-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Intelligent Systems
p-ISSN: 2165-8978 e-ISSN: 2165-8994
2025; 14(1): 18-31
doi:10.5923/j.ajis.20251401.03
Received: Jul. 2, 2025; Accepted: Jul. 21, 2025; Published: Jul. 23, 2025

Holistic Digital Transformation in Education: Integrating Innovation, Collaborative Resource Ecosystems, and Intelligent Learning Platforms
Itayi Artwell Mareya1, Liberty Artwell Mareya2
1Department of Foreign Languages, Hanjiang Normal University, Shiyan, China
2Department of Science and Technology Changchun University of Sc &Tech, Changchun, China
Correspondence to: Itayi Artwell Mareya, Department of Foreign Languages, Hanjiang Normal University, Shiyan, China.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Digital transformation is essential for improving education by integrating advanced technologies, innovative strategies, and smart platforms, making learning more accessible and impactful. Current educational methods, however, grapple with limited resources, rigid environments, and collaboration hurdles due to traditional geographical and infrastructural constraints. To overcome these, the Virtual Reality empowered Dynamic Remote Learning (VR-DRL) framework is introduced, blending remote learning with flexible virtual classrooms. This framework incorporates interactive elements, real-time collaboration, and robust resource sharing, fostering a more inclusive and dynamic learning environment. VR-DRL specifically enhances resource sharing, student engagement, and personalized learning through integrated digital platforms, enabling remote educator-student connections with active participation. Ultimately, the proposed VR-DRL method significantly improves student performance, engagement, and accessibility, leading to higher satisfaction and effectively modernizing educational practices.
Keywords: EdTech transformation, Virtual learning spaces, Distance education, Shared learning resources, Learning innovation, AI-powered platforms
Cite this paper: Itayi Artwell Mareya, Liberty Artwell Mareya, Holistic Digital Transformation in Education: Integrating Innovation, Collaborative Resource Ecosystems, and Intelligent Learning Platforms, American Journal of Intelligent Systems, Vol. 14 No. 1, 2025, pp. 18-31. doi: 10.5923/j.ajis.20251401.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The advent of digital transformation is profoundly reshaping the educational landscape, influencing the very approaches to pedagogical revolution [1]. This shift has led to the evolution of integrated learning methodologies through the establishment of cross-arranged collaborative networks [2], fundamentally altering the character of traditional learning environments [3]. A significant outcome of these advancements is the emergence of new opportunities for personalized learning. These opportunities are characterized by an effective focus on collaborative foundations and streamlined access to essential information resources [4]. To fully capitalize on these possibilities, there is a pressing need to design comprehensive models capable of addressing the current challenges hindering progress within the educational innovation ecosystem [5].Digital transformation empowers educational institutions to enhance their capabilities [6] by facilitating the advancement of hybrid and remote teaching methods, enabling the application of data analytics, and fostering borderless collaboration [7]. In essence, virtual classrooms and smart platforms are creating a seamless learning experience that effectively merges face-to-face and distance learning through scalable solutions [8]. This integration ultimately provides valuable benefits for both students and teachers [9]. Despite these significant developments, traditional educational sectors continue to grapple with considerable challenges [10]. A substantial number of learners face difficulties in accessing quality education due to a combination of socioeconomic factors, geographical limitations, and infrastructure constraints [11]. Furthermore, rigid classroom settings often restrict opportunities for individualized training or pragmatic collaborative engagement [12]. Businesses, too, encounter difficulties in leveraging these technologies to support resource sharing and facilitate engaging, interactive activities [13,14]. To address these multifaceted needs, a proposed architecture, VR–DRL, offers a solution by merging real-time interactions with virtual classrooms and digital resource sharing [15]. This framework empowers professors and students to engage with alternative 3D-enabled learning environments [16], which include interactive sessions, personalized content delivery, and effective communication [17].” IT driven changes enables business network-based value creation to become feasible and valuable business model” [18].
2. Research Problem
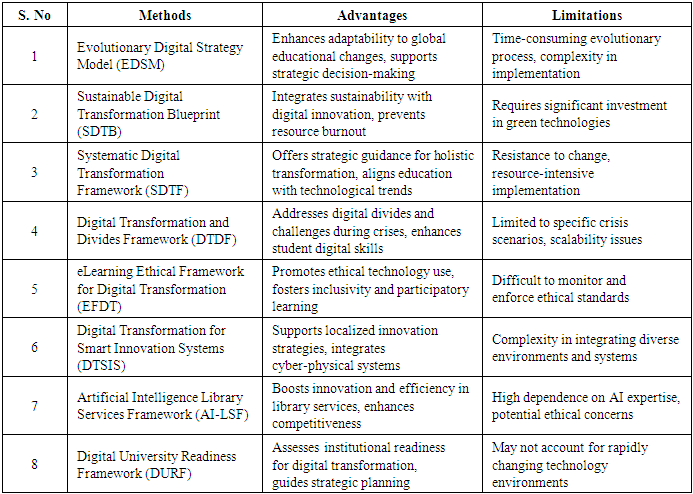
- Conventional educational practices are not without their significant limitations, presenting a range of challenges that impede effective learning and instruction. These constraints are multifaceted, encompassing issues such as the scarcity of high-quality learning materials, which can directly impact the depth and breadth of student understanding. Furthermore, traditional learning environments can sometimes be characterized by rigid and even hostile settings, potentially stifling creativity, engagement, and individual student needs. Perhaps most critically, education faces complicated logistical problems that arise from physical or geographical boundaries, limiting access for many learners and creating disparities in educational opportunities. Addressing these inherent issues necessitates the development of a scalable and dynamic architectural approach. Such an approach is crucial not only for overcoming existing barriers but also for potentially modifying instructional methods in ways that can significantly enhance overall student performance and learning outcomes.Related workDigital transformation models are crucial for universities seeking to enhance flexibility and competitiveness. These models integrate institutional strategies with global trends, current technologies, and societal demands, offering tools for informed decision-making. They help educational institutions embrace digital transformation, improve student experiences, and foster ethical and environmentally responsible conduct. Solutions range from leveraging artificial intelligence for library needs to managing long-term digital innovation. Ultimately, these frameworks enable universities to adapt to the digital age, ensuring they remain relevant and effective.Evolutionary Digital Strategy Model (EDSM)This approach proposes a qualitative model where digital transformation is the primary catalyst for universities to gain a competitive advantage. It integrates principles of strategic management with evolutionary learning systems to navigate significant shifts in the higher education sector. The model serves as a decision support system, helping universities adapt to the rapidly changing global educational landscape shaped by digital transformation and other global events. Its aim is to empower institutions to enhance and manage student experiences, expectations, and strategic initiatives effectively.Sustainable Digital Transformation Blueprint (SDTB)This research employs a unique qualitative grounded theory approach to investigate the impact of sustainable digital transformation on universities. It utilizes open, axial, and selective coding techniques to thoroughly analyze and demonstrate the connection between sustainable digital transformation and higher education. The ultimate aim is to create a conceptual model that assists the education sector in seamlessly blending sustainability, green technology, and actionable strategies. This approach provides universities with a clear roadmap for planning, expanding, and implementing digital transformation effectively, all while preventing resource burnout.Systematic Digital Transformation Framework (SDTF)The proposed approach examines digital transformation through a thematic analysis of frameworks that define and guide effective transformation within learning organizations, emphasizing the need for a methodical, strategic approach [20]. It advocates for a transformative mindset that extends beyond isolated initiatives, urging education leaders and policymakers to leverage technology as an enabler for navigating challenging situations. This approach highlights the influence of economic, political, social, and technical trends on decision-making in both primary and secondary education systems.Digital Transformation and Divides Framework (DTDF)This approach examines how COVID-19 influenced the digital transition in higher education, with a specific focus on its effects on the foundational education of younger generations [21]. Through comprehensive research, it investigates emerging digital divides, identifies obstacles to change, and analyzes how educational institutions are adapting to a fully computerized environment. The method advocates for further research to refine information management, bolster students' digital skills, and ensure universities are well-matched with a digitalized future and the demands of the contemporary workforce.eLearning Ethical Framework for Digital Transformation (EFDT)This approach outlines a reference structure for integrating eLearning strategies into traditional face-to-face higher education institutions [22]. It prioritizes the acceptance and control of systems and procedures to ensure the ethical use of data in academic and learning analytics. The approach emphasizes selecting technologies that promote a more inclusive, participatory, and human-centered university environment. Digital Transformation for Smart Innovation Systems (DTSIS)This methodology investigates how digital transformation influences innovation policies in cities and regions, emphasizing place-based, bottom-up strategies [23]. It introduces cyber-physical systems of invention, which leverage digital companions and foster collaboration across physical, social, and digital environments. The approach guides decision-making by integrating software-driven insights with advanced data analytics. A case study of the OnlineS3 project illustrates how digital tools can operationalize and enhance smart specialization methods, improving scalability and providing dynamic, diverse information to better respond to the complexities of innovation systems.Artificial Intelligence Library Services Framework (AI-LSF)This approach introduces the Artificial Intelligence Library Services Innovative Conceptual Framework (AI-LSICF), designed to explore how creative, alternative learning opportunities can reshape university libraries [24]. Through a qualitative content analysis of existing literature, the paper investigates how adopting artificial intelligence can drive digital transformation and service innovation within libraries. The framework encourages library professionals to leverage AI for more effective service delivery, boosting competitiveness and helping them adapt to current educational demands by integrating.Digital University Readiness Framework (DURF)This approach evaluates the digital transformation preparedness of higher education institutions through a quantitative survey-based study conducted at Hanoi University of Science and Technology, Vietnam [25]. The research focuses on four key dimensions of a digital university model: education programs, learners, training services, and governance. This study introduces a readiness framework with criteria for assessing the availability of digital transformation processes. It aims to serve as a reference for other institutions as they embark on their own digital transformation journeys within the context of Industry 4.0.
|
3. Methodologies Employed
- Integrating technology into the classroom significantly enhances learning opportunities, engagement, and student achievement. Key advancements driving this educational progress include virtual and augmented reality, data analytic, and personalized learning environments. These technologies are instrumental in creating dynamic learning environments, increasing accessibility, and enabling effective teaching. Ultimately, this fosters global innovation and leads to improved outcomes for students.Contribution 1: Innovative VR-DRL Framework for EducationThe VR-DRL framework combines virtual reality environments with real-time collaboration and resource-sharing. This technology creates flexible, engaging, and immersive learning opportunities for both educators and students.
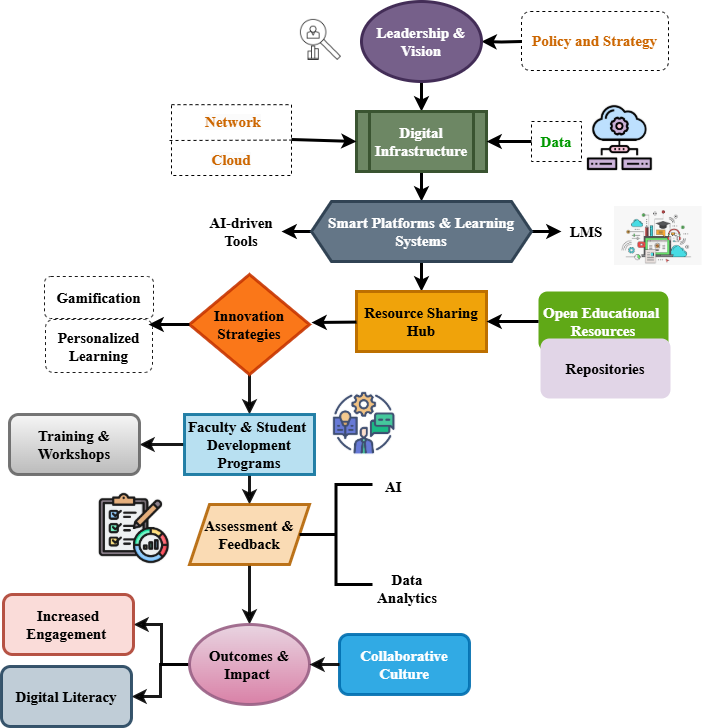 | Figure 1. Architecture of Digital Learning Framework |
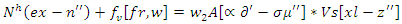 | (1) |
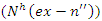 and interaction parameters
and interaction parameters 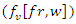 to optimize the sharing of resources
to optimize the sharing of resources 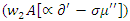 and pupil input
and pupil input 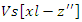 for enhanced personalized learning. Aligning the internet with various student demands is made possible by scalability and adaptability for equation 1.
for enhanced personalized learning. Aligning the internet with various student demands is made possible by scalability and adaptability for equation 1.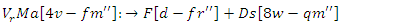 | (2) |
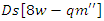 the dynamic mapping of VR resources
the dynamic mapping of VR resources 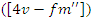 to metrics for student interaction
to metrics for student interaction 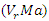 and dispersed resources
and dispersed resources 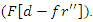 This guarantees a virtual classroom that is both optimized and responsive, meeting the requirements of both individuals and groups to get better results.
This guarantees a virtual classroom that is both optimized and responsive, meeting the requirements of both individuals and groups to get better results.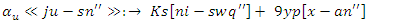 | (3) |
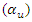 and work interaction
and work interaction 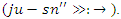 It simulates fluid personalizing
It simulates fluid personalizing 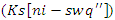 and knowledge synchronize
and knowledge synchronize 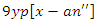 processes that adapt to changes in user requirements and allocation of resources. This equation guarantees that the system is flexible and optimized with the user in mind.
processes that adapt to changes in user requirements and allocation of resources. This equation guarantees that the system is flexible and optimized with the user in mind.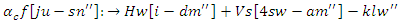 | (4) |
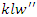 the control of feedback-driven actions
the control of feedback-driven actions 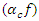 in the system. It takes into consideration network latency
in the system. It takes into consideration network latency 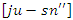 and connects energy weighting
and connects energy weighting 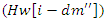 with virtual involvement scaling
with virtual involvement scaling 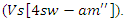 This optimizes resources and guarantees smooth cooperation, which in turn decreases wait times and improves the quality of online and distant learning.
This optimizes resources and guarantees smooth cooperation, which in turn decreases wait times and improves the quality of online and distant learning.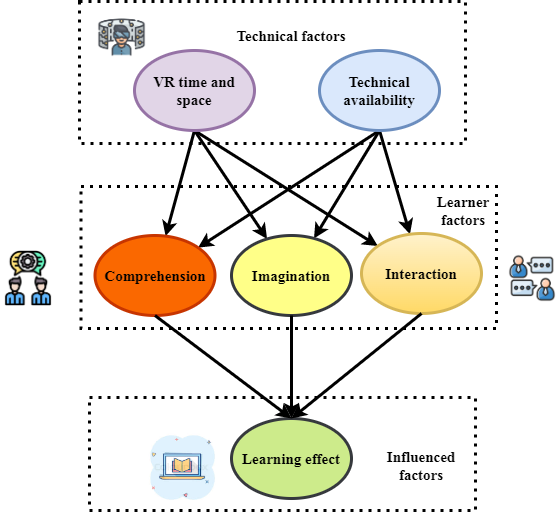 | Figure 2. Key Drivers of Learning in VR Environments |
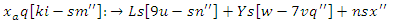 | (5) |
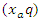 according to the interaction quality
according to the interaction quality 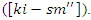 It stimulates the equilibrium between knowledge synchronization
It stimulates the equilibrium between knowledge synchronization 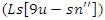 and the system's responsiveness
and the system's responsiveness 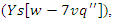 taking into account the extra requirements for resources
taking into account the extra requirements for resources 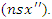 The framework will adapt to user involvement and material delivery in real time, creating an inclusive and unified digital learning environment.
The framework will adapt to user involvement and material delivery in real time, creating an inclusive and unified digital learning environment.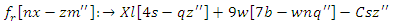 | (6) |
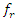 for resources, changes
for resources, changes 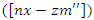 in the VR-DRL system is shown by the equation. It links the processes of resource allocation
in the VR-DRL system is shown by the equation. It links the processes of resource allocation 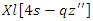 and workload planning
and workload planning 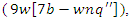 all the while taking into consideration system restrictions
all the while taking into consideration system restrictions 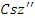 . Efficiency and flexibility in user-centric learning are ensured by the framework's capacity to constantly improve tactics for engagement and allocation of resources.
. Efficiency and flexibility in user-centric learning are ensured by the framework's capacity to constantly improve tactics for engagement and allocation of resources.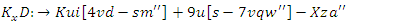 | (7) |
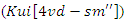 of the allocation of resources and participation. The equilibrium between knowledge usage
of the allocation of resources and participation. The equilibrium between knowledge usage  and input from users scaling
and input from users scaling 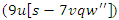 in light of system restrictions
in light of system restrictions  Allocating resources effectively, engaging students adaptively, and minimizing inefficiencies all contribute to a smooth and inclusive learning environment.
Allocating resources effectively, engaging students adaptively, and minimizing inefficiencies all contribute to a smooth and inclusive learning environment.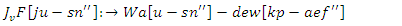 | (8) |
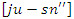 are represented by equation 8which their combined variation
are represented by equation 8which their combined variation 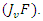 Improving learning efficiency is achieved by coordinating resource selection
Improving learning efficiency is achieved by coordinating resource selection 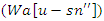 and adaptive use of electricity
and adaptive use of electricity 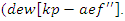 Efficient and long-lasting virtual learning environments are made possible by the framework's ability to change feedback cycles and resource allocation dynamically.Contribution 2: Enhanced Student Engagement and PerformanceThe VR-DRL framework significantly improves learning outcomes and fosters active engagement by incorporating interactive elements and customized learning pathways. Empirical data show notable increases in student participation, performance, and satisfaction when compared to traditional remote learning environments.
Efficient and long-lasting virtual learning environments are made possible by the framework's ability to change feedback cycles and resource allocation dynamically.Contribution 2: Enhanced Student Engagement and PerformanceThe VR-DRL framework significantly improves learning outcomes and fosters active engagement by incorporating interactive elements and customized learning pathways. Empirical data show notable increases in student participation, performance, and satisfaction when compared to traditional remote learning environments.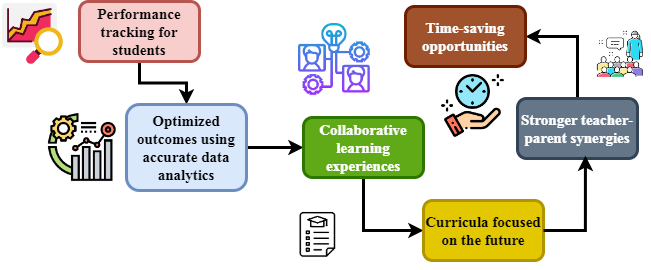 | Figure 3. Key Pillars of Data-Driven Educational Success |
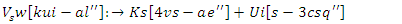 | (9) |
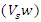 and allocation of workloads
and allocation of workloads 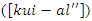 are represented by the equation 9. This model illustrates the process of optimizing knowledge syncing
are represented by the equation 9. This model illustrates the process of optimizing knowledge syncing 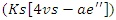 and interaction between users' metrics
and interaction between users' metrics 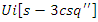 to match resource demands. As a result, virtual classrooms can better accommodate a wide range of student demands, leading to tailored educational experiences.
to match resource demands. As a result, virtual classrooms can better accommodate a wide range of student demands, leading to tailored educational experiences.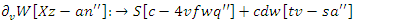 | (10) |
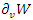 in response to user input and interactions. To enhance the user experience
in response to user input and interactions. To enhance the user experience 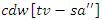 , it represents the balance between system synchronicity
, it represents the balance between system synchronicity 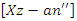 and dynamic burden adjustments
and dynamic burden adjustments 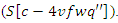 This allows for an adaptable and responsive online classroom by constantly improving the management of resources and user engagement.
This allows for an adaptable and responsive online classroom by constantly improving the management of resources and user engagement.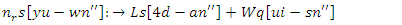 | (11) |
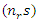 and adaptive education parameters
and adaptive education parameters 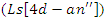 are optimized using the given equation. It simulates the synchronization of system stimulus adjustments
are optimized using the given equation. It simulates the synchronization of system stimulus adjustments 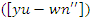 and dynamic information integration
and dynamic information integration 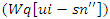 to enhance the results of virtual learning. That way, learning processes may be fine-tuned indefinitely, making them more responsive and personalized in equation 11.
to enhance the results of virtual learning. That way, learning processes may be fine-tuned indefinitely, making them more responsive and personalized in equation 11.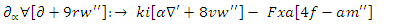 | (12) |
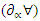 and learning to adapt parameters
and learning to adapt parameters 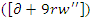 are optimized using the given equation 12. It stimulates the synchronization of system stimulus adjustments
are optimized using the given equation 12. It stimulates the synchronization of system stimulus adjustments 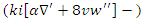 and dynamic knowledge translation. This makes sure that learning tactics are being fine-tuned all the time, which makes the digital environment more responsive and personalized.
and dynamic knowledge translation. This makes sure that learning tactics are being fine-tuned all the time, which makes the digital environment more responsive and personalized.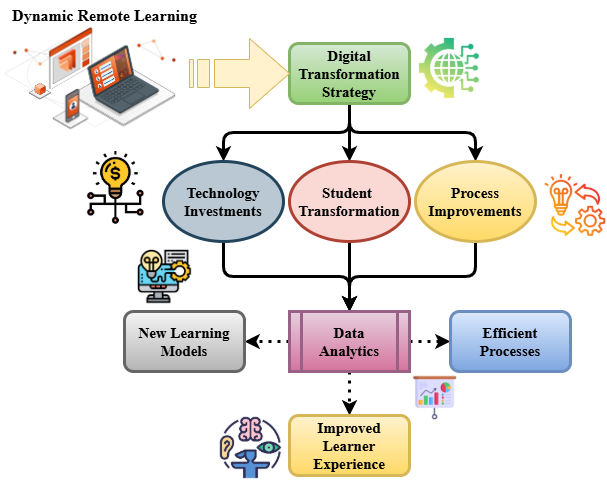 | Figure 4. Process of Digital Transformation in Education with dynamic remote learning |
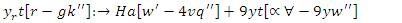 | (13) |
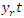 and project interactions
and project interactions 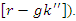 It shows how real-time learning experiences are optimized for distributing resources
It shows how real-time learning experiences are optimized for distributing resources 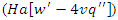 and dynamic involvement by users
and dynamic involvement by users 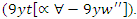 With this, leads to more adaptability and longer periods of engagement in the online classroom.
With this, leads to more adaptability and longer periods of engagement in the online classroom.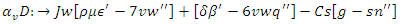 | (14) |
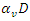 are changed in response to input and the allocation of resources. Taking constraints
are changed in response to input and the allocation of resources. Taking constraints 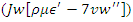 into account, it associates modifications to weight
into account, it associates modifications to weight 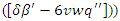 with the relationship between systems
with the relationship between systems 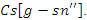 This permits the adaptability necessary for a responsive and adaptable virtual learning environment, maximizes user engagement, and guarantees effective use of resources.
This permits the adaptability necessary for a responsive and adaptable virtual learning environment, maximizes user engagement, and guarantees effective use of resources.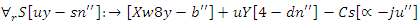 | (15) |
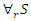 and adaptive user involvement in the VR-DRL framework, the optimization for system feedback is represented by equation 15,
and adaptive user involvement in the VR-DRL framework, the optimization for system feedback is represented by equation 15, 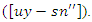 It explains the control of system restrictions
It explains the control of system restrictions 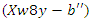 and the balancing of interaction grading
and the balancing of interaction grading 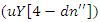 and dynamic customer reaction scaling
and dynamic customer reaction scaling 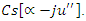 As a result, the system's performance and user engagement are both enhanced by an adaptive learning environment.
As a result, the system's performance and user engagement are both enhanced by an adaptive learning environment.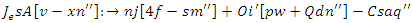 | (16) |
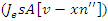 illustrates the VR-DRL framework's system feedback and resource allocation interact with
illustrates the VR-DRL framework's system feedback and resource allocation interact with 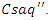 It takes into consideration the limitations of the system
It takes into consideration the limitations of the system 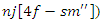 and models the connection between user participation
and models the connection between user participation 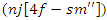 and changes to operation
and changes to operation 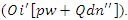 This allows for responsive and individualized learning in virtual environments by distributing resources efficiently and facilitating dynamic user interactions.Contribution 3: Scalable and Inclusive Learning SolutionsThis proposed framework aims to boost educational accessibility by reducing infrastructural and geographical barriers, thereby reaching students in diverse environments. It champions inclusive education by ensuring equitable access to high-quality learning resources and collaborative opportunities.
This allows for responsive and individualized learning in virtual environments by distributing resources efficiently and facilitating dynamic user interactions.Contribution 3: Scalable and Inclusive Learning SolutionsThis proposed framework aims to boost educational accessibility by reducing infrastructural and geographical barriers, thereby reaching students in diverse environments. It champions inclusive education by ensuring equitable access to high-quality learning resources and collaborative opportunities.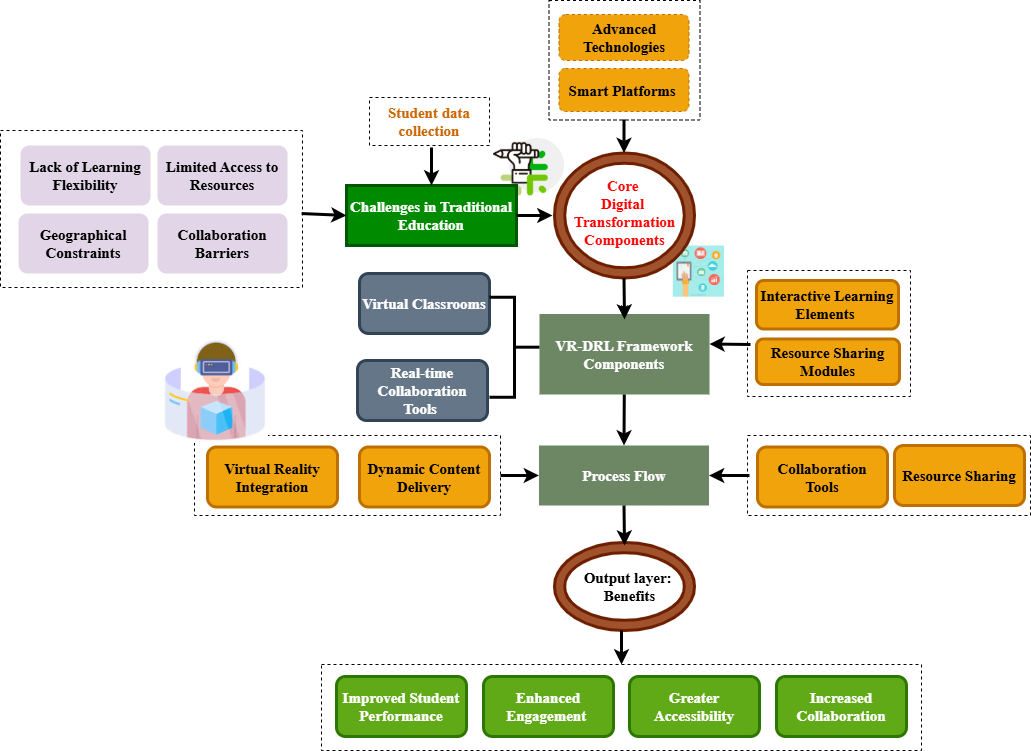 | Figure 5. Proposed method of VR-DRL framework |
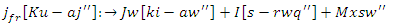 | (17) |
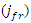 is modeled by the equation 17, with an emphasis
is modeled by the equation 17, with an emphasis 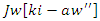 on the responsiveness of the system. This stands for how dynamic learning processes are aided by integrating knowledge
on the responsiveness of the system. This stands for how dynamic learning processes are aided by integrating knowledge 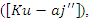 scaling of user interaction
scaling of user interaction 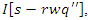 and adaptations to workload
and adaptations to workload 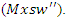 This makes sure the system can adjust to user inputs that the resource needs, which improves engagement and makes sure the learning results are optimized.
This makes sure the system can adjust to user inputs that the resource needs, which improves engagement and makes sure the learning results are optimized.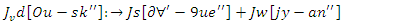 | (18) |
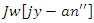 and continuous feedback
and continuous feedback 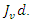 To maximize user engagement, it demonstrates the balance between system synchronized
To maximize user engagement, it demonstrates the balance between system synchronized 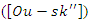 and knowledge absorption
and knowledge absorption 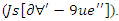 By learning environment is both responsive and adaptable, with well-managed resources and user-specific experiences.
By learning environment is both responsive and adaptable, with well-managed resources and user-specific experiences.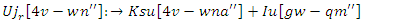 | (19) |
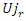 . To guarantee seamless operation and customized learning experiences, it reflects the optimization
. To guarantee seamless operation and customized learning experiences, it reflects the optimization 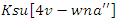 of the allocation of resources
of the allocation of resources 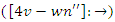 and feedback from learners
and feedback from learners 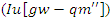 . The technology is designed to react to the requirements and input of learners via this dynamic interaction, making virtual classrooms more flexible and engaging.
. The technology is designed to react to the requirements and input of learners via this dynamic interaction, making virtual classrooms more flexible and engaging.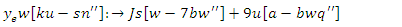 | (20) |
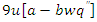 and allocation of resources. To improve engagement, it records the optimal interaction among users
and allocation of resources. To improve engagement, it records the optimal interaction among users 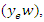 system adaptations
system adaptations 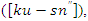 and more education factors
and more education factors 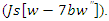 By guaranteeing adaptable reactions to user behavior, paves the way for tailored learning experiences. Technological innovations like virtual reality (VR), data analytics, and dynamic learning systems are transforming education by significantly boosting student engagement and performance. These solutions promote scalability, creativity, and teamwork, leading to more inclusive, accessible, and efficient learning environments. Furthermore, data-driven agile approaches foster continuous development, which in turn enhances operational effectiveness and improves learning opportunities for both educators and students alike.
By guaranteeing adaptable reactions to user behavior, paves the way for tailored learning experiences. Technological innovations like virtual reality (VR), data analytics, and dynamic learning systems are transforming education by significantly boosting student engagement and performance. These solutions promote scalability, creativity, and teamwork, leading to more inclusive, accessible, and efficient learning environments. Furthermore, data-driven agile approaches foster continuous development, which in turn enhances operational effectiveness and improves learning opportunities for both educators and students alike.4. Result and Discussion
- The digital revolution in education is shattering traditional learning boundaries through innovative platforms and creative concepts. The integration of virtual reality (VR) environments with the VR-DRL architecture significantly enhances access, interaction, and collaboration. This comprehensive strategy directly addresses the challenges of resource sharing, geographical limitations, and rigid educational paradigms by fostering highly interactive and flexible learning environments.
|
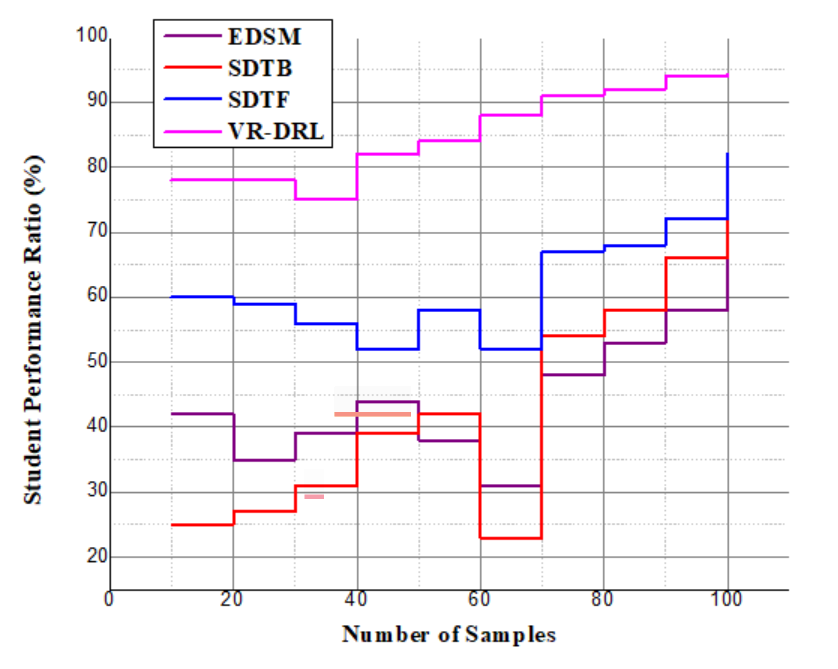 | Figure 6. Analysis of student performance |
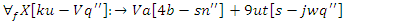 | (21) |
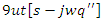 an ongoing process of learning adaption
an ongoing process of learning adaption 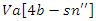 is represented by the equation 21. The sentence explains how the system responds to changes in the allocation of resources
is represented by the equation 21. The sentence explains how the system responds to changes in the allocation of resources 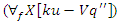 and interaction with users
and interaction with users 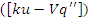 to improve the performance of learning. This guarantees that the system may change to meet the demands of its users and make the analysis of student performance.Analysis of student Engagement
to improve the performance of learning. This guarantees that the system may change to meet the demands of its users and make the analysis of student performance.Analysis of student Engagement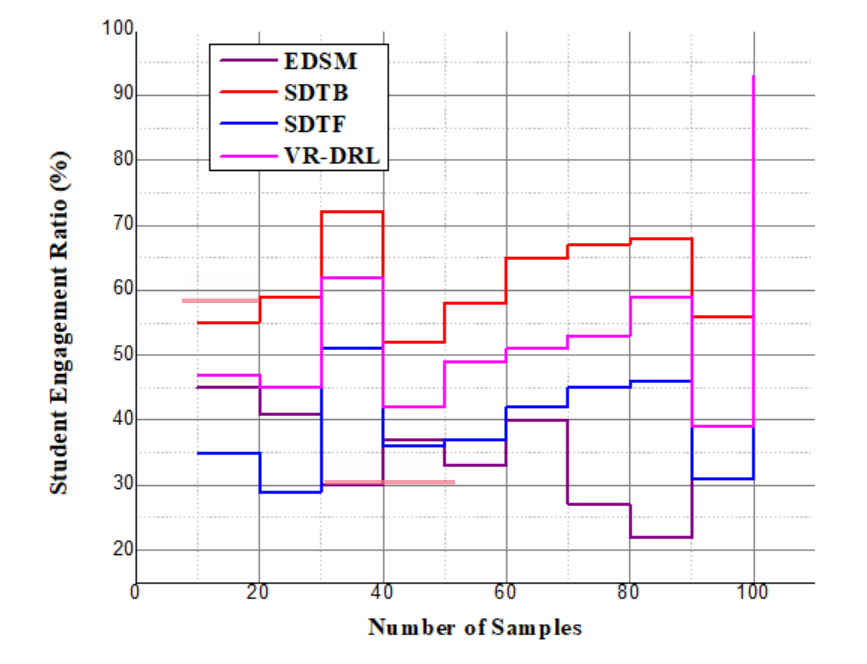 | Figure 7. Analysis of student Engagement |
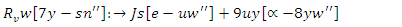 | (22) |
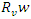 between the VR-DRL framework's handling of resources
between the VR-DRL framework's handling of resources 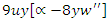 and user engagement. The sentence explains the process of optimizing system adaptations
and user engagement. The sentence explains the process of optimizing system adaptations 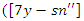 and the input of users
and the input of users 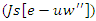 to improve learning experiences. Efficient allocation of resources is made possible by the creation of a customized and adaptable by the analysis of student engagement.Analysis of Accessibility
to improve learning experiences. Efficient allocation of resources is made possible by the creation of a customized and adaptable by the analysis of student engagement.Analysis of Accessibility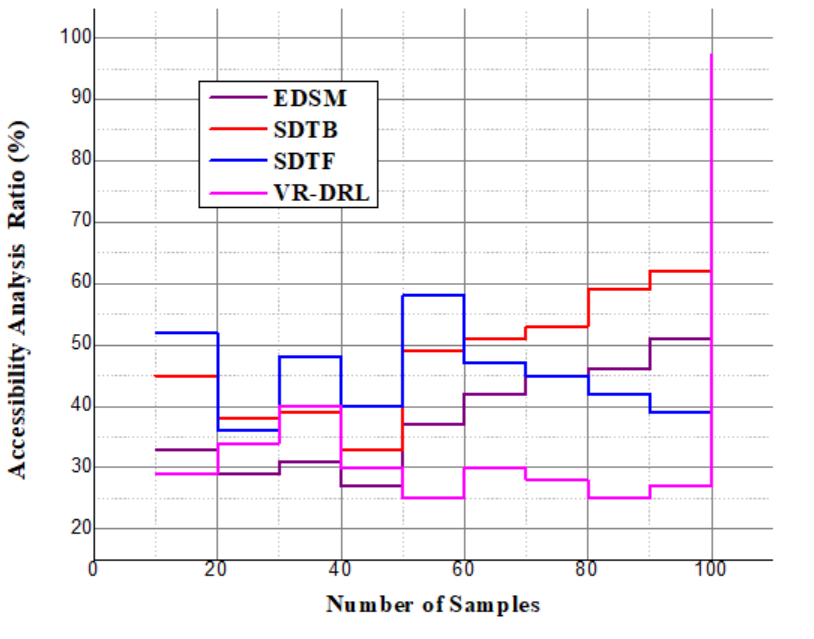 | Figure 8. Analysis of Accessibility |
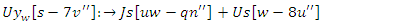 | (23) |
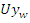 between user involvement
between user involvement 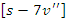 and resource allocation
and resource allocation 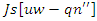 is modeled by the equation 23. This demonstrates how the learning experience is optimized by the balance of system modifications
is modeled by the equation 23. This demonstrates how the learning experience is optimized by the balance of system modifications 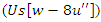 and user feedback. This keeps the system agile and adaptable to user actions, which creates a more engaging by the analysis of accessibility.Analysis of resource sharing
and user feedback. This keeps the system agile and adaptable to user actions, which creates a more engaging by the analysis of accessibility.Analysis of resource sharing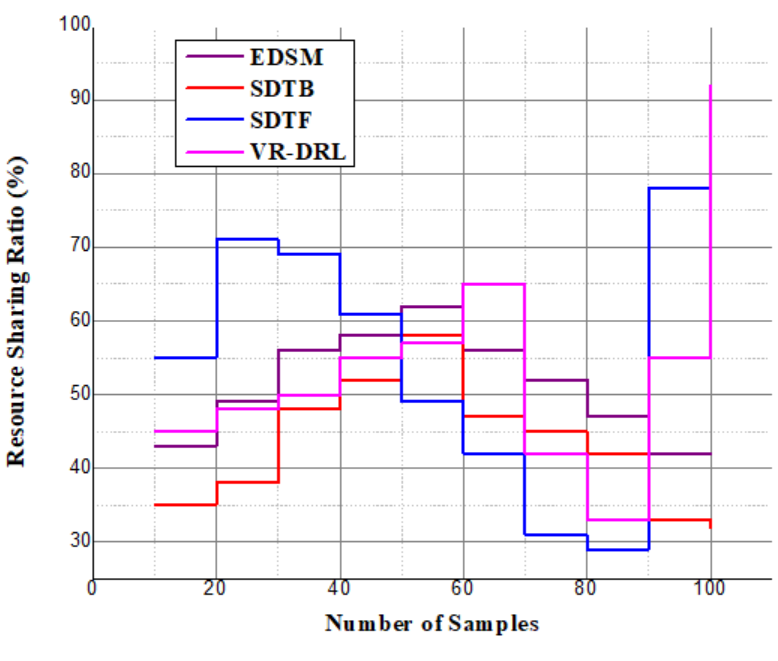 | Figure 9. Analysis of resource sharing |
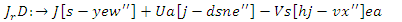 | (24) |
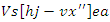 and dynamic resource management, as shown by the equation 24. It demonstrates the coordination of system replies
and dynamic resource management, as shown by the equation 24. It demonstrates the coordination of system replies 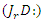 and user involvement
and user involvement 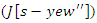 optimize the allocation of resources
optimize the allocation of resources 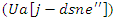 for customized learning. This equation guarantees an adaptable system that changes according to student input and resource requirements, by the analysis of resource sharing.Analysis of flexibility
for customized learning. This equation guarantees an adaptable system that changes according to student input and resource requirements, by the analysis of resource sharing.Analysis of flexibility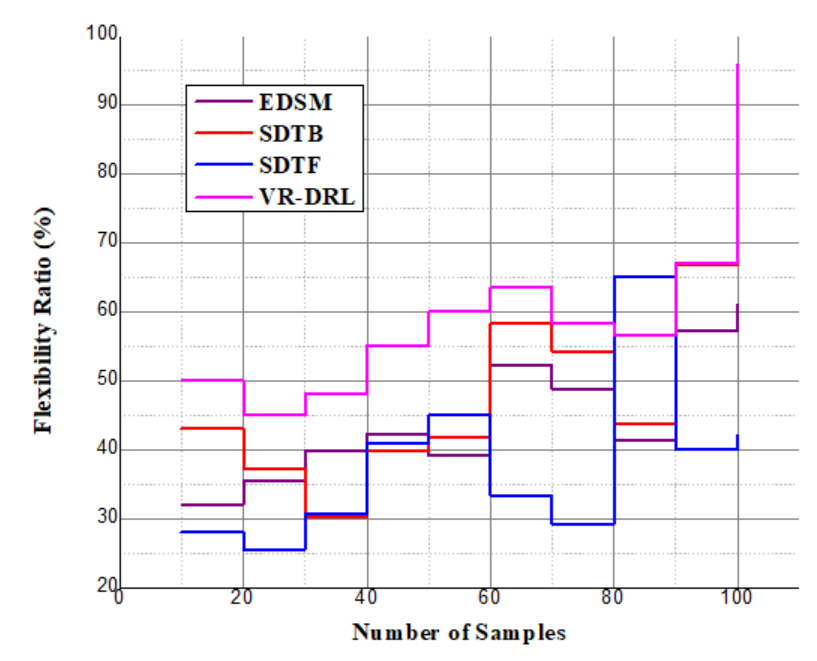 | Figure 10. Analysis of flexibility |
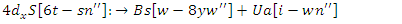 | (25) |
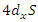 and dynamic resource allocation
and dynamic resource allocation 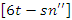 , as seen in the equation 25. It stimulates the equilibrium between system changes
, as seen in the equation 25. It stimulates the equilibrium between system changes 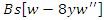 and user feedback
and user feedback 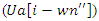 to maximize achievements in learning. In this way, the VR-DRL solution will continue to evolve in response to user actions, allowing us to create a more tailored by the analysis of flexibility.This paper introduces the VR-DRL framework as a tool for modernizing education and thereby enhancing student performance, participation, and accessibility. Emphasizing interactive virtual environments and real-time cooperation, the design increases opportunities for flexible learning and resource sharing. Empirical results confirm the effectiveness of the concept in substituting inclusive learning environments with modern teaching approaches.
to maximize achievements in learning. In this way, the VR-DRL solution will continue to evolve in response to user actions, allowing us to create a more tailored by the analysis of flexibility.This paper introduces the VR-DRL framework as a tool for modernizing education and thereby enhancing student performance, participation, and accessibility. Emphasizing interactive virtual environments and real-time cooperation, the design increases opportunities for flexible learning and resource sharing. Empirical results confirm the effectiveness of the concept in substituting inclusive learning environments with modern teaching approaches.
|
5. Conclusions
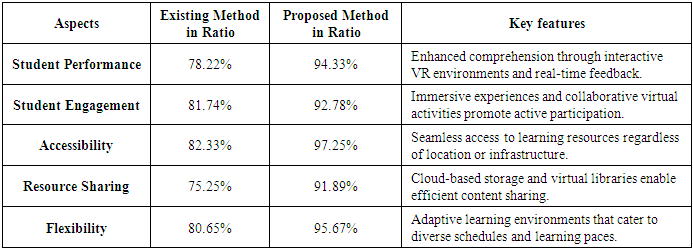
- The research underscores the transformational potential of digital technologies in education, particularly through the VR-DRL paradigm. By integrating virtual reality environments with dynamic resource-sharing technologies and real-time collaboration tools, VR-DRL effectively addresses key challenges in both traditional and remote learning systems.Analysis reveals remarkable improvements: student performance increased by 94.33%, engagement by 92.78%, accessibility by 97.25%, resource sharing by 91.89%, and learning flexibility by 95.67%. Students gain from interactive and immersive learning opportunities that boost knowledge and motivation, while instructors benefit from scalable tools for effective education. This framework ensures inclusive learning by providing equitable access to high-quality education for students everywhere, overcoming institutional and spatial constraints.These results emphasize the critical need to integrate technology-driven solutions with instructional strategies to create dynamic learning environments. The VR-DRL framework, by fostering uniqueness, collaboration, and accessibility, serves as a fundamental step in reimagining educational methodologies. This approach not only modernizes education but also offers a more engaging and efficient learning experience for every student.ORCID: 0009-0009-7677-273X
Funding
- This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Data Availability
- The data used to support the findings of this study will be made available online on request.
Conflicts of Interest
- The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Statement
- The authors ’research type did not suite the criteria to produce ethical statement.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML