-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2012; 2(4): 62-70
doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20120204.01
Formulation and Optimization of Drug-Resin Complex Loaded Mucoadhesive Chitosan Beads of Repaglinide Using Factorial Design
Ashwini R. M. , Mangesh R. B. , Rahul R. P. , Nilkanth S. P. , Devaki C. U.
AISSMS College of Pharmacy, Kennedy Road, Near RTO, Pune-411 001, India
Correspondence to: Ashwini R. M. , AISSMS College of Pharmacy, Kennedy Road, Near RTO, Pune-411 001, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Some ion exchange resins like Cholestyramine (Duolite AP-143), provide extended gastric retention and have the ability to coat the gastric mucosa uniformly. The use of such mucoadhesive ion exchange resins is another attractive approach in the development of targeted formulations for the GIT. In pesent work, a mucoadhesive gastroretentive system for Repaglinide was developed and optimized using Duolite AP-143 resin by RSM. Studies were carried out to develop and optimize oral mucoadhesive beads for Repaglinide using ion exchange resin and chitosan. Resinates prepared were studied for the effect of pH and drug resin ratio on drug loading. Resin and resinates were evaluated for mucoadhesive property using falling liquid film method. Resin and resinates showed sufficient mucoadhesion strength when compared with other mucoadhesive polymers and other ion exchange resins. Dissolution study of Repaglinide resinate showed that Duolite AP-143 was able to sustain the release of drug. The study suggests that the mucoadhesive beads of Repaglinide provide sustained release over 8 h and also shows sufficient mucoadhesive strength with rabbit gastric mucosa.
Keywords: Response Surface Methodology (RSM), Mucoadhesion, Gastroretentive, Cholestyramine
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The control of gastrointestinal transit of orally administered dosage forms using gastroretentive drug delivery systems (GRDDS) can improve the bioavailability of drugs that exhibit site-specific absorption. Oral bioavailability of certain drugs can be limited by the residence time of the pharmaceutical formulations in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Gastric emptying plays an important role in the dynamics of drug absorption and can lead to variable and unpredictable bioavailability. The ability to maintain an oral delivery system at the absorption site for an extended period of time has great appeal for treatment of both local conditions as well as for sustained systemic absorption. Various approaches have been pursued to increase the retention of an oral dosage form in the stomach, including swelling and expanding systems (R.C. Mamajek et al, 1980 and J. Urquhart et al, 1984), bioadhesive systems (C.M. Lehr, 1994 and G. Ponchel et al, 1998), modified- shape systems (L.J. Caldwell et al, 1988 and R.I. Cargill et al, 1988), high-density systems (S.S. Davis et al, 1986) and floating systems.Mucoadhesive drug delivery is one of the approaches to design a formulation, which can adhere to the lining of the stomach, thus retaining the drug at the absorption site for a prolonged period. This concept utilizes the phenomenon of bioadhesion − an adhesive interaction between the dosage form and the biological surface. It has been suggested that a delay in GI transit, brought about by an intimate and extended contact between bioadhesive systems and mucus/mucosal lining, will improve drug bioavailability and duration of action. A prolonged retention at the mucosal surface provides intimate contact between the dosage form and absorbing tissues which results in a prolonged period of drug exposure to the region. Therefore, an increased retention time is a desirable property of bioadhesive drug delivery systems.Oral controlled release dosage forms possessing gastric retention capabilities will provide us new and therapeutic options especially for drugs exhibiting an absorption window in the upper g.i.t or drugs with stability problem in alkaline pH medium.Literature survey reveals that some ion exchange resins, especially anion exchange resins such as cholestyramine (Duolite AP-143), possess mucoadhesive property and have also proved useful as drug carriers releasing the drug from resinate following an influence of competing ions. In present work, Cholestyramine (Duolite AP-143), an anion exchange resin was selected to develop and optimize mucoadhesive dosage form of repaglinide. A factorial design for two factors at three levels was selected as experimental design.Therefore the objective of present study is to design, develop and optimize the gastroretentive mucoadhesive beads using ion exchange resin and chitosan.Chitosan (CS) is a natural and abundant polysaccharide obtained by N-deacetylation of chitin. Chitin is extracted from crustaceans and insect shells, algae and certain fungi. The physicochemical and biological properties of CS (such as biodegradability, biocompatibility, non-toxicity, mucoadhesion, absorption enhancement and pH-dependent swelling) are of great interest in the biomedical and pharmaceutical fields (Leticia Martinez et al, 2007). CS is a polycation, well known for its reactivity with negatively charged components, either ions or molecules, leading to the formation of a network through ionic bridges between polymer chains (Shilan Chen et al, 2008). The single-unit mucoadhesive systems are more popular but have a disadvantage owing to their ‘all-or-nothing’ emptying process leading to high variability of the gastrointestinal transit time. In contrast, multiple-unit particulate dosage forms (e.g. microspheres, beads) have the advantages that they pass uniformly through the GIT to avoid the vagaries of gastric emptying and provide an adjustable release, thereby reducing the intersubject variability in absorption and risk of local irritation.Factorial design methodology was used to prepare chitosan mucoadhesive beads. This enabled to study the effect of different variables either separately or combined on different parameters including rel8h, drug entrapment efficiency, and mucoadhesion index. Repaglinide beads with maximum drug entrapment, higher percent of floating beads and with the most extended drug release over 8 h were evaluated in vivo. Repaglinide, a fast and short-acting meglitinide analogue was chosen as the drug candidate since it is indicated for the development of a dosage form with increased GRT. It has a very short half-life (1 h), low bioavailability (50%) and poor absorption in the upper intestinal tract. Moreover it produces hypoglycemia after oral administration (S.N. Davis et al, 2001).Drugs that are easily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) and have a short half-life are eliminated quickly from the blood circulation and require frequent dosing. To avoid this problem, the oral controlled release (CR) formulations have been developed in an attempt to release the drug slowly into the GIT and maintain a constant drug concentration in the serum for longer period of time. Such oral drug delivery devices have a restriction due to the gastric emptying.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- Repaglinide was generously supplied as a gift sample by M/s Torrent Pharmaceuticals (Ahmedabad, India). Duolite AP/143 and Chitosan were gifted by Rohm and Haas Limited, France; Bliss GVS Pharma Ltd., Mumbai respectively. Sodium tripolyphoshphate was purchased from New Modern Chemical Corporation, Mumbai. All other reagents and chemicals used were of analytical grade.The in vivo study was performed using the protocol approved by the Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animals (CPCSEA), Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, Government of India. Institutional Animals Ethical Committee of AISSMS College of Pharmacy, Pune, India granted permission for the study. In vivo X-ray radiological examination was performed at Kotbagi Hospital, Pune, India.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Drug-Resin Complex
- The drug resin complexes were prepared by batch process. An accurately weighed amount of repaglinide (500 mg) was taken and added in 100 ml of distilled water. Then known weight of ion exchange resin was added to the solution and stirred on propeller stirrer. Time to reach equilibrium was determined by periodically measuring concentration of drug solution. Resinate thus formed was washed with 0.1 N HCl to remove the unloaded drug, which was collected and added to previous filtrates. Resinate was dried overnight in an hot air oven at 50ºC. The drug content in the final filtrate and washings was analyzed by UV-spectroscopy at 243 nm.
2.2.2. Preparation of Mucoadhesive Beads
- Chitosan beads were prepared by ionotrophic gelation method by using sodium tripolyphoshphate as cross-linking agent (Anal A.K. et al, 2006 and Gupta K.C et al, 2006). Chitosan solution of 2.5 w/v concentration was prepared in 2%aqueous acetic acid. Core material i.e. drug resin complex was dispersed in to the chitosan solution. This dispersion was subsequently added drop-wise through a spray gun of 2 mm nozzle diameter into 100 ml of sodium tripolyphosphate (TPP) (3%w/v) to form chitosan beads. The droplets instantaneously gelled into discrete chitosan beads upon contact with the surface of the TPP solution. Then the beads were left, to cure, for a period of 1 h in the TPP solution. After this period, the TPP solutions were decanted and the beads were washed several times with distilled de -ionised water so as to remove the surface adsorbed drug and TPP and then air dried for 12 h.
2.2.3. Experimental Design
- Preliminary studies revealed that concentration of chitosan and sodium tripolyphosphate affected the performance of the beads. Therefore a 32 full factorial design was selected as it allows minimum runs and combines all levels of one factor with that of another. The levels of each factor were based on preliminary trials. The response parameters evaluated were drug release after 8 hr, entrapment efficiency and % muco adhesion. The composition of formulations as per this design is shown in Table 1.
2.2.4. Evaluation of the Drug-Resin Loaded Chitosan Beads
- a) Micromeritic PropertiesAngle of repose (θ) of different formulations, which measures the resistance to particle flow, was determined by a fixed funnel method. Tapped density was determined using tapped density apparatus (Lab Hosp.) and compressibility index using the formula described by Keith Marshall.b) Particle SizeThe particle size of the beads was measured using an optical microscope and the mean particle size was calculated by measuring 100 particles with the help of a calibrated ocular micrometer.c) Swelling CharacteristicsSwelling experiments were performed by immersing a known amount of dried repaglinide loaded chitosan beads (about 50 mg) in specified pH buffer solutions (50 mL) at 37±0.5°C. The specified pH buffer solutions were prepared with HCl (pH from 1.0 to 1.8), C8H5O4K (potassium acid phthalate)–HCl (pH from 3.0 to 5.0), NaH2PO4 (sodium dihydrogen phosphate)–NaOH (pH from 6.0 to 7.5) (Waterman et. al. 2006). The weight of swollen samples was measured after the surface solution was removed by filter paper. The swelling ratio (SR) was calculated by the following expression:
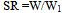 | (4) |
 | (5) |
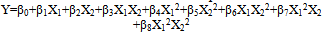 | (6) |
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of Drug Resin Complex
- Resinate of repaglinide was prepared with cholestyramine using the batch method. Optimum time for drug loading was decided to be 4 h from initial experiments. Drug content of resinates was found to be 30 mg/ 100 mg of resinate.
3.2. Micromeritic Properties
- The angle of repose of formulations of microspheres ranged from 15.29±1.3 to 19.29±0.7. The tapped density values of formulations of microspheres ranged 0.4754±1.23 to 0.6511±1.21gm/cm3. The % compressibility index (carr’s index) ranged between 0.75±2.0 to 3.46±0.9%. The values of Carr’s index and angle of repose indicate excellent flow properties Table 2.
3.3. Swelling Characteristic
- The swelling ability of ionic cross-linked gel beads was found to be strongly dependent on the pH value of swelling medium. The beads showed high degree of swelling at low pH, whereas, low swelling degree at pH greater than 5.0. The higher swelling degree is attributed to the strong protonation of amino groups on chitosan, which bring strong electrostatic repulsion among intra-chain and inter-chain of chitosan, resulting in the relaxation of polymer network. Formulation batches F3, F6 and F9 showed more swelling index than other batches. High swelling index was required to retard drug release for extended period of time. In order to determine the experimental conditions for optimum loading and release of repaglinide from chitosan beads, the swelling behavior was studied at different time intervals in the specified pH buffer solutions prepared with HCl (pH from 1.0 to 1.8), C8H5O4K (potassium acid phthalate)–HCl (pH from 3.0 to 5.0), NaH2PO4 (sodium dihydrogen phosphate)–NaOH (pH from 6.0 to 7.5). The swelling behavior of beads depends on the molecular weight of chitosan, degree of deacetylation, crosslinking density, and concentration of crosslinking agent. The microspheres with medium molecular weight chitosan were more useful to prepare controlled delivery systems. In the present investigation, the concentration of TPP mainly affects the drug release because chitosan used throughout the study was having same degree of deacetylation and molecular weight. As the concentration of TPP increases, the crosslinking density also increases which was due to the increase in the firmness/compactness of the polymer matrix Table 2.
|
3.4. Drug Entrapment Efficiency
- The entrapment efficiency of drug within a bead depends on resinate used for the preparation of beads. The resinate having maximum drug loading was used for the preparation of beads. As the concentration of resinate increased, drug entrapment efficiency also increased. Also the drug entrapment depends upon the concentration of polymer used i.e. the ratio of resinate to polymer, concentration of sodium tripolyphoshphate and curing time. As concentration of polymer increases the drug entrapment also increases. As curing time increases drug entrapment efficiency decreases significantly due to the high cross linking of polymer. Since repaglinide is insoluble in water, it was not dissolved in solution during crosslinking and hardening process. Therefore, the loss of repaglinide from beads was minimal during the hardening and washing process. High encapsulation efficiencies were obtained, at high drug loading capacity of the resin, with drugs with high binding affinity Table 3.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy
- The morphology of TPP-chitosan beads prepared with various concentrations of chitosan and TPP was studied. The concentration of chitosan and TPP affects the morphology of bead surface. As the concentration of chitosan increased, the viscosity of chitosan solution increased and it resulted in the formation of relatively strong walls of beads upon interaction with TPP. Therefore, higher the concentration of chitosan, more spherical was the shape of beads. The particle sizes of drug loaded chitosan beads ranged between 2.52 mm to 2.78 mm. The scanning electron micrograph of the chitosan beads cross-linked with TPP had an irregular shape.SEM was performed on the optimised chitosan bead formulations to assess their surface and cross-sectional morphological characteristics. In addition, the surface morphology of the beads before and after dissolution was assessed. When examined at a magnification of 1000x and 3000x (Figure 1a), the polymer surfaces of the beads appeared heterogeneous and porous. These findings are concordant with those of other researchers who also reported rough surface morphologies for chitosan beads prepared by the ionotrophic gelation technique.
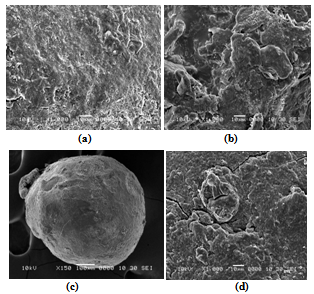 | Figure 1. a) Surface morphology of a chitosan beads (1000x); b) Cross-section of a chitosan beads (3000x); c) Bead surface before dissolution (100x); d) Bead surface after dissolution (1000x) |
3.6. In Vitro Drug Release Study
- In-vitro dissolution studies of repaglinide from mucoadhesive beads were performed in 0.1 N HCl (pH 1.2) for 12 h using USP Type I dissolution test apparatus. In formulations F1, F2, F3 the concentration of chitosan was 2 % and the concentration of TPP employed was 2.5, 5, and 7.5 % respectively. It was found that the formulations F1, F2 and F3 showed 95.82, 92.77 and 87.62 % of drug release after 8h respectively. As drug release was not sustained considerably the concentration of chitosan was increased to achieve further retardation in drug release. For Formulations F4, F5 and F6, the drug release was 93.85, 85.42, and 82.31% after 8 h. While, Formulations F7, F8 and F9 showed 89.19, 84.73, and 81.54% release after 8 h. (Figure 2). It was observed that as the concentration of chitosan was increased the % cumulative release of repaglinide decreased. These results indicate that the release behavior of drug is dependent on the viscosity of chitosan solution. Increased chitosan concentration leads to the increased viscosity of chitosan solution forming relatively strong walls of beads upon interaction with TPP. Increased crosslinking density of TPP-chitosan matrix resulted in less swelling ability, therefore the release of drug decreased. Also, increase in particle size which results in an increased diffusional path length and consequent retardation in drug release was observed at higher concentration of chitosan. But, when the concentration of TPP was increased, keeping the concentration of chitosan constant, it leaded to the retardation of drug release and this may be due to the increased packing ability of the polymeric network. In addition, the swelling and permeability characteristics of chitosan films were dependent on concentration of crosslinking agent.
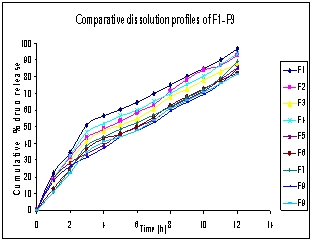 | Figure 2. Comparitive cumulative % drug release profiles of formulations F1-F9 |
3.7. Data Analysis
- The outcomes of the experimental design were processed using Design Expert 7.1.2 software. Mathematical models generated for predicting the values of response parameters at selected values of the formulation factors within the design space were:
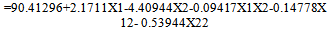 | (7) |
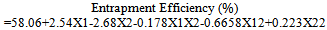 | (8) |
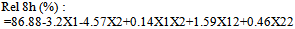 | (9) |
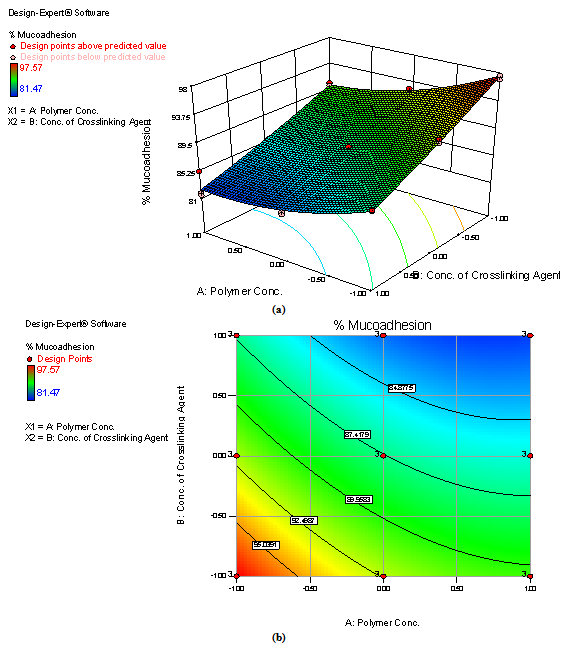 | Figure 3. Response surface plot (a) and Contour plot (b) showing the influence of concentration of chitosan and concentration of TPP on % mucoadhesion of mucoadhesive beads formulations of repaglinide |
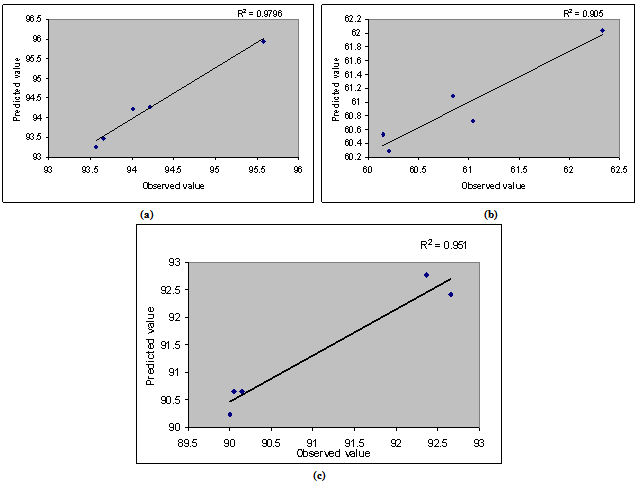 | Figure 4. Linear plots between observed and predicted values of (a) mucoadhesion index, (b) drug entrapment efficiency, (c) rel 8 h |
3.8. Validation of Statistical Models
- For all 5 checkpoint formulations, the results of the physical evaluation and microspheres’ drug content were found to be within limits. Table 4 lists the composition of the checkpoints, the predicted and experimental values of all the response variables, and the percentage error in prognosis. Figure 4 shows linear correlation plots between the observed and predicted values of mucoadhesion index, drug entrapment efficiency and rel8h. The linear correlation plots drawn between the predicted and observed responses demonstrated higher values of R2 (ranging between 0.905 and 0.9796), indicating excellent fitting of model (P<0.001). Upon comparison of the observed responses with that of the anticipated responses, the prediction error varied between -0.51 and 0.66 %. Thus, the low magnitudes of error as well as the significant values of R2 in the current study indicate a high prognostic ability of the statistical models.i) In Vivo Evaluation of Mucoadhesion by Radiological ExaminationThe X-ray studies showed that (Figure 1) the beads formulated with chitosan were intact and remained in the stomach region even after 10 h of administration indicating good adhesion of the beads.
4. Conclusions
- It was concluded from the present work that mucoadhesive beads prepared using cholestyramine and crosslinked chitosan resulted in a gastroretentive drug delivery system for repaglinide. The rough and porous surface of the beads helped in mucoadhesion process. Increase in the concentration of the crosslinking agent (TPP) and chitosan, delayed the release of repaglinide from the beads. Mucoadsesion was found to be increased with increase in the levels of both chitosan and TPP. Entrapment efficiency decreased with increase in the concentration of TPP and increased as the levels of chitosan increased. Drug release from the beads was found to follow diffusion mechanism and matrix model. X-ray studies showed that the beads were intact and gastroretentive even after 10 hr. The statistical models generated for the experimental design were found to be valid for predicting the values of the response parameters at selected values of the formulation factors within the design space.The results of a 32 full factorial design revealed that the concentration of chitosan and TPP significantly affected the dependent variables such as drug entrapment efficiency, drug rel8h and mucoadhesion index. The optimum bead formulation exhibited 58.92% drug entrapment efficiency, mucoadhesion index 92.54% and 85.42% rel8h. An appropriate balance between the levels of the polymer and TPP was imperative to acquire maximum drug entrapment efficiency, sustained release of the drug and adequate mucoadhesion.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors gratefully acknowledge M/s Torrent Pharmaceuticals, Ahmedabad, India for the supply of repaglinide as a gift sample. The authors also wish to thank Mr. Tanaji Jagtap, X-ray Technician Kotbagi Hospital Pune, India for providing the facility of X-ray Photography.
References
| [1] | Mamajek, R. C. and Moyer, E. S., 1980, Drug-dispensing device and method, US Patent 4,207,890 |
| [2] | Urquhart, J. and Theeuwes, F., 1984, Drug delivery system comprising a reservoir containing a plurality of tiny pills, US Patent 4,434,153 |
| [3] | Lehr C. M., 1994, Bioadhesion technologies for the delivery of peptide and protein drugs to the gastrointestinal tract, Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst, 11, 119–160 |
| [4] | Ponchel G. and Irache J. M., 1998, Specific and non-specific bioadhesive particulate systems for oral delivery to the gastrointestinal tract, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 34, 191–219 |
| [5] | Caldwell L. J., Gardner C. R. and Cargill R. C., 1988, Drug delivery device which can be retained in the stomach for a controlled period of time, US Patent 4,767,627 |
| [6] | Cargill R. I., Caldwell J., Engle K. J., Fix A., Porter P. A. and Gardner C. R., 1988, Controlled gastric emptying. I. Effects of physical properties on gastric residence times of non-disintegrating geometric shapes in beagle dogs, Pharm. Res., 5 (8), 533–536 |
| [7] | Davis S. S., Stockwell A. F., Taylor M. J., Hardy J. G., Whalley D. R., Wilson C. G., Bechgaard H. and Christensen F. N., 1986, The effect of density on the gastric emptying of single- and multiple-unit dosage forms, Pharm. Res., 3, 208–213 |
| [8] | Iannucelli V., Coppi G., Bernabei M.T. and Cameroui R., 1998, Air compartment multiple-unit system for prolonged gastric residence, I: Formulation study, Int. J. Pharm., 174, 47–54 |
| [9] | Martinez L., Agnely F., Leclerc B., Siepmann J., Cotte M., Geiger S. and Couarraze G., 2007, Cross-linking of chitosan and chitosan/poly(ethylene oxide) beads: A theoretical treatment, Eur. J. Pharma. and Biopharm, 67, 339–348 |
| [10] | Chen S., Liu M., Jin S. and Wang B., 2008, Preparation of ionic-crosslinked chitosan-based gel beads and effect of reaction conditions on drug release behaviors, Int. J. Pharm, 349, 180–187 |
| [11] | Davis S. N. and Granner D. K., 2001, Insulin, oral hypoglycemic agents and the pharmacology of the endocrine pancreas. In: J. G. Hard- man, L.E. Limbrid (10th Eds.), Goodman and Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics ( pp. 1704– 1705), McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, USA |
| [12] | Anal A. K., Stevens W. F., and Lopezd C. R., 2006, Ionotrophic cross-linked chitosan microspheres for controlled release of ampicillin, Int. J. Pharm., 312. 166–173 |
| [13] | Gupta K. C. and Jabrail F. H., 2006, Preparation and characterization of sodium hexametaphosphate cross-linked chitosan microspheres for controlled and sustained delivery of centchroman, Int. J. Bio Macro., 38, 272–283 |
| [14] | Waterman and Kenneth C., 2006, In vitro evaluation of the mucoadhesive properties of chitosan microspheres, J Pharm Sci., 95(9), 2051-2061 |
| [15] | Govender S., Pillay V., Chetty D. J., Essack S. Y., Dangor C. M. and Govender T., 2005, Optimisation and characterisation of bioadhesive controlled release tetracycline microspheres, Int J Pharm, 306, 24–40 |
| [16] | Qing H. E., Qiang A. O., Aijun W., Yandao G., Nanming Z. and Xiufang Z., 2007, In Vitro Cytotoxicity and Protein Drug Release Properties of Chitosan/Heparin Microspheres, Tsinghua Sci and Tech., 12(4):361-365 |
| [17] | Chowdary KPR, Suresh B, Sangeeta B and Reddy GK, 2003, Design and evaluation of diltiazem mucoadhesive tablets for controlled release, Saudi Pharm J, 11(4) 201-205 |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML