-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Intelligent Systems
p-ISSN: 2165-8978 e-ISSN: 2165-8994
2017; 7(3): 100-103
doi:10.5923/j.ajis.20170703.13

Health Monitoring using RFID
Gokuldas Pai, Jenifer Maria D'souza, Jevita Tina D'souza, Sahana R. Acharya, Ms Chaitra
Department of Computer Science Engineering, St. Joseph Engineering College, Vamanjoor, India
Correspondence to: Gokuldas Pai, Department of Computer Science Engineering, St. Joseph Engineering College, Vamanjoor, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The RFID card is used to create secure access to the patient's personal data and medical records.Thehealth monitoring using RFID project mainly aims at building a better means of storing and retrieving data. This project uses the hardware kit to get the patient id. The hardware kit will send the patient id to the serial port of the system. The patient ID can be accessed by the respective doctor by scanning the RFID card, after logging into doctor's account. The doctor can view and update patient's medical records and prescriptions. The patient can login into his account and he can perform functionalities that is view his previous medical reports and prescriptions. The admin registers doctors and patients and assigns unique doctor id and patient id along with password to the respective doctors and patients. Certain records, like medical records requires high privacy. Using this technology, all medical information is stored and retrieved online at any given point of time. It is easy to update, adapt and grow. Trying to identify an unconscious patient or patient who is unable to communicate can lead to delays in treatment. With this system emergency departments improve efficiency while enhancing the level of patient care.
Keywords: RFID card, RFID reader, Electronic Health Record
Cite this paper: Gokuldas Pai, Jenifer Maria D'souza, Jevita Tina D'souza, Sahana R. Acharya, Ms Chaitra, Health Monitoring using RFID, American Journal of Intelligent Systems, Vol. 7 No. 3, 2017, pp. 100-103. doi: 10.5923/j.ajis.20170703.13.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- In the current digital era, technology is ruling mankind. A little contribution of one, will take world to a higher level of living which makes them afford almost everything at ease. The world is at its extremes in upgrading itself to present technologies and innovations. To provide a better medical care to all categories of people, medical field is also in its path towards up gradation. An online medical service would enable people to the available quick, better, safe and secured medical treatment. The services helps doctors and receptionists to record day-to-day services provided to the people which would be stored for many years, that in turn helps people in cases of emergency.Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a communication technology which allows for defining some unique characteristics of an object or a living being, usually its identification information, by relating it to a numeric serial number within a tag, and ensures that this number is conveyed by using radio waves. RFID provides a communication infrastructure at the radio frequencies between a special tag and reader device that can detect the tag, and allows for establishing communication between devices within the system without any physical contact, or even without seeing each other. In this regard, communication comfort can be provided with RFID technologies in environments where technologies which require that the devices must exactly see each other, like the case in barcode systems, cannot be used.There are different applications of using RFID technologies in health industry. When the significance of human health is considered, it is necessary that information is transferred in a correct and fast manner to rapidly perform the first aid to the patient. By using RFID technologies as integrated with patient information systems, it will easily be possible to identify patients with the RFID card that they carry and to rapidly process the previously recorded information about that patient. Based on this reasonable motivation, an RFID-supported patient monitoring system is designed. The theme comprises of a website that is designed for hospital database for the welfare of patients.
2. Background
- The advancements of science and technology in the field of healthcare has improved the quality of people's life. Prior to the adoption of RFID technology in the field of healthcare, barcode technology was used. A barcode is a visual representation of data that is scanned and interpreted for information. Barcode scanners needed a direct line of sight to the barcode, barcodes had less security than RFID and were more easily damaged. These limitations were overcome by RFID technology. The RFID tags can be read from greater distance than barcodes. RFID tags don't need to be positioned in a line of sight with scanner, RFID tags can be read faster than barcodes and contain high levels of security. The RFID card is used to store all the details of the patient as well as to retrieve the details of the patient and doctor by scanning the card using the RFID reader. The RFID card is of great importance in the field of healthcare [2]. The patients need not carry the files of their previous medical records and prescriptions to the hospital. All the details of the patient such as health record, prescription are stored in the RFID card which can retrieved by the doctor.
3. Objectives
- The proposal in this dissertation focuses on the main objectives as mentioned below:• To reduce the carrying load of the treatment details and the records.• To develop a centralized and distributed server and database where the information is shared between different servers• To provide assistance to patients at home when there is no one beside them.• To also intimate the relative of the patient and the nearest hospital so that they are there when needed.
4. Terminologies
4.1. RFID Tag
- The tags are transponders that have an identifier of the object with which it is associated. The tags typically consist of an antenna and an electronic microchip. The antenna is responsible for making communication between the tag and the reader. There are two main energy classifications of a tag. They can be passive, obtaining energy through the magnetic field generated by readers through antennas, or they can be active, with a battery that provides the energy required to perform processing and modulation of the signal.
4.2. RFID Reader
- An RFID Reader can read through most anything with the exception of conductive materials like water and metal, but with modifications and positioning, even these can be overcome. The RFID Reader emits a low-power radio wave field which is used to power up the tag so as to pass on any information that is contained on the chip. In addition, readers can be fitted with an additional interface that converts the radio waves returned from the tag into a form that can then be passed on to another system, like a computer or any programmable logic controller.
5. Proposed System
- Software design of the system mainly consists of the patient information system. Once the card information is obtained by RFID communication [4-6], they can be processed in the information system in the application. The architectural diagram is shown in Figure 1.
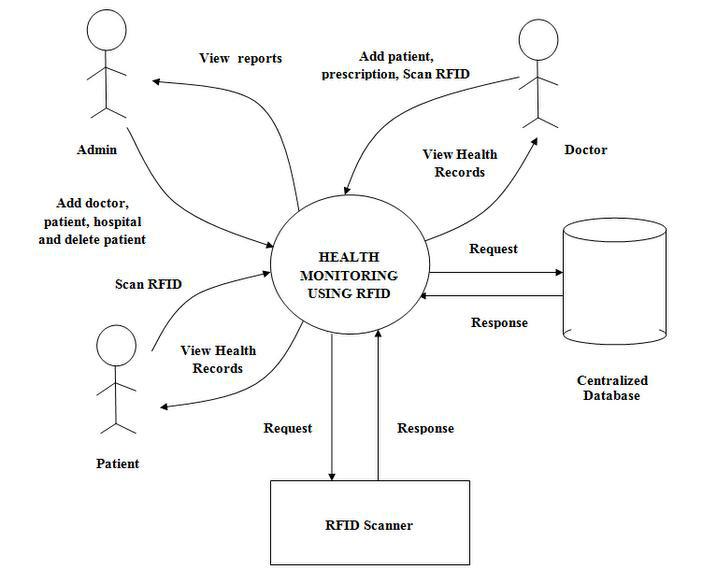 | Figure 1. Architectural Diagram |
6. Methodology and Framework
6.1. Admin Activities
- This module is used to add doctor, hospital and patient details. It is also used to register for doctor and patient. The admin also includes the authorization to delete the patient, doctor and the hospital details.Only the authorized persons can operate the system. Based on the clarity of the authentication process, the login screen has a basic interface as simple as shown in Figure 2.
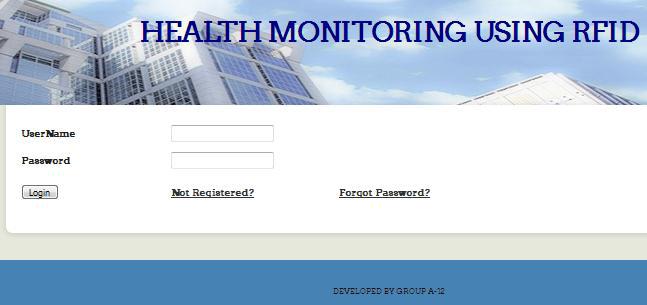 | Figure 2. Login Page |
6.2. Patient Personal Information
- This module is used to retrieve the personal information that is used in the time of emergency. Personal details contain information regarding the person’s name, age etc. It also contains the app that is designed to help the patient in case of emergency. The personal information can only be updated by the patient.
6.3. Medication and Dosages
- Depicts the logical process of RFID adoption in healthcare [1]. Doctor can add prescription details which can be viewed by the patient. To better understand how RFID can help improve healthcare practices, identify the existing problems and challenges faced by this industry.
7. Modular Design
- Health Monitoring using RFID is the main module. There are three sub-modules, namely:• Admin• Doctor• Patient
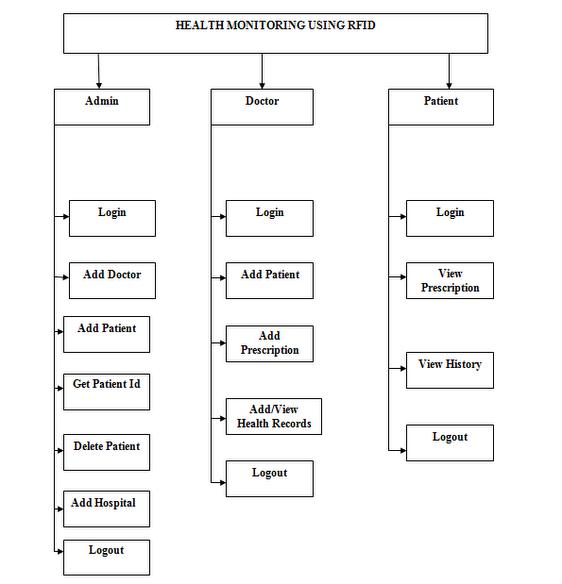 | Figure 3. Modular Design |
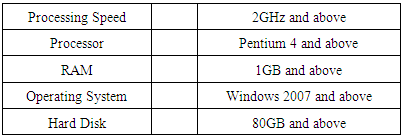
8. Hardware Requirements
9. Conclusions and Future Work
- Using Health Monitoring System, health care providers (e.g., hospitals) improve patient’s safety by capturing basic data (such as patient unique ID, name, blood group, drug allergies, drugs), prevent/reduce medical errors, in-creases efficiency and productivity, and cost savings through wireless communication. The RFID technology has tangible benefits such as reduced cost and time, reduced human resources and improve productivity.In the future version of health monitoring using RFID, we will explore the functionality to access patient's medical records from other health care providers databases through internet. Also developing the functionalities for accessing and updating patient records remotely by medical professionals or consultant using devices such as smart phones. We can add the emergency contacts of a particular patient.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML