-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Intelligent Systems
p-ISSN: 2165-8978 e-ISSN: 2165-8994
2019; 9(1): 1-28
doi:10.5923/j.ajis.20190901.01

Proposed Neural Network with FFT Transfer Function to Estimate Henon Dynamical Map
Salah H. Abid, Saad S. Mahmood, Yaseen A. Oraibi
Department of Mathematics, College of Education, AL-Mustansiriyah University, Iraq
Correspondence to: Salah H. Abid, Department of Mathematics, College of Education, AL-Mustansiriyah University, Iraq.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The aim of this paper is to design a feed forward artificial neural network (Ann) to estimate two-dimensional Henon dynamical map by selecting an appropriate network, transfer function and node weights. The proposed network side by side with using Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) as transfer function is used. For different cases of the system, chaotic and noisy, the experimental results of proposed algorithm will compared empirically, by means of the mean square error (MSE) with the results of the same network but with traditional transfer functions, Logsig and Tagsig. The performance of proposed algorithm is best from others in all cases from both sides, speed and accuracy.
Keywords: FFT, Logsig, Tagsig, Feed Forward neural network, Transfer function, Henon map, Logistic noise, Normal noise
Cite this paper: Salah H. Abid, Saad S. Mahmood, Yaseen A. Oraibi, Proposed Neural Network with FFT Transfer Function to Estimate Henon Dynamical Map, American Journal of Intelligent Systems, Vol. 9 No. 1, 2019, pp. 1-28. doi: 10.5923/j.ajis.20190901.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Ann is a simplified mathematical model of the human brain. It can be implemented by both electric elements and computer software. It is a parallel-distributed processor with large numbers of connections; it is an information processing system that has certain performance characters in common with biological neural networks. Ann has been developed as generalizations of mathematical models of human cognition or neural biology, based on the assumptions that:1- Information processing occurs at many simple elements called neurons that are fundamental to the operation of Ann's.2- Signals are passed between neurons over connection links.3- Each connection link has an associated weight which, in a typical neural net, multiplies the signal transmitted.4- Each neuron applies an action function (usually nonlinear) to its net input (sum of weighted input signals) to determine its output signal [15].The units in a network are organized into a given topology by a set of connections, or weights.Ann is characterized by [28] as:1- Architecture: its pattern of connections between the neurons.2- Training Algorithm: its method of determining the weights on the connections.3- Activation function.Ann are often classified as single layer or multilayer. In determining the number of layers, the input units are not counted as a layer, because they perform no computation. Equivalently, the number of layers in the net can be defined to be the number of layers of weighted interconnects links between the slabs of neurons [44].
1.1. Multilayer Feed Forward Architecture [21]
- In a layered neural network the neurons are organized in the form of layers. We have at least two layers: an input and an output layer. The layers between the input and the output layer (if any) are called hidden layers, whose computation nodes are correspondingly called hidden neurons or hidden units. Extra hidden neurons raise the network’s ability to extract higher-order statistics from (input) data.The Ann is said to be fully connected in the sense that every node in each layer of the network is connected to every other node in the adjacent forward layer; otherwise the network is called partially connected. Each layer consists of a certain number of neurons; each neuron is connected to other neurons of the previous layer through adaptable synaptic weights w and biases b.
1.2. Literature Review
- Pan and Duraisamy in 2018 [31] studied the use of feedforward neural networks (FNN) to develop models of non-linear dynamical systems from data. Emphasis is placed on predictions at long times, with limited data availability. Inspired by global stability analysis, and the observation of strong correlation between the local error and the maximal singular value of the Jacobian of the ANN, they introduced Jacobian regularization in the loss function. This regularization suppresses the sensitivity of the prediction to the local error and is shown to improve accuracy and robustness. Comparison between the proposed approach and sparse polynomial regression is presented in numerical examples ranging from simple ODE systems to nonlinear PDE systems including vortex shedding behind a cylinder, and instability-driven buoyant mixing ow. Furthermore, limitations of feedforward neural networks are highlighted, especially when the training data does not include a low dimensional attractor. The need to model dynamical behavior from data is pervasive across science and engineering. Applications are found in diverse fields such as in control systems [41], time series modeling [37], and describing the evolution of coherent structures [12]. While data-driven modeling of dynamical systems can be broadly classified as a special case of system identification [22], it is important to note certain distinguishing qualities: the learning process may be performed off-line, physical systems may involve very high dimensions, and the goal may involve the prediction of long-time behavior from limited training data. Artificial neural networks (ANN) have attracted considerable attention in recent years in domains such as image recognition in computer vision [17, 35] and in control applications [12]. The success of ANNs arises from their ability to effectively learn low-dimensional representations from complex data and in building relationships between features and outputs. Neural networks with a single hidden layer and nonlinear activation function are guaranteed to be able to predict any Borel measurable function to any degree of accuracy on a compact domain [16]. The idea of leveraging neural networks to model dynamical systems has been explored since the 1990s. ANNs are prevalent in the system identification and time series modeling community [19, 26, 27, 33], where the mapping between inputs and outputs is of prime interest. Billings et al. [5] explored connections between neural networks and the nonlinear autoregressive moving average model (NARMAX) with exogenous inputs. It was shown that neural networks with one hidden layer and sigmoid activation function represent an infinite series consisting of polynomials of the input and state units. Elanayar and Shin [13] proposed the approximation of nonlinear stochastic dynamical systems using radial basis feedforward neural networks. Early work using neural networks to forecast multivariate time series of commodity prices [9] demonstrated its ability to model stochastic systems without knowledge of the underlying governing equations. Tsung and Cottrell [42] proposed learning the dynamics in phase space using a feedforward neural network with time-delayed coordinates. Paez and Urbina [29, 30, 43] modeled a nonlinear hardening oscillator using a neural network-based model combined with dimension reduction using canonical variate analysis (CVA). Smaoui [38, 39, 40] pioneered the use of neural networks to predict fluid dynamic systems such as the unstable manifold model for bursting behavior in the 2-D Navier-Stokes and the Kuramoto-Sivashinsky equations. The dimensionality of the original PDE system is reduced by considering a small number of proper orthogonal decomposition (POD) coefficients [4]. Interestingly, similar ideas of using principal component analysis for dimension reduction can be traced back to work in cognitive science by Elman [14]. Elman also showed that knowledge of the intrinsic dimensions of the system can be very helpful in determining the structure of the neural network. However, in the majority of the results [38, 39, 40], the neural network model is only evaluated a few time steps from the training set, which might not be a stringent performance test if longer time predictions are of interest. ANNs have also been applied to chaotic nonlinear systems that are challenging from a data-driven modeling perspective, especially if long time predictions are desired. Instead of minimizing the pointwise prediction error, Bakker et al. [3] satisfied the Diks’criterion in learning the chaotic attractor. Later, Lin et al. [20] demonstrated that even the simplest feedforward neural network for nonlinear chaotic hydrodynamics can show consistency in the time-averaged characteristics, power spectra, and Lyapunov exponent between the measurements and the model. A major difficulty in modeling dynamical systems is the issue of memory. It is known that even for a Markovian system, the corresponding reduced-dimensional system could be non-Markovian [10, 32]. In general, there are two main ways of introducing memory effects in neural networks. First, a simple workaround for feedforward neural networks (FNN) is to introduce time delayed states in the inputs [11]. However, the drawback is that this could potentially lead to an unnecessarily large number of parameters [18]. To mitigate this, Bakker [3] considered following Broomhead and King [6] in reducing the dimension of the delay vector using weighted principal component analysis (PCA). The second approach uses output or hidden units as additional feedback. As an example, Elman’s network [18] is a recurrent neural network (RNN) that incorporates memory in a dynamic fashion. Miyoshi et al. [24] demonstrated that recurrent RBF networks have the ability to reconstruct simple chaotic dynamics. Sato and Nagaya [36] showed that evolutionary algorithms can be used to train recurrent neural networks to capture the Lorenz system. Bailer-Jones et al. [2] used a standard RNN to predict the time derivative in discrete or continuous form for simple dynamical systems; this can be considered an RNN extension to Tsung’s phase space learning [42]. Wang et al. [45] proposed a framework combining POD for dimension reduction and long-short-term memory (LSTM) recurrent neural networks and applied it to a fluid dynamic system.
1.3. Fast Fourier Transform
- The first to propose the techniques that we now call the fast Fourier transform (FFT) for calculating the coefficients in a trigonometric expansion of an asteroid’s orbit in 1805 [8]. However, Fast Fourier transform is an algorithm that calculates the value of the discrete Fourier transform in faster. The speed this algorithm Is due to the fact that it does not calculate the parts that are equal to zero. The algorithm is discovered by James W. Cooley and John W. Tukey who published the algorithm in 1965 [11]As know today
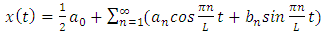 | (1) |
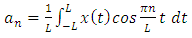 | (2) |
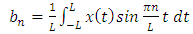 | (3) |
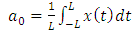 | (4) |
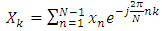 | (5) |
2. Henon Map [23]
- The Henon map is one of the dynamical systems that exhibit chaotic behaviors. The Henon map is defined by the following two equations;
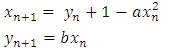 | (6) |
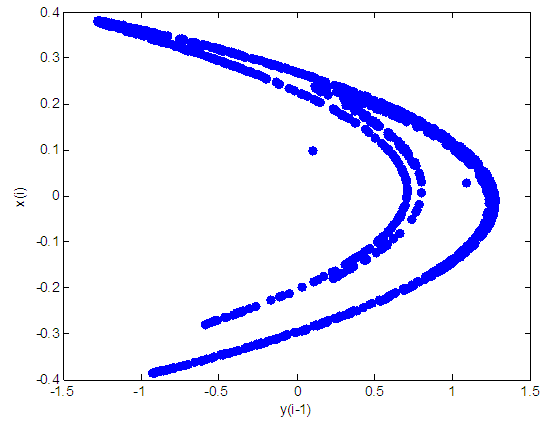 | Figure 1. Henon attractor for a = 1.4 and b = 0.3 |
2.1. Henon Map Solution
- In this section we will explain how this approach can be used to find the approximate solution of the Henon map that is stated in equation (6) and H(x) is the solution to be computed. Let yt(x, p) denotes a trial solution with adjustable parameters p.In the proposed approach, the trial solution yt employs a FFNN and the parameters p corresponding to the weights and biases of the neural architecture. We choose a form for the trial function yt(x) such that yt(x,p) = N(x, p) where N(x, p) is a single-output FFNN with parameters (weights) p and n input units fed with the input vector x.
2.2. Computation of the Gradient
- The error corresponding to each input vector xi is the value E (xi) which has to force near zero. Computation of this error value involves not only the FFNN output but also the derivatives of the output with respect to any of its inputs. Therefore, for computation the gradient of the error with respect to the network weights, consider a multilayer FFNN with n input units (where n is the dimensions of the domain), two hidden layer with H sigmoid units, q hidden layer and a linear output unit.For a given input vector x (x1, x2, …, xn ) the output of the FFNN is:
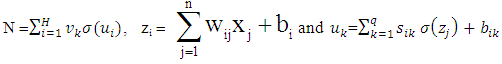 Where,wij denotes the weight connecting the input unit j to the hidden unit i
Where,wij denotes the weight connecting the input unit j to the hidden unit i 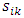 denotes the weight connecting the hidden unit i to the hidden unit kvk denotes the weight connecting the hidden unit k to the out put unit,bi denotes the bias of hidden unit i,bik denotes the bias of hidden unit i to the hidden unit k, andσ is the transfer functionThe gradient of suggested FFNN, with respect to the coefficients of the FFNN can be computed as:
denotes the weight connecting the hidden unit i to the hidden unit kvk denotes the weight connecting the hidden unit k to the out put unit,bi denotes the bias of hidden unit i,bik denotes the bias of hidden unit i to the hidden unit k, andσ is the transfer functionThe gradient of suggested FFNN, with respect to the coefficients of the FFNN can be computed as: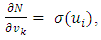 | (7) |
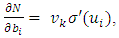 | (8) |
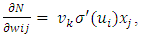 | (9) |
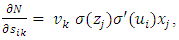 | (10) |
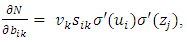 | (11) |
3. Suggested Network
- It is well known that a multilayer FFNN consist with one hidden layer can approximate any function to any accuracy [25], but dynamical maps they have more completed behavior than other functions, thus, we suggest FFNN contains two hidden layer, one input and one output to estimate a solution for dynamic maps.The suggested network divided the inputs in to two parts 60% for training and 40% for testing. The error quantity to be minimized is given by:
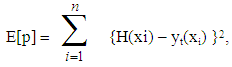 | (12) |
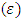 - performance function (MSE)Step 4: calculations in each node in the first hidden layer.In each node in hidden layer, computing the sum of the product of weights and inputs and adding the result to the bias.Step 5: compute the output of each node for the first hidden layer.Take the active function for sum value in step4, then its output is sent to the second hidden layer as input.Step 6: calculations in each node in the second layer.In each node in second hidden layer, computing the sum of the product of weights and inputs and adding the result to the bias.Step 7: compute the output of each node for the second hidden layer.Take the active function for sum value in step6, then its output is sent to the output layer as input.Step 8: calculations in output layer.There is only one neuron (node) in the output layer. The node sum is the product of weights by inputs.Step 9: compute the output of node in output layerThe value of active function for node output is also considered as the output of overall network.Step 10: compute the mean square error (MSE).The mean square error is computed as follows
- performance function (MSE)Step 4: calculations in each node in the first hidden layer.In each node in hidden layer, computing the sum of the product of weights and inputs and adding the result to the bias.Step 5: compute the output of each node for the first hidden layer.Take the active function for sum value in step4, then its output is sent to the second hidden layer as input.Step 6: calculations in each node in the second layer.In each node in second hidden layer, computing the sum of the product of weights and inputs and adding the result to the bias.Step 7: compute the output of each node for the second hidden layer.Take the active function for sum value in step6, then its output is sent to the output layer as input.Step 8: calculations in output layer.There is only one neuron (node) in the output layer. The node sum is the product of weights by inputs.Step 9: compute the output of node in output layerThe value of active function for node output is also considered as the output of overall network.Step 10: compute the mean square error (MSE).The mean square error is computed as follows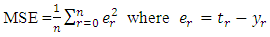 the MSE is a measure of performance.Step 11: The checking.When
the MSE is a measure of performance.Step 11: The checking.When 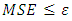 such that
such that 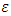 is small value close to zero, then stop the training and the bias and weights are sent. Otherwise training process goes to the next step.Step 12: when select the training rule, the low for update weights and bias between the hidden layer and the output layer are calculatedStep 13: the update weights and bias in output layer.At end for each iteration, the weights and bias are updating as follows:
is small value close to zero, then stop the training and the bias and weights are sent. Otherwise training process goes to the next step.Step 12: when select the training rule, the low for update weights and bias between the hidden layer and the output layer are calculatedStep 13: the update weights and bias in output layer.At end for each iteration, the weights and bias are updating as follows: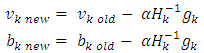 When (new) means the current iteration and (old) means the previous iteration,
When (new) means the current iteration and (old) means the previous iteration, 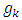 represent the gradient for weights and bias,
represent the gradient for weights and bias, 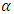 is the parameter selected to minimize the performance function along the search direction,
is the parameter selected to minimize the performance function along the search direction, 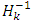 represent the invers hessian matrix, v is the weight in the output layer and b is the bias.Step 14: the update of weights and bias in the first hidden layer.Each hidden node in the first hidden layer updates the weights and bias as follow:
represent the invers hessian matrix, v is the weight in the output layer and b is the bias.Step 14: the update of weights and bias in the first hidden layer.Each hidden node in the first hidden layer updates the weights and bias as follow: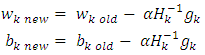 Where w is the weight of hidden layer and b is the bias.Step 15: the update of weights and bias in the second hidden layer as follow.
Where w is the weight of hidden layer and b is the bias.Step 15: the update of weights and bias in the second hidden layer as follow.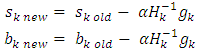 Where s is the weight of hidden layer and b is the bias.Step 16: return to step2 for next iteration.Figure 2 shows the flowchart for training algorithm with BFGS.
Where s is the weight of hidden layer and b is the bias.Step 16: return to step2 for next iteration.Figure 2 shows the flowchart for training algorithm with BFGS.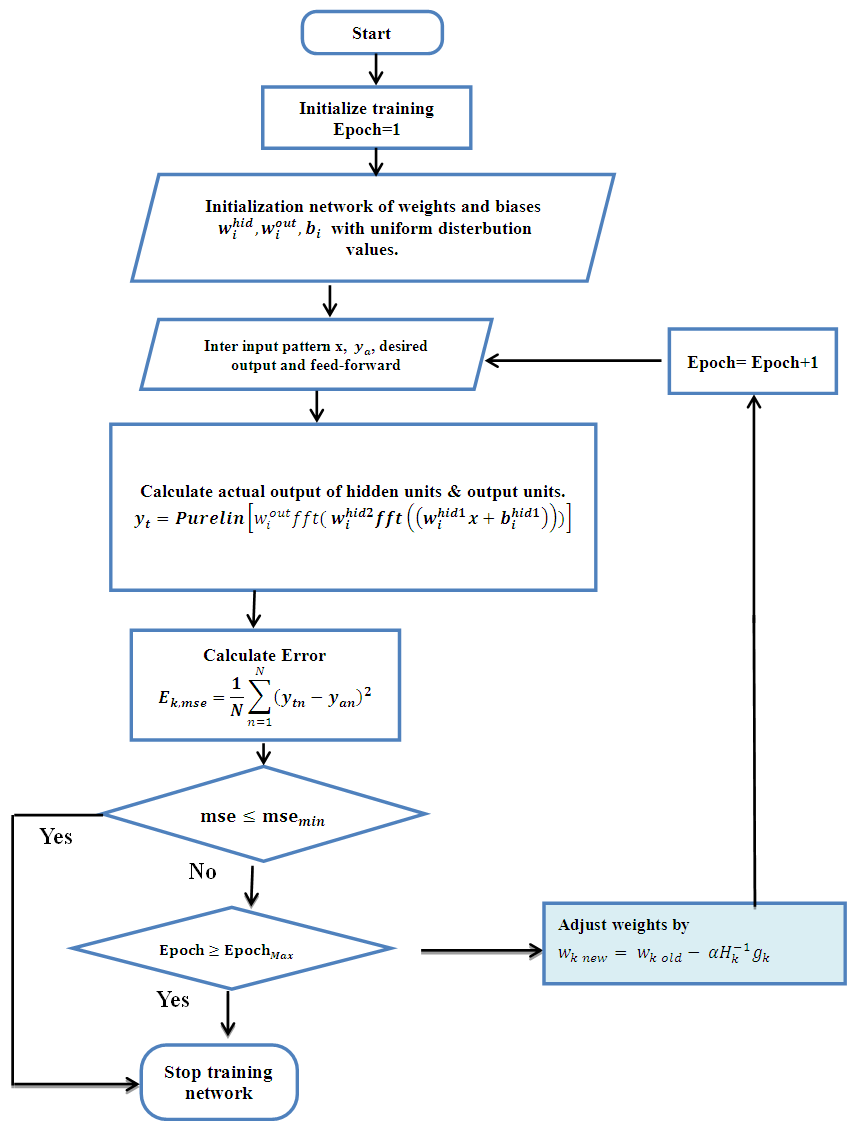 | Figure 2. Flowchart for training algorithm with BFGS |
4. Description of Training Process for Henon Map
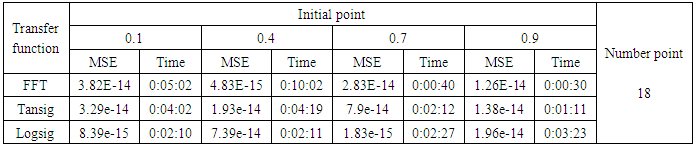
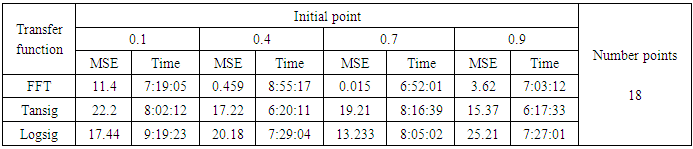
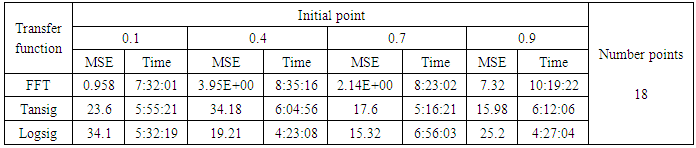
- We will train the case when the Henon map is chaotic when a=1.4 and b= 0.3 and train the input data (x and y ) separately using the proposed FFNNs with one input, one liner output and two hidden layers and we train this case with three types of transfer functions Tansig, logsig, and FFT.Table (1) contains the results. Figures from (3) to (14) show the Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with different situations.The weighted MSE is used as performance function according to x and y performance function weights.
|
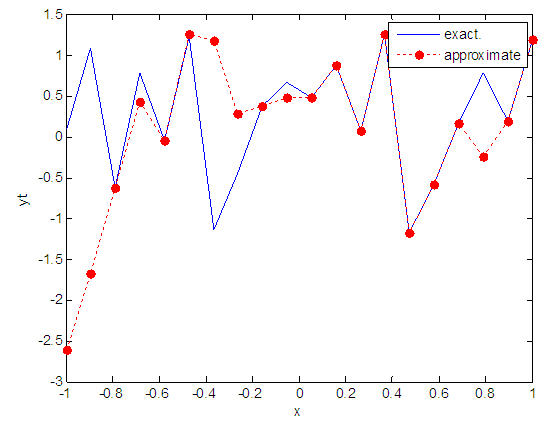 | Figure 3. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with initial x=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
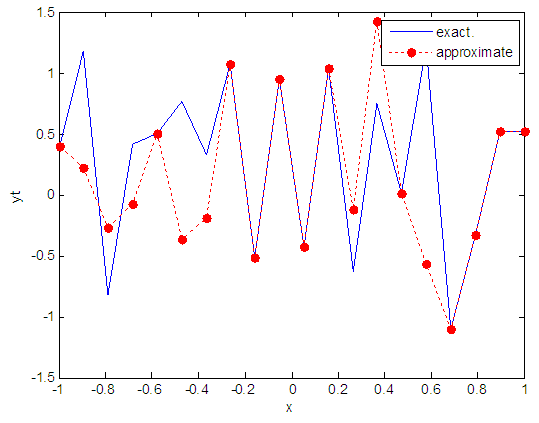 | Figure 4. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with initial x=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
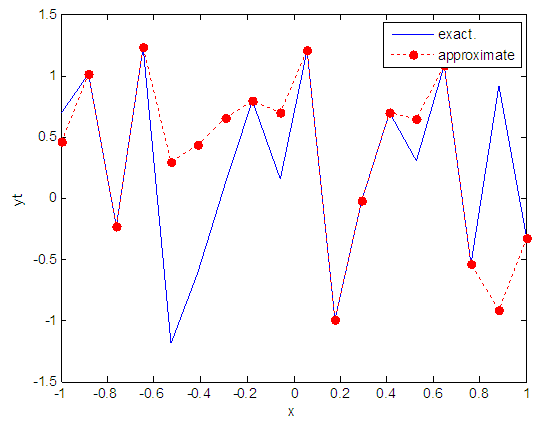 | Figure 5. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with initial x=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
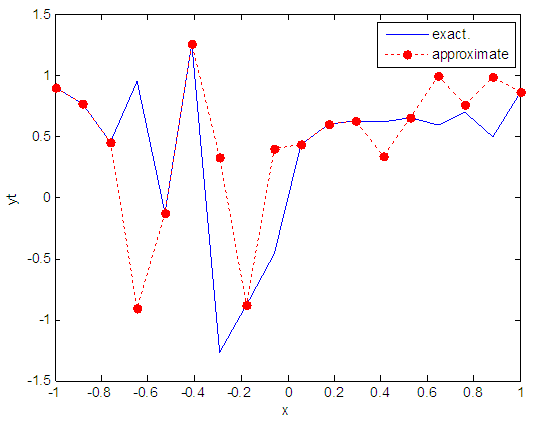 | Figure 6. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with initial x=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
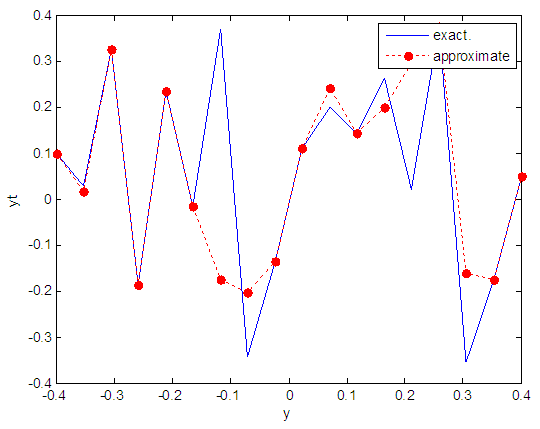 | Figure 7. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with initial y=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
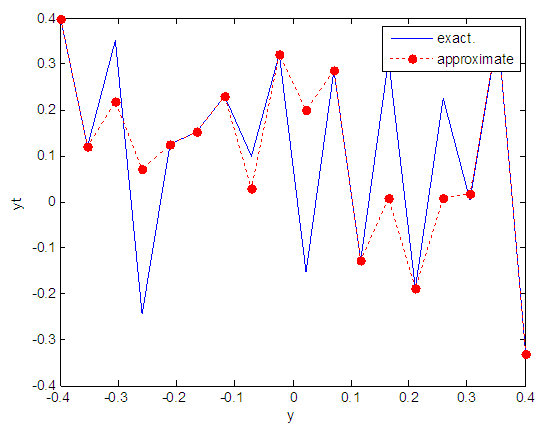 | Figure 8. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with initial y=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
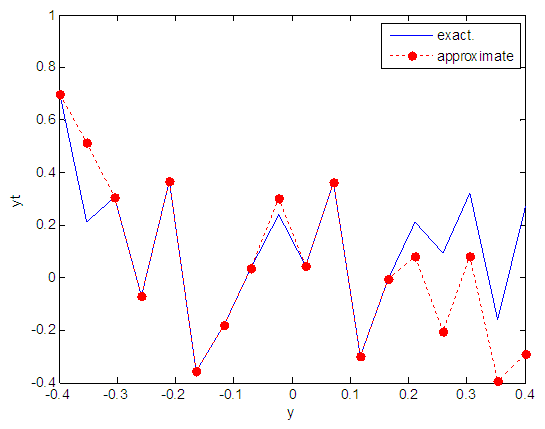 | Figure 9. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with initial y=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
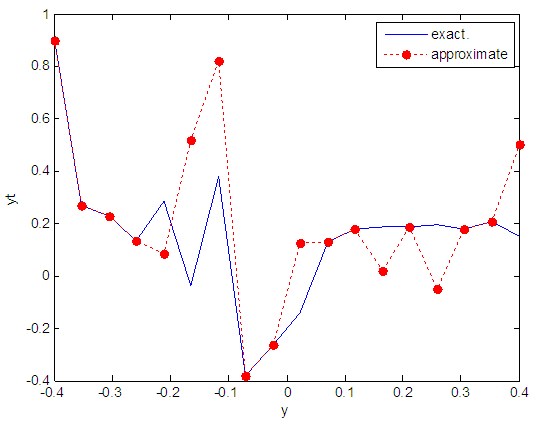 | Figure 10. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with initial y=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
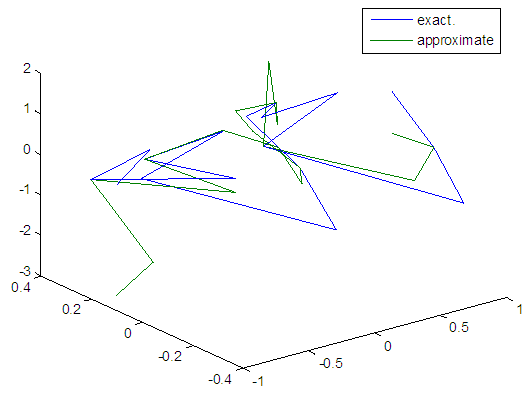 | Figure 11. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with initial x=0.1 & y=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
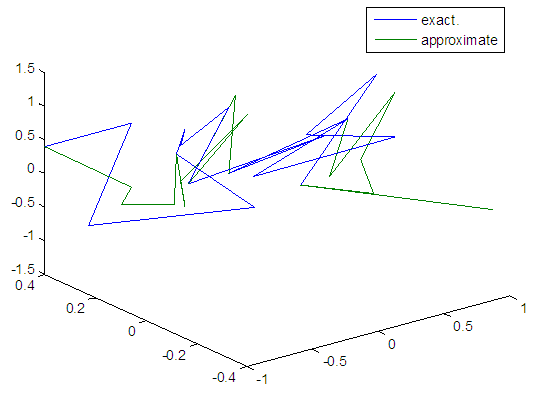 | Figure 12. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with initial x=0.4& y=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
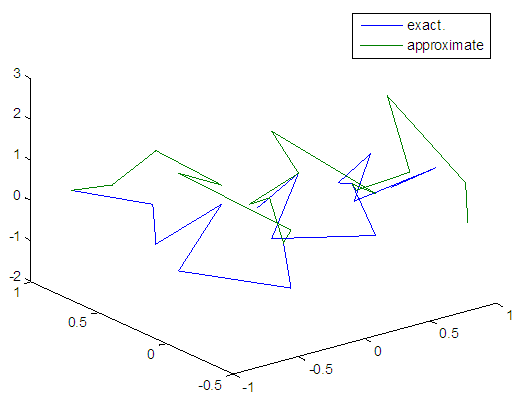 | Figure 13. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with initial x=0.7& y=0.7 using FFT transfer Function |
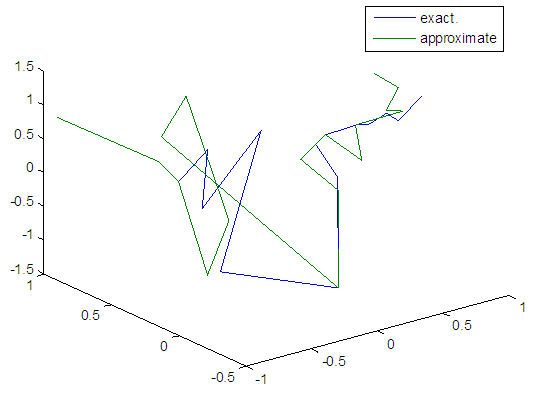 | Figure 14. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with initial x=0.9 & y=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
4.1. Results Discussion
- The experimental results from the above table and figures show that, show that the logsig, tansig and FFT transfer functions side by side with FFNN, have a very good performance when Henon map is chaotic. The use FFT transfer function is faster than logsig, tansig to get results when initial points 0.1 and 0.4.
5. Description of Training Process for Henon Map with Noise
- Here we train the normal and logistic noisy data of Henon map by using the suggested network with tansig, logsig and FFT transfer functions. It is suitable to choose the maximum number of epochs to reach high performance. It is worth to mention that the run size is k=1000.
5.1. Normal Distribution [34]
- Let x be a normally distributed random variable with mean
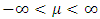 and variance
and variance 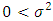 , where
, where 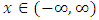 with probability density function and cumulative distribution function are respectively,
with probability density function and cumulative distribution function are respectively,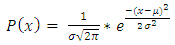 | (13) |
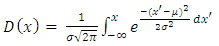 | (14) |
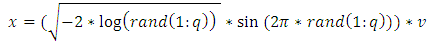 | (15) |
5.2. Logistic Distribution [34]
- Let x be a Logistic distributed random variable with parameters
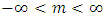 and
and 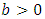 , where
, where 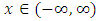 with probability density function and cumulative distribution function are respectively,
with probability density function and cumulative distribution function are respectively,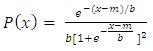 | (16) |
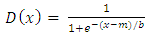 | (17) |
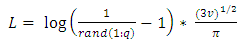 | (18) |
5.3. Training the Case with Normal Noise
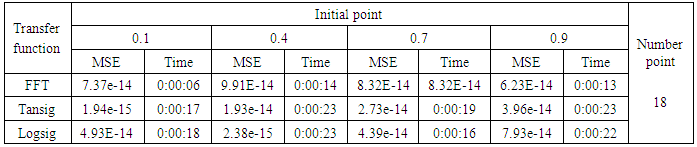
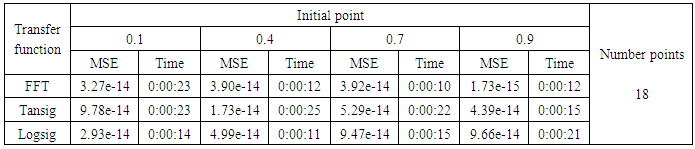
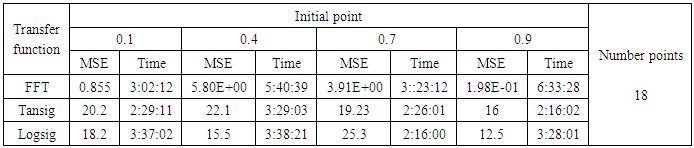
- The training process is conducted with variances 0.05, 0.5, 40 and 60. Tables from (2) to (5) contain the results. Figures from (15) to (62) show the Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with different situation.
|
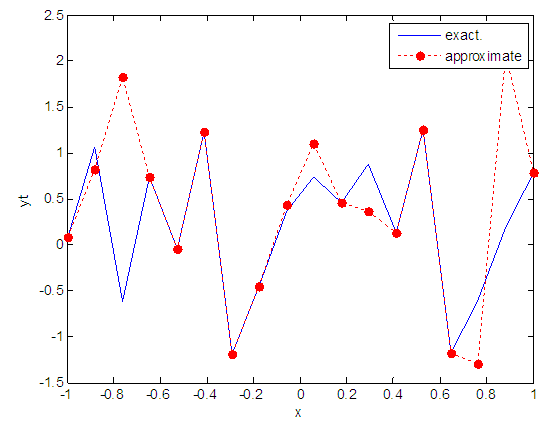 | Figure 15. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.05) and initial x=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
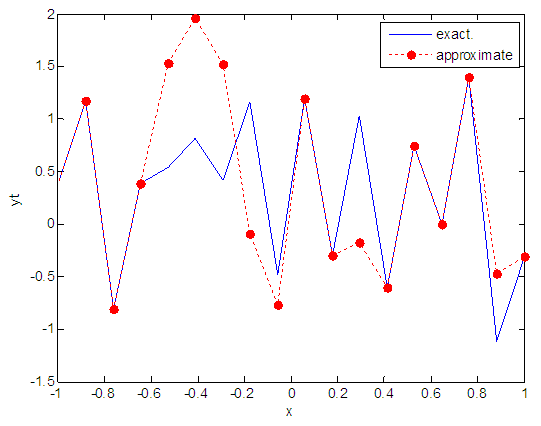 | Figure 16. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.05) and initial x=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
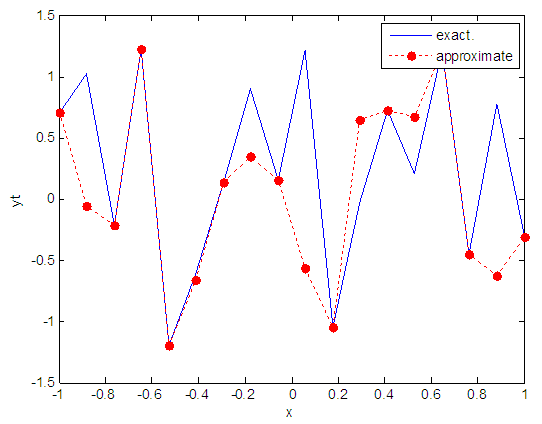 | Figure 17. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.05) and initial x=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
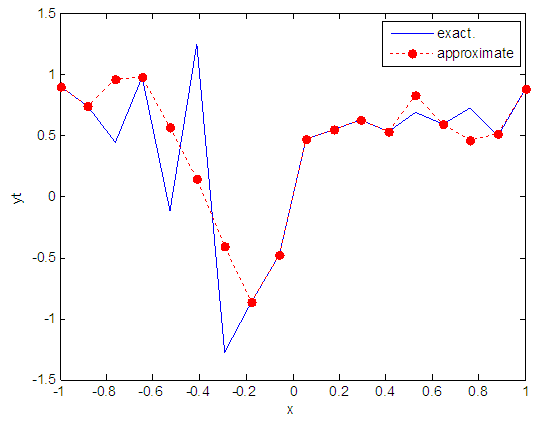 | Figure 18. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.05) and initial x=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
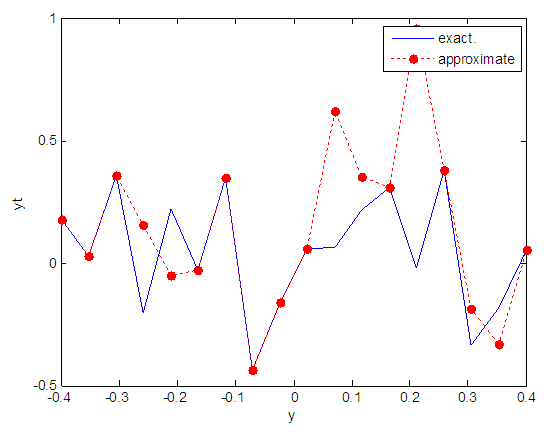 | Figure 19. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.05) and initial y=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
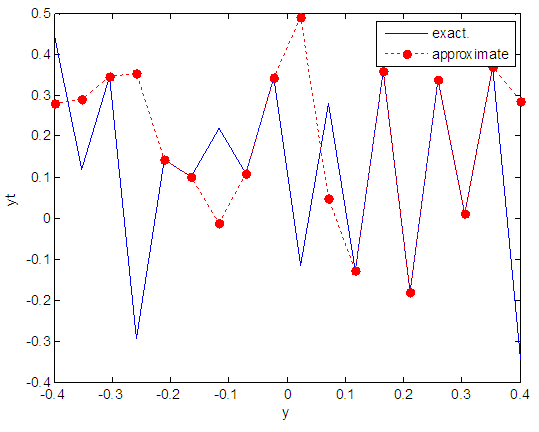 | Figure 20. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.05) and initial y=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
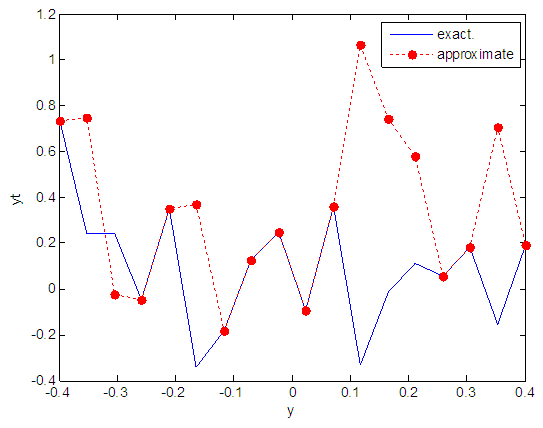 | Figure 21. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.05) and initial y=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
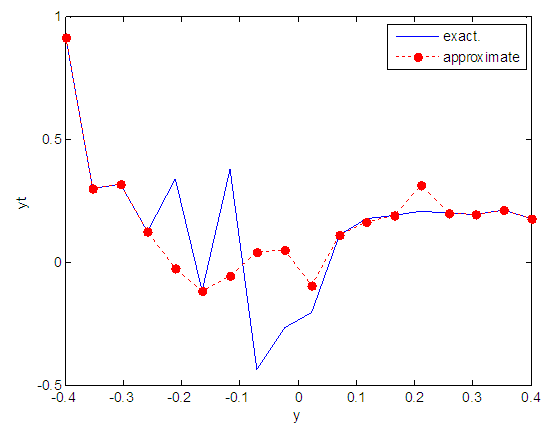 | Figure 22. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.05) and initial y=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
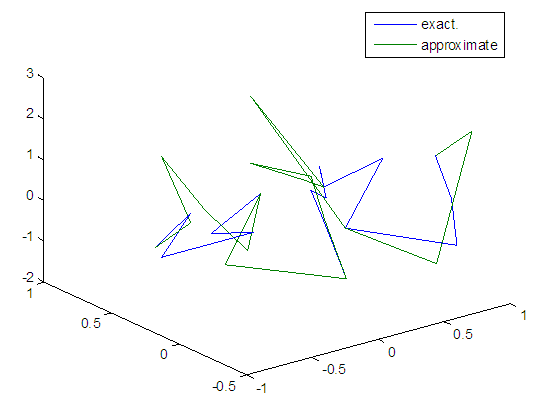 | Figure 23. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.05) and initial x=0.1 & y=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
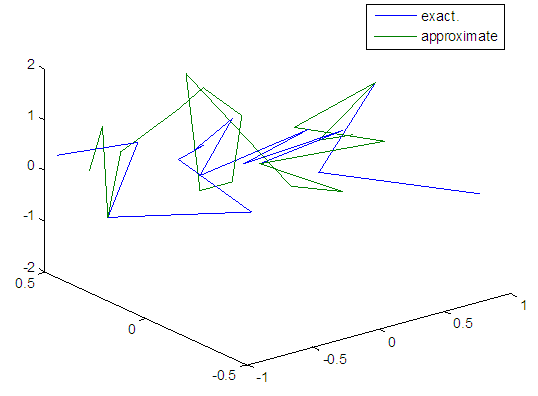 | Figure 24. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.05) and initial x=0.4 & y=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
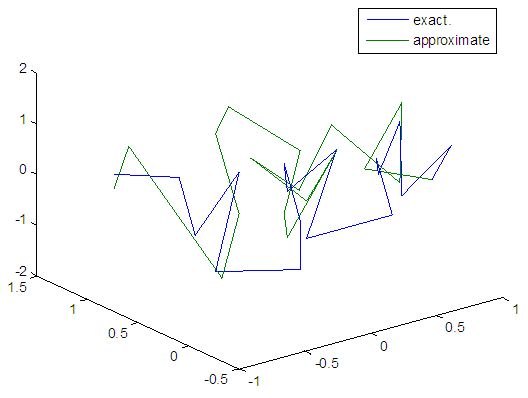 | Figure 25. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.05) and initial x=0.7 & y=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
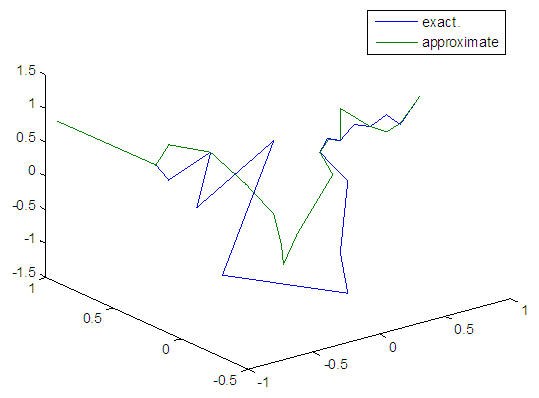 | Figure 26. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.05) and initial x=0.9 & y=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
|
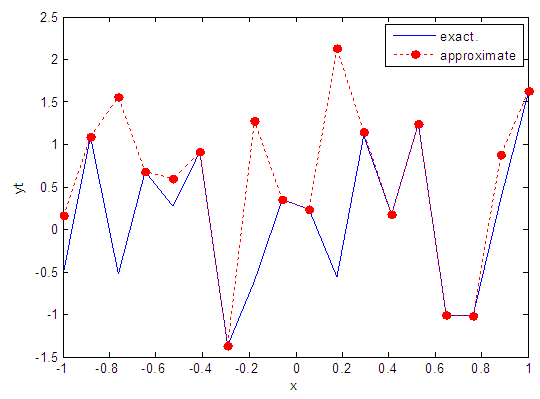 | Figure 27. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.5) and initial x=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
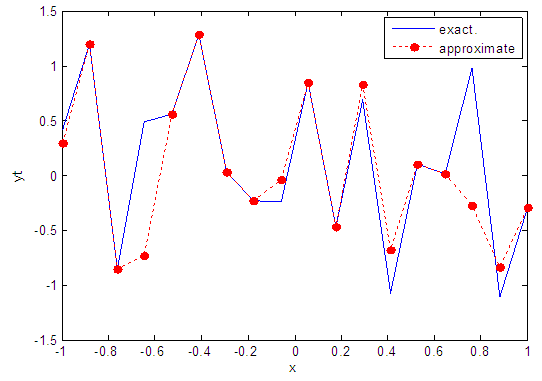 | Figure 28. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.5) and initial x=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
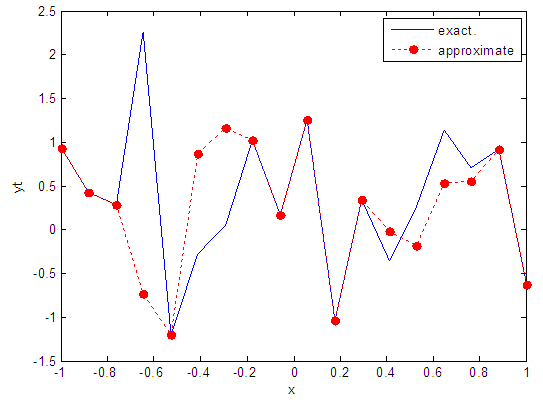 | Figure 29. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.5) and initial x=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
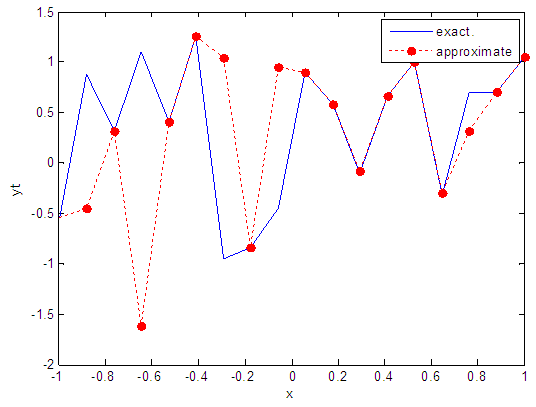 | Figure 30. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.5) and initial x=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
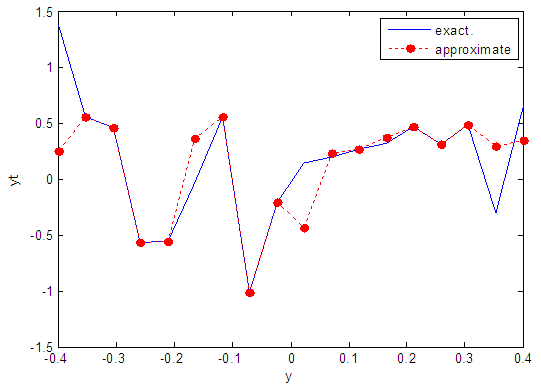 | Figure 31. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.5) and initial y=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
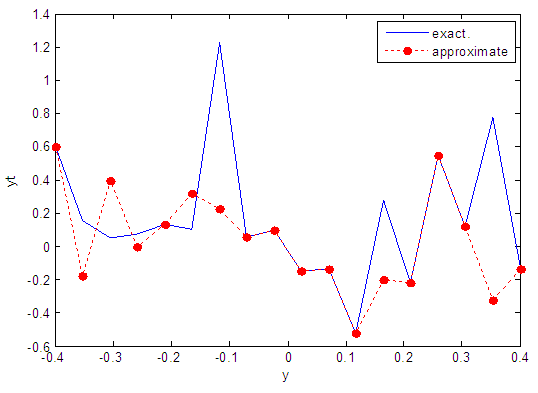 | Figure 32. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.5) and initial y=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
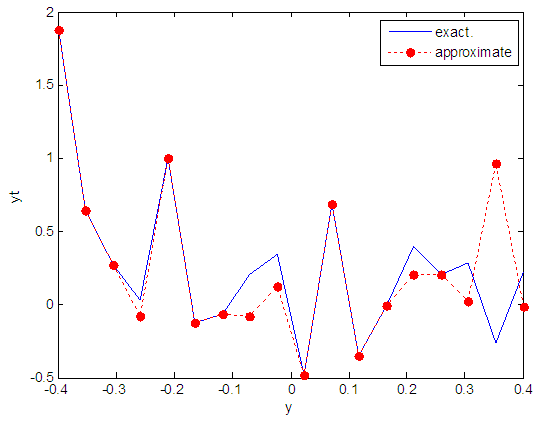 | Figure 33. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.5) and initial y=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
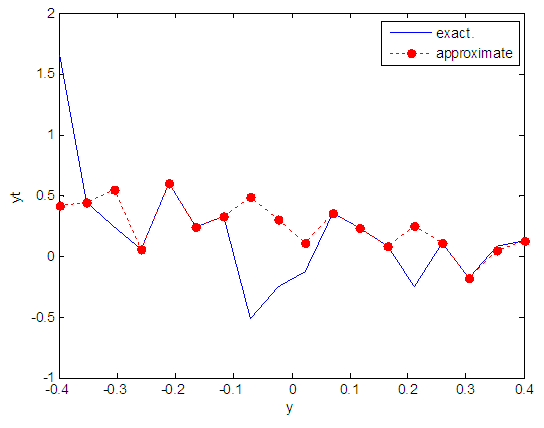 | Figure 34. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.5) and initial y=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
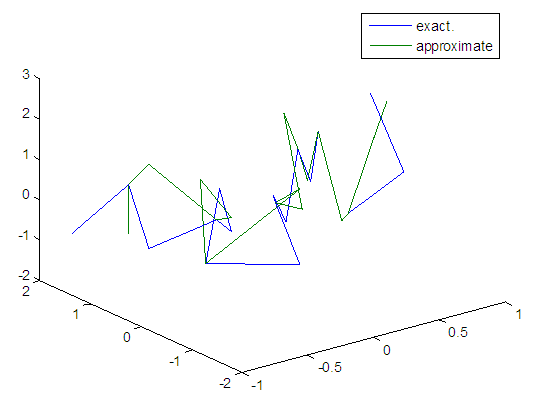 | Figure 35. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.5) and initial x=0.1 & y=0.1using FFT transfer function |
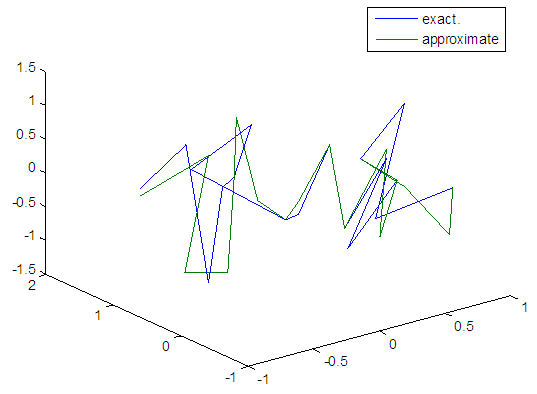 | Figure 36. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.5) and initial x=0.4 & y=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
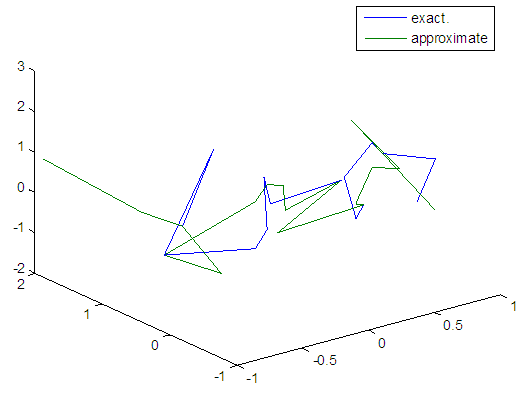 | Figure 37. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.5) and initial x=0.7 & y=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
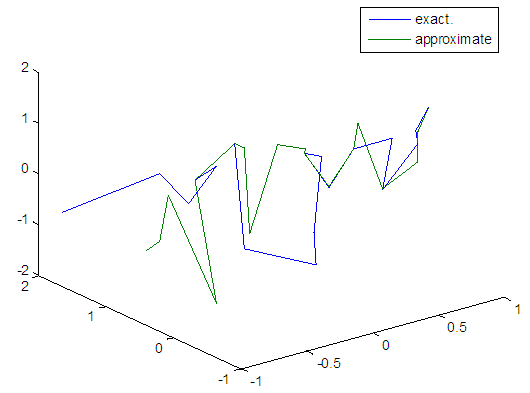 | Figure 38. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=0.5) and initial x=0.9 & y=0.9using FFT transfer function |
|
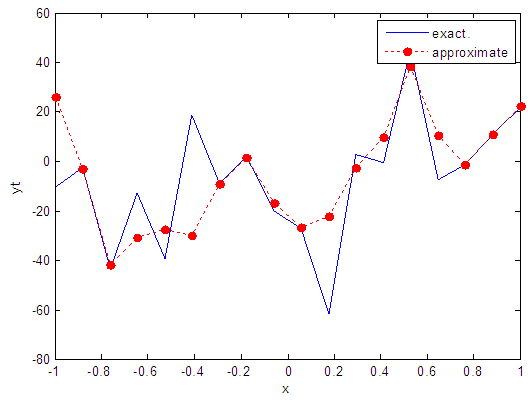 | Figure 39. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=40) and initial x=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
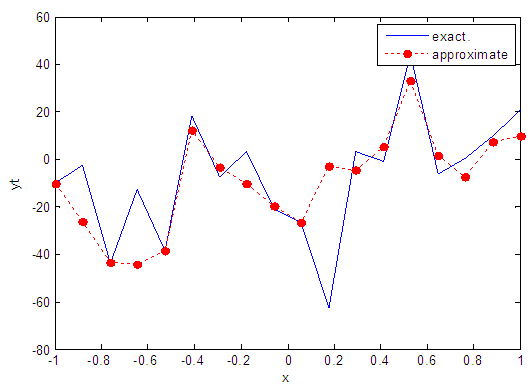 | Figure 40. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=40) and initial x=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
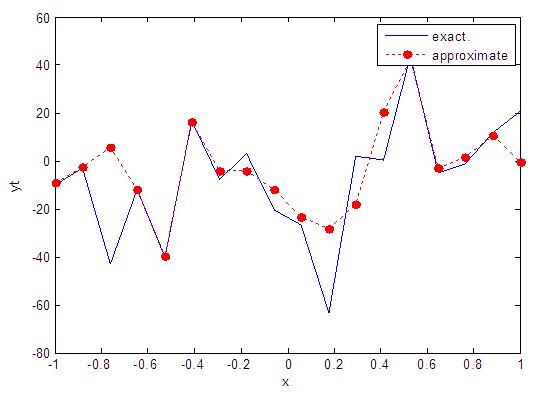 | Figure 41. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=40) and initial x=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
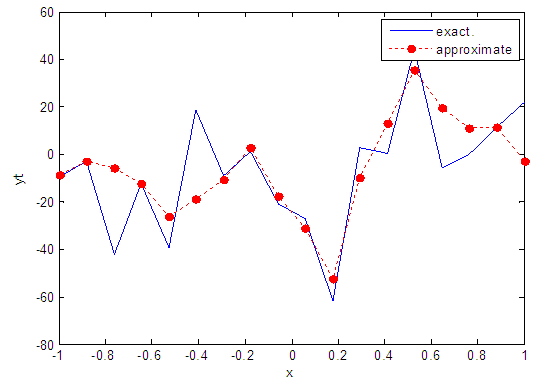 | Figure 42. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=40) and initial x=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
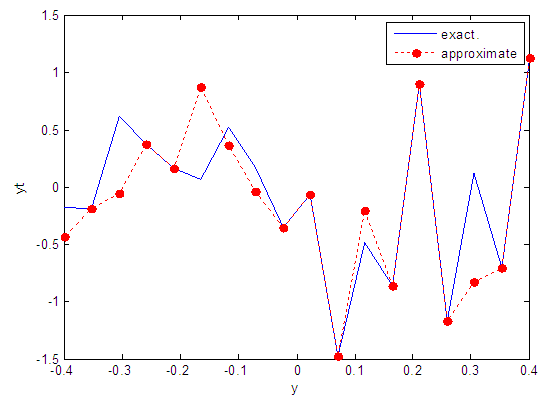 | Figure 43. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=40) and initial y=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
 | Figure 44. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=40) and initial y=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
 | Figure 45. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=40) and initial y=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
 | Figure 46. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=40) and initial y=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
 | Figure 47. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=40) and initial x=0.1 & y=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
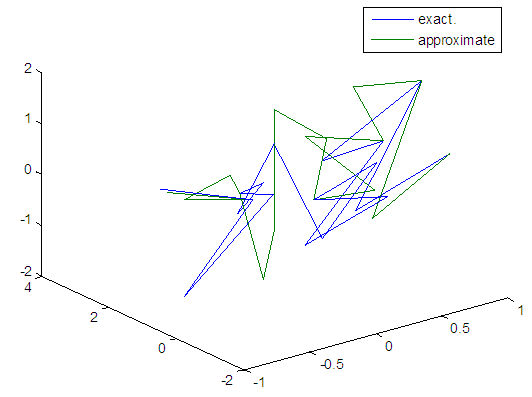 | Figure 48. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=40) and initial x=0.4 & y=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
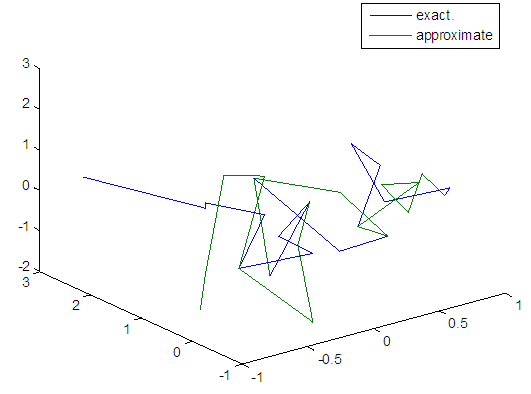 | Figure 49. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=40) and initial x=0.7 & y=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
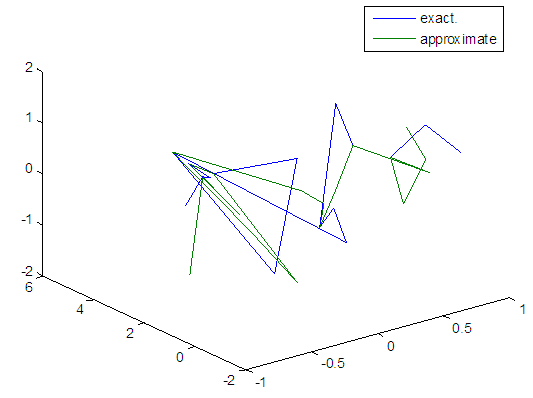 | Figure 50. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=40) and initial x=0.9 & y=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
|
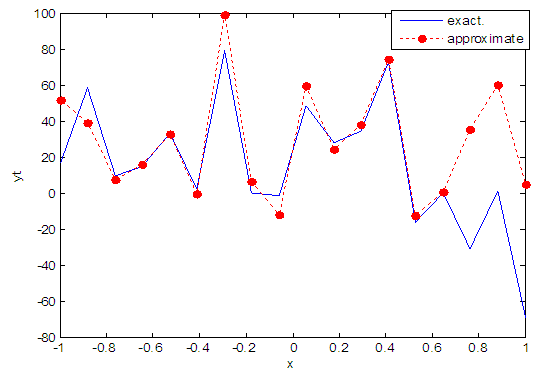 | Figure 51. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=60) and initial x=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
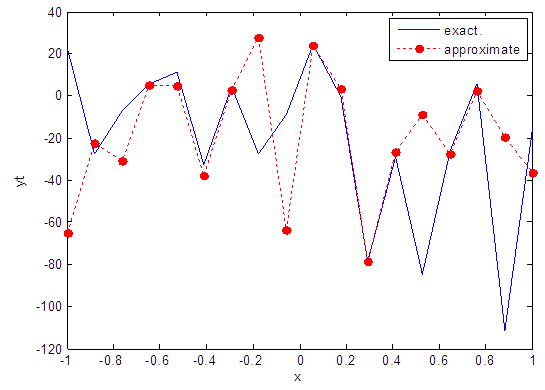 | Figure 52. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=60) and initial x=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
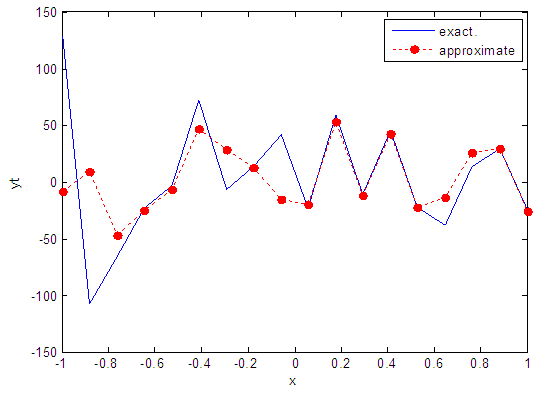 | Figure 53. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=60) and initial x=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
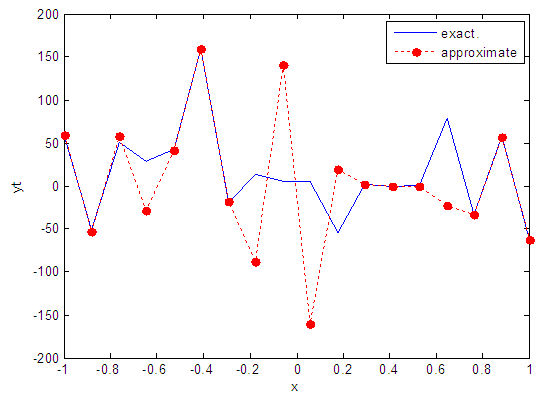 | Figure 54. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=60) and initial x=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
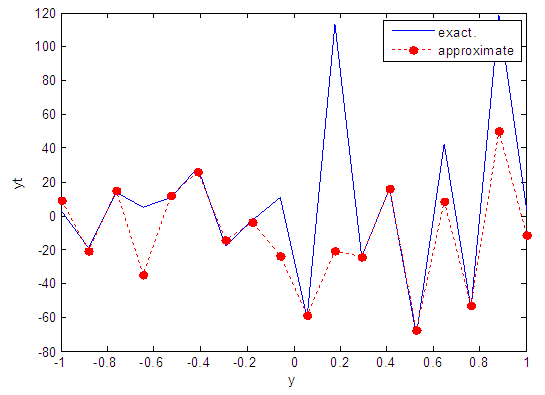 | Figure 55. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=60) and initial y=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
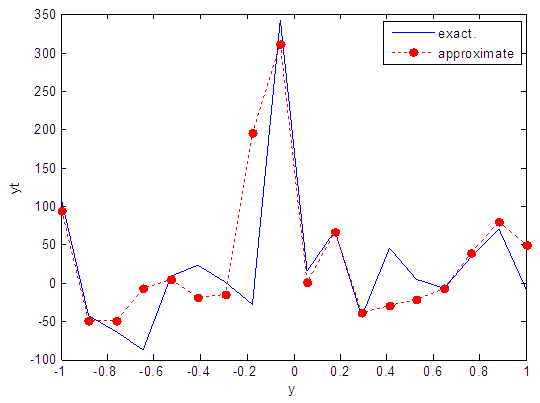 | Figure 56. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=60) and initial y=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
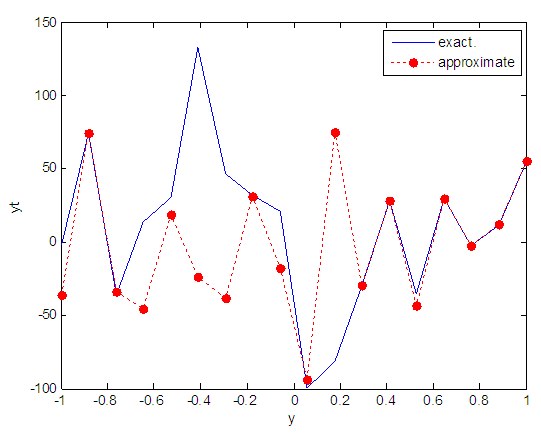 | Figure 57. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=60) and initial y=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
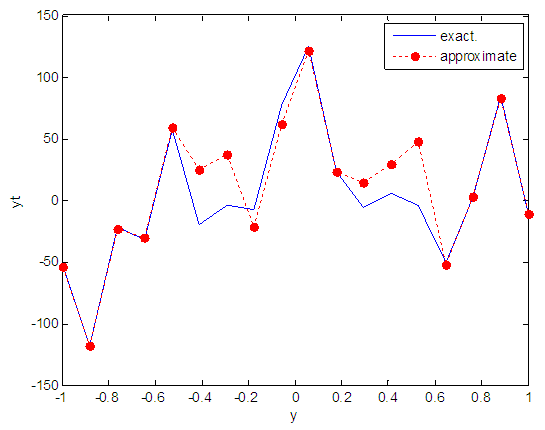 | Figure 58. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=60) and initial y=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
 | Figure 59. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=60) and initial x=0.1 & y=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
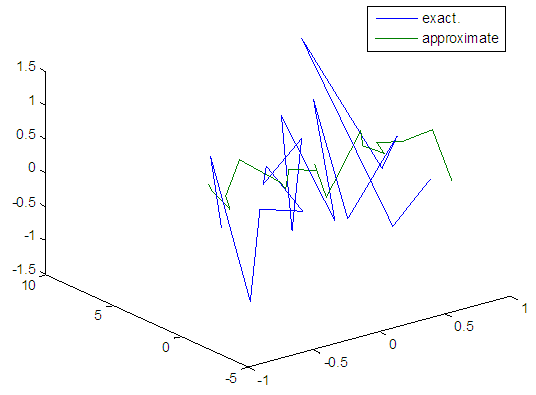 | Figure 60. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=60) and initial x=0.4 & y=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
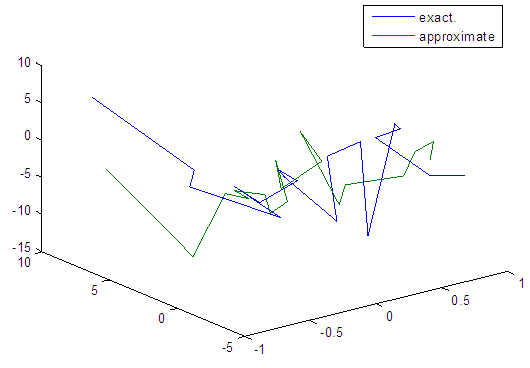 | Figure 61. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=60) and initial x=0.7 & y=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
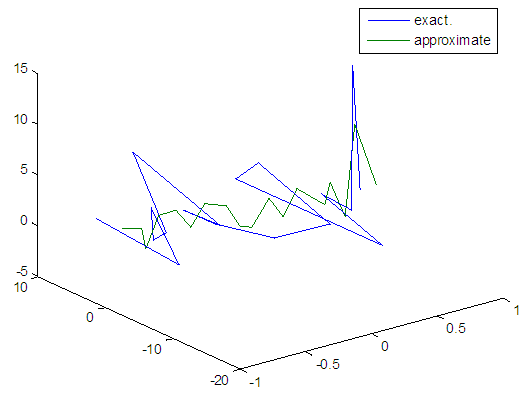 | Figure 62. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with normal noise (v=60) and initial x=0.9 & y=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
5.4. Training with Logistic Noise
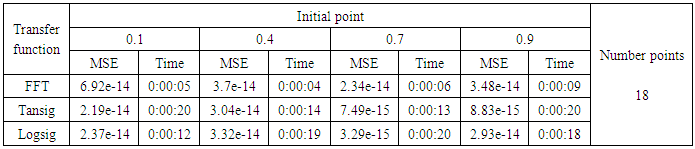
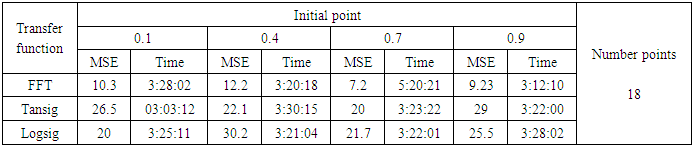
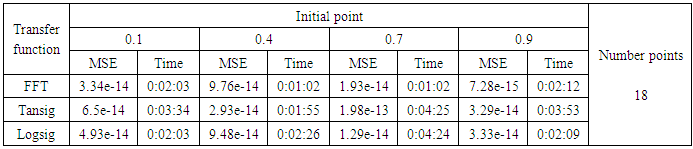
- The training process is conducted with variances 0.05, 0.5, 40 and 60.Tables from (6) to (9) contain the results. Figures from (63) to (110) show the Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with different situation.
|
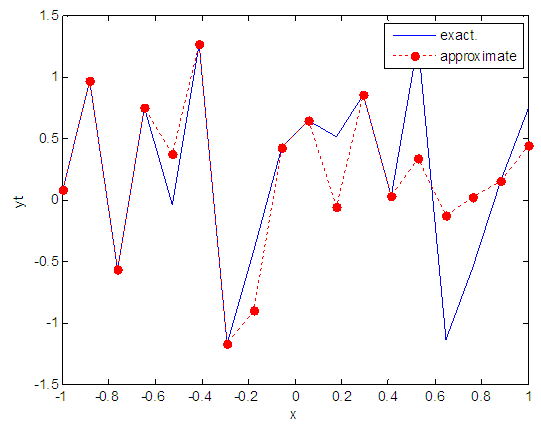 | Figure 63. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.05) and initial x=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
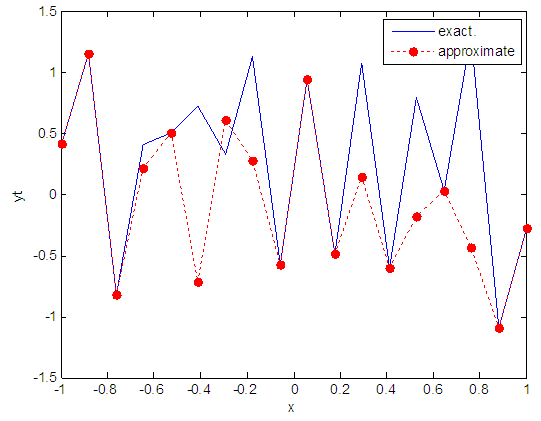 | Figure 64. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.05) and initial x=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
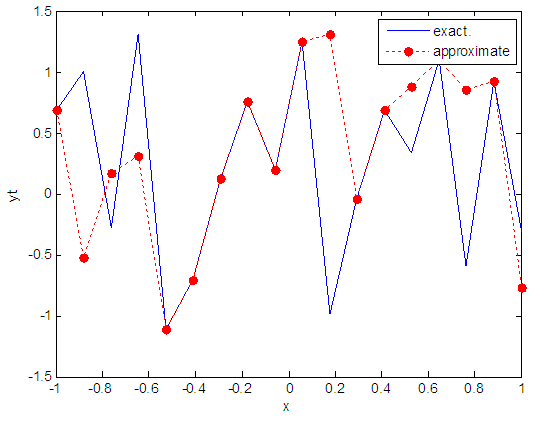 | Figure 65. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.05) and initial x=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
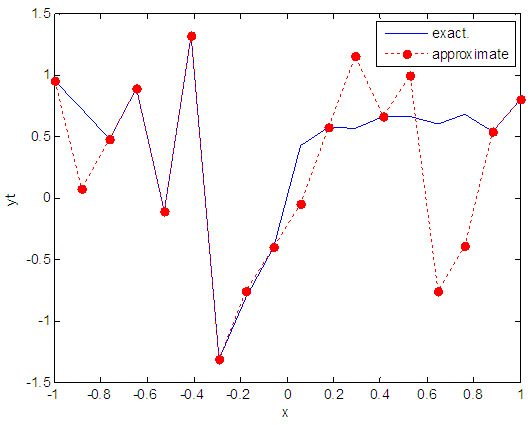 | Figure 66. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.05) and initial x=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
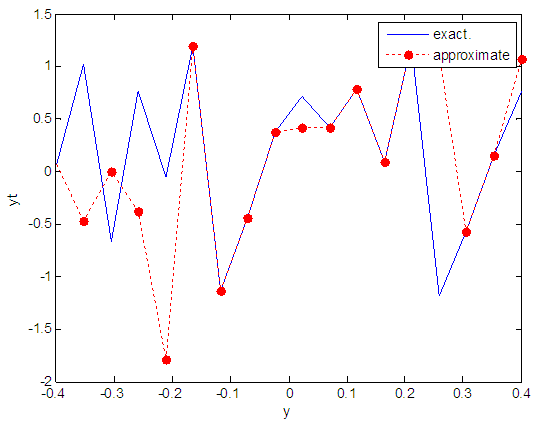 | Figure 67. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.05) and initial y=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
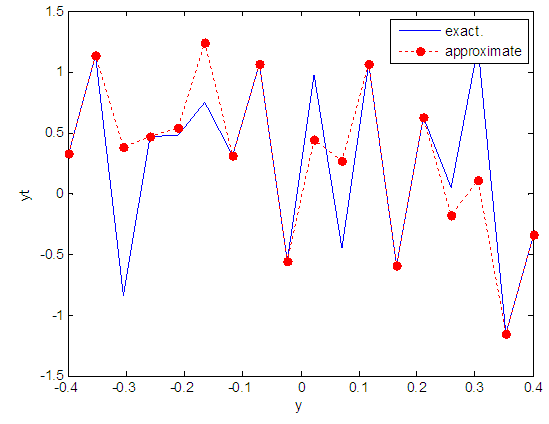 | Figure 68. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.05) and initial y=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
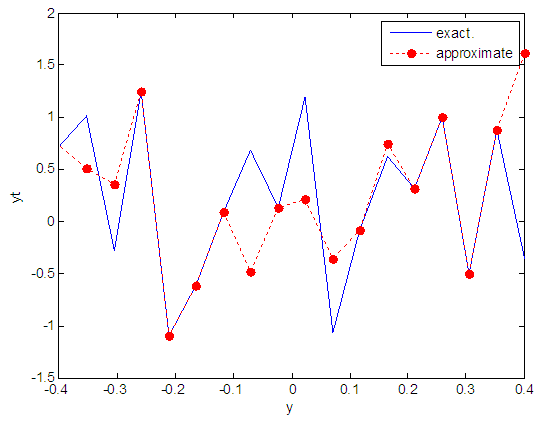 | Figure 69. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.05) and initial y=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
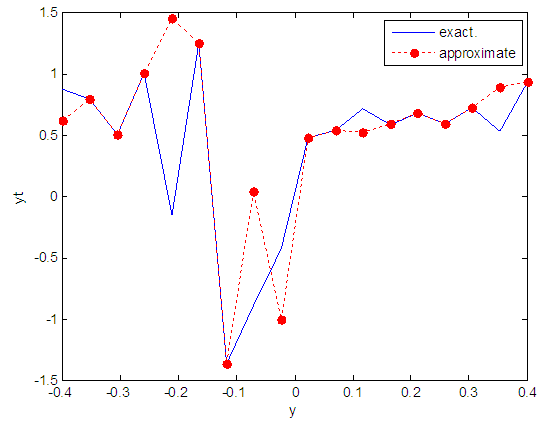 | Figure 70. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.05) and initial y=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
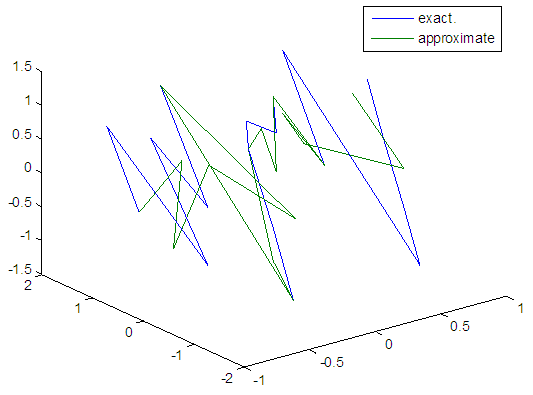 | Figure 71. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.05) and initial=0.1 & y=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
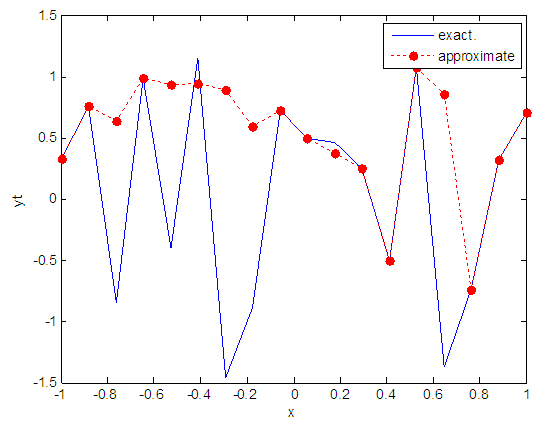
 | Figure 72. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.05) and initial=0.4 & y=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
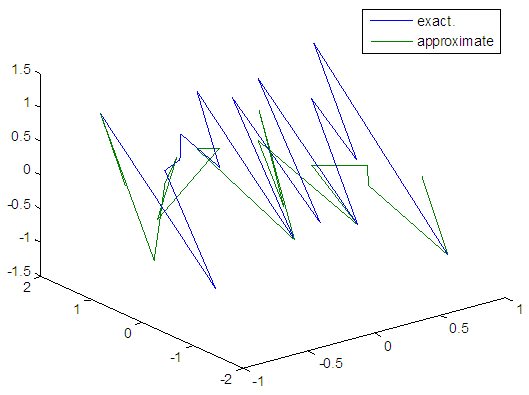
 | Figure 73. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.05) and initial=0.7 & y=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
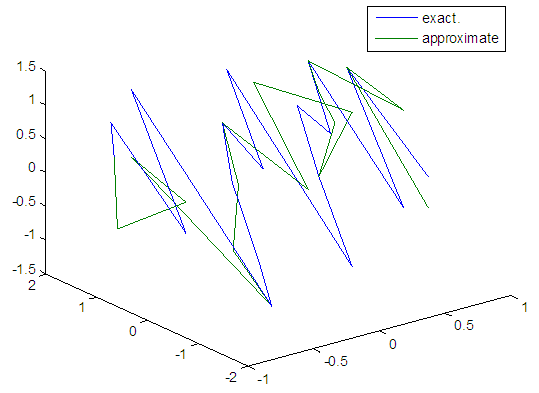
 | Figure 74. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.05) and initial=0.9 & y=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
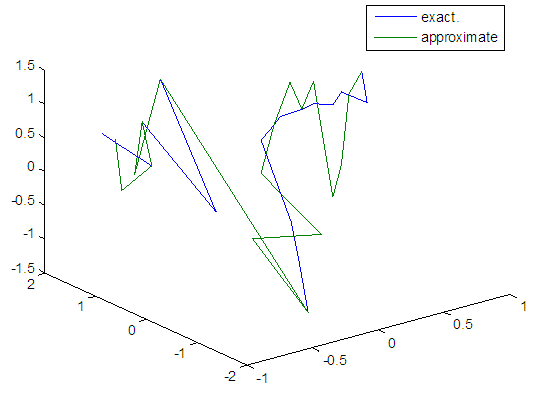
|
 | Figure 75. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.5) and initial x=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
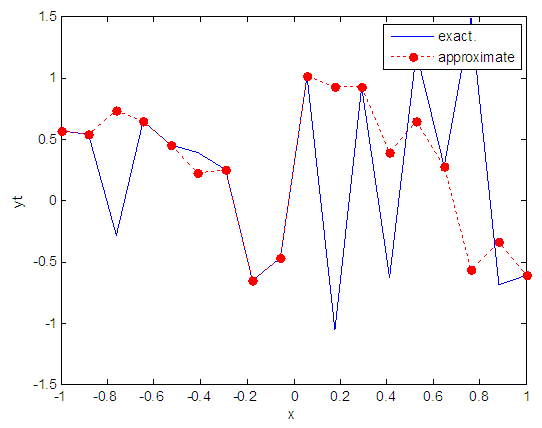 | Figure 76. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.5) and initial x=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
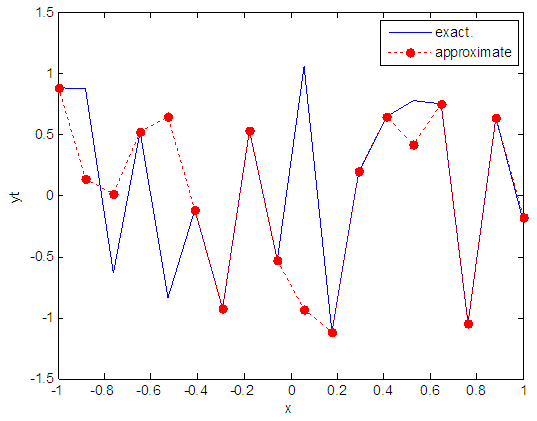 | Figure 77. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.5) and initial x=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
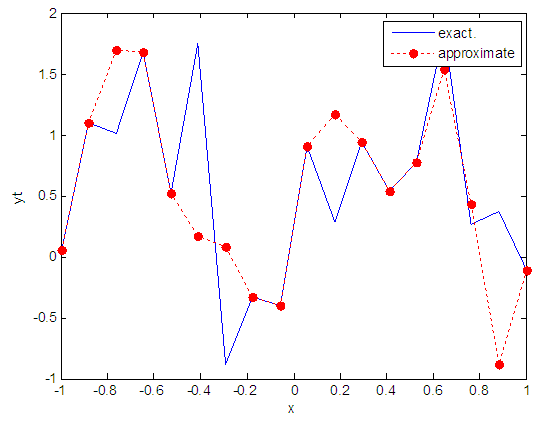 | Figure 78. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.5) and initial x=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
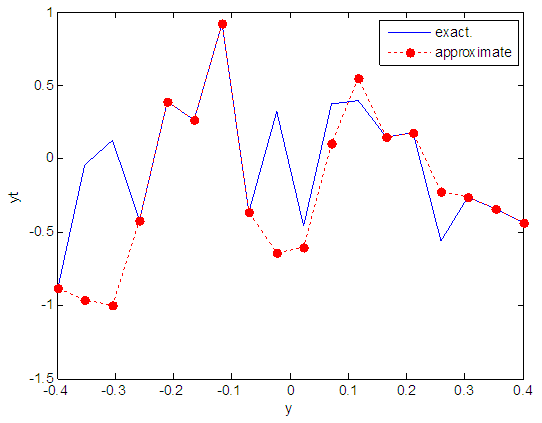 | Figure 79. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.5) and initial y=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
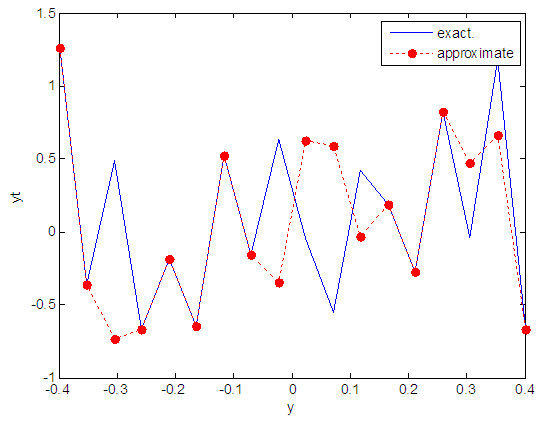 | Figure 80. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.5) and initial y=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
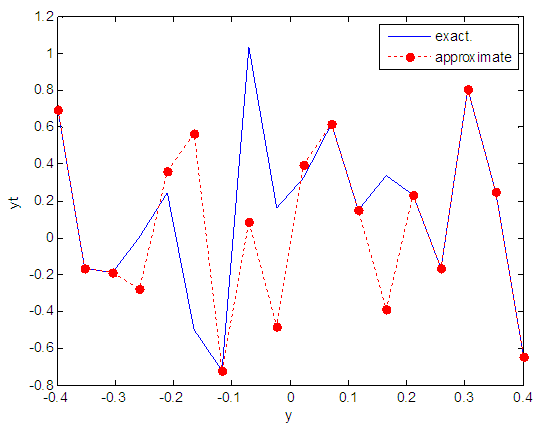 | Figure 81. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.5) and initial y=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
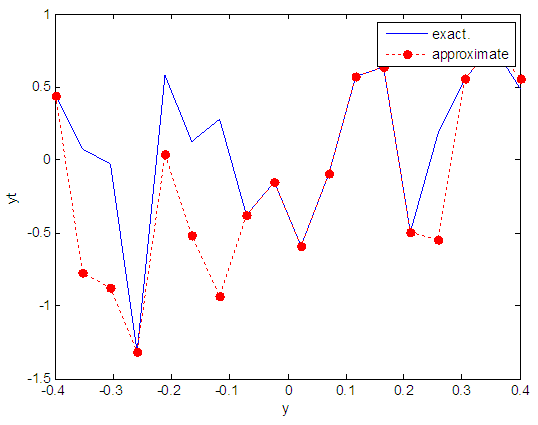 | Figure 82. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.5) and initial y=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
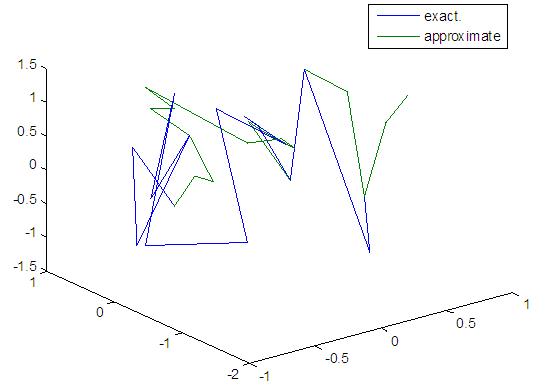 | Figure 83. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.5) and initial=0.1 & y=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
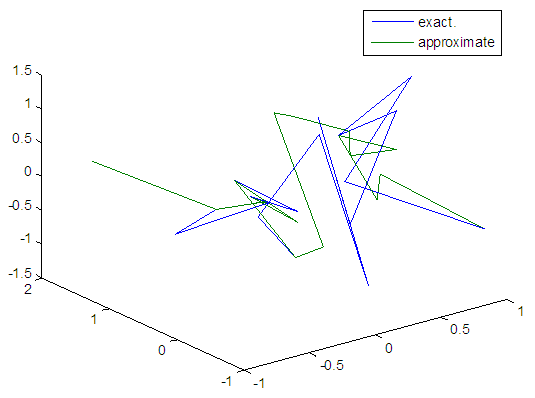 | Figure 84. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.5) and initial=0.4 & y=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
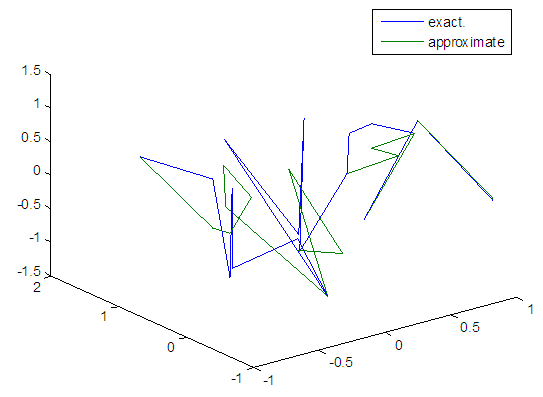 | Figure 85. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.5) and initial=0.7 & y=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
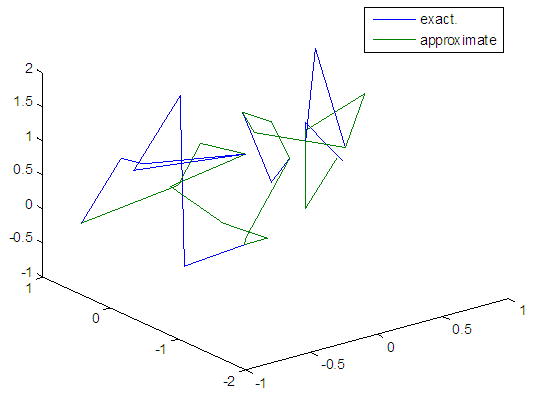 | Figure 86. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=0.5) and initial=0.9 & y=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
|
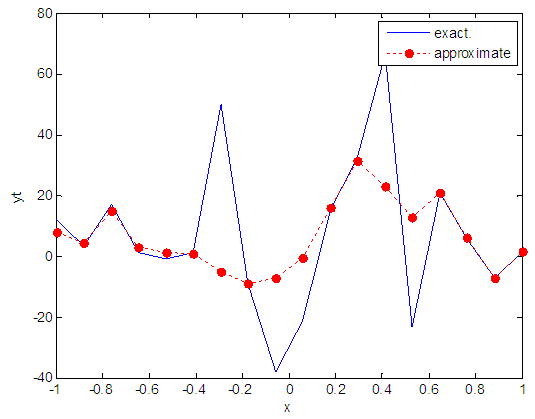 | Figure 87. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=40) and initial x=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
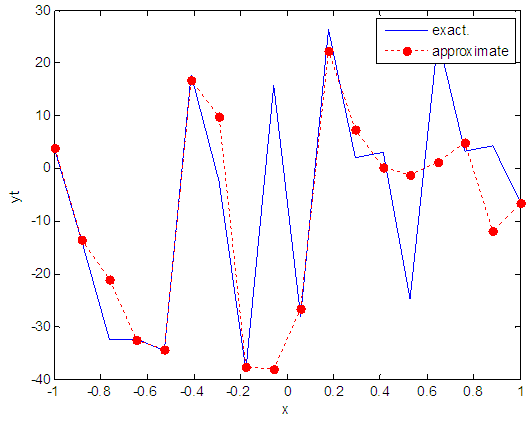 | Figure 88. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=40) and initial x=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
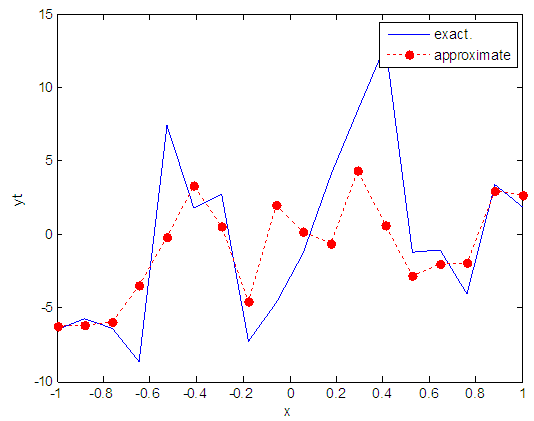 | Figure 89. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=40) and initial x=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
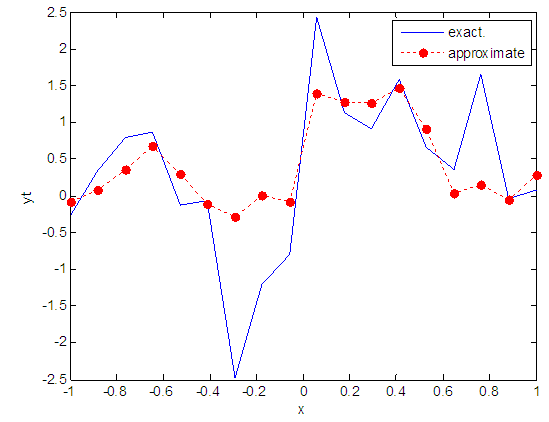 | Figure 90. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=40) and initial x=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
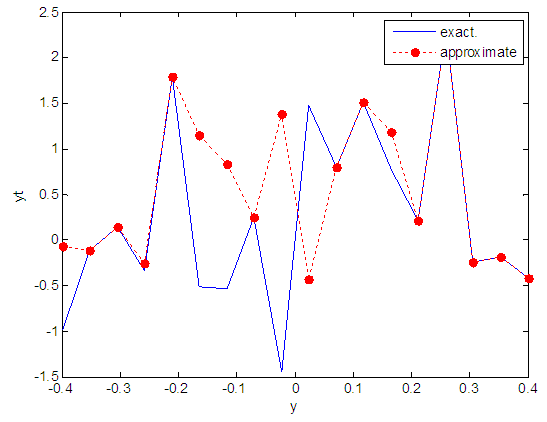 | Figure 91. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=40) and initial y=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
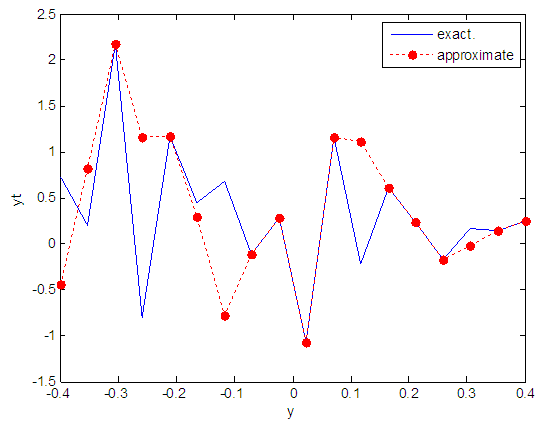 | Figure 92. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=40) and initial y=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
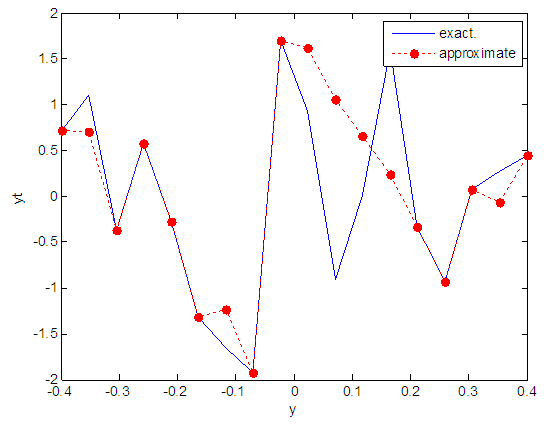 | Figure 93. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=40) and initial y=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
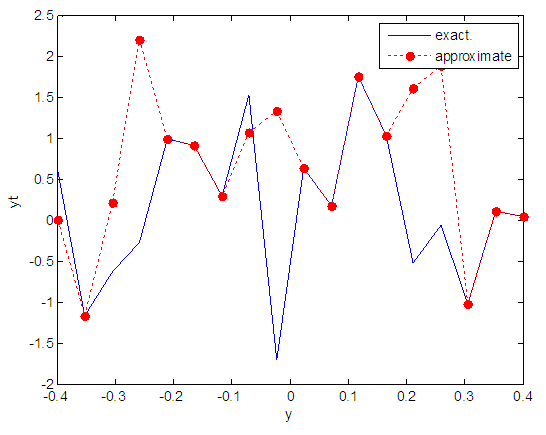 | Figure 94. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=40) and initial y=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
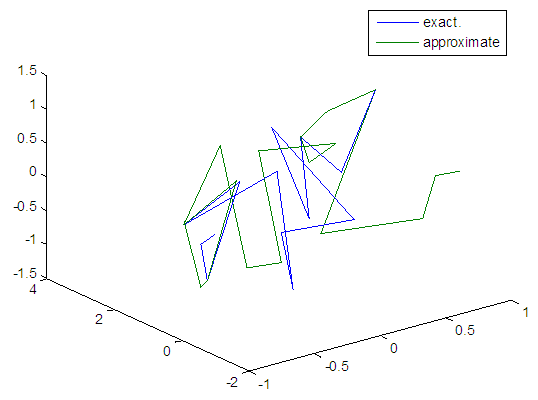 | Figure 95. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=40) and initial=0.1 & y=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
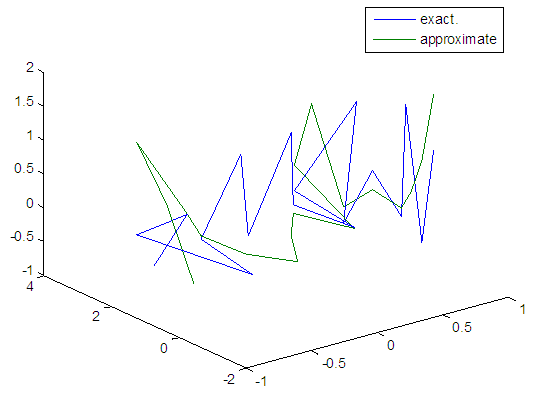 | Figure 96. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=40) and initial=0.4 & y=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
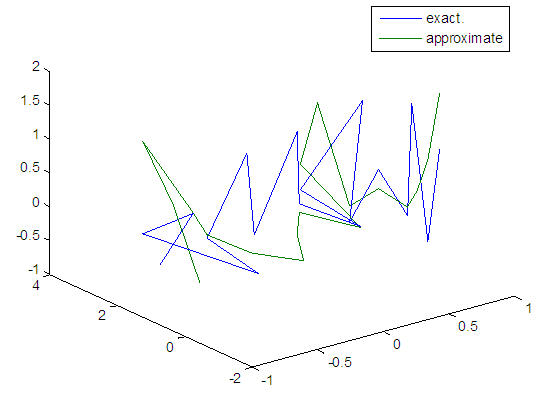 | Figure 97. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=40) and initial=0.7 & y=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
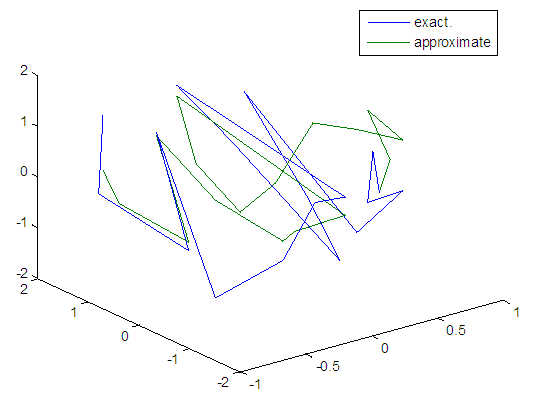 | Figure 98. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=40) and initial=0.9 & y=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
|
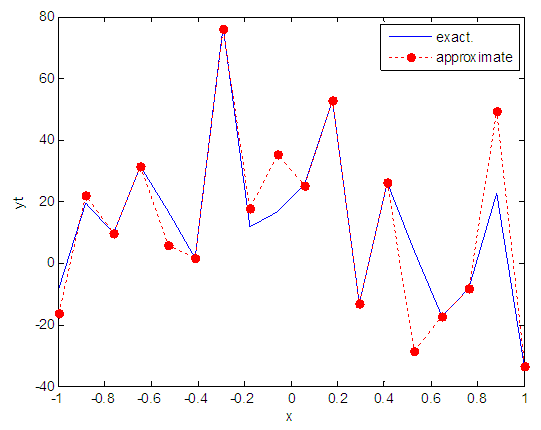 | Figure 99. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=60) and initial x=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
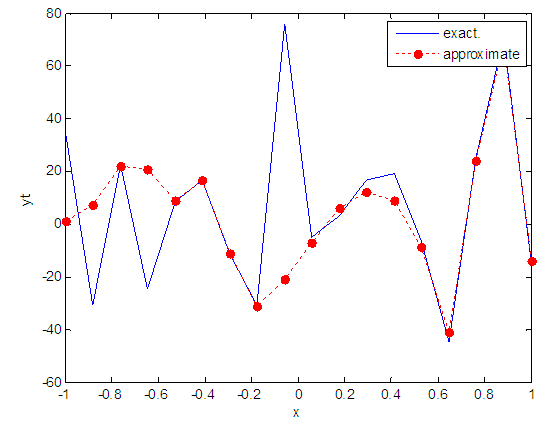 | Figure 100. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=60) and initial x=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
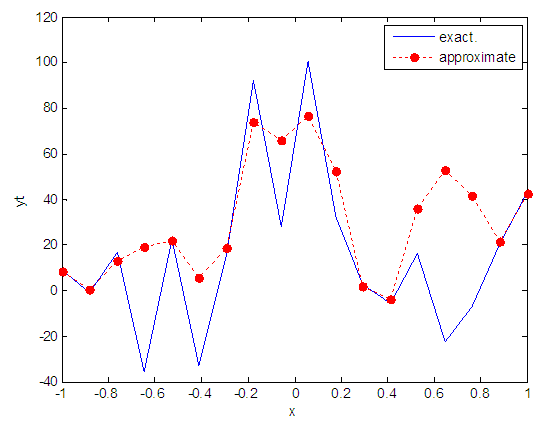 | Figure 101. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=60) and initial x=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
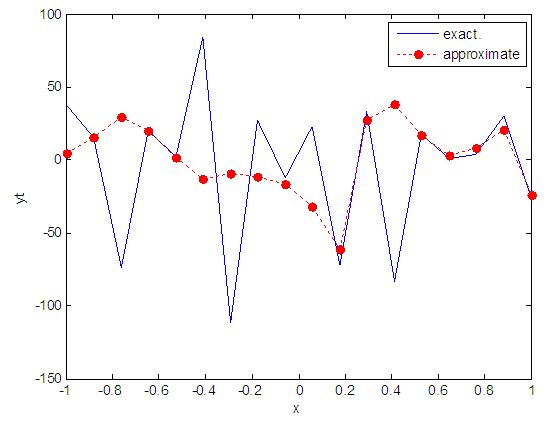 | Figure 102. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=60) and initial x=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
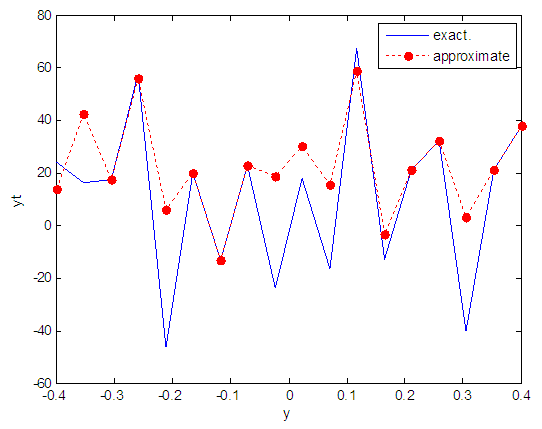 | Figure 103. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=60) and initial y=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
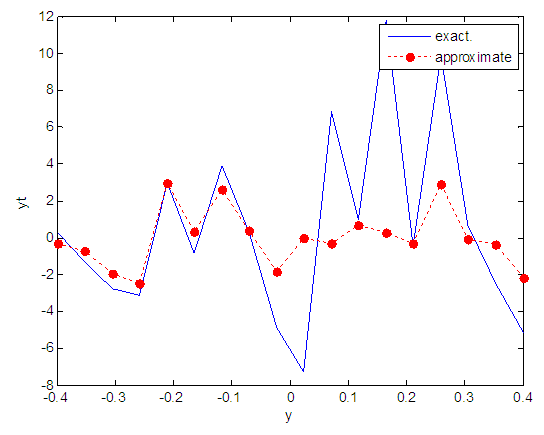 | Figure 104. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=60) and initial y=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
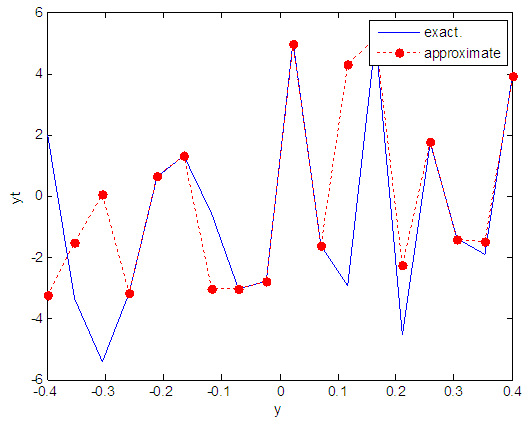 | Figure 105. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=60) and initial y=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
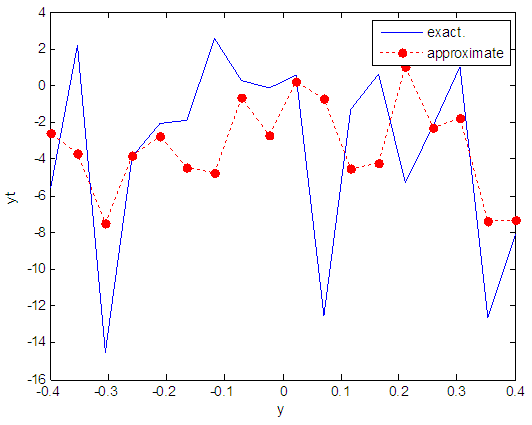 | Figure 106. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=60) and initial y=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
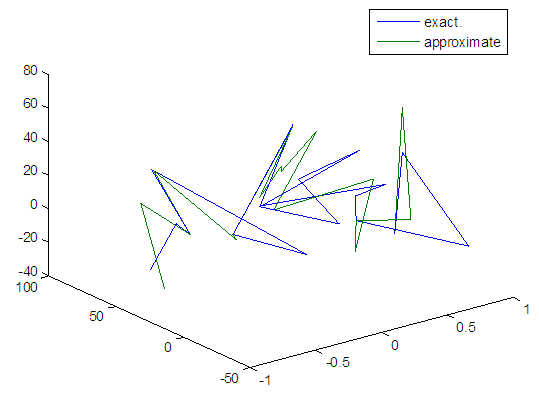 | Figure 107. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=60) and initial=0.1 & y=0.1 using FFT transfer function |
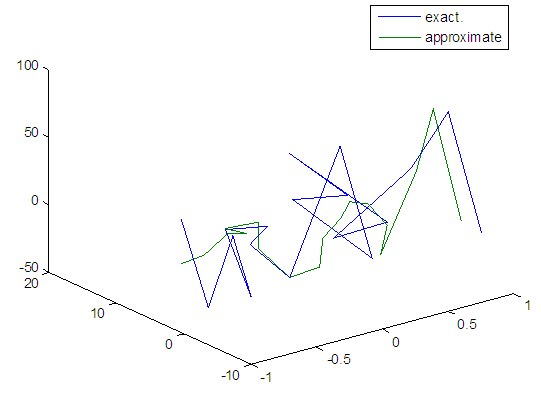 | Figure 108. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=60) and initial=0.4 & y=0.4 using FFT transfer function |
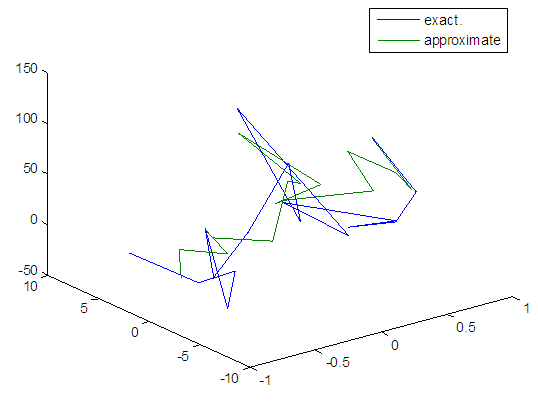 | Figure 109. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=60) and initial=0.7 & y=0.7 using FFT transfer function |
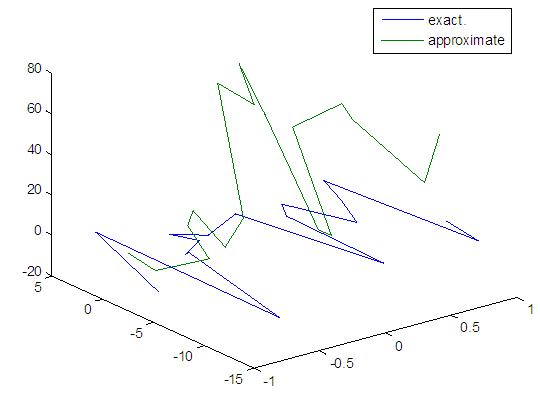 | Figure 110. Real and approximate Henon dynamical map with logistic noise (v=60) and initial=0.9 & y=0.9 using FFT transfer function |
5.5. Results Discussion
- The performance is convergent for logsig, tansig and FFT transfer functions at low values of variance 0.05 and 0.5 in the cases of normal noise and logistic noise. However, in the case of using FFT as transfer function when noise is normally distributed, the results got faster than using logsig and tansig as transfer functions. When the variances are increased to 40 and 60, the performance at using FFT as transfer function is better than the performance at using logsig and tansig as transfer functions, although the time to get the results is increased.
6. Summary
- From the above cases, it is clear that the suggestion of FFT as transfer function in artificial neural network gives excellent results and good accuracy with and without noise in compare with traditional transfer functions. Therefore, we can conclude that the FFNN with FFT as transfer function which we proposed can handle effectively on the two dimension dynamical maps and provide accurate approximate solution throughout the whole domain and not only at the training set. As well, one can use the interpolation techniques to find the approximate solution at points between the training points or at points outside the training set.The estimation of Henon dynamical map obtained by trained Ann's offer some advantages, such as:1- Complexity of computations increases with the increase of the number of sampling points in Henon dynamical map.2- The FFNNs with FFT transfer function provides a solution with excellent performance (according to MSE) in compare with other traditional transfer functions 3- The proposed transfer function FFT gave best rustles especially when the Henon dynamical map is chaotic and noisy chaotic.Some future works can be recommended. These works is as follows1- Using networks with three or more hidden layers.2- Using the architecture feedback neural network. 3- Increase the neurons in each hidden layer.4- Use anther random variables as noise on Henon dynamical map.5- Choose initial weights to be distributed as different random variables.6- We recommended using FFT as transfer function in practical application
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML