-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2013; 3(6): 150-155
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20130306.07
Enhancement of Bilirubin Excretion in Alloxan - Induced Diabetic Rats Treated with Crude Aloe vera Gel
U. P. Akpan 1, V. U. Nna 2, U. A. Okon 1, E. E. Osim 2
1Department of Physiology, Faculty of Basic Medical Sciences, College of Health Sciences, University of Uyo, Uyo, Akwa Ibom State
2Department of Physiology, Faculty of Basic Medical Sciences, College of Medical Sciences, University of Calabar, Cross River State
Correspondence to: U. P. Akpan , Department of Physiology, Faculty of Basic Medical Sciences, College of Health Sciences, University of Uyo, Uyo, Akwa Ibom State.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This study was aimed at determining the effect of type 1 diabetes mellitus on bilirubin excretion, and to ascertain the impact of treatment with crude Aloe vera gel on bilirubin excretion. The phyto-constituents and median lethal dose of the plant material were determined before administration. Forty albino wistar rats were randomly assigned into four groups of 10 rats each as follows; control group, alloxan - induced diabetic untreated group (DM), alloxan - induced diabetic treated group (DMT) and control treated group (CT). The dose of crude Aloe vera gel used for this study was 0.2ml/100g body weight daily, per oral route. Biliary total bilirubin (BTB) and serum total bilirubin (STB) concentrations were significantly (p<0.001) increased in the DM group compared to control, DMT and CT group. BTB and STB concentrations were significantly lower (p<0.001) in DMT group compared to DM group. BTB and STB concentrations were significantly reduced in the CT group compared to control. Biliary conjugated bilirubin (BCB) and serum conjugated bilirubin (SCB) concentrations were significantly lower (p<0.001) in the DM, DMT and CT group compared to control. BCB and SCB concentrations were significantly lower (p<0.001) in the DMT group compared to DM group. BCB and SCB concentrations were significantly lower (p<0.001) in the CT group compared to control. Biliary unconjugated bilirubin (BUB) and serum unconjugated bilirubin (SUB) concentrations were significantly increased (p<0.001) in the DM group compared to control, DMT and CT group. BUB and SUB concentrations were significantly reduced (p<0.001) in CT group compared to control. These results are suggestive of the fact that crude Aloe vera gel enhances excretion of bilirubin in diabetic and normal conditions.
Keywords: Aloe vera, Bilirubin, Bile, Diabetes Mellitus, Serum
Cite this paper: U. P. Akpan , V. U. Nna , U. A. Okon , E. E. Osim , Enhancement of Bilirubin Excretion in Alloxan - Induced Diabetic Rats Treated with Crude Aloe vera Gel, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 3 No. 6, 2013, pp. 150-155. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20130306.07.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- At the age of about 120 days, the membranes of erythrocytes become more susceptible to damage because of increased membrane fragility[1]. As these cells attempt to squeeze through the capillaries of the reticuloendothelial system, their membranes become ruptured, leading to cell damage and release of hemoglobin in the process[1,2]. The released haemoglobin undergoes a series of reaction leading to the formation of bilirubin. Bilirubin is also formed by breakdown of myoglobin, cytochromes, catalase, peroxidase and tryptophan pyrrolase[2-4]. Eighty percent of the daily bilirubin production is derived from hemoglobin[5]; the remaining 20 percent being contributed by other hemoproteins and a rapidly turning-over small pool of free heme[5]. Enhanced bilirubin formation is found in conditions like liver damage, presence of immature erythrocytes in circulation, and in all conditions associated with increased red blood cell turnover[3,4]. The liver through its detoxification and excretory function conjugates bilirubin (conjugated bilirubin) and excretes it as bile pigment[6]. However, not all the bilirubin molecules are conjugated by the liver. The unconjugated fraction forms unconjugated bilirubin[6]. This process is highly efficient under normal conditions, so plasma unconjugated bilirubin concentrations remain low. Intestinal bacteria degrades bilirubin into urobilinogen, most of which is absorbed from the intestine and undergoes enterohepatic recirculation[6].Some studies have claimed that increased serum levels of bilirubin may be beneficial in treatment of some form of cancer and gastric ulcer by virtue of its antioxidative effect[5,7]. Amidst these acclaimed benefits of mild hyperbilirubinemia, several detrimental effects exist. Bilirubin is toxic to the central nervous system and may cause a sequence of neurological symptoms called acute bilirubin encephalopathy[8]. A considerable proportion of infants develop chronic bilirubin encephalopathy, a clinical condition consisting of movement disorders, auditory dysfunction, oculomotor impairments, and dental enamel hypoplasia of the deciduous teeth[8]. Although hyperbilirubinemia is most frequently observed in infants, as seen in jaundice and kernicterus, it is becoming pronounced in adults, with the likely causes being, but not limited to liver damage, hemolysis and Gilbert syndrome [8,9].Aloe vera is a cactus-like, succulent perennial plant with over 360 species. The plant belongs to family Liliaceae, native to North Africa and cultivated in warm climatic areas[10]. Out of the 360 species of Aloe, Aloe vera barbadensis has been identified as the species that is most therapeutically effective[11]. Aloe can be utilized therapeutically, in three forms – Aloe gel, Aloe latex and Aloe whole leaf extract. Aloe vera gel is well known for its healing potentials. The latex of Aloe vera contains the anthraquinone glycosides aloin A and B, which are potent laxatives[12,13]. Aloe vera has been found beneficial in the following body systems - cardiovascular system[14-16], endocrine system[17,18], respiratory system[13], blood and immune system[19]. Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disorder that has been proven to be associated with multiple complications. Alterations in the function of the liver, biliary system and exocrine pancreas are common in DM. Considering the fact that increased serum bilirubin could worsen the health conditions of type 1 diabetics, it became important to determine the influence of type 1 DM on bilirubin excretion, and to ascertain the impact of treatment of type 1 DM with crude Aloe vera gel on bilirubin excretion.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Preparation of Crude Aloe vera Gel
- Fresh Aloe vera plant with leaves within 40 – 60 cm long was obtained from University of Calabar Botanical Garden and identified by the Chief Herbarium Officer of Botany Department of University of Calabar. Using a knife, the leaves were sliced longitudinally. This made the Aloe vera gel visible. The gel was gently scraped into an electric blender to shatter the block and thereafter, administered immediately without storage[20]. This preparation was done daily. The median lethal dose (LD50) of the plant extract was determined by method of Lorke[21].
2.2. Animal Preparation and Protocol
- Forty albino wistar rats were used for this study. The animal cages were well ventilated, exposed to normal temperature and 12/12 hours light/dark cycle. After fourteen days of acclimatization, the animals were randomly divided into four groups, such that each group contained ten animals. The groups were labeled thus; control group, alloxan – induced diabetic untreated group (DM), alloxan – induced diabetic group; treated (DMT) with crude Aloe vera gel (0.2ml/100g body weight) orally and control group; treated (CT) with crude Aloe vera gel (0.2ml/100g body weight) orally.
2.2.1. Induction of Diabetes
- Diabetes was induced by intraperitoneal injection of alloxan. The dose used in this study was 120 mg/kg body weight. Fasting blood glucose level of each animal was taken before alloxan administration. Forty eight hours after alloxan administration, diabetes was confirmed in the groups administered by using the Finetest glucose meter (IMFOMED IMPEX, INDIA) to measure the blood glucose levels. Animals with blood glucose level >200 mg/dl after 24 hours fast were confirmed diabetic and selected for this study.
2.2.2. Extract Administration
- Crude Aloe vera gel was orally administered to the DMT and CT groups at a dose of 0.2ml/100g[20] body weight daily for 21 days. Administration was facilitated by the use of a syringe and orogastric tube. All experiments involving the animals and their care were in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki.
2.3. Determination of Blood Glucose Levels
- The blood glucose level of the animals was measured using the Finetest glucose meter (INFOMED IMPEX, INDIA). Blood used for the test was obtained by pricking the distal end of the tail and placing the drop of blood on the test strip. Blood glucose level before and after alloxinization was determined and recorded in all the groups. Blood glucose level was also measured at the end of 21 days.
2.4. Determination of Rate of Biliary Secretion
- Biliary secretion was collected by the method of Vickers et al[22]. The animals were starved for 12 hours prior to the experiment. They were weighed and anaesthesized by intraperitoneal administration of sodium thiopentone (6mg/100g body weight), and were quickly pinned to a dissecting board for a tracheostomy performed to clear the airway for easy breathing. The stomach was opened along the linea alba to minimize bleeding. A laparotomy was performed and the liver lobes deflected anterolaterally to expose the common bile duct. The common bile duct was then cannulated with a portex Cannula (0.5mm in diameter) after a small incision was made. A thread was used to tie round the common bile duct to hold the cannula in place. The bile content was collected at 3 hours interval for each group.
2.5. Determination of Biliary and Serum Bilirubin
- Biliary bilirubin was measured by colorimetric method as described by Jendrassik and Grof,[23]. Serum bilirubin was measured by the method described by Sherlock[24].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
- Results are presented as mean + standard error of mean. The One – way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) was used to determine the differences between means, followed by post hoc multiple comparisons, with P=.05 considered significant. Computer software SPSS version 17.0 and Excel Analyzer were used for the analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Fasting Blood Glucose Levels
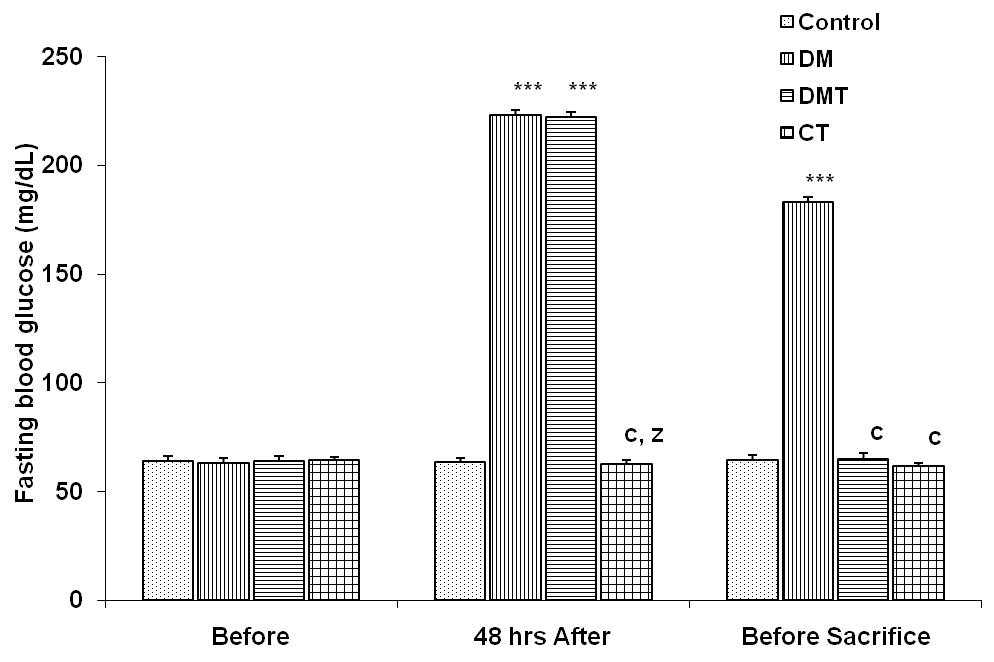
- There was no significant difference in the fasting blood glucose level of the animals before alloxan administration. Forty eight hours after alloxan administration, the blood glucose level in the control, DM, DMT and CT group was 64 + 1.9, 223 + 3.3, 222 + 2.4 and 63 + 1.4 mg/dl respectively, (Fig. 1). The fasting blood glucose level was significantly increased (p<0.001) in the DM and DMT group compared to control and CT group. At the end of 21 days, the fasting blood glucose level in the control, DM, DMT and CT group was 65 + 2.0, 183 + 2.0, 65 + 2.3 and 62 + 1.5 mg/dl respectively. Fasting blood glucose level was significantly reduced (p<0.001) in the DMT group compare to DM group (Fig. 1).
3.2. Rate of Bile Secretion
- The rate of bile secretion in the different experimental groups was 0.34 + 0.02, 0.39 + 0.04, 0.34 + 0.02 and 0.33 + 0.01 ml/hr respectively. The rate of bile secretion was significantly reduced (p<0.05) in the CT group compared to DM group (Fig. 2). Although the bile secretory rate in the DM group was greater than that of the DMT group, it was not significantly different.
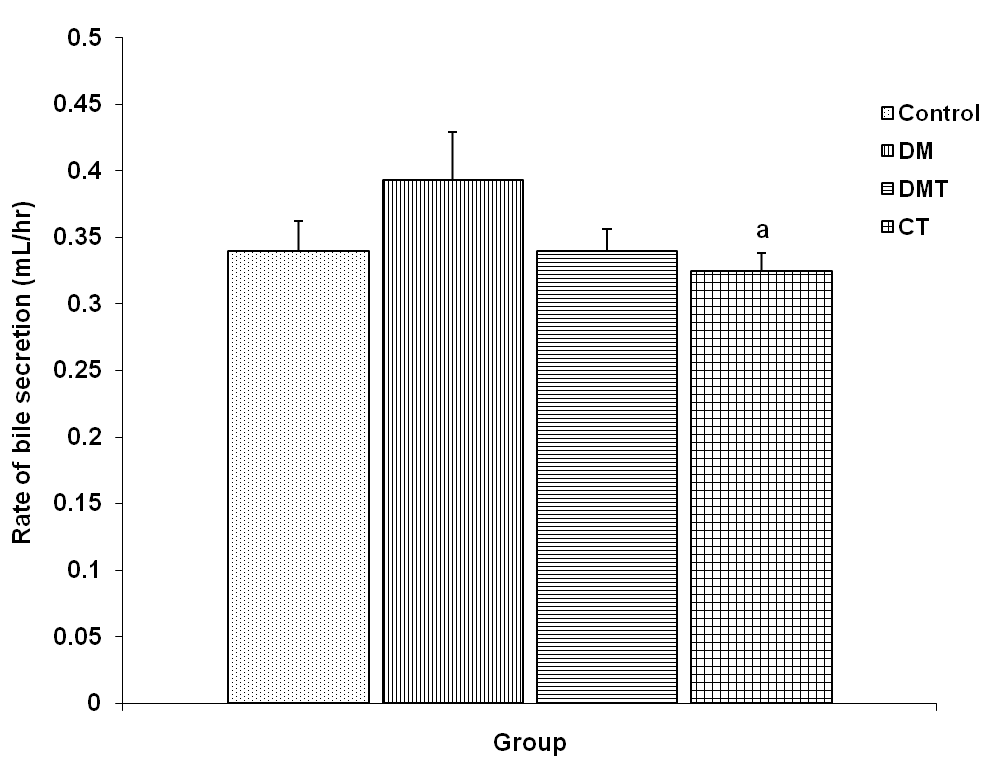 | Figure 2. Comparison of rate of bile secretion in control and test groups. Values are mean + SEM, n = 10. a = p<0.05 vs DM |
3.3. Biliary Total Bilirubin, Conjugated and Unconjugated Bilirubin Concentration
3.3.1. Biliary Total Bilirubin Concentration
- The biliary total bilirubin concentration in the control, DM, DMT and CT group was 63.88 + 0.85, 75.80 + 0.32, 33.30 + 0.69 and 25.98 + 0.24 μmol/L respectively. Biliary total bilirubin (BTB) concentration was significantly increased (p<0.001) in the DM group compared to control, DMT and CT group. BTB concentration was significantly reduced (p<0.001) in DMT group compared to DM group. CT group had a significantly lower (p<0.001) BTB concentration compared to control (Fig. 3).
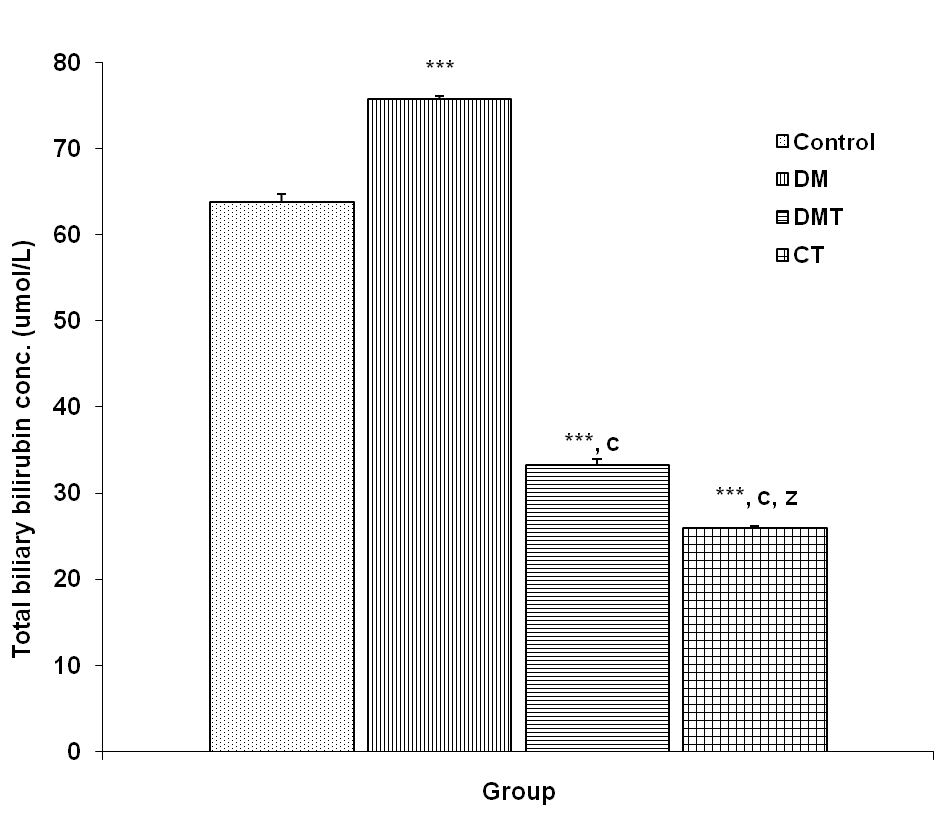 | Figure 3. Comparison of total biliary bilirubin concentration in control and test groups. Values are mean + SEM, n = 10. ***p<0.001 vs control; c = p<0.001 vs DM; z = p<0.001 vs DMT |
3.3.2. Biliary Conjugated Bilirubin Concentration
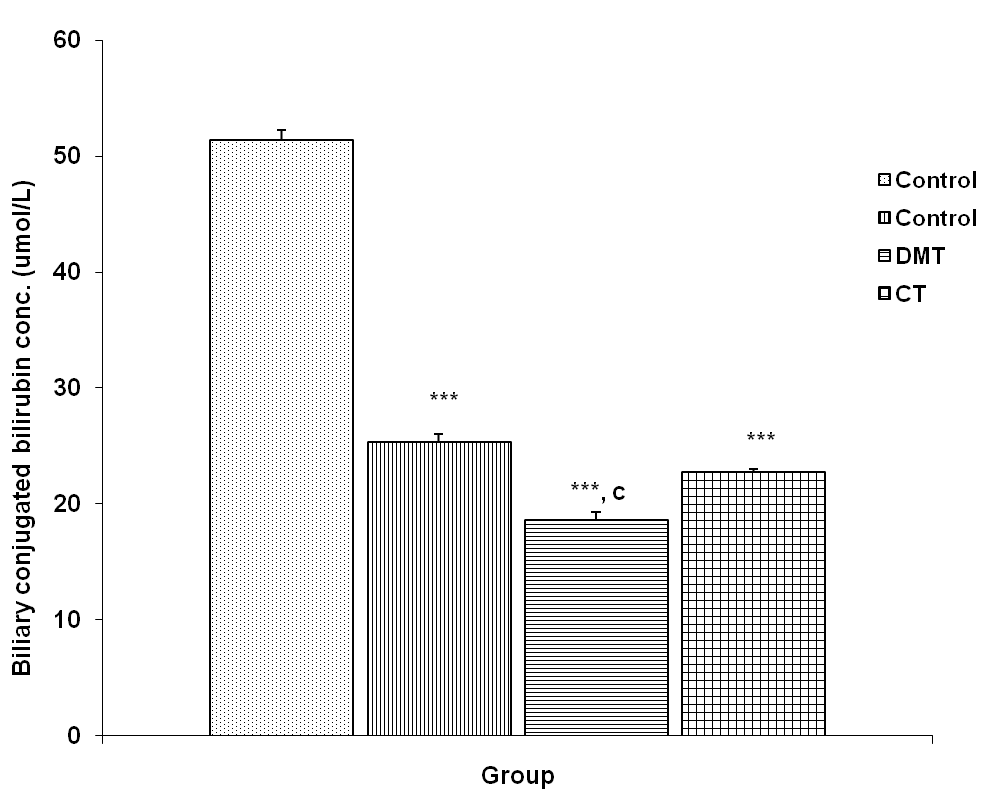 | Figure 4. Comparison of biliary conjugated bilirubin concentration in control and test groups. Values are mean + SEM, n = 10. ***p<0.001 vs control; c = p<0.001 vs DM |
3.3.3. Biliary Unconjugated Bilirubin Concentration
- The biliary unconjugated bilirubin (BUB) concentration in the control, DM, DMT and CT group was 12.55 + 0.96, 50.51 + 0.82, 14.71 + 0.98 and 3.25 + 0.30 μmol/L respectively. BUB concentration was significantly increased (p<0.001) in DM group compared to control, DMT and CT group. BUB concentration in the DMT group was significantly reduced (p<0.001) compared to DM group. The BUB concentration was also significantly reduced (p<0.001) in CT group compared to control and DMT (Fig. 5).
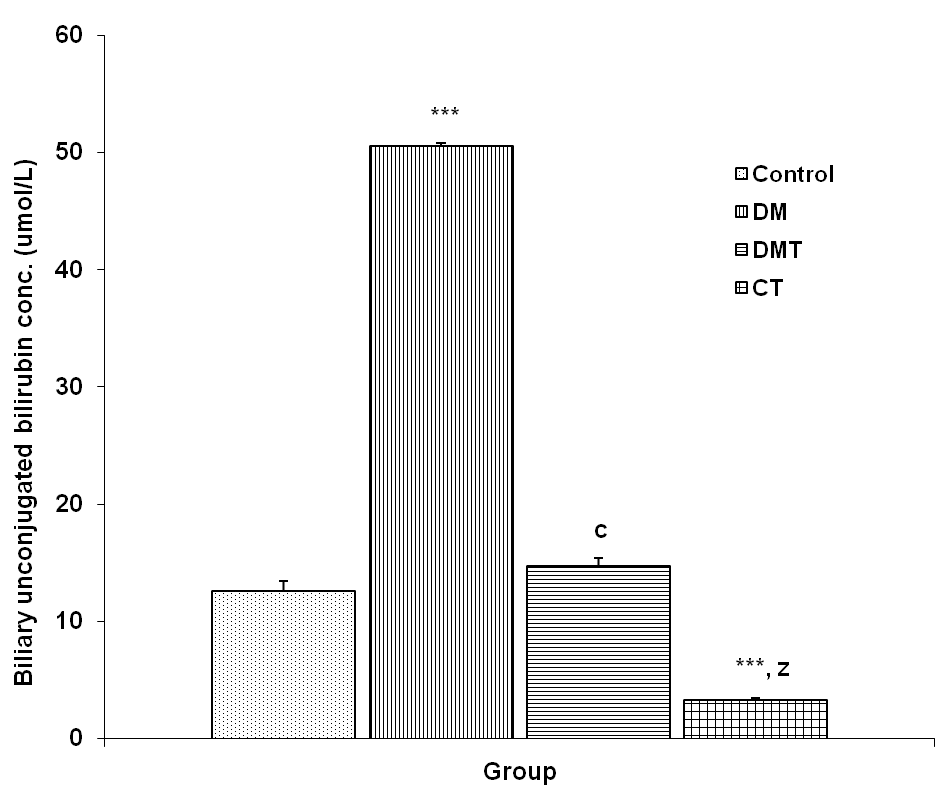 | Figure 5. Comparison of biliary unconjugated bilirubin concentration in control and test groups. Values are mean + SEM, n = 10. ***p<0.001 vs control; c = p<0.001 vs DM; z = p<0.001 vs DMT |
3.4. Serum Total Bilirubin, Conjugated and Unconjugated Bilirubin Concentration
3.4.1. Serum Total Bilirubin Concentration
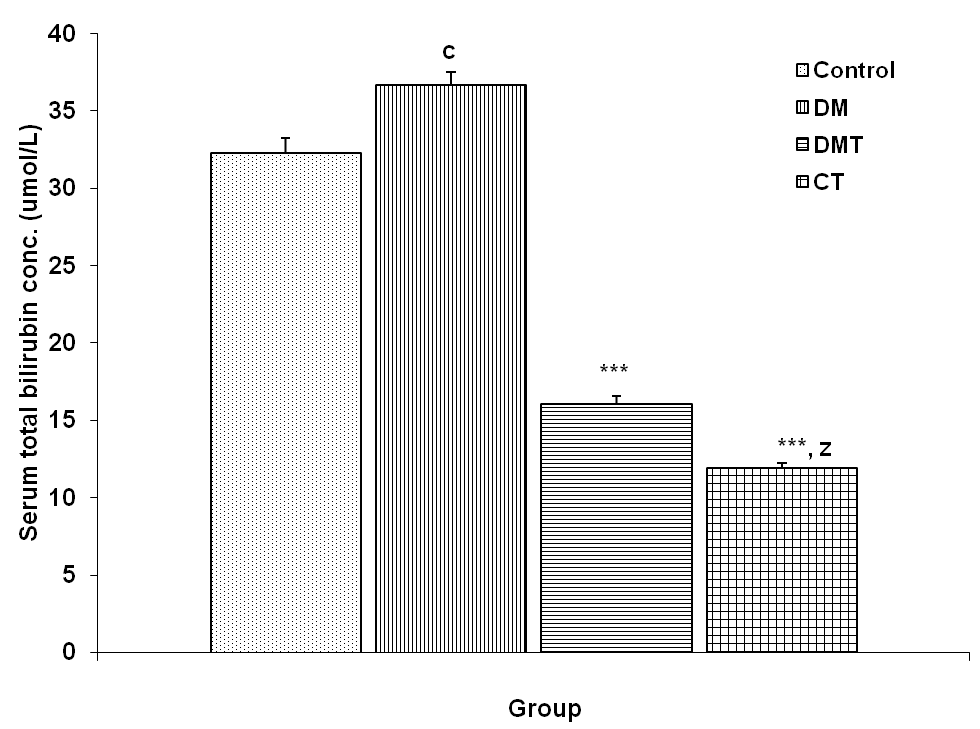 | Figure 6. Comparison of serum total bilirubin concentration in control and test groups. Values are mean + SEM, n = 10. ***p<0.001 vs control and DM; c = p<0.05 vs control; z = p<0.001 vs DMT |
3.4.2. Serum Conjugated Bilirubin Concentration
- The serum conjugated bilirubin (SCB) concentration in the control, DM, DMT and CT group was 25.58 + 0.82, 12.76 + 0.70, 8.94 + 0.46 and 10.43 + 0.24 μmol/L respectively. SCB concentration was significantly reduced (p<0.001) in DM compared to control. SCB concentration in the DMT group was significantly reduced (p<0.001) compared to DM group. The SCB concentration was also significantly reduced (p<0.001) in CT group compared to control (Fig. 7).
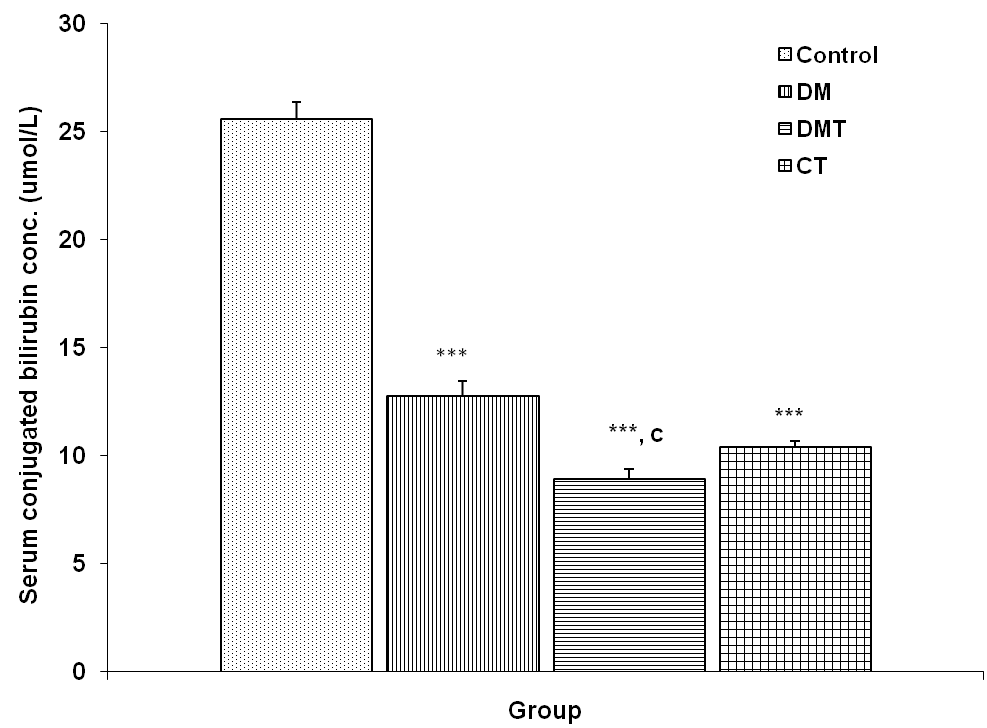 | Figure 7. Comparison of serum conjugated bilirubin concentration in control and test groups. Values are mean + SEM, n = 10. ***p<0.001 vs Control; c = p<0.001 vs DM |
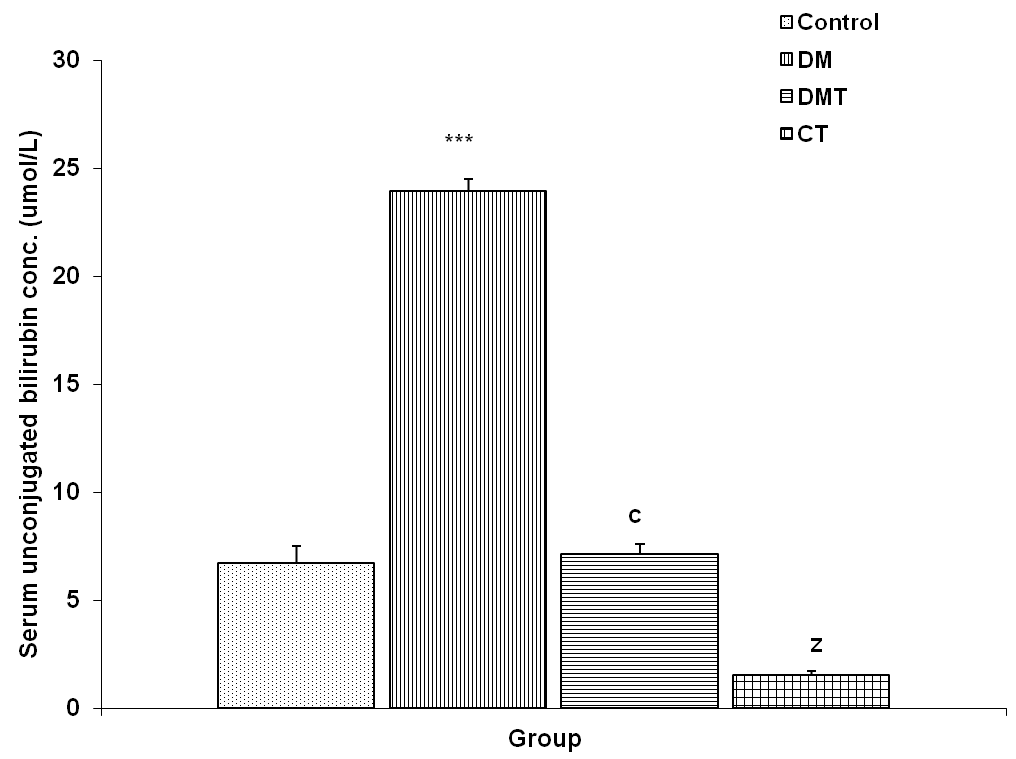
3.4.3. Serum Unconjugated Bilirubin Concentration
4. Discussion
- A number of plant materials have been reported to exhibit glycemic control by stimulating insulin release[25]. Crude Aloe vera gel significantly reduced (P<0.001) the blood glucose level in the DMT group compared to DM group (Fig. 1). This result is highly correlated with the work of Okayar et al.[18], Nna et al[20] and Eman et al.[25]. Aloe vera leaf extract has been found to be significantly effective in lowering blood glucose in experimental diabetics. Crude Aloe vera gel did not significantly alter the blood glucose level of fasted rats in the control treated group when compared to control, suggesting a possible negative feedback that ensures blood glucose levels do not become lower than normal (hypoglycemia), which is even more life threatening.Although some studies have claimed that bilirubin and biliverdin may exert some beneficial effects by virtue of their strong antioxidant properties, this may be relevant during the newborn period, when the level of other natural antioxidants is low. As bilirubin enters the liver, most of it becomes conjugated through a series of catalysed reactions before being secreted into bile together with some amount of unconjugated bilirubin as bile pigment[6]. Conjugated bilirubin is not reabsorbed from the intestine, but the small amount of unconjugated bilirubin that appears in the bile is partially reabsorbed. Intestinal bacteria degrades bilirubin into urobilinogen, most of which is absorbed from the intestine and undergoes enterohepatic recirculation[6]. A minor fraction is then excreted in the urine. Urobilin, the oxidation product of urobilinogen, contributes to the colour of normal urine and stool. During severe cholestasis (e.g. the early phases of hepatitis A or B) or near-complete biliary obstruction (e.g. in carcinoma of the pancreas), bilirubin excretion in bile is markedly reduced, and the resulting lack of formation of urobilinogen causes the pale, so-called ‘clay-coloured’ stool[6].Despite reports that mild hyperbilirubinemia may be beneficial to health because of the antioxidant property of bilirubin[26], the health hazards associated with hyperbilirubinemia cannot be overemphasized. Animal models using disruption of the BBB to induce entry of bilirubin into the brain have shown that bilirubin induces a decline in brain energy metabolites[27,28].Bilirubin-induced ATP depletion has also been demonstrated in cultured neurons[29]. Studies have shown the inhibitory effects of bilirubin on 28 different enzymes, grouped into respiratory and oxidative phosphorylation, carbohydrate metabolism, tricarboxylic acid cycle metabolism, amino acid and protein metabolism, and lipid metabolism[30].Although bile secretory rate was high in DM group compared to control and DMT group, the increase was not significant (Fig. 2). Biliary and serum total and unconjugated bilirubin concentrations were significantly increased (p<0.001) in DM group compared to control, DMT and CT groups (Fig. 3, 4, 6 and 7). This is suggestive of a possible decrease in liver function as a result of diabetes mellitus. The DMT group had a significantly lower (p<0.001) BTB, BUB, STB and SUB compared to DM group (Fig. 3, 5, 6 and 8). Reduced level of SCB and BCB in the DM group compared to control is suggestive of the fact that diabetes mellitus reduces the liver's ability to conjugate bilirubin. This was further confirmed in figure 5 and 8 as there was significant increase (p<0.001) in biliary and serum unconjugated bilirubin concentrations. Significant reduction (p<0.001) in STB, SUB, BTB and BUB was also observed in CT group compared to control. Aloe vera gel's efficacy in lowering serum and biliary total bilirubin concentration in DMT and CT groups may be attributed to its hepatoprotective property[31-34]. Aloe vera gel is known to contain flavonoids and alkaloids, and this may be responsible for its enhanced bilirubin excretory property.The puzzle therefore is; following reports that hyperbilirubinemia may be beneficial to health because of the antioxidant property of bilirubin[26], should hyperbilirubinemia be encouraged considering the health hazards?[27-30]. It is interesting to note that Aloe vera gel has strong antioxidant effect and if used in treating hyperbilirubinemia, will assume the antioxidant effect while at the same time ameliorating hyperbilirubinemia.
5. Conclusions
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus is associated with altered bilirubin concentration. Administration of crude Aloe vera gel to the diabetic treated group and the control treated group reduced the bilirubin concentration. The results obtained from this study are suggestive of the fact that crude Aloe vera gel enhances excretion of bilirubin in diabetic and normal conditions and can therefore be used to ameliorate hyperbilirubinemia.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML