-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2011; 1(1): 15-22
doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20110101.03
Evaluation of Hepatoprotective and Anticancer Properties of Aqueous Olive Leaf Extract in Chemically Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Rats
N. M. Abdel-Hamid 1, M. A. Fawzy 1, M. A. El-Moselhy 2
1Biochemistry Department, College of Pharmacy, Minia University, Egypt
2Pharmacology Department, College of Pharmacy, Minia University, Egypt
Correspondence to: N. M. Abdel-Hamid , Biochemistry Department, College of Pharmacy, Minia University, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Objectives: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifth most common cancer worldwide. We aimed to test the role of aqueous olive leaf extract (AOLE) in modulating metabolic disorders occurring in hepatic malignancy induced by trichloroacetic acid (TCA). Design: Eight groups of rats were assigned as follows: First, untreated normal control. Second, treated with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), (75mg/kg), intraperitoneally (IP) once weekly for 3 weeks. Third, treated with oral AOLE (500mg/kg) once daily for 28 days. The 4th group co-treated with AOLE and 5-FU as mentioned above. The 5th group treated with oral daily doses of TCA (500mg/kg) for five days. The 6th group treated with TCA for 5 days, from the sixth day with 5-FU for 3 weeks. Group 7 given TCA then, with AOLE. Group 8 received TCA, 5-FU and AOLE. Blood samples were withdrawn after 28 days from carotid vein. Liver tissues were histologically studied. Results: TCA showed neoplastic tissue features, greatly improved by treatment with AOLE and 5-FU combination. TCA significantly increased blood ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and acetyl CoA synthase (fatty acid synthase , FAS) activities, total bilirubin (T Bil) , triglycerides (TG), total glycosaminoglycans (TGAGs), alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), reduced serum total lipoprotein lipase (TLPL) activity. AOLE, combined with 5-FU produced a pronounced improvement in most of studied parameters. Conclusion: AOLE showed promising hepatoprotective and adjuvant anticancer properties if combined with 5-FU.
Keywords: HCC, 5-FU, Olive Leaves, Acyl Co Synthase, Lipase, Adjuvant Herbal
Cite this paper: N. M. Abdel-Hamid , M. A. Fawzy , M. A. El-Moselhy , "Evaluation of Hepatoprotective and Anticancer Properties of Aqueous Olive Leaf Extract in Chemically Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Rats", American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 1 No. 1, 2011, pp. 15-22. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20110101.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifth most common cancer worldwide, and the third most common cause of cancer-related death[1]. Chemotherapy for cancer is associated with side effects that include myelosuppression and its consequent risks of infection, anemia and bleeding[2]. For patients with advanced cancer, traditional herbal medicine is frequently prescribed in Taiwan, either in conjunction with or, as an alternative, to mainstream medicine. However, the efficacy of this therapy hasn't been studied systematically[3]. Trichloroacetic acid (TCA) is a common organic contaminant of drinking water formed as a by-product during chlorine disinfection[4]. It affects liver as a primary target tissue and may induce cancer[5]. Olive tree (Olea europaea), is a species belonging to the family Oleaceae, native to the Mediterranean basin, Asia and parts of Africa[6]. The aqueous extract of olive leaf contains poly- phenols with an antioxidant potential, the major constituents of the leaf extract are oleuropein and its hydrolysis product, hydroxytyrosol. The antioxidant capacity of olive leaf contributes to many health benefits. The in vitro antioxidant action of olive has been documented and linked to such benefits as chemoprotection, anti-inflammatory action and prevention of atherosclerotic plaque formation[7]. Hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein scavenge free radicals, inhibit low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) oxidation, prevent DNA damage, mutagenesis and carcinogenesis. Hydroxytyrosol, however, has biological activity beyond its antioxidant capacity, it can affect some enzymes, including cyclooxygenase and NAD(P)H oxidase and reduce platelet aggregation[8]. It has been found to protect cells from hydrogen peroxide damage and DNA from peroxynitrite-induced damage, blocking cell cycle progression at the G1 phase, inducing apoptosis[9]. Oleuropein showed, in addition to antioxidant properties, anti-angiogenic and anti-invasiveness properties. It disrupts purified actin filaments, providing direct antitumor effects through mitotic disruption[10]. There is growing evidence that reactive oxygen species are involved in the etiology of fat-related neoplasms such as breast and colorectal cancers. Hydroxytyrosol showed potent inhibition of both cancers[11].Currently, serum AFP is useful for diagnosis and as a predictive marker for tumor invasiveness and recurrence. Patients with high AFP levels at diagnosis mostly have greater tumor size, bilobar involvement, massive or diffuse types, and portal vein thrombosis. AFP is also an important prognostic factor for recurrent HCC[12]. The specificity of AFP is very high, only when the levels are above 400ng / ml and patients are without testicular tumor[13] .Basic and clinical studies on human cancer have found high levels of de novo fatty acid synthase (FAS). It has been identified immunohistochemically in cancers of the breast[14,15,16], colon[17], prostate[18], ovary[19] , and endometrium[20]. Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) catalyses the hydrolysis of the triacylglycerol component of circulating chylomicrons and very low density lipoproteins, thereby providing non-esterified fatty acids and 2-monoacylglycerol for tissue utilization. Research carried out over the past two decades have not only established a central role for LPL in the overall lipid metabolism and transport but have also identified additional non-catalytic functions for the enzyme. Furthermore, abnormalities in LPL function have been found to be associated with a number of pathophysiological conditions, including atherosclerosis, chylomicronaemia, obesity, Alzheimer’s disease, and dyslipidaemia associated with diabetes, insulin resistance, and infection[21]. In tumor-bearing mice and rats, the earliest change was a decline in the activity of adipose tissue LPL that may be the cause of cancer-induced hypertriglyceridemia[22]..Both glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) and proteoglycans play major roles in multiple cancer-related processes. Changes in expression of these molecules, as well as of enzymes involved in their biosynthesis and degradation, contribute to the different steps of tumor progression[23]. The role of GAGs on tumor growth has been reported for few years before. GAGs, through their binding and regulation of a large number of ligands and receptors, are important mediators of normal and tumor cell behaviors, such as proliferation, differentiation, migration, and adhesion [24,25,26]. Fluoropyrimidines, particularly5-fluorouracil 5-FU, have been widely used in the treatment of HCC. 5-FU is characterized by a high hepatic extraction rate and a relatively low hepatic and systemic toxicity[27]. Chemotherapy for cancer is associated with side effects that include myelosuppression and its consequent risks of infection, anemia and bleeding, nausea and vomiting, hair loss, gastrointestinal irritation, fatigue and an accelerated menopause in women[2].In the present study, we aimed to examine the anticancer and hepatoprotective properties of aqueous olive leaf extract (AOLE), which is a cost effective herbal treatment with well known benefits, hoping to be used either alone or in combination with conventional chemotherapy in order to reduce its side effects.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Chemicals and Drugs
- Aqueous extract was prepared by boiling olive leaves (300g ) in water (3000 ml ) for 60 minutes then filtered through Whatman filter paper No.2 and the filtrate was dried, the yield of dried extract was about 30gm when dissolved in 300ml water (final concentration was 0.1gm\ml). Rats were given (AOLE) orally by gavage as (0.5gm\kg bw), given daily for continuous 28 days[28]. 5-FU was purchased from Roche Int. Co as ampoules (250mg\5ml) and rats were given 5-FU by intraperitoneal injection (IP) of as75mg/kg once per week for 3 successive weeks[2,29,30]. This is a standard dose that is well-tolerated showing minimal weight loss, as higher doses caused weight loss or death of animals.Trichloroacetic acid (TCA) was purchased from (El-Gomhorya Co, ARE). Rats were given TCA by gavage as 500mg/kg once a day for 5 days[31]. TCA was chosen because it has been reported to increase liver growth, cell proliferation, and lipid peroxidation in mice[32-35]. All other chemicals used are of analytical grade obtained from Sigma (USA).2.1.2. Animals Adult male Wistar rats weighing 150-200gm, supplied from animal house of National Research Center (Dokki, Giza, Egypt) were used for experimental investigation in this study. They were kept for 2 weeks to accommodate with laboratory conditions, under constant environmental and nutritional conditions with free access to food and water2.1.3. Experimental DesignThe rats were classified into eight groups (8 per each ), group I, untreated normal control group, group II, treated with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) once weekly for 3 successive weeks, group III, treated with AOLE once daily for 28 continuous days, group IV, treated with AOLE and 5-FU for same periods as mentioned above for each drug, group V, received daily doses of TCA for five days, group VI, received daily doses of TCA for 5 days then the next day treated with 5-FU for 3 weeks , group VII, received daily doses of TCA for 5 days then the next day treated with olive leaf extract and group VIII, received daily doses of TCA) for 5 days then the next day treated with 5-FU and AOLE as before.Animals were sacrificed after 28 days, the blood was withdrawn from the carotid vein, collected into EDTA containing and non-EDTA tubes. Plasma and sera were stored in aliquots and frozen at –80ºC. Sections from lobes of the livers were preserved in 10% formalin solution for histological study.
2.2. Methods
- Serum ALT, AST[36] , and ALP[37,38] activities were investigated as biochemical markers for the early hepatic damage using commercial Kits (Biodiagnostic, ARE), total bilirubin was determined[39,40], using Randox Diagnostic kits (USA). Serum total glycosaminoglycans (TGAGs) determination depends on the formation of soluble complex with Alcian blue 8GX dye according to[41]. Serum triglycerides(TG) was determined according to the method of[42,43] using Diamond kits (ARE). Total LPL (TLPL) activity was determined according to the method of[44,45] using Biostc kits (Italy). Serum alpha-fetoproein (AFP) was determined according to the method of[46,47,48] using ELISA Biocheck kits (USA) following the instructions of the manufacturer. Serum Acetyl CoA synthase (fatty acid synthase, FAS) activity was determined as a possible new marker for hepatic cancer. The assay is based on the established pyrophosphate (PPi) detection system. FAS activity is indexed by the amount of PPi released from reaction- utilized ATP after its conversion into ADP, with ACAS catalysis[49].
2.3. Statistical Analysis
- All statistical analysis, including the calculations of mean ± SE., the Student's t-test, and the simple linear regression analysis, were carried out using SPSS and Graph Pad Prism programs. Significance was set at P >0.05 level.
3. Results
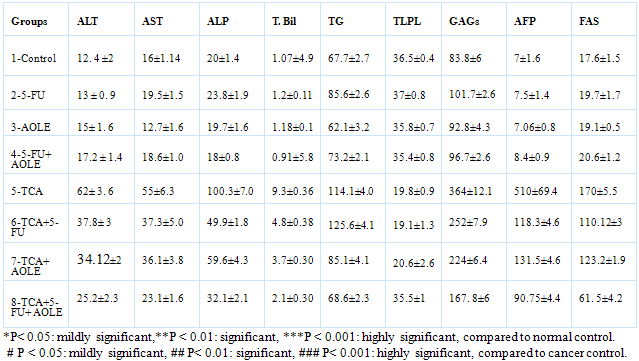
3.1. Effect of AOLE on liver functions and serum triglycerides (TG)
- TCA administration showed an increase in the activity of serum ALT, AST and ALP, in addition to total bilirubin (T Bil) and TG at (P<0.001). After treatment with AOLE, a significant reduction in these parameters was observed. 5-FU treatment of TCA-intoxicated rats reduced these elevated values. The most significant reduction was observed in-group VIII, which was treated with AOLE plus 5-FU (Table 1).
3.2. Effect on Serum Total Lipoprotein Lipase (TLPL) Activity
- TCA administration produced a significant decrease in serum TLPL activity at (P<0.001) compared to control. Administration of 5-FU or AOLE individually has non significant effect on serum TLPL activity but the combination of both produced a significant increase at (P<0.001) compared to TCA treated group (Table 1).
3.3. Effect on Serum Total Glycosaminoglycans (TGAGs) Concentration
- Serum total GAGs level in TCA-intoxicated rats showed a significant increase than normal control (P<0.001), after treatment of TCA-intoxicated rats with AOLE, a significant reduction was observed (P<0.001) and the best reduction was observed in AOLE plus 5-FU rats (Table 1).
3.4. Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) Concentration
- Serum AFP level of TCA-intoxicated rats was significantly increased, compared to normal (P<0.001). After treatment with 5-FU, a significant reduction in serum AFP was observed at (P<0.001). AOLE a significantly reduced serum AFP (P<0.001), the reduction by the combination of 5-FU and AOLE was more pronounced (Table 1).
3.5. Serum FAS Activity
- Serum FAS activity of TCA-intoxicated rats showed a significant increase compared to control (P<0.001), 5-FU and AOLE significantly reduced this activity, their combination showed a more significant reduction (P<0.001), (Table 1).
4. Histopathological Results
- Liver tissue after TCA administration showed loss of normal architecture with oval- or irregular-shaped hepatocytes. Many transformed liver cells of foci were substantially enlarged, largely vesiculated and frequently binucleated, which were clearly distinguishable from the surrounding normal parenchyma. The nuclei were mostly found to be pleomorphic and hyperchromatic. These changes were reduced by the treatment of 5-FU, AOLE and more by their combination as shown in Figures 1-8.
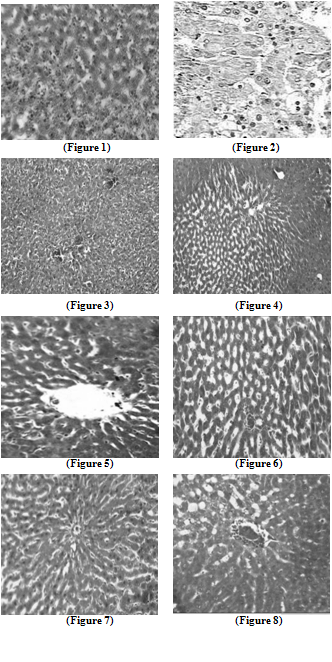 | Figure 1. Liver section in control animals showing normal parenchymal cells with granulated cytoplasm and normal architecture |
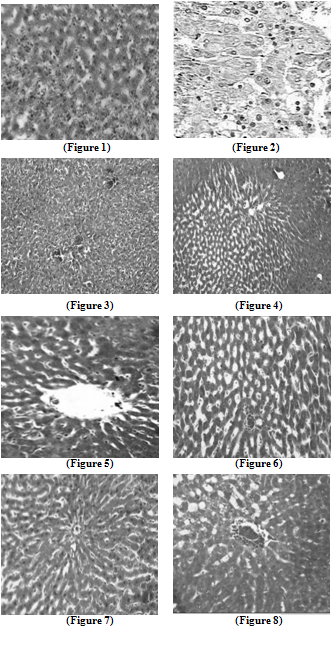 | Figure 2. TCA-treated rats showing loss of normal architecture with oval- or irregular-shaped hepatocytes, denser nuclear chromatin, the ratio of nucleus to cytoplasm was increased, many transformed liver cells were frequently binucleated and hyperchromatic (basophilic) |
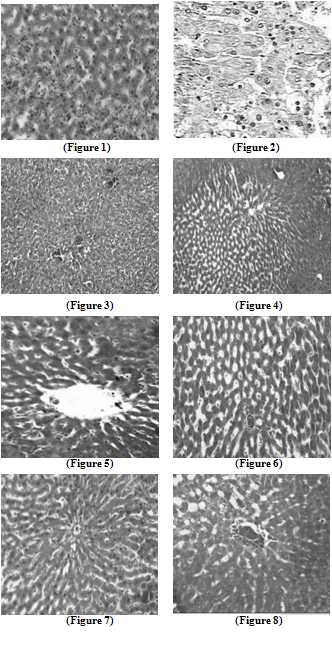 | Figure 3. The liver of 5-FU-treated rats showing normal central vein and architecture, some liver cells around central vein showed ballooning that may be due to cyotoxic effect of 5-FU |
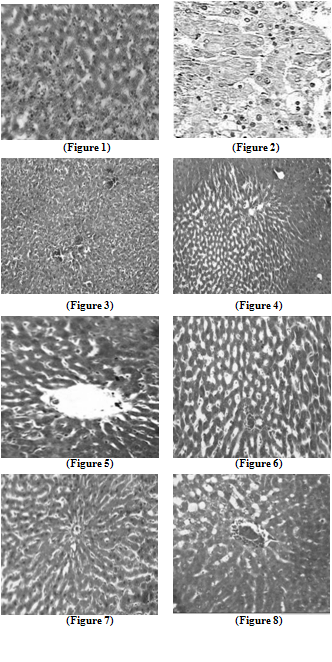 | Figure 4. Liver section in TCA and 5-FU treated rats showing reversed changes as central vein congestion and ballooning but generally is less than TCA-treated group indicating some improvement |
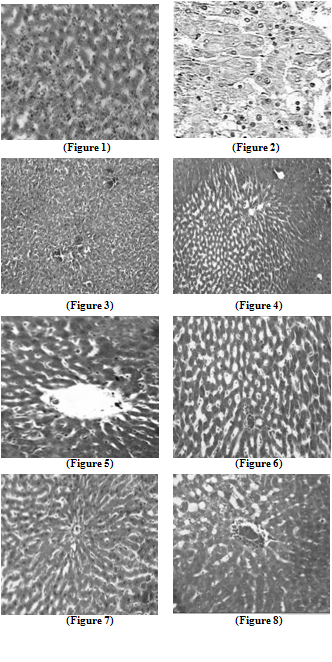 | Figure 5. Liver section in AOLE-treated rats shows a normal central vein and blood sinusoids |
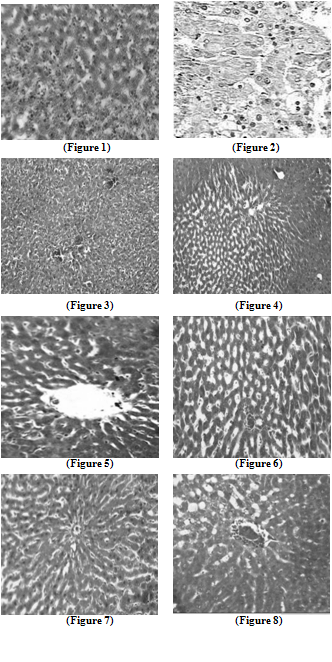 | Figure 6. Liver section in TCA and AOLE treated rats showing a moderate improvement in hepatocellular structure, evidenced as a moderate improvement in vacuolation and compactness of hepatocytes compared to TCA treated group but dilated sinusoids are still present |
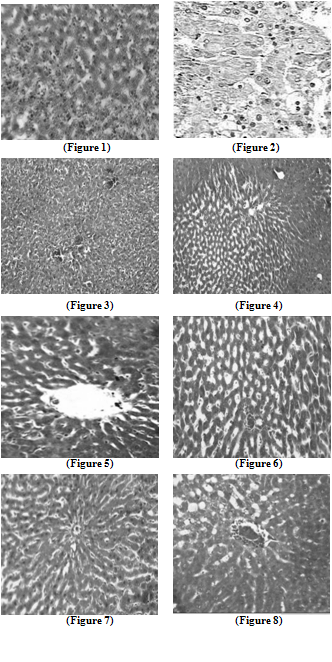 | Figure7. Liver section in 5-FU and AOLE-treated rats shows a normal pattern of healthy hepatocytes |
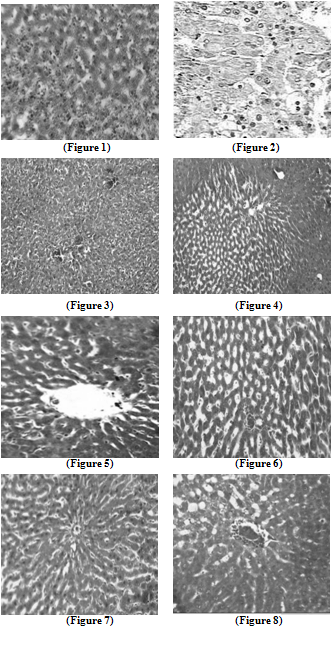 | Figure 8. Liver section in TCA, 5-FU and AOLE-treated rats showed almost normal hepatocytes with small degree of central vein congestion as the cellular architecture of liver sections in this group seemed to be almost comparable to that of their normal counterparts. |
5. Discussion
- HCC is a worldwide problem including Egypt. TCA is a powerful carcinogen produced during chlorination of drinking water as a byproduct. We aimed in this study to examine the anticancer and hepatoprotective properties of AOLE, which is a cheap and available herbal treatment with many well known benefits hoping to be used either alone or in combination with chemotherapy in order to reduce its side effects. AOLE contains polyphenolic compounds, oleuropein and its hydrolysis product hydroxytyrosol, both are potent antioxidants[7]. In the present study, liver function tests performed for TCA-intoxicated rats showed an increase in the activity of serum ALT and AST compared to their corresponding control values, The elevation of both enzymes is presumed to be due to leakage from damaged or necrotic cells[50]. After treatment with 5-FU, a significant reduction in liver enzyme activities was observed. These results were in accordance with that of[51] who showed that transaminase activities were reduced after 5-FU treatment. After treatment with AOLE, a significant reduction in both ALT, AST was observed and a highly significant reduction was after treatment with combination of 5-FU and AOLE. This decline in liver enzyme activities showed some proof about liver recovery and hepatoprotective effect of AOLE. Regarding serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity, our results showed a significant increase in its level in TCA-intoxicated rats compared to the control group. Such elevated level may be due to a mechanical obstruction of bile ducts as failure to excrete the enzyme through the relatively narrower bile passages results in its accumulation and increase in the blood that as in accordance with[52]. After treatment with AOLE, a significant reduction in ALP activity was observed and a highly significant reduction was seen after treatment with the combination. These observations may be explained by an assumption that the treatment decreased the mechanical obstruction in bile duct. T Bil level of TCA-intoxicated rats showed a significant increase than that of normal control group. Such elevated level may be due to hepatocellular or obstructive jaundice in hepatocellular carcinoma[53]. After treatment with AOLE a significant reduction in T Bil level was observed (P<0.001), These result were in agreement with the findings of[51] and[54] in which low bilirubin level was related to longer survival of HCC patients after systemic therapy. Our results also confirm the therapeutic and hepatoprotective effecacy of AOLE. In the present work, a significant increase of serum TG in TCA-intoxicated rats was observed, in agreement with the previous findings of[55] and[56]. Administration of 5-FU to normal rats led to a significant increase in TG that may be due to the peroxidation of unsaturated membrane lipids by free radicals produced as a side effect following administration of cytotoxic drugs[57]. After treatment of TCA- treated rats with AOLE, a significant reduction in TG level was observed while treatment with 5-FU showed non-significant result. Treatment with combination led to significant reduction. The mechanism of the TG lowering effect of AOLE may be attributed to many factors such as reducing the oxidative stress (one of the factors causing lipid peroxidation and hyperlipidemia) by the antioxidant activity of its polyphenols and it could be supported by the ability of AOLE to neutralize the harmful effect of 5-FU, this is in accordance with[58] and[59]. Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) catalyses the hydrolysis of the triacylglycerol component of circulating chylomicrons and very low density lipoproteins, thereby providing non-esterified fatty acids and 2-monoacylglycerol for tissue utilization. In the present study, serum LPL activity of TCA-intoxicated rats showed a significant decrease compared to that of normal control, as result in agreement with that of[22]. Treatment of TCA-intoxicated rats with 5-FU and AOLE each alone had no significant effect on LPL activity, while the combination of both showed significant elevation in LPL activity. Glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans are involved in the pathobiology of all stages of cancer progression [60]. In the present study, serum TGAGs level of TCA-intoxicated rats showed a significant increase compared to that of normal group. Such elevated level may be due to the induced premalignant changes confirmed by the histopathological results as GAGs are usually elevated in most types of cancer including human laryngeal carcinoma[61]. The elevated TGAGs level may be referred to an increased breakdown of liver tissue content, followed by escape into circulation[24]. After treatment with AOLE a significant reduction in serum TGAGs level was observed which was more significant by the combination of 5-FU and AOLE. Alpha-fetoprotein is a well-known tumor marker for HCC and its serum value is useful not only for diagnosis, but also as a predictive marker for tumor invasiveness and recurrence of HCC[62]. In the present study, serum AFP level of TCA-intoxicated rats showed a significant increase compared to that of control group, proving the occurrence of premalignant liver changes in intoxicated rats. The elevation of serum AFP in HCC was well documented[53,63]. Treatment with AOLE significantly reduced serum AFP and the best results were obtained by combination of AOLE and 5-FU that may indicate the curative effect of AOLE attributed to its polyphenol and flavonoid content having anticancer properties. These result were similar to that of[64] in which flavonoids of Semecarpus anacardium nut milk extract reduced serum AFP level in aflatoxin-B1 induced HCC in rats into normal range. There is a strong association between increased FAS activities and some other prognostic indicators in primary breast, prostate, colorectal and ovarian cancers[16]. In the present study, serum FAS activity of TCA-intoxicated rats showed a significant increase compared to that of normal control group. This elevation can be explained on a basis that there is a link between cellular proliferation and fatty acid synthesis, as fatty acid synthesis has been observed to be activated when cells enter into proliferative phase in several systems[65]. This result is in agreement with findings of[16] in which FAS activity was increased in breast and colorectal cancer. Treatment with AOLE significantly reduced FAS activity, best results were achieved by combination that may indicate some anticancer properties of AOLE along with the anticancer drug 5-FU that can be referred to decreased FAS expression due to inhibitory effect of cellular proliferation by AOLE. Histological findings clearly showed that the normal architecture of hepatic tissue was damaged due to TCA treatment. The clear and acidophilic cells represent small preneoplastic focal lesions, leading to malignant transformation in late stages of carcinogenesis with the formation of neoplastic nodules and ultimately HCC[66]. On the other hand, exposure to AOLE and 5-FU treatment reduced hepatocyte aggregation and basophilicity with a reversal of heterogeneity towards normal cellular architecture.
6. Conclusions
- The present study produced convincing evidence that AOLE has a protective effect against chemically induced HCC, through these passages:a. It has a remarkable anticancer, hepatoprotective properties and can increase the sensitivity to 5-FU and decrease its side effects, so we recommend it as a combination with chemotherapy to minimize its side effects and possibly reduce its doses or even duration and it can be used as a prevention and hepatoprotective in risk HCC people.b. Serum TGAGs, FAS and LPL activities can be considered as new promising markers for early diagnosis of HCC, in addition to AFP, we recommend the detection of these three parameters in addition to AFP in patients having risk factors for HCC. Mostly, the results will assume more decisive and sensitive tools for HCC early assessment and follow-up. c. TCA is a powerful carcinogen and so chlorination of drinking water is a critical process as chlorination byproducts as TCA are so harmful to human and strict measures have to be taken to control this process and find more safe water disinfection process.d. TCA induction of liver cancer may be through disturbing lipogenesis rate favoring TG accumulation by activating FAS and depressing LPL , an action greatly modulated by AOLE with or without 5-FU.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The histological part of the study was executed and interpreted by Prof Manal Ismail Abdel-Ghany, PhD, Pathology Department, College of Medicine, Minia University, Egypt.
References
| [1] | W. Y. Lau, Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J R Coll Surg Edinb 47 (2002) 389-99 |
| [2] | T. A. Ahles, A. J. Saykin, C. T. Furstenberg, B. Cole, L. A. Mott, K. Skalla, M. B. Whedon, S. Bivens, T. Mitchell, E. R. Greenberg, and P. M. Silberfarb, Neuropsychologic impact of standard-dose systemic chemotherapy in long-term survivors of breast cancer and lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 20 (2002) 485-93 |
| [3] | H. M. Cheng, and M. C. Tsai, Regression of hepatocellular carcinoma spontaneous or herbal medicine related? Am J Chin Med 32 (2004) 579-85 |
| [4] | Raymond M. Hozalski, William A. Arnold, , Chanlan Chun, Timothy M. LaPara, Jeong-Yub Lee, Carrie R. Pearson, and , Ping Zhang, Degradation of Halogenated Disinfection Byproducts in Water Distribution Systems., ACS Symposium Series, USA, 2008 |
| [5] | H. J. Clewell, and M. E. Andersen, Applying mode-of-action and pharmacokinetic considerations in contemporary cancer risk assessments: an example with trichloroethylene. Crit Rev Toxicol 34 (2004) 385-445 |
| [6] | R. Lumaret, and N. Ouazzani, Plant genetics. Ancient wild olives in Mediterranean forests. Nature 413 (2001) 700 |
| [7] | E. Waterman, and B. Lockwood, Active components and clinical applications of olive oil. Altern Med Rev 12 (2007) 331-42 |
| [8] | F. Visioli, A. Poli, and C. Gall, Antioxidant and other biological activities of phenols from olives and olive oil. Med Res Rev 22 (2002) 65-75 |
| [9] | R. Fabiani, A. De Bartolomeo, P. Rosignoli, M. Servili, G. F. Montedoro, and G. Morozzi, Cancer chemoprevention by hydroxytyrosol isolated from virgin olive oil through G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Eur J Cancer Prev 11 (2002) 351-8 |
| [10] | H. K. Hamdi, and R. Castellon, Oleuropein, a non-toxic olive iridoid, is an anti-tumor agent and cytoskeleton disruptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 334 (2005) 769-78 |
| [11] | R. W. Owen, A. Giacosa, W. E. Hull, R. Haubner, B. Spiegelhalder, and H. Bartsch, The antioxidant/anticancer potential of phenolic compounds isolated from olive oil. Eur J Cancer 36 (2000) 1235-47 |
| [12] | M. Kaibori, Y. Matsui, H. Yanagida, N. Yokoigawa, A. H. Kwon, and Y. Kamiyama, Positive status of alpha-fetoprotein and des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin: important prognostic factor for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Surg 28 (2004) 702-7 |
| [13] | A. S. Befeler, and A. M. Di Bisceglie, Hepatocellular carcinoma: diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology 122 (2002) 1609-19 |
| [14] | P. L. Alo, P. Visca, A. Marci, A. Mangoni, C. Botti, and U. Di Tondo, Expression of fatty acid synthase (FAS) as a predictor of recurrence in stage I breast carcinoma patients. Cancer 77 (1996) 474-82 |
| [15] | P. L. Alo, P. Visca, G. Trombetta, A. Mangoni, L. Lenti, S. Monaco, C. Botti, D. E. Serpieri, and U. Di Tondo, Fatty acid synthase (FAS) predictive strength in poorly differentiated early breast carcinomas. Tumori 85 (1999) 35-40 |
| [16] | Y. Wang, F. P. Kuhajda, J. N. Li, E.S. Pizer, W. F. Han, L. J. Sokoll, and D. W. Chan, Fatty acid synthase (FAS) expression in human breast cancer cell culture supernatants and in breast cancer patients. Cancer Lett 167 (2001) 99-104 |
| [17] | A. Rashid, E. S. Pizer, M. Moga, L. Z. Milgraum, M. Zahurak, G. R. Pasternack, F. P. Kuhajda, and S. R. Hamilton, Elevated expression of fatty acid synthase and fatty acid synthetic activity in colorectal neoplasia. Am J Pathol 150 (1997) 201-8 |
| [18] | M. S. Shurbaji, J. H. Kalbfleisch, and T. S. Thurmond, Immunohistochemical detection of a fatty acid synthase (OA-519) as a predictor of progression of prostate cancer. Hum Pathol 27 (1996) 917-21 |
| [19] | T. S. Gansler, W. Hardman, 3rd, D. A. Hunt, S. Schaffel, and R.A. Hennigar, Increased expression of fatty acid synthase (OA-519) in ovarian neoplasms predicts shorter survival. Hum Pathol 28 (1997) 686-92 |
| [20] | E. S. Pizer, S. F. Lax, F. P. Kuhajda, G. R. Pasternack, and R. J. Kurman, Fatty acid synthase expression in endometrial carcinoma: correlation with cell proliferation and hormone receptors. Cancer 83 (1998) 528-37 |
| [21] | J. R. Mead, S. A. Irvine, and D. P. Ramji, Lipoprotein lipase: structure, function, regulation, and role in disease. J Mol Med 80 (2002) 753-69 |
| [22] | R. W. Clark, and R. C. Crain, Characterization of Alterations in Plasma Lipoprotein Lipid and Apoprotein Profiles Accompanying Hepatoma-Induced Hyperlipidemia in Rats. Cancer Res 46 (1986) 1894-1903 |
| [23] | R. D. Sanderson, Y. Yang, L. J. Suva, and T. Kelly, Heparan sulfate proteoglycans and heparanase--partners in osteolytic tumor growth and metastasis. Matrix Biol 23 (2004) 341-52 |
| [24] | N. M. Abdel-Hamid, Recent insights on risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 1 (2009) 3-7 |
| [25] | N. M. Abdel-Hamid, and M. A. Morsy, Novel biochemical pathways for 5-Fluorouracil in managing experimental hepatocellular carcinoma in rats. J Membr Biol 234 (2010) 29-34 |
| [26] | E. J. Joo, G. B. ten Dam, T. H. van Kuppevelt, T. Toida, R. J. Linhardt, and Y. S. Kim, Nucleolin: acharan sulfate-binding protein on the surface of cancer cells. Glycobiology 15 (2005) 1-9 |
| [27] | G. Milano, and A. L. Chamorey, Clinical pharmacokinetics of 5-fluorouracil with consideration of chronopharm- acokinetics. Chronobiol Int 19 (2002) 177-89 |
| [28] | M. Y. Hung, T. Y. Fu, P. H. Shih, C. P. Lee, and G. C. Yen, Du-Zhong (Eucommia ulmoides Oliv.) leaves inhibits CCl4-induced hepatic damage in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 44 (2006) 1424-31 |
| [29] | C. M. Bender, S. M. Sereika, S. L. Berga, V. G. Vogel, A. M. Brufsky, K. K. Paraska, and C. M. Ryan, Cognitive impairment associated with adjuvant therapy in breast cancer. Psychooncology 15 (2006) 422-30 |
| [30] | G. Winocur, J. Vardy, M. A. Binns, L. Kerr, and I. Tannock, The effects of the anti-cancer drugs, methotrexate and 5-fluorouracil, on cognitive function in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 85 (2006) 66-75 |
| [31] | L. Tao, S. Yang, M. Xie, P. M. Kramer, and M. A. Pereira, Effect of trichloroethylene and its metabolites, dichloroacetic acid and trichloroacetic acid, on the methylation and expression of c-Jun and c-Myc protooncogenes in mouse liver: prevention by methionine. Toxicol Sci 54 (2000) 399-407 |
| [32] | S. R. Channel, J. R. Latendresse, J. K. Kidney, J. H. Grabau, J. W. Lane, L. Steel-Goodwin, and M.C. Gothaus, A subchronic exposure to trichloroethylene causes lipid peroxidation and hepatocellular proliferation in male B6C3F1 mouse liver. Toxicol Sci 43 (1998) 145-54 |
| [33] | C. Dees, and C. Travis, Trichloroacetate stimulation of liver DNA synthesis in male and female mice. Toxicol Lett 70 (1994) 343-55 |
| [34] | J. L. Larson, and R. J. Bull, Metabolism and lipoperoxidative activity of trichloroacetate and dichloroacetate in rats and mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 115 (1992) 268-77 |
| [35] | J. A. Styles, I. Wyatt, and C. Coutts, Trichloroacetic acid: studies on uptake and effects on hepatic DNA and liver growth in mouse. Carcinogenesis 12 (1991) 1715-9 |
| [36] | S. Rietman, and S. Frankle, A Colorimetric Method for Determination of Serum Glutamic Oxaloacetic and Glutamic Pyruvic Transaminases. Am. J. Clin. Path 28 (1957) |
| [37] | N. Gond, and S. Khadabadi, Hepatoprotective activity of Ficus carica leaf extract on rifampicin-induced hepatic damage in rats. Indian J Pharm Sci 70 (2008) 364-6 |
| [38] | A. Belfield, and D.M. Goldberg, Revised assay for serum phenyl phosphatase activity using 4-amino-antipyrine. Enzyme 12 (1971) 561-73 |
| [39] | L. Jendrassik, and P. Grof, Biochem. J 297 (1938) 81 |
| [40] | P. J. Bosma, J. R. Chowdhury, C. Bakker, S. Gantla, A. de Boer, B. A. Oostra, D. Lindhout, G. N. Tytgat, P. L. Jansen, R. P. Oude Elferink, and et al., The genetic basis of the reduced expression of bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyl- transferase 1 in Gilbert's syndrome. N Engl J Med 333 (1995) 1171-5 |
| [41] | E. W. Gold, A simple spectrophotometric method for estimating glycosaminoglycan concentrations. Anal Biochem 99 (1979) 183-8. |
| [42] | N. J. Jacobs, and P. J. Vandemark, The purification and properties of the alpha-glycerophosphate-oxidizing enzyme of Streptococcus faecalis 10C1. Arch Biochem Biophys 88 (1960) 250-5. |
| [43] | P. Trinder, Enzymatic Calorimetric Test Clin. Biochem. J 6 (1969) 24-27. |
| [44] | N. W. Tietz, Textbook of Clinical Chemistry. W. B. Saunders CO Philadelphia (1999) |
| [45] | D. S. Young, Effect of Drugs on Clinical Lab Test. 5th Ed. AACC press (2000) |
| [46] | G. I. Abelev, Alpha-fetoprotein as a marker of embryo-specific differentiations in normal and tumor tissues. Transplant Rev 20 (1974) 3-37 |
| [47] | D. W. Chan, and Y. C. Miao, Affinity chromatographic separation of alpha-fetoprotein variants: development of a mini-column procedure, and application to cancer patients. Clin Chem 32 (1986) 2143-6 |
| [48] | M. Uotila, E. Ruoslahti, and E. Engvall, Two-site sandwich enzyme immunoassay with monoclonal antibodies to human alpha-fetoprotein. J Immunol Methods 42 (1981) 11-5 |
| [49] | Y. Kuang, N. Salem, F. Wang, S. J. Schomisch, V. Chandramouli, and Z. Lee, A colorimetric assay method to measure acetyl-CoA synthetase activity: application to woodchuck model of hepatitis virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Biochem Biophys Methods 70 (2007) 649-55 |
| [50] | M. C. Kew, Serum aminotransferase concentration as evidence of hepatocellular damage. Lancet 355 (2000) 591-2 |
| [51] | T. W. Leung, A. M. Tang, B. Zee, S. C. Yu, P. B. Lai, W. Y. Lau, and P. J. Johnson, Factors predicting response and survival in 149 patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated by combination cisplatin, interferon-alpha, doxorubicin and 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy. Cancer 94 (2002) 421-7 |
| [52] | D. V. Gopal, and H. R. Rosen, Abnormal findings on liver function tests. Interpreting results to narrow the diagnosis and establish a prognosis. Postgrad Med 107 (2000) 100-2, 105-9, 113-4 |
| [53] | W. Yeo, F. K. Mo, J. Koh, A. T. Chan, T. Leung, P. Hui, L. Chan, A. Tang, J. J. Lee, T. S. Mok, P. B. Lai, P. J. Johnson, and B. Zee, Quality of life is predictive of survival in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Oncol 17 (2006) 1083-9 |
| [54] | W. Yeo, T. S. Mok, B. Zee, T. W. Leung, P. B. Lai, W. Y. Lau, J. Koh, F. K. Mo, S. C. Yu, A. T. Chan, P. Hui, B. Ma, K. C. Lam, W. M. Ho, H. T. Wong, A. Tang, and P. J. Johnson, A randomized phase III study of doxorubicin versus cisplatin/interferon alpha-2b/doxorubicin/fluorouracil (PIAF) combination chemotherapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 97 (2005) 1532-8 |
| [55] | G. Zhang, Y. Miura, and K. Yagasaki, Effects of dietary powdered green tea and theanine on tumor growth and endogenous hyperlipidemia in hepatoma-bearing rats. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66 (2002) 711-6 |
| [56] | G. Muralikrishnan, V. Amalan Stanley, and K. Sadasivan Pillai, Dual role of vitamin C on lipid profile and combined application of cyclophosphamide, methotrexate and 5-fluorouracil treatment in fibrosarcoma-bearing rats. Cancer Lett 169 (2001) 115-20 |
| [57] | S. Subramaniam, S. Subramaniam, and C. S. Shyamala Devi, Erythrocyte antioxidant enzyme activity in CMF treated breast cancer patients. Cancer Biochem Biophys 14 (1994) 177-82 |
| [58] | S. Acin, M. A. Navarro, J. S. Perona, J. M. Arbones-Mainar, J. C. Surra, M. A. Guzman, R. Carnicer, C. Arnal, I. Orman, J. C. Segovia, J. Osada, and V. Ruiz-Gutierrez, Olive oil preparation determines the atherosclerotic protection in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. J Nutr Biochem 18 (2007) 418-24 |
| [59] | M. Kawasaki, R. Funabiki, and K. Yagasaki, Effects of dietary methionine and cystine on lipid metabolism in hepatoma-bearing rats with hyperlipidemia. Lipids 33 (1998) 905-11 |
| [60] | G. W. Yip, M. Smollich, and M. Gotte, Therapeutic value of glycosaminoglycans in cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 5 (2006) 2139-48 |
| [61] | S. S. Skandalis, M. Stylianou, D. H. Vynios, N. Papageorgakopoulou, and D. A. Theocharis, The structural and compositional changes of glycosaminoglycans are closely associated with tissue type in human laryngeal cancer. Biochimie 89 (2007) 1573-80 |
| [62] | L. X. Qin, and Z. Y. Tang, Metastasis and Recurrence after Surgical Resection of Hepatocellular Recent Progress in Clinical and Related Basic Aspects Carcinoma. Current Cancer Therapy Reviews 1 (2005) 71-80 |
| [63] | L. P. Borges, V. C. Borges, A. V. Moro, C. W. Nogueira, J. B. Rocha, and G. Zeni, Protective effect of diphenyl diselenide on acute liver damage induced by 2-nitropropane in rats. Toxicology 210 (2005) 1-8 |
| [64] | B. Premalatha, and P. Sachdanandam, Effect of Semecarpus Anacardium Nut Milk Extract on Rat Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein Level in Aflatoxin B -Mediated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Fitoterapia 70 (1999) 279-283 |
| [65] | N. Yahagi, H. Shimano, K. Hasegawa, K. Ohashi, T. Matsuzaka, Y. Najima, M. Sekiya, S. Tomita, H. Okazaki, Y. Tamura, Y. Iizuka, K. Ohashi, R. Nagai, S. Ishibashi, T. Kadowaki, M. Makuuchi, S. Ohnishi, J. Osuga, and N. Yamada, Co-ordinate activation of lipogenic enzymes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Cancer 41 (2005) 1316-22 |
| [66] | C. Peraino, E. F. Staffeldt, and V. A. Ludeman, Early appearance of histochemically altered hepatocyte foci and liver tumors in female rats treated with carcinogens one day after birth. Carcinogenesis 2 (1981) 463-5 |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML