-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2014; 4(2): 35-46
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20140402.01
Oxidant Hepatic & /or Haem. Injury on Fuel-Station Workers Exposed to Benzene Vapor, Possible Protection of Antioxidants
Ragia M. Hegazy1, 2, Hala F. M. Kamel3, 4
1College of Pharmacy, Umm Al-Qura University (UQU), Makkah, Saudi Arabia
2College of medicine, Benha University, Egypt
3College of Medicine, Umm Al-Qura University (UQU), Makkah, Saudi Arabia
4College of medicine, Ain Shams University, Egypt
Correspondence to: Ragia M. Hegazy, College of Pharmacy, Umm Al-Qura University (UQU), Makkah, Saudi Arabia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Background: Workers in the fuel stations are routinely exposed tobenzene.Aim of the work:to assess haemoglobin % and serum liver transaminases as biomarker for early benzene toxicity and the protective roles of the antioxidant (vitamin A) Subjects and Methods: sixty workers are divided into Three groups (Group 1): 20workers never occupationally exposed to benzene (control), (Group 2): 20fuel stationworkers that had been exposed to benzene for 5 years or more and administered vitamin (A) 10000 IU daily for three months and (Group 3) 20 workers consisted of fuel stations workers had not been administered vitamin (A). Urinary Trans-Trans Muconic Acid Level, Blood Hemoglobin Concentration, Liver Enzymes, Total Antioxidant Capacity and Malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were estimated. Results: Trans-trans muconic acid (ttMA) in urine samples were highly significantly increased (P = 0.0001) in benzene exposed workers compared with control, the liver enzymes (AST and ALT) in exposed workers were highly significant higher (P =0.0001 and 0.004 respectively) compared to control. No significant difference in hemoglobin concentration among groups (P = .055). The benzene exposures also led to significant reductions in total antioxidant capacity activities (P=0.01) and highsignificant increased plasma MDA levels (P=0.0001). After treatment with vitamin A: Urinary trans-trans muconic acid (ttMA) was significantly reduced (P = 0.01), Hemoglobin concentration is non-significantly increased (P= 0.04), meanwhile the AST and ALT, were highly significant and significantly reduced (P = 0.004 and 0.014) respectively. There was no correlation between Hb% and liver enzymes. On the other hand there were significant reduction of MDA and increase in total antioxidant capacity (P = 0.01 and 0.04 respectively). Conclusion: occupational exposure to benzene had Toxic effects on hemoglobin %, and the liver enzymes. Additionally, the vitamin A had antioxidants effect in ameliorating the toxic effects in exposed workers.
Keywords: Benzene, Hematotoxicity, Hepatotoxicity, Antioxidants
Cite this paper: Ragia M. Hegazy, Hala F. M. Kamel, Oxidant Hepatic & /or Haem. Injury on Fuel-Station Workers Exposed to Benzene Vapor, Possible Protection of Antioxidants, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 4 No. 2, 2014, pp. 35-46. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20140402.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Benzene is a major monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons largely used as solvent in a variety of industrial and commercial processes. Benzene is used as a feeder chemical in the manufacture of lubricants, detergents, rubber, dyes and pesticides. It is often found in automobiles and solvent benzene. A large section of population is occupationally exposed to benzene through work environment [1]. Chronic exposure to benzene results in progressive decline of hematopoietic function and may lead to the onset of various disorders, including aplastic anemia, myelo-dysplastic syndrome and leukemia [2]. Liver injury had long been associated with occupational exposure to a wide variety of chemicals. Its susceptibility to chemical injury is a result of its unique position within the circulatory system, and also because it is the primary organ for the biotransformation of chemicals within the body, as liver is the main organ involved in the metabolism of toxins and medicinal agents [1]. Such metabolism is always associated with the disturbance of hepatocyte biochemistry and generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [3] which are assumed to induce oxidative damage on liver, kidney and hematopoietic system. The concentrations of ROS have to be controlled by several defense mechanisms, which involve also a number of antioxidant and detoxifying enzymes. Their induction reflects a specific response to pollutants. A balance between free radical reactions and antioxidant activities is very important for normal liver functioning. This balance is altered in pathological processes [4].A lot of liver damages ranging from subclinical hepatitis to necrosis inflammatory hepatitis, cirrhosis, and carcinoma have been proved to associate with the redox imbalance and oxidative stress [5]. The most common chemicals known to cause liver injury are the organic solvents as benzene, acetone, ether, and so on. There is some evidence that organic solvents especially benzene may express their toxicity by the way of ROS that was found to induce cell damage [6]. Moreover, higher incidence of cancer is suspected in subjects exposed to organic solvents as benzene characterized by reactive metabolic intermediates [7].Trans, trans-muconic acid (ttMA) is a non-phenolic metabolite of benzene [8] that has been recommended as a as a reliable biomarker that is relatively convenient to measure [9] for benzene exposure [10-12] which allows the detection of low exposure to benzene [13].Workers in the fuel stations are routinely exposed to benzene vapor that has been reported to increase the risks for acute and chronic health problems in motor fuel workers [14]. Activation of benzene and its reactive metabolites leads to continuous production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which leads to lipid peroxidation and damages DNA, RNA, leading to genetic modification and alterations in the functions of important enzymes and proteins [15] Chronic benzene exposure leads to decrease in antioxidant enzymes activity and hematologic disorders.Benzene affects many enzyme activities in the liver, tissues, and peripheral blood and this can lead to a decrease in the activity of antioxidants enzymes and may result in oxidative stress [16] which can be defined as the unbalance between the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the rate of their consumption by antioxidants [17].Oxidative stress occurs when the critical balance between oxidants and antioxidants is disrupted due to the depletion of antioxidants or excessive accumulation of the reactive oxygen species (ROS), or both, leading to a damage of the cells [16, 18-22]. No single component of serum antioxidant complex could fully reflect the protective efficiency of blood, probably because of interactions that occur in vivo among different antioxidant compounds. Total antioxidant capacity (TAC) considers the cumulative effect of all antioxidants present in blood and body fluids [23].
2. The Aim of the Present Study
- This study was aimed to evaluate:I. The hazardous effects of occupational exposure to benzene vapor in fuel-station workers on the liver and hemopoeitic system through:I.1. Measurement of Trans, trans-muconic acid (ttMA) as a reliable metabolites of benzene exposure in urine.I.2. Measurement of liver enzymes (AST, ALT), I.3. Measurement of hemoglobin percent (Hb%) and complete blood count (CBC) where complete blood counts have been recognized as an easy and readily available screen for hematoxicity following occupational exposure to benzene.I.4. Measurment of the extent of oxidative stress by measuring the Malondialdehyde (MDA) level in blood and evaluation of cumulative effect of all antioxidants by measurement of total antioxidant capacity (TAC).II. The protective roles of the antioxidant as retinol (Vitamin A) in reduction of toxicity of benzene on the liver and hemopoeitic system.
3. Subjects and Methods
- Subjects:Inclusion criteria: The present study included 60 male workers in different fuel stations, Makkah, KSA, recruited with consent during the year of 2013, and aged 20-50 years, all were males and they are divided into 3 groups. All workers completed a questionnaire, which included information about: their occupational histories with their food habits, smoking status and consumption of alcohol…. etc. Approval consent to joined the study had been signed by each worker. A brief physical and general examination was carried out and relevant data (age, sex, height, weight and smoker or non smoker) were collected. The UQU local ethics committee had been approved the steps of the study.The workers involved in this study were divided into 3 groups as follow:Group I (control): Healthy workers working in places away from fuel stations or other industries using benzene in Makkah, KSA.Group II (treated with vitamins A): Male workers working in different fuel stations in Makkah, KSA, more than five year, treated with vitamins A (retinol) in therapeutic dose (10,000 IU).Group III (cases exposed to benzene): Male workers, working in different fuel stations in Makkah, KSA, more than five year.Exclusion criteria: subjects with gross anemia, known history of diabetes mellitus, cardiopulmonary disease, acute or chronic infection, or both, autoimmune disease, malignancy, history of viral hepatitis, bilharziasis, blood transfusion, or hospitalization for surgery, subjects current or with previous history of tobacco or cigarette smoking were excluded from the study. All selected cases worked in different fuel station for at least 5 years, 3 cases had been excluded due to heavy cigarettes smoking. Twenty healthy persons had been selected to be used as control group in the study. Methods:Blood Samples Collection and Assay: About 10 ml of venous blood was collected from each of them by sterile disposable syringes. Venous blood samples collected in plain tubes without using an anticoagulant and was left to clot for 30 min. at 25℃, the blood was centrifuged at 4,000 rpm for 15 min. at 4℃. The top yellow serum layer was pipette off without distributing the white buffy layer. The separated serum was used for estimation of liver enzymes; Total antioxidant capacity (TAOC) and Malonaldhyde (MAD), the other part was collected in clean tubes with EDTA as anticoagulant substance for estimation of Hemoglobin concentration.1- Hemoglobin concentration (Hb) analysis: Hemoglobin levels were determined by methods described by Alexander and Griffiths (1993) (24).All absorbance readings for hemoglobin determinations were taken using DREL 3000 HACH (England) model spectrophotometer.2- Liver enzymes:**Serum aminotransferases (ALT and AST):Were estimated by the method of provisional Recommendations on IFCC methods for the measurement of catalytic concentrations of enzymes [25].3- Determination of TAOCTotal antioxidant capacity (TAC) was measured using the commercially available kit (Quanti Chrome Antioxidant Assay Kit (DTAC-100) from BioAssay Systems, USA.(cat No MBS164846). principle of the test for Total antioxidant capacity was measured by the reaction of antioxidants in the sample with a defined amount of added hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) following the standardized procedure (ELIZA test).Antioxidants in the sample eliminate a certain amount of added hydrogen peroxide. The residual H2O2 is determined colourimetrically in a microtitre plate reader.The difference between the applied and measured peroxide concentration in a defined time period is proportional to the reactivity of the antioxidants in the sample (antioxidant capacity). Briefly, Cu2+ is reduced by antioxidant to Cu+. The resulting Cu+ specifically forms a colored complex with a dye reagent. The color intensity at 570 nm is proportional to TAC in the sample.4- Determination of MAD Serum lipid peroxide levels were determined by measuring malondialdehyde, which is an end-product of lipid peroxidation. We used the spectrophotometric method. The color intensity of the complex obtained by the reaction of MDA and thiobarbituric acid is proportional to the concentration of. Malondialdehyde (MDA) which was measured using QuantiChrome TBARS Assay Kit (DTBA-100) from BioAssay Systems. Principle of the assay is based on the reaction of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) with thiobarbituric acid (TBA) to form a pink colored product. The color intensity at 535 nm is directly proportional to TBARS concentration in the sample.5- Determination of Trans,trans-muconic acid (ttMA) in urine:Urine samples were collected in white sterile plastic bottles and transported in ice box to the laboratory and stored frozen up till analyzed. Determination of ttMA level was performed using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) methods previously described [26] in the Centre of poisoning and Forensic Chemistry, Jeddah, KSA. Briefly, 0.5 ml of urine sample was mixed with 2 ml of Tris Buffer containing vanillic acid as internal standard (IS). Then this mixture was percolated through a preconditioned ion-exchange column. After rinsing the column with phosphoric acid solution, acetate buffer, and deionized water, the analytes was eluted with 2 ml of an equivolume solution of 1.5 M NaCl methanol. Of this, 100 microliter is injected into the HPLC column. The mobile phase used consisted of, per liter, 10 ml of acetic acid, 100 ml of methanol, and, the rest, 5 mM sodium acetate.Statistical Analysis: All quantitative data were presented as mean (X) ± Standard Deviation (SD) and were compared using the unpaired Student's test. Data entered and analyzed using SPSS v 17.0. P value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
4. Results
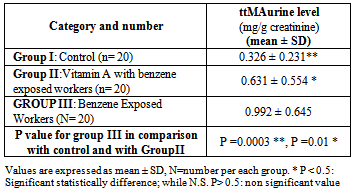
- In this study we compared the hemato-toxic and hepato-toxic effect of low benzene exposure among general population (control) and exposed workers to benzene vapor by analysis of the liver enzymes, hemoglobin concentration during five months period of study. Subjects were youth (mean age ± SD was 35 ± 15).The post shift urine samples in the exposed individuals and control groups were monitored repeatedly over the period of the study (3 months), and at the end of the study the level of (ttMA) in urine samples were highly significantly increased (P = 0.0001) in group III (benzene exposed workers without supplementation) compared with negative control group I meanwhile after treatment with vitamin A at the end of the study the level of (ttMA) in urine samples were significantly decreased (P = 0.01) in group II compared with group I control group (Table 1).
|
|
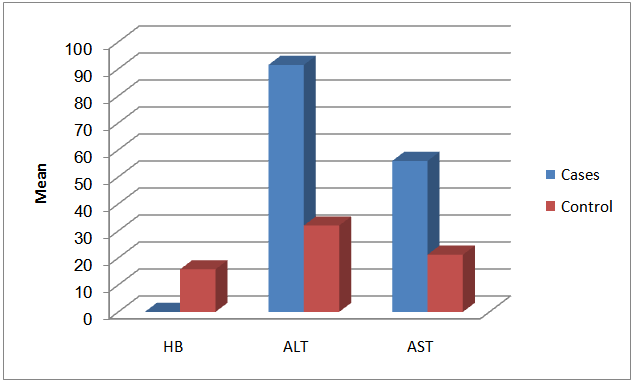 | Figure (1). The effect of low exposure to benzene among fuel stations workers on hemoglobin concentration and liver enzymes in comparison to control |
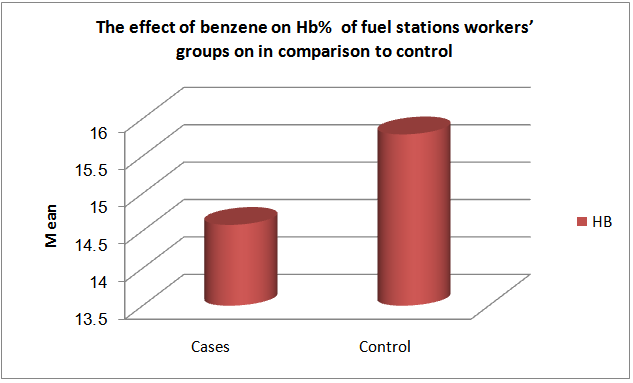 | Figure (2). The effect of low exposure to benzene among fuel stations workers’ groups on hemoglobin concentration in comparison to control |
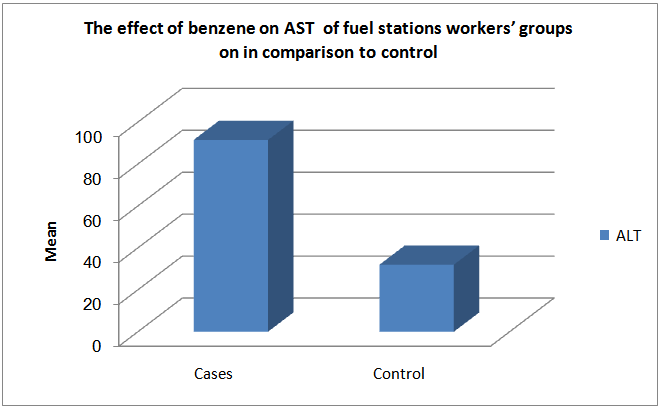 | Figure (3). The effect of low exposure to benzene among fuel stations workers’ groups on ALT in comparison to control |
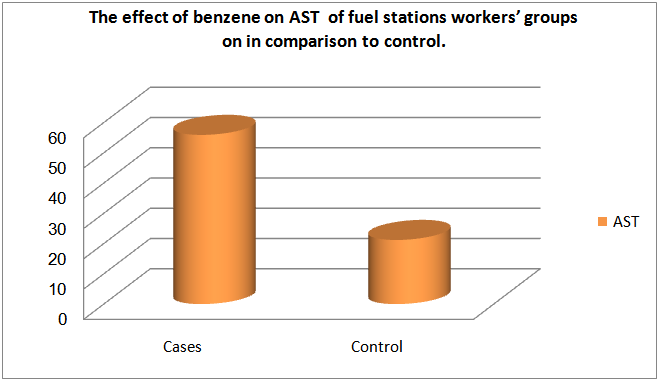 | Figure (4). The effect of low exposure to benzene among fuel stations workers’ groups on AST in comparison to control |
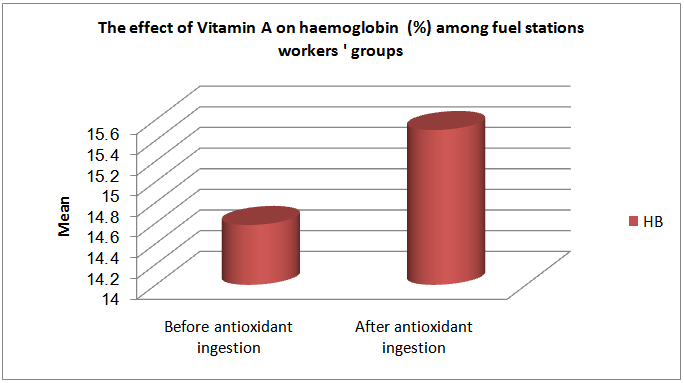 | Figure (5). The effect of Vitamin A on hemoglobin % among fuel stations workers |
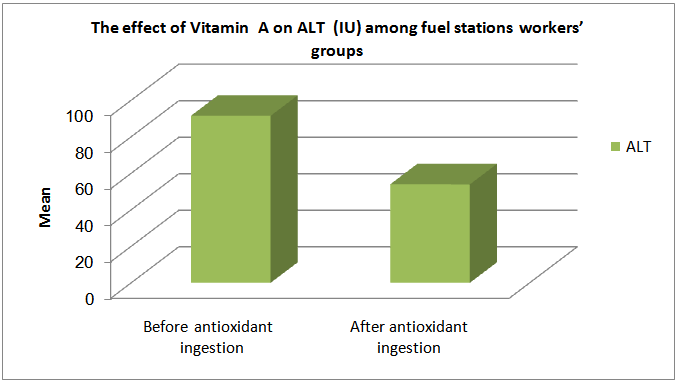 | Figure (6). The effect of Vitamin A on ALT among fuel stations workers |
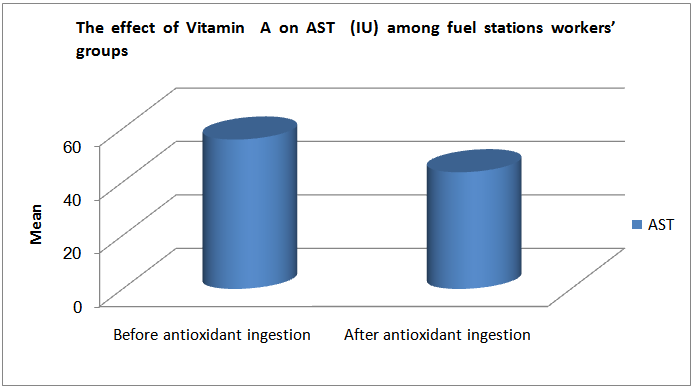 | Figure (7). The correlation between Hb reduction and AST increase among the fuel stations workers |
|
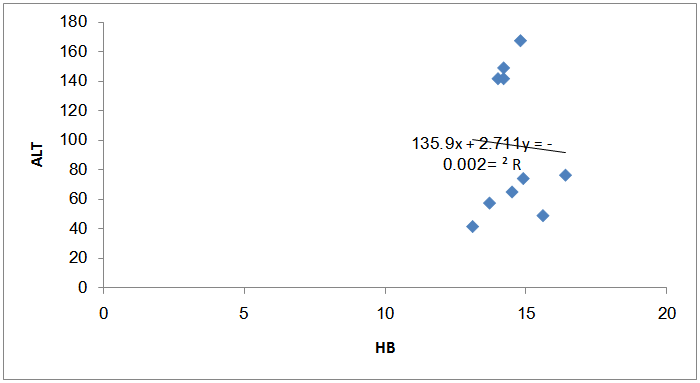 | Figure (8). The correlation between Hb reduction and ALT increase among the fuel stations workers with significant benzene level |
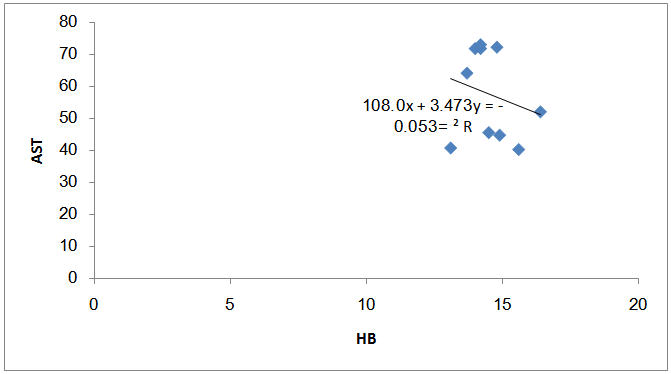 | Figure (9). The correlation between Hb reduction and AST increase among the fuel stations workers with significant benzene level |
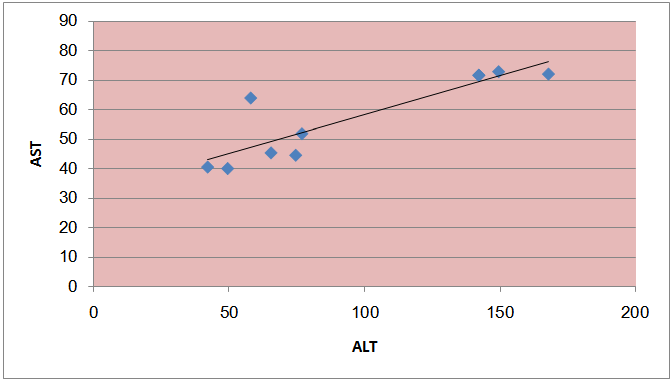 | Figure (10). The correlation between liver enzymes (AST & ALT) among the fuel stations workers with significant benzene level |
5. Discussion
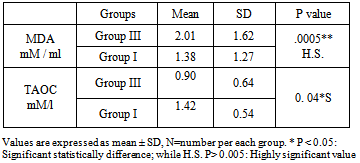
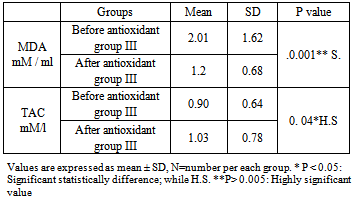
- Benzene vapors' may be derived from direct evaporation or combustion of liquid benzene. These vapours, being ubiquitous in the environment, constitute some components of petroleum pollutants in the air. The commonest sites of exposure to these pollutants from benzene vapours include refineries, oil fields, refueling stations, petrochemical industries, motor mechanical workshops and traffic - congested areas. Hence, the population at greater risk of frequent exposure includes those occupationally exposed, as well as those residing in traffic-congested areas. Reports indicate that chronically exposed individuals are the oil drillers, refinery works, petrochemical works, refuel station attendants and mechanics [2, 27-29].The goal of focusing on benzene induced toxicity is not only to find the pattern and pathological effect of exposure but also to explore the pathogenesis of adverse effects on different biological systems; but also, to explore the potential protective agents that may help and ameliorate the toxicity. Although a number of studies reported the adverse effects of benzene in humans involved in different occupations but the novelty of the present study is to elucidate the relationship between the benzene exposure hematological and/or hepatic toxicity with oxidative stress and the protective effect of vitamin A supplementation. In fuel stations, the risk of hepatotoxicity due to exposure to organic solvents has already been suggested. Prolonged exposure to organic solvents such as benzene, toluene and xylene may represent a risk factor for liver cancer [30, 31].Additionally, they reported that benzene has an established hematotoxicity as itmay cause resistant anemia, aplastic anemia, and multiple myeloma, among the workers who are occupationally exposed to benzene [2, 27-29].Since the toxicity effect associated with exposure to benzene constituents may be an indication of tissue components-reactive metabolite species interactions in the body, it is believed that the presence of antioxidant may ameliorate the toxicity effect. Among the antioxidants that has attracted the attention of researches in recent time vitamin A [32].Exposed workers to benzene in our study showed high significant levels of Trans, trans-muconic acid (ttMA), that finding was in agreements with other reports which elucidated significant correlation between benzene exposure and (ttMA) in urine even they concluded that (ttMA) may be a biomarker which allows the detection of low exposure to benzene [33,34]. According to the results related by previous studies [10,12] smokers who are occupationally exposed to benzene excreted more ttMA so smokers were excluded from all studied groups also we excluded tobacco smokers from our studied groups, Tobacco smoke is a rich source of oxidants. It has been argued that, the increased production of reactive oxygen species associated with smoking may exceed the capacity of oxidant defense system, resulting in oxidative damage [35].Malondialdehyde (MDA) is one of the end-products of the peroxidation of membrane lipids caused by ROS formation, especially by the superoxide ion. It is currently considered to be a basic marker of oxidative stress [36]. This study showed high statistical significant difference among exposed group compared to control group regarding the level (MDA) which was higher among exposed. This is in agreement with other studies which illustrated that Benzene exposure has been associated with increases in the overall formation of MDA [37,38], also this study is consistent with other studies which found a significant increase in the level of MDA in petrol station workers compared to their control group [39]. Exposed workers to benzene in our study showd high significant levels of Trans, trans-muconic acid (ttMA), and Malondialdehyde (MDA) while the level of TAOC significantly decreased. This is in agreement with other studies that showed workers who had significant uptake of benzene due to prolonged work hours and increased years of exposure which will also leads to the formation of ROS, decreases antioxidant activity and hence increases oxidative stress [40,41] and this is consistent with other studies that showed levels of benzene and its metabolites were significantly elevated among all gasoline filling workers compared to their control [40, 42, 43].This study is aimed to assess the hemoglobin concentration and liver enzymes as an easy and readily available screen for hematoxicity and hepatotoxicity following occupational exposure to benzene. Additionally, to evaluate the protective roles of the antioxidant (vitamin A) on hematoxic and hepatotoxic effects amongrefuel stations workers who exposed to low levels of benzene.The statistical results of the current study showed that the hemoglobin of the refuel station workers were significantly lower in the benzene exposed group compared to the control. Estimation of the hemoglobin concentration in clinical practice is useful screening test in routine medical check-up.Also, hemoglobin concentration show mixed evidence of an association with benzene exposure. The strongest evidence is for hemoglobin; several studies show a decrease in hemoglobin in benzene exposed populations [44, 45].These studies have found a positive relationship between benzene exposure and Hbconcentration [46], and a couple has found an inverse association with platelet count [44-47]. Contradictory, several studies have shown that, exposure to benzene neither affect Hb concentration nor the CBCs [48].Very few studies have examined hematological changes in exposed populations and followed the affected populations to determine subsequent disease states, such as resistant anemia, aplastic anemia and leukemia [46, 49, and 50].Therefore, little is known about what hematologic effects are likely to lead to more permanent and serious disease. Without long-term follow-up data, no conclusions can be made on the sensitivity of using hematology as a biomarker of benzene effect [44, 51, and 52].In this study, there were associations between benzene exposure and hemoglobin concentration at various exposure levels. Other very low exposure studies (<= 1 ppm) have found no association with a decrease in red blood cells [53].According to Synder and Hedli (1996) [54], hematotoxic mechanism associated with benzene involves both bone marrow depression and leukaemogenesis caused by damage to multiple classes of hematopiotic cells and a variety of hematopoietic functions. Benzene metabolites cause destruction of the bone marrow, leading to aplastic anemia, in a dose-responsive fashion.In screening for possible effects of hepatotoxicants, it is important to select the liver enzymes tests with the best combination of specificity and sensitivity. The alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) are the most commonly measured enzymes that detect hepatocellular injury due to the toxicant's effect on all or part of the hepatocyte, including the cell membrane [54]. For routine screening of chemicals that are known or suspected to cause hepatocellular injury, the ALT is considered to be the aminotransferase most specific for the liver, while, routine screening with "profiles" which also include GGT, bilirubin, LDH and protein determinations, provide limited additional information. Abnormal ALT can sound as an alarm to alert medical staff to the possibility of some kinds of liver problem, which require further medical workup [55]. So we select these enzymes in the current study where the liver enzymes (ALT, and AST of the refuel station workers were significantly elevated compared to their controls. The liver enzymes of all the control subjects were within the normal levels.Nasterlack et al, 1994 had found that ALT and AST are used as sensitive biomarkers for possible hepatocellular damage due to exposure to organic solvents [56].Also, in agreement with the present results, several studies proved that liver enzymes were significantly elevated in workers exposed to organic solvents compared to controls. The levels of ALT and AST enzymatic activities in the workers in refuel stations were found to be higher than that control group [57-59].Also cumulative exposure to a mixture of organic solvents might cause a significant variability in the abnormality of liver enzymes (AST, and ALT) in male shipyard workers. In car painters exposed to organic solvents, statistical analysis also revealed a significant increase in AST level in the exposed workers compared with their controls [57]. Contradictory, several studies have shown that, exposure to amixture of organic solvents does not affect the levels of the liver enzymes, such as ALT, and AST [59, 60]. Protective effect of antioxidant vitamins has been previously reported on animal exposed to benzene inhalation such as vitamin C which reduced the structural changes of trachea and lung and diminished the toxic effects of benzene on the lung of studied rats [61]. Others reported that vitamin E was able to protect the oxidative damage induced by Benzene in rats [62] and recently beneficial effects of retinol, at prophylactic dosage, against gasoline vapours hepatotoxicity in male and female rats, thereby suggesting that retinol may be used to prevent hepatotoxicity in individuals frequently exposed to gasoline vapours [63].The antioxidative and protective roles of vitamin A reported may be suggested to be implicated. Another study reported the protective role of 30 days administration of pharmaceutical preparation containing vitamins A, C & E and the trace elements selenium and zinc to the porcelain workers in reduction of levels of MDA and increase levels of protective antioxidants enzymes: erythocytic reduced glutathione (GSH), enzyme activities of catalase and superoxide dismutase (SOD) hence protection against oxidative stress inducing cellular damage, hepatotoxity or hemotoxic effects of exposed workers [65].Findings of this study arebased mainly on male worker. But other study shows that due to hormonal differences, the vitamins interacted with growth factors and metabolic processes more in female than male to stimulate growth signaling systems and various growth factors to stimulate rapid synthesis of blood cells as well as haematopoietic growth factors and erythropoietin systems [66].However, the antioxidative and protective roles of vitamin A reported by some studies suggested that the vitamin A interact with haematopoietic growth factors/ committed stem cells, the growth stimulation signaling systems and various growth factors to stimulate rapid synthesis of blood cells, [23, 64]. Another study suggested that benzene, as an organic solvent, induce hepatic injury that was related to the formation of free radicals. She also proved that dietary supplement with antioxidants and Zn and Se in experimental animals prevented this toxicity. Se and Zn are essential trace elements involved in cellular protection against the deleterious effects of ROS [67].Conclusion: From the results of this study, we concluded that occupational exposure to benzene found to have hazardous effects on Hemoglobin concentration, and the liver enzymes. Additionally, the vitamin A was observed to be potent in ameliorating the haematotoxic and hepatotoxic effects in exposed workers.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML