-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Intelligent Systems
p-ISSN: 2165-8978 e-ISSN: 2165-8994
2019; 9(2): 49-53
doi:10.5923/j.ajis.20190902.01

Robotic Process Automation
Vinay Kommera
Sr IT Project Manager, Cognizant Technology Solutions, Washington DC, USA
Correspondence to: Vinay Kommera , Sr IT Project Manager, Cognizant Technology Solutions, Washington DC, USA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

RPA, or Robotic Process Automation, is a software that mimics the steps a human takes to complete rules-based, repetitive tasks. The robot carries out work with speed and precision, utilizing the same applications your employees use every day. In traditional automation, all the actions are primarily based on the programming/scripting, APIs or other ways of integration methods to the backend systems or internal applications. In distinction, RPA automates software that can migrate the work from the human to the computer which can stop paying humans to do work ripe for automation, faster front and back office transaction processing, near “Instant On” integration at the lowest cost, optimization of User Interface to drive long call/transaction times down, accelerate digital transformation objectives, eliminate errors thereby improving productivity by making workers smarter.
Keywords: Robots, IT Automation, Intelligent Process Automation, Concept of Bots, Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning
Cite this paper: Vinay Kommera , Robotic Process Automation, American Journal of Intelligent Systems, Vol. 9 No. 2, 2019, pp. 49-53. doi: 10.5923/j.ajis.20190902.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is being leveraged by many businesses around the world in a wide variety of sectors to provide a vital competitive advantage in business process automation. IT Automation is enabled by software including APIs, scripts, jobs, schedulers, programs, events and a broad range of automation tools. With the advent of Cloud Computing, resources are exposed by APIs and accessible in real-time. When combined with automation toolsets, automated application build & releases, workload, server & infrastructure resources, configuration management updates are now feasible. On-premise environments are pressured to catch up to the speed, flexibility, provided by Cloud environments. Automation toolsets are being used to enhance on premise environments. Heuristic automation leveraging Machine Learning is an emerging class of IT Automation. However, currently there are few vendors with niche offerings and an increased maturity is forecasted over the next 3-5 years.To understand more on IT automation, Automation refers to a non-manual way to complete a task. The term takes on different meaning based upon the context and situation. Within IT there are 5 broad types or building blocks of automation and associated tasks like Process Automation, Service Automation, Workload Automation, Infrastructure Automation, and Application Build & Release Automation. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a subset of Process Automation.RPA is an application of technology which is programmed as a “robot” to capture and interface with existing applications for processing a transaction, manipulating data, triggering responses and communicating with other digital systems. RPA intends to assist or remove a human activity, using software to carry out tasks. RPA tool can be triggered manually or automatically, move or populate data between prescribed locations, document audit trails, conduct calculations, perform actions and trigger downstream activities.Robotic Automation is a sum of two parts:● Robotic Desktop Automation (RDA) – Used for personal robots for every employee, front office (call center, retail, branches) and back office, Toolbars, Wizards, UI enhancements and Task automation● Robotic Process Automation (RPA) – Unattended robots replicating 100% of algorithmic work, back-office operations, repetitive in nature, offload front office work, 100% improvement across smaller subgroupsRPA allows organizations to implement automation in a non-invasive way, which makes RPA unique among other types of automation. It can also reduce the need for constant IT involvement and application development.● Overall Cost Reduction – Automates processes by closing data integration gaps without changes to underlying technology investments. Lowers the cost of operations and increase customer satisfaction. The average cost of implementing and running a robot is much less than the equivalent full-time employee costs and decreases the large scale deployment. By automating, standardizing labor-intensive & error-prone tasks, configuration errors and lengthy, costly processes are reduced.● Speed and Productivity – RPA is typically 2X-3X faster than humans even if robots work at the same pace as humans they can work round the clock, unlike humans.● Scalability and Flexibility – Robots can easily be scaled up and down to handle demand fluctuations and seasonal variances.● Accuracy and Compliance – Robots work to 100% accuracy levels and enable compliance avoiding human error saves costs. Reduction in security vulnerabilities from improved software and increased configuration standardization.
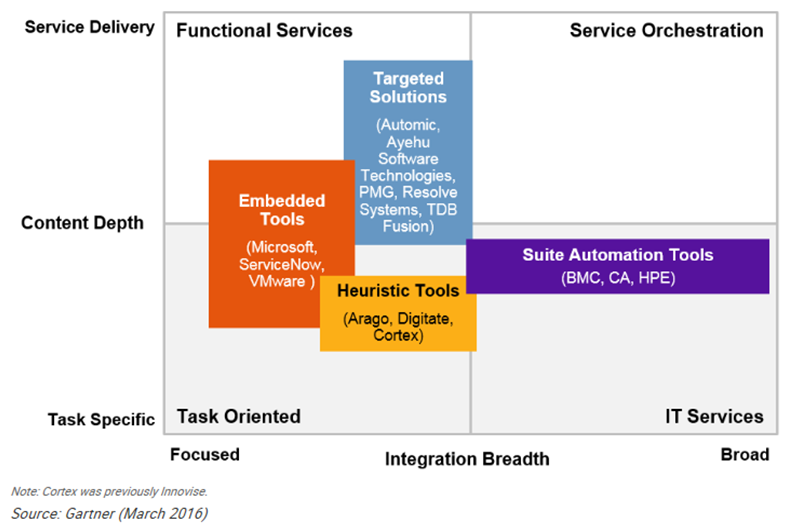 | Figure 1 |
2. RPA Evolution
- Gartner predicts that by 2020, company spending on Robotic Process Automation software will reach $1 billion, at a rate of 41% from 2015 through 2020. By 2020, RPA tools will have evolved to include functionalities such as Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning capabilities. With so many players in the market, it will experience strong downward pricing pressure. Some industries, like financial services and retail, have taken the lead with RPA, but manufacturing and healthcare are catching up quickly.
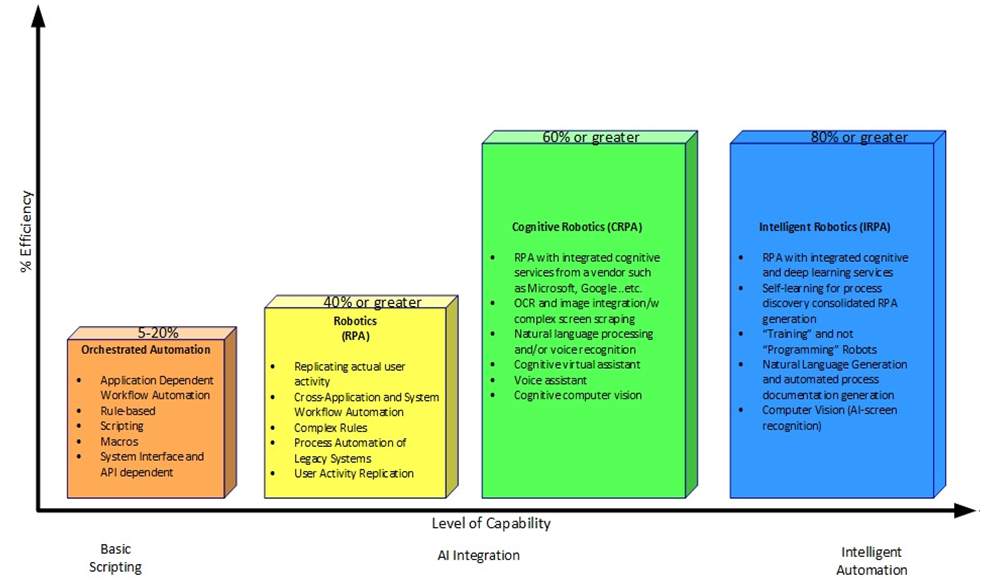 | Figure 2 |
3. Challenges in Traditional RPA Adoption
- ● Pace of change – Most companies are experiencing a typical two-year journey to make any real progress with automation.● Skilled People – Limited availability of skilled resources – domain + technology against the market demand.● Governance – Poor/Inefficient operating model of governance in managing and mitigating risks.● Data intake – many companies are inundated by the challenges of getting started that they overlook data architecture, intake and coding.● Industry expertise – As automation program evolves, the path for what should be automated becomes less clear and more industry-specific.● Digital Workforce – Many companies don’t plan for the maintenance of resources required when automation breaks or underlying systems changes.● Technology overhead – one especially large obstacle is the number of automation vendors and the larger-than-life claims some intake 93% of organizations say they are not fully prepared to handle the issues arising out of their automation journey. – Forrester.
4. RPA Effectiveness Test
- The vital role of Robotic Process Automation is to offer improved customer experience and operation excellence by increasing performance, efficiencies, and agility in the process. However, the integration of RPA requires proper planning beforehand to ensure processes are fit for robotic automation. Consider below checklist for ideal automation candidates:● Rules-based and repetitive?● Accesses structured data?● High volumes or fluctuations in volume?● Utilizes a user interface?● Performed by more than 1 FTE?● Stable (not changing often)?● Has business value?The total value of automation goes well beyond financial impact. Consider the below factors when determining ROI:● Optimized operation costs● Reduced cycle time● Increased quality: rework, errors and variance• Total flexibility: timeliness, scalability, seasonality● Reduced penalties: payment interest, government● Greater compliance: onshore, extremely detailed audit logs● Better insights: real-time visibility into work and outcomes● Improved customer experience
5. Are You Ready to Take the next Step
- There are ample opportunities for automation across the organization to improve operational efficiency and provide significant cost savings. Percentage of decision makers realizing at least 15% cost savings across front-, middle- and back-office functions. Some of the industry-leading RPA software vendors are UIPath, Automation Anywhere, BlackLine, Blue Prism and Datamatics. What do you see as the main obstacle in implementing an RPA solution?● Budget or Key stakeholders identification – the key element of RPA adoption is in identifying the stakeholders and make them understand RPA and its benefits, requirements of RPA, so they know what to do and how to support the program objectives. Someone in the organization who fully understands the operations, and can analytically own and define a process.● Buy-in from the stakeholders – Metrics that we are trying to show, optimized operation costs and greater compliance would lead to get a buy-in from the leadership. Do not short cut the development of stakeholder buy-in, change control management, internal communications for alignment with key business units, IT involvement for successful deployment of complex transformations.● Knowledge / skill gap – Make sure IT and Business teams are well educated on RPA initiative, be aware of the tasks at hand and ensure technical teams are well equipped with the usage of the toolset. Often times, integrating RPA into internal company systems could be a tedious task which could require more effort and time than anticipated. So it is very critical to get prepared well in advance to handle the pitfalls.● Standardization of processes – Like any other automation, standardization of processes continues to be a hurdle in expanding technological capabilities. Avoiding processes with no formal processing standard is a key to a successful deployment of RPA. Use qualifying criteria to assess potential processes ripe for automation and efficiency drivers can help determine automation capability.● Selecting a Tool – It is important to pick the right tool at the enterprise level than processes, partners. Tools have evolved relatively quickly, and there are a class real market leaders now proving RPA tools.● Integration with systems – The end state vision is to leverage integrated automation toolsets, command line interfaces and APIs to the creation of server & infrastructure resources, backward compatible upgrades & patches, use of smoke and regression tests to support automated verification. Also, RPA should be able to integrate seamlessly with Legacy systems.● Process mapping and configuration – It is critically important that need to be used as an opportunity to catalyze the change and process that have evolved organically over and over. Organizations should spend more time around process mapping in the earliest stages on modelling, transformations and automation should come second to that. Identify which processes to automate and how the proof of concept can harness digital behavioral change.● Documentation – Understand ways to simplify the scope by identifying the processes that you are currently automating or looking to automate, the main driver for implementing RPA, number of robots that are currently been deployed and department which is responsible for RPA implementation.● Choose the right deployment model – The RPA industry recognizes three deployment models which are centered around bot execution:○ User Desktop – Can interact with human users communicating information bi-directionally○ Shared Server – Intended for large scale background, batch, and parallel processing. Allows the Robot Bot Farm where no human interaction is necessary○ Virtual Desktop – Individual desktop Bots supports some interaction with a human but with latency
6. RPA Implementation Approaches
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) tools can help organizations optimize business efficiency and effectiveness of their operations much faster, improves the accuracy of execution by reducing human interventions and lowers the overall cost. With the use of RPA tools, Organization can use the saved bandwidth towards more useful activities.There are many challenges faced by organizations during RPA implementation such as lack of skilled resources, pace of change, technology overhead. A key to the successful RPA implementation is in finding ways to overcome these obstacles by following a proven approaches like stated below:● Project identification and prioritization: It is very critical to identify a suitable project that qualifies for business process automation, develop the right strategy, define timelines and skilled resource alignment. Prioritize the processes based on the current resource spent, automation efforts and complexity of the solution.● Use Case identification and scoring: Determine the suitable business process for intelligent automation and prioritize these processes based on metrics. Each of the criteria will have its own positive and negative impacts. Based on the derived scoring and assignment criteria, organizations will be able prioritize the processes for automation.● Use Case development: By focusing on business case which is fit for RPA adoption and then deriving the ROI analysis would help organizations build a strong case towards RPA journey. RPA assessment should also include strong governance, leveraging best practices and ensuring the reusability of the components.● RPA development and operations: RPA development involves basis SDLC (system development life cycle) steps such as design, develop, test, deploy and process leaning. Defining process definition documentation, solution design, bot creation and scheduling for different use cases.
7. Getting the Most ROI from RPA
- Whether you are just embarking on an automation journey or your organization is well on its way, below set up capabilities between RPA and non-RPA products would give a guide to maximize the ROI of the RPA program.
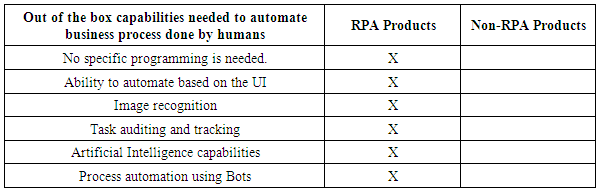
8. Conclusions
- For successful implementation of RPA it cannot be a single functional ownership, instead it must be a more collaborative approach between IT and business. This all stands on the shoulders on fundamentals that should be reminded of in a big complex transformational change, need of a blueprint, need of a plan, change management and education internally, need to come up with a holistic plan of roll-out journey. Organize all the initiatives around true enterprise strategy around optimization, efficiency, audit, compliance for better visibility to create a better customer experience. RPA and automation tools are a component, piece of a hybrid toolset that will get the organization towards the transformation objective. This is a technology that enables the business to achieve greater outcomes and both IT & Business have to work closely together.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML