-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Intelligent Systems
p-ISSN: 2165-8978 e-ISSN: 2165-8994
2025; 14(1): 10-17
doi:10.5923/j.ajis.20251401.02
Received: Feb. 16, 2025; Accepted: Feb. 28, 2025; Published: Mar. 5, 2025

Rise & Impact of AI Agents in Digital Landscape
Anirban Majumder
Amazon Science, Amazon, Seattle, USA
Correspondence to: Anirban Majumder, Amazon Science, Amazon, Seattle, USA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The shift from Artificial Intelligence (AI) to a new generation of intelligent agents has ushered in a transformative era, redefining digital experiences and driving innovation across various industries. AI agents are changing the way we interact with customers, operate businesses, and make decisions about which way to go, using machine learning, natural language processing, and a few other technologies set to automate business tasks. These agents boost efficiency, scalability, and user experience in various applications, ranging from personalized virtual assistants, to autonomous systems in healthcare, finance, and education. Yet alongside these opportunities and advancements come growing concerns about the ethical implications thereof, as well as potential bias and security risks. In this paper we provide an overview of the history of AI Agents, the evolution of how AI agents will change the world, and finally the future AI-generated ecosystems that are changing the world around us to be more digital. AI agents are not just automating tasks, they are enabling predictive analytics, adaptive learning processes, in real time, bringing in paradigm shifts in the digital ecosystem. AI-Powered data-driven workflows are being employed in businesses to streamline processes, improve personalization, and fuel innovation. On the other hand, AI agents are also vulnerable to abuse, including deepfake generation, automated misinformation, and algorithmic manipulation. Therefore, it's important for regulators and policy design ethical frameworks that can safeguard such adverse outcomes. In an interconnected digital economy, the future of AI agents is complemented with both human oversight as well as a technological evolution as AI agents continue to build human potential while minimizing risks.
Keywords: AI Agents, Machine Learning, Natural Language Processing, Predictive Analytics, Ethical Implications
Cite this paper: Anirban Majumder, Rise & Impact of AI Agents in Digital Landscape, American Journal of Intelligent Systems, Vol. 14 No. 1, 2025, pp. 10-17. doi: 10.5923/j.ajis.20251401.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- AI-powered Agents, also known as AI agents, have evolved significantly over the past few decades, transforming from simple rule-based systems to systems using highly sophisticated models capable of complex reasoning and natural language processing [1]. In the early days, AI systems were limited to performing particular tasks through pre-programming instructions, which are often required for human intervention and oversight. AI agents began to learn from data through the advent of Deep Learning and Machine Learning, which enables them to identify the prediction of marks, patterns, and task performance with higher [2]. These allowed AI agents to engage in a wide range of activities, from offering customer services and personalized recommendations to autonomous driving. AI agents powered by vast computational resources and large-scale datasets, have the remarkable ability to adapt to environmental changes and refine their decisions over time. This ability of AI agents increases their utility value across various different industries, extending a promising outlook in years to come [3]. The rapid development of AI technology has also raised concerns, especially regarding its potential for abuse, fraud, and misuse. The AI agents have the power to regulate large amounts of data and decision-making based on the patterns learned activities which helps detect financial fraud, campaigns of misinformation, and identity theft [7]. AI models can be used to convince and generate automated cyber-attacks, fake content, and spread misinformation campaigns, which are often initiated at a scale that would be impossible for humans to track & stop. The association of risk with the misuse of AI is not only limited to data-driven or financial fraud but also extends to areas such as discrimination, privacy violations, and algorithmic bias that can lead to unethical practices and societal risks [8].Abuse and mitigating fraud in the system requires a multi-faceted approach with a focus on both regulatory frameworks and technological safeguards. On the technology front, AI models must be designed with transparency, interpretability, and accountability to ensure the decisions taken by the AI agents can be audited and understood [9]. The technique of explainable AI makes it possible to provide reasoning behind the decisions for the stakeholders while adversarial testing, can help in identification of vulnerabilities that might be exploited for carrying out fraudulent activities [10]. It is of utmost importance for governments, organizations, and regulatory stakeholders to come together and establish an ethical standards for the development and deployment of AI. The set standards will help the industry not only to prevent misuse but also ensure responsible use in AI agents. This can in-turn pave way towards fostering an environment where AI's potential can be harnessed safely for greater societal development [11].This study's outlook lies in its comprehensive exploration of the evolution of AI agents, emphasizing their transformative impact across industries while addressing the developmental challenges of fraud and abuse. It outlines the context of technological safeguards that, when combined with regulatory measures, can mitigate misuse [12].
2. Evolution & Impact of AI Agents in Industries
- The evolution of AI powered agents has been transformative over the period of time. The digital landscape has witnessed a phenomenal shift from being a simple rule-based algorithms to sophisticated machine learning and deep learning models capable of autonomous decision-making along with reasoning. In the early days of AI agents were limited to the predefined instructions and the data structure, making them more effective only in the specific domains like basic automation and chess playing [13]. However, with advancements in natural language processing, deep learning, and reinforcement learning have enabled the AI agents to process huge volumes of unstructured data, learn from experience, and dynamically adapt to the complex environments. AI Agents, today powered by huge language models and neural networks, are being used in different applications with capabilities of predictive analytics, conversational flow, to robotics. AI integration along with cloud computing and the analytics of big data has further accelerated its development, making the solutions more accessible and scalable across multiple industries [14].Impact of AI agents across various industries have been profound like making decisions, revolutionizing operations, and automated interactions with customers. Artificial Intelligence is revolutionizing diverse sectors, making more effective decisions in a more efficient manner. In the healthcare sector, diagnostic systems are capable of analyzing medical images at an accuracy level higher than humans, assisting drug discovery, and allowing for personalized treatment plans for individual patients [16]. AI agents help to detect frauds, algorithmic trading and risk management and thus improve the efficiency of the financial sector and reducing human errors. AI powered predictive maintenance in manufacturing amends equipment analytics with real time feed to cut cost, prevent breakdowns and function optimally [34], [11]. Retailers implemented AI for various functionalities, such as personalized recommendations and AI-powered chatbots, thus enhancing the customer experience and engagement. The role of AI in supply chain management and logistics optimizes the routes, reduces waste, and increases the overall efficiency. As AI agents continue to evolve, industries are witnessing enhanced automation, increased decision-making, and improved accuracy, which leads to higher profitability and productivity [13].
 | Figure 1 |
3. Rise & Rise of AI Agents across Industries
- AI agents are evolving rapidly, revolutionizing industries with next-level capabilities such as real-time decision-making, hyper-personalization, and seamless automation. These agents, in contrast to traditional AI models, use generative AI, reinforcement learning, and multimodal processing to provide more autonomous, flexible, and intelligent operation. The integration of AI capabilities into various industries has not only increased efficiency but also promoted unprecedented innovation, customer service, and predictive analytics.Here are the few areas where AI Agents are helping industries in multiple areas-Healthcare: Next-generation AI agents are revolutionizing healthcare diagnostics, drug discovery, and patient care. AI agents have helped doctors diagnose diseases earlier and personalize treatment plans earlier by scanning trillions of unstructured data from medical records, imaging, and genetic sequencing. Now, virtual health assistants powered by AI can perform preliminary consultations, monitor health status of patients remotely and even solve most common mental health issues through Conversational AI thus, making healthcare proactive and accessible, [31].Finance: is using modern AI agents for risk assessment, fraud prevention and investment strategies. The use of AI has made it easier for new financial advisors to provide recommendations for hyper-personalized portfolio by studying market trends and user behavior in real-time. AI-based fraud detection systems monitor transactions in real-time, utilizing deep learning algorithms to detect suspicious activities and mitigate cyber threats. With the combination of AI and blockchain, smart contracts will achieve a new level of automation and security, minimizing manual errors and promoting transparency of transactions, making financial operations more efficient, [28].Supply Chain & Logistics: AI agents in industry are changing into the supply chain logistics, production efficiency, and in predictive maintenance. The factory of the future would be a self-optimizing facility, where AI-powered robotic systems work alongside human workers, to achieve improved precision and efficiency. Using IoT sensor data for predictive analytics reduces downtime and maintenance costs by predicting possible equipment failures. Automation powered by AI is also simplifying demand forecasting and inventory management, allowing manufacturers to build cost-effective and flexible manufacturing systems [30].Retail & E-Commerce: Retail sector is rapidly adopting AI agents for hyper-personalized shopping experience, real-time demand forecasting and automated customer support. When it comes to how generative AI enhances product recommendation systems, it efficiently analyzes past purchases, websites browsed, and social media activity. Pioneering AI-Powered Virtual Shopping Assistants, act as human-like advisors equipped to instantly guide customers with their multiple queries and suggesting products. Retailers are implementing AI-powered dynamic pricing systems that identify and analyze demand fluctuations, competitor pricing, and consumer behavior to optimize revenue generation, [29].Hospitality and Multifamily Real Estate, AI agents are ushering in a new era of guest and tenant experiences with personalized, immediate interactions and automated services. AI is being used by hotels for setting dynamic prices, anticipating maintenance needs of facilities, and intelligent virtual concierges that improve guest experiences. AI-driven property management systems in multifamily housing aid in tenant screening, smart home technologies, and predictive maintenance, resulting in modern, tech-enabled residences. Thanks to sentiment analysis even those sectors could benefit from advices and real time feedback from customers.Generative AI Agents: Generative AI agents are transforming industries through machines producing human-like content, automating complex tasks, and augmenting decision-making. Unlike conventional AI, which uses some rules that are defined intolerably, a generative AI model that runs on deep learning and neural networks can be implemented to provide text, images, code, and even simulations with accurate and creative results. These AI Agents are developing over time to not only enhance efficiency but also driving towards a future where creativity, automation, and human-AI collaboration across several industries will be redefined.Mainstream applications of advanced AI language models like ChatGPT are changing the way of business and how customers interact with AI. With deep learning and natural language processing capabilities, ChatGPT is able to generate human-like text, have conversations, and respond to prompts across a wide variety of topics. With its contextual awareness, ability to generate creative content, and capacity to aid in solving complex problems, it proves to be indispensable in countless fields ranging from customer service to education, healthcare, and software development. To automate workflows, improve user engagement and provide personalized experiences through AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants, businesses are using ChatGPT. ChatGPT continues to evolve augmenting human intelligence, with efficiency, reshaping the sphere of the future artificial intelligence, [27].And as these AI agents get smarter and interact with the world around them, we will see them become an integrated part of smart cities, educational systems, and sustainability, leading to more energy-efficient planning, tailored learning pathways, and improved resource management. This next-gen AI is going to redefine the industry standard, allowing companies to be more dynamic, smart, cost-effective and customer-centric, while overcoming challenges of ethical AI deployment, bias mitigation and data security. These new practices have guided a wave of new AI-driven industries to the future of automation the future founded on automation, collaboration with AI models, and intelligent decision-making.
4. Risk and Mitigation of Fraud & Abuse in AI Agents
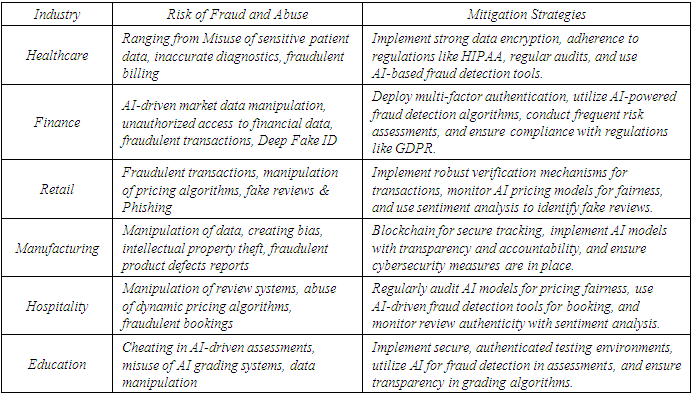
- The reliance on the AI agents across industries has significantly introduced risks related to abuse and fraud, as actors exploit vulnerabilities of AI for cybersecurity, social manipulation purposes, and finance. The primary risk is the adversarial attacks, where attackers regulate the models of AI by deceptive inputs to mislead the system, which leads to the incorrect outputs, [18]. For example, in the system of finance, fraudsters use AI- generated artificial identities and deepfake the technologies to deceive the process of authentication, identity theft and financial fraud. Furthermore, the chatbots powered by AI and recommendation systems that can be regulated to spread misinformation, promote the schemes of fraudulent, or phishing attacks. The AI power of decision making, especially in the models of deep learning, makes detecting fraudulent regulations challenging, enhancing the risk of exploitation across different applications, [19].AI fraud and abuse mitigating techniques requires an approach of multi-layer that includes a robust framework of security, transparency of AI model, and continuous monitoring. The implementation of adversarial training techniques, where the models of AI are exposed to attack potential development to increase their resilience against fraud and abuse, [20]. The methodologies of explainable AI can play an essential role in making the decisions of AI interpretable, enabling the organizations to detect the anomalies and suspicious flag activities in real time. Furthermore, the identity of robust verification measures like blockchain based management identity and multi-factor authentication can help to prevent fraud driven by AI in financial transactions [9]. The strategies of cybersecurity like AI-based anomaly detection systems that can proactively identify fraudulent activities before they escalate. The security of regular audits and the models of AI update are essential to ensure that the AI agents remain resilient against evolving tactics of fraud [11].Beyond the safeguards of technical and ethical governance of AI and regulatory frameworks are crucial in mitigating fraud and abuse in the systems of AI. Organizations and Governments must establish the policies to clear on accountability of AI, ensuring that developers adhere to the guidelines and regulate the misuse of Artificial Intelligence [18].The strict regulations on the privacy of data, like AI ethics compliance frameworks and General Data Protection Regulation, that help to limit unauthorized access of data and prevent the exploitation of AI. Furthermore, the awareness of public campaigns and collaborations industry-wide can strengthen the security of AI by promoting sharing knowledge and best practices. As the technology of AI advances, a responsible fostering of the AI ecosystem that balances the risk of innovation to mitigate an essential fraud preventing technology to ensure the positive impact of AI on society [20].Here’s a table outlining the risks and mitigation strategies related to fraud and abuse in AI agents across various industries:
|
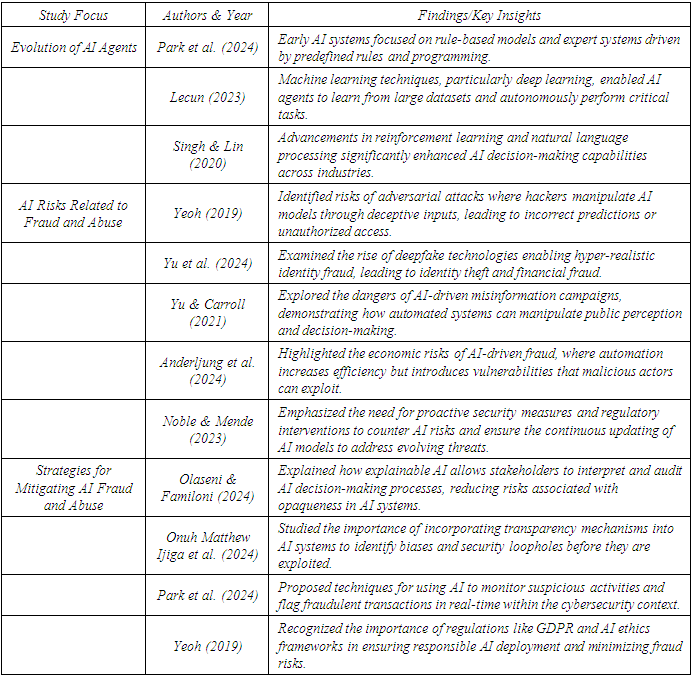
5. Literature Review
- The evolution of AI agents, which has been extensively studied in recent literature, highlights their transformation from the systems of rule-based to sophisticated models of machine learning. Findings on the evolution of AI agents, risks related to fraud and abuse, and the mitigation strategies being explored across various sectors.
|
6. Case Studies
- Case Study 1: AI-Powered Fraud Detection in the Financial Sector (JP Morgan Chase)JP Morgan Chase, one of the largest global financial institutions, has leveraged AI agents to detect fraudulent transactions and mitigate financial risks. The company implemented AI-driven anomaly detection systems that analyze real-time transaction data to identify suspicious activities. According to a report by the bank, their AI-powered fraud detection system prevented millions in financial losses by recognizing unusual spending patterns, deepfake-generated identities, and unauthorized account access. However, adversarial attackers attempted to bypass these AI defences by generating synthetic data that mimicked legitimate transactions. To counter this, JP Morgan Chase integrated explainable AI (XAI) into their systems, allowing fraud analysts to interpret AI decisions and take necessary corrective actions. This case highlights both the effectiveness of AI-driven fraud prevention and the ongoing challenges posed by adversarial threats in the financial industry [4].Case Study 2: AI Misinformation and Manipulation in Political Campaigns (Cambridge Analytica & Facebook)The Analytica scandal of Cambridge demonstrated the potential dangerous misinformation of powered AI and targeted regulation. During the 2016 U.S. election of presidential and the Brexit referendum, the algorithms of AI-driven processes huge volumes of social media data to create profiles of psychographic users. This information was then targeted to use individuals with charged political content that influences the behaviour of voters. The use of chatbots powered by AI, fake news generators, and advertising personalized campaigns showcased how AI agents could be weaponized for large-scale misinformation. In response, the regulatory bodies such as U.S. and the Union of Europe lawmakers pushed for stricter data laws of protection, like General Data Protection Regulation, to curb election interference enabled by AI. This case underscores the need for urgent robust governance of AI frameworks to prevent unethical applications of AI in political and social domains, [6].Case Study 3: Deepfake Technology and Identity Theft (The Zao App Controversy)A Chinese Zao powered by AI deepfake application, became a viral sensation in 2019 by allowing users to swap their faces with video clips of celebrities. However, the experts of security quickly raised concerns of privacy risks, as the AI model app stored and user processed for facial data without stringent measures of security. Soon cybercriminals exploited the deep fake technology to create identities of fraud, enabling financial scams and unauthorized access for the systems of biometric authentication. A case involved notable fraudsters using deep fake videos to trick the measures of bank security, leading to the financial losses. The surrounding controversy of Zao led to the intervention of regulation in China, where authorities enforce ethics of AI policies and recognition of facial data protection laws. This case highlights the nature of dual innovation of AI which offers value of entertainment while also presenting the risks of security [7].
7. Future Scope
- The future of AI agents is poised for significant advancements, specifically in increasing collaboration of human AI, automation, and improved accuracy in decision-making. As AI continues to evolve, the integration of self-learning models of AI enables autonomous systems with minimal human intervention to operate while improving adaptability and efficiency. In healthcare sectors, AI-driven diagnostics and robotics surgeries will become more precise, decreasing medicine errors and increasing patient care. Financial institutions will refine further based on AI fraud detection by incorporating blockchain for increased transparency and transaction security. The supply of AI-powered blockchain management and predictive analytics will logistically optimize, decreasing costs and environmental impact. Furthermore, the role of AI in personalized education, digital assistants, and smart cities will continue to expand, making human interaction more intuitive and seamless. The AI convergence with computing quantum and computing edge is expected to unlock unprecedented capabilities, enabling real-time decision-making in complex environments like autonomous vehicles and smart infrastructure.From a security perspective, future AI agents will focus on strengthening defenses against threats of cyber, misinformation, and AI-driven fraud. The AI-enhanced cybersecurity solutions adopted by organizations that leverage adversarial to counteract machine learning evolving hacking techniques. The explainable AI development will become essential in ensuring accountability and transparency in decision-making AI, decreasing bias and potential exploitation. To refine AI standards continuously, the regulatory bodies will need to ensure the deployment of ethical AI while addressing issues like manipulation of deepfakes, misinformation of generated AI, and privacy violations.Furthermore, the AI agents will play an essential role in digital forensics, helping enforcement of law agencies to detect the patterns of cybercrime and regulate the activities of fraud in real time. The future research will develop focusing on the models of AI that are not only secure and robust but also aligned with the ethical values of humans, ensuring that AI remains that force for transformation in positive ways across industries.
8. Challenges and Considerations
- The potential transformation of AI agents, have various challenges hindering their adoption of widespread responsible deployment. The most pressing concern is an ethical development of AI, specifically regarding fairness, transparency, and bias. AI Agents pose significant challenges, including that of ethical concerns, data privacy issues, and displacement of jobs. The widespread adoption of AI raises the questions about bias in the making of decisions for algorithms, as the systems of AI learn from the historical data that may contain biases inherent [14].The concern of the workforce disruption, as AI automates traditional tasks which were performed by humans, leading to shifts in the roles of job and the need for reskilling. Furthermore, the security of data and privacy risks emerge as the systems of AI rely heavily on huge datasets, making them the potential targets for the threats of cyber [16]. The organizations and Governments are working on frameworks to address these concerns while ensuring the development of AI which remains transparent and ethical, [17].Transparency into the outcomes of AI-driven. Additionally, the models of AI which often function as “black boxes” make it to interpret with their difficult processing of decision making. The transparency lacks and raises the concerns in the applications of high-stakes, like criminal sentencing or medical diagnosis, where accountability is essential. Addressing these ethical challenges requires collaborative efforts between the researchers Furthermore, the frameworks of regulatory governance of AI remain across fragmented various regions, leading to the ethical inconsistencies of AI enforcement and deployment. The regulation of data privacy like the General data protection regulation aims to safeguard the information of users, A balance between to strike regulation and innovation is crucial to ensure the development of AI aligns with ethical considerations while regulating robust mechanisms of security.
9. Conclusions
- To conclude, AI agents will continue to alter the course of industries. The way they carry out decision making, or even their automation and overall operational efficiency. But this progress also brings in new challenges, especially cybersecurity risks, algorithmic bias, and fraud. While deep-learning solutions offer the prospect of enormous market share across industries like cybersecurity, finance, and healthcare, they also pose challenges in terms of ethical transparency, adversarial attacks and biased decision-making. Such problems highlight the pressing need for adequate regulation and more sophisticated safeguard technology to reduce risks.By focusing on improving adversarial machine learning techniques, embedding explainable artificial intelligence, and developing data governance policies will help to mitigate fraud and abuse across industries. Therefore, implementing a balanced approach that encourages both innovation and security will be crucial in ensuring that we can take advantage of the benefits of AI while minimising the risks it brings. The advent of "Explainable AI" should be pave way for reasonable, ethical and trustworthy usage of AI powered agents and more research needs to be carried out to harness the potential of Explainable AI and Its benefits.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML