patients and normal subjects.
5. Conclusions
- This study concluded that D-Dimer levels were higher among Sudanese hypertensive patients than in controls and confirmed the hypercoagulable state among hypertensive patients.Special thanks to the Staff of Haematology Department, Faculty of Medical Laboratory Sciences, Alneelain University.
Authors Contributions
- H. M. A. Ibrahim and M.H.A. Abdalla conceived the idea of the study, collected and analyzed samples and data and wrote the manuscript.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML