-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2012; 2(1): 12-15
doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20120201.03
Antifertility Effects of Ethanolic Extract of Xylopia aethiopica on Male Reproductive Organ of Wistar Rats
Eze Kingsley Nwangwa
Department of Physiology, Faculty of Basic Medical Sciences College of Health Sciences, Delta State University, P.M.B. 001 Abraka. Delta State. Nigeria
Correspondence to: Eze Kingsley Nwangwa , Department of Physiology, Faculty of Basic Medical Sciences College of Health Sciences, Delta State University, P.M.B. 001 Abraka. Delta State. Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The effects of ethanolic extract of Xylopia aethiopica on male reproductive organ in Wistar rats was studied. A total of twenty-four adult male rats were randomly divided into three experimental groups (n=8). Group 1 (control) was given rat chow and distilled water ad libitum, Group II and III received 0.5mls and 1.0mls of ethanolic extract of Xylopia aethiopica once daily for a period of 28 days. The results showed a significant (P<0.05) and dose dependent decrease in the semen parameters (count, motility) and a non significant decrease in the percentage of sperm with normal morphology. The testicular photomicrograph also shows dose dependent degenerative changes. Therefore, the extract may have some anti fertility effects which may be further explored for a possible use as male contraceptive agent.
Keywords: Xylopia Aethiopica, Male Contraceptives, Antifertility, Semen Parameters
Cite this paper: Eze Kingsley Nwangwa , "Antifertility Effects of Ethanolic Extract of Xylopia aethiopica on Male Reproductive Organ of Wistar Rats", American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 2 No. 1, 2012, pp. 12-15. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20120201.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The exclusive use of herbal remedies to treat and manage ailments had served from the outset as the most important therapeutic approach available to man. However, the decline from its use due to the introduction of modern synthetic medicine started at about the beginning of the 20th century up to the 1970s[1].Traditional medicine accounts for about 80% of the health needs of the rural populace in most regions of Africa, Xylopia aethiopica is one of the medicinal plants, the parts of which are of high medicinal value in many countries of Africa[2]. Mythilypriya et al (2007) reported that traditional medicines are used by about 60% of the world population both in the developing and developed countries where modern medicines are predominantly used[3]. The use of herbs requires good knowledge of the toxicity dosage, purity, suitable extraction solvent and adverse effects[4].The prolonged usage of these herbal products without proper monitoring of the usage had brought about a number of health related problems like infertility which is a common problem affecting most couples all over the world[5].Decline in male fertility has been a great concern from time as male infertility accounts for about 30% of fertility cases worldwide[6]. Male infertility is an important issue, a common problem occurring worldwide. It is a neglected reproductive health issue in Nigeria[7]. Reports indicate thatthe male factor accounts for 20-50% of the causes of infertility in different parts of Nigeria[8,9]. Several plant products like ethanol extract of Dioscorea esculanta[10], Andrograpis paniculata[11], inhibit male and female fertility and may be developed into contraceptives. Even though many indigenous plants have been shown to prevent birth, only few plants have so far been investigated for their anti-fertility activity[12]. Xylopia aethiopica, a West African “pepper tree”, with straight stem and smooth bark, it remains ever green with a consistent aroma[13]. Xylopia aethiopica (X. aethiopica) commonly known as “African guinea pepper” or “Ethiopian pepper” is wide spread in tropical Africa, Zambia, Mozambique and Angola[14]. In Nigeria, it is found all over the lowland rain forest and most fringe forest in the Savanna zones of Nigeria. Negro pepper as it is also known has been used as a pepper substitute in Europe and India[15]. The aromatic roots of the plant are used to arrest bleeding and owing to antiseptic properties, the aqueous concoction is usually administered after child birth[2]. It has also been reported to be an antioxidant[16]. Its anti-hypertensive and diuretic effects have also been reported[17].The aim of the present study, therefore, is to determine the effects of the extract of Xylopia aethiopica on the reproductive organ of male Wistar rats.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
- The dried fruits of Xylopia aethiopica were purchase from the central market in Abraka, Delta State, Nigeria. They were authenticated by a staff in the Department of Botany, Faculty of Science, Delta State University, Abraka, Nigeria, and a voucher specimen kept in the laboratory
2.2. Preparation of Extract
- The powdered fruit (226 g) was extracted with 300ml ethanol using Maceration extraction method for 24 hours in an air tight container. Using a vacuum rotary evaporator, the ethanol filtrate was concentrated at a low temperature, under reduced pressure. This yielded 43.03 g (19.0%) (jelly-like) oil extracts, 25g of which was then dissolved in 5ml ethanol stored in a refrigerator from which fresh solution was prepared using distilled water when required.
2.3. Animals
- The experiment was performed with twenty-four (24) adult male albino rats weighing between 180-240 g obtained from Animal house in Ambrose Alli University, Ekpoma and kept at the Animal Care Unit of the College of Health Sciences, Delta State University, Abraka. The animals were allowed to acclimatize to the laboratory condition (temperature 24-28°C and 12 hour light-dark cycle) for fourteen days before commencement of the experiment with free access to rat chow(Top feeds Nigeria) and water ad libitum throughout the study. All the animals were treated according to the declaration of Helsinki on guiding principles in the care and use of animals, approval was received from a local research ethical committee of the university.
2.4. Experimental Design
- Twenty four male rats were randomly divided into three groups (n=8) with their initial body weight measured. Group I served as the control and the rats were fed normal rat chow, 0.5ml of ethanol mixed with distilled water (vehicle for the extract). Groups II and III rats were given 0.5ml, 1.0ml respectively, of Xylopia aethiopica fruit extract. The vehicle and extract were given orally once daily for 28 days. At the end of the experiment, the final body weights, sperm parameters and testicular histology of the rats were determined.
2.5. Preparation
- The rats were sacrificed by decapitation, 24 hours after last administration of the extract. The caudal epididymis was dissected and semen milked out of epididymis on slides and counting chambers used in estimating semen parameters[18]. The morphology was assessed after staining with papanicolaou[19]. The testes were isolated and placed in a container with 10% formal saline for fixation and tissues were stained for histological study. The rat semen were analyze with the various procedures as laid down by Monica[20]
2.6. Statistical Analysis
- Data were expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance difference between means was determined by student t-test and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). P value <0.05 was considered as significant.
3. Results
- The result of the study is as shown below:
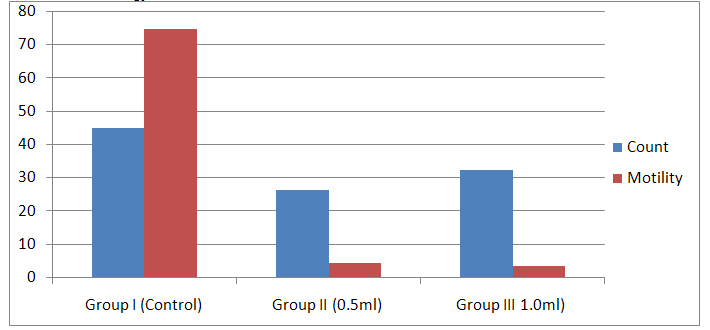 | Figure 1. Statistical Graph of sperm count (X 106) and motility (%) showing a comparison between control and treated group |
|
3.1. Microscopic Examination of Testes
- Group 1 – (control) shows a normal histoarchitecture of the seminiferous tubules. The seminiferous tubules are attached to each other.
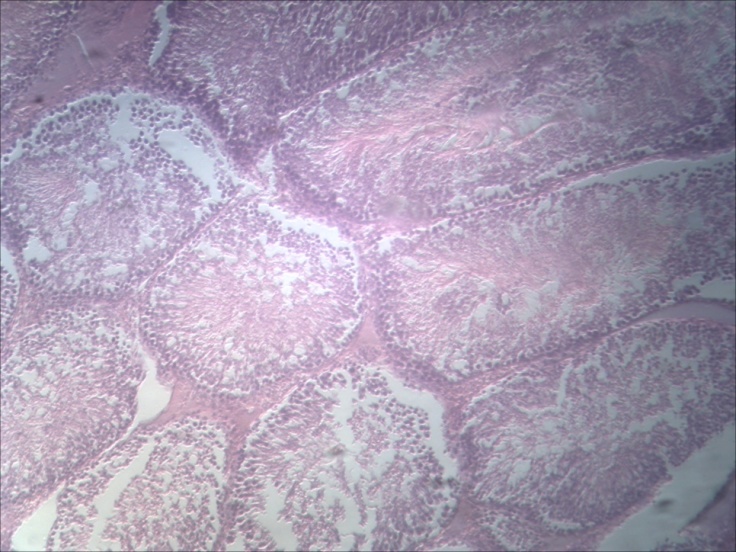 | Figure 2. Longitudinal section of testes. Group 1 (distilled water) H & E stain x 100 Note: IS- Interstitial space, BV – Blood vessel, ST – Seminiferous tubule |
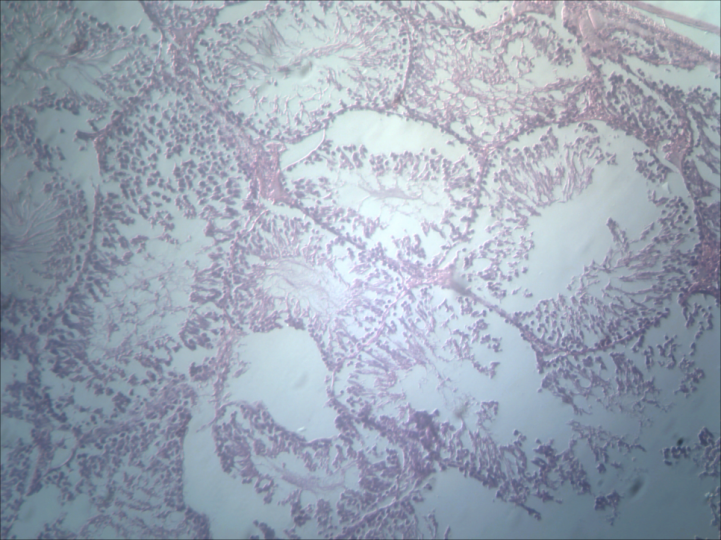 | Figure 3. Longitudinal section of testes Group 2 (0.5ml of Xylopia aethiopica): H & E stain x100 Note: IS – Interstitial space, ST – Seminiferous Tubules |
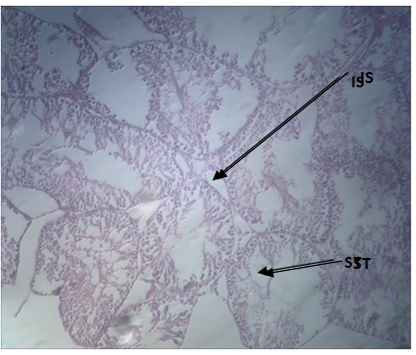 | Figure 4. Longitudinal section of testes Group 3 (1.0ml of Xylopia aethiopica): H & E stain x100 Note: IS – Interstitial space, ST – Seminiferous Tubules |
4. Discussion
- The present study has revealed that the ethanolic extract of the fruits of Xylopia aethiopica caused a significant (P<0.05) dose related reduction in sperm parameters (count and motility), but does not affect the morphology significantly. The testicular histology revealed a disorientation of the basal layer of the histoarchitecture of the seminiferous tubules in the groups that received higher dose were more affected than those with lesser dose, indicating its dose dependency. Another study by Akbarsha et al,[11] shows that a dose of 20mg per day dried leaf powder of Andrograpis paniculata, fed to male albino rats for 60 days resulted to decreased spermatogenesis, and degenerative changes in seminiferous tubules. Omobowale et al,[21] in his histopathologic studies on the effect of ethanolic extract of Garcinia kola on selected organs of dog, observed severity of histopathological changes in the animal’s testes. This finding is similar to that of[22,23].This present study also revealed a significant dose dependent decrease in body weight of the animals treated with the extract. This finding is in line with the earlier report of Ameyaw and Owusu-Ansah[16] that the fruits preparations act as an anti-oxidant and also possess a hypolipidemic activity. Burkhills[2] in his book documented that Xylopia aethiopica alongside other plants can cause adverse effects on the reproductive system of males through affecting the sperm count, motility and viability.
5. Conclusions
- The present study shows that Xylopia aethiopica has antifertility effects on male reproduction, a further study is required to investigate the reversibility of this effect for its possible use as male contraceptive agent.
AcknowledgementS
- The researcher wish to express his appreciation to Miss Evelyn Nwudu for the preliminary study and Ehitare Ekhoye for the statistical analysis.
References
| [1] | Wills, R.B.H., Bone, K., Morgan, M (2000) Herbal products: active constituents, mode of action and quality control. Nutr. Res. Rev. 13: 47-77 |
| [2] | Burkhills, H.M.,(1985) Useful plants of West Tropical Africa, 2nd edi Royal botanical garden vol 1 Pp130-132 |
| [3] | Mythilypriya R, Shanthi P, Sachdanandan P. (2007) Oral acute and sudacute toxicity studies with Kalpaamruthaa., amodified indigenous preparation on rats J Health Sci; 53(4): 351-358. |
| [4] | Murray A. (1998) Dietary reference intake for antioxidant nutrients; 100: 637-640 |
| [5] | Leke, R. (2008) Reproductive health in Cameroon. Geneva, WHO. collaborating centre for Research in Human Reproduction |
| [6] | WHO, 1991. Traditional medicine and modern health care. Progress report by the Director General, Document A. 44(10): 22 March 1991. World Health Organization, Geneva |
| [7] | Okonofua, F., Menakaya,U., Onemu, S.,Omo- Aghoja,L.O., Staffan,B. (2005) A case control study of risk factors for male infertility in Nigeria. Asian Journal Andrology 7(4) 351-361 |
| [8] | Chukwudebelu, W.O., Esege, N., Megafu, U. (1979) Etiological factors in infertility in Enugu, Nigeria. Infertility. 2:193-200 |
| [9] | Esimai, O.A., Orji, E.O., Lasisi, A.R.(2002) Male contribution to infertility in IIe-Ife, Nigeria. Niger J. Med. Med 11:70-72 |
| [10] | Shajeela, P.S., Mohan V.R., Louis Jesudas L. and Tresina Soris P. (2011): Antifertility acitivity of ethanol extract of Dioscorea esculenta (L.) Schott on male albino rats. International Journal of PharmTech Research Vol. 3, No.2, pp 946-954 |
| [11] | Akbarsha, M. A. Mavivannan, B., Hamid, K. S., and Vijayan, B. (1990): Antifertility effect of Andrographis paniculata (Nees) in albino rats. Indian Journal. Exp. Biol. 28 (5): 421 – 426 |
| [12] | Kamboj, V.P. (1988): A review of Indian Medicinal Plant with interceptive activity. Ind. J. Med. Res., 87: 336 – 355 |
| [13] | Nnodim, J.,Emejulu, A.,Amaechi, a., and NwosuNjoku, E.C.,(2011) Influence of Xylopia aethiopica fruits on Some haematological and biochemical Profile. Al Ameen J Med Sci.4(2): 191-196 |
| [14] | Puri S.G. and Talata O, (1978): Paper presented in A Symposium on Recent Advances in the Development, Productionand Utilization of Medicinal and Aromatic plants in India: A survey of some plants used in Native Medicine of West Africa of interest to India; p. 35 |
| [15] | Sofowara, E. A. (1978): Medical Plants and traditional medicine in Africa. The pitman Press, Bath, Avon, pp314-8 |
| [16] | Amayaw, Y., Owusu-Ansah, E. (1998). Morphohistological studies of two plants species used in Ethnomedicine J.Herds, spices med plants 5 (4):60-85 |
| [17] | Somova LI, Shode FO, Moodley K, Govender Y, J Ethnopharmacol (2001), 77(2-3):165-174 |
| [18] | World Health Organisation (1999) WHO laboratory manual for the examination of Human semen and Sperm-cervical mucu interaction, Cambridge University press |
| [19] | Kruger, T.F., Acosta, A.A., Simmons, K.F., Swanson, R.J., Matta, J.F., Oehringer, S.(1988) Predictive values of abnormal Sperm morphology in vitro fertilization. Fertil. Steril 49: 112-117 |
| [20] | Cheesbrough, M.,(2000) Haematological test In: District laboratory practice in tropical countries part 2 Pp 237-320 |
| [21] | Omobowale, T. O.; Taiwo, V. O. & Omotoso, M. A. (2008): Histopathological studies on the effects of the ethanolic extract of the fruits of garcinia kola on selected organs of the dog. Int. J. Morphol.,26 (4):1069-1072 |
| [22] | Akinloye, A. K.; Igbarha, O. O.; Olaniyi, M. O.; Alaka, O. O. & Oke, B. O. (2000): Preliminary investigation on the effects of Garcinia kola on rabbit testes and epididymes. Trop. Vet., 18:49- 4 |
| [23] | Bradie, V. B.; Agube, C. A.; Essien, G. E. & Udoh, F. V. (2003): Effect of Garcinia kola seed alkaloid extract on levels of gonadal hormones and pituitary gonadotrophins in rat serum. Nig. J. Phys. Sci., 18(1-2):59-64 |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML