-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Intelligent Systems
p-ISSN: 2165-8978 e-ISSN: 2165-8994
2013; 3(1): 40-49
doi:10.5923/j.ajis.20130301.06
Development of a Real-Time Intelligent Biometric Face Detection and Recognition System in LabVIEW
Muralindran Mariappan, Manimehala Nadarajan, Rosalyn R Porle
Robotics & Intelligent Systems Group, Artificial Intelligent Research Unit, Universiti Malaysia Sabah, Kota Kinabalu, 88400, Malaysia
Correspondence to: Muralindran Mariappan, Robotics & Intelligent Systems Group, Artificial Intelligent Research Unit, Universiti Malaysia Sabah, Kota Kinabalu, 88400, Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Face detection and recognition plays a vital role with broad application in areas like crowd surveillance, security system, human computer interface, etc. In principle, biometric system is preferred for people identification due to its reliability and accuracy. The biggest challenge in face recognition arises when a real-time application system is designed for frontal and non-frontal images. The variations in face poses and expressions greatly impact the identification accuracy of a moving person. To circumvent this issue, in this paper, a real-time biometric system using face region is designed to detect and recognize a person in a pre-defined range using LabVIEW. Face region is proposed to eliminate any physical contact with the system. Neural Network (NN) is employed by training the face images in different distance and angle which allows this system to work for frontal and non- frontal face recognition. Algorithms in LabVIEW are developed to detect and extract the face region in a captured frame which is then sent to NN for recognition process. Consecutive frames video processing was implemented for a real-time face recognition system. About 128 images were used for training and 160 images were tested and it achieves an accuracy of 96.8% in real-time testing.
Keywords: Face Detection, Face Recognition, Frontal Images, Non- frontal Images, Neural Network, LabVIEW
Cite this paper: Muralindran Mariappan, Manimehala Nadarajan, Rosalyn R Porle, Development of a Real-Time Intelligent Biometric Face Detection and Recognition System in LabVIEW, American Journal of Intelligent Systems, Vol. 3 No. 1, 2013, pp. 40-49. doi: 10.5923/j.ajis.20130301.06.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Detection and tracking of human activity takes major role in this current technology. This technology can be widely used in crowd surveillance, bank security, airport security, human computer interface and others[1][2]. Biometric systems have been implemented in hospitals for several usages. The most common one is the fingerprintrecognition system that is used for registration purposes and login system to various departments. Biometric method can be classified into physiological characteristics likefingerprint, iris, face and DNA which are non- alterable except by severe injuries. Behavioral pattern like keystroke and voice print may fluctuate due fatigue or illness[3]. In addition, using face as a biometric system does not require the person to be directly involved in the system unlike fingerprintsystem where physical contact is needed to activate the system. The designed system can be useful to detect and recognize the presence of doctors within a hospital building. In general, doctors are assigned to different departments according to the need and specialization. Doctors are not allowed to use mobile phones when attending a patient to avoid improper treatment to the patients. Besides that, mobile phones are not allowed to be used at places where medical equipments are placed. Intensive care ventilators, dialysis machines, external pacemaker machines are one of those equipments that suffer from electromagnetic interference from mobile phones. There is a need of a system to know the location of the doctors even if the mobile phone facility is not used. The exact location of the doctor must be known so that the doctor could be located in any case of emergency. This research focuses on designing a system that is able to detect, identify and recognize a person in a pre- defined distance. LabVIEW is utilized as major platform forsoftware design. There is several reasons for utilizing LabVIEW for system design in this research. LabVIEW is very suitable and easier for both hardware and software interfacing. Here, it is used for interfacing to read the data from sensor,microcontroller and for external webcam communication. Besides, MATLAB can be integrated in LabVIEW via MathScript for Neural Network approach. Moreover, it offers easy-to-use construction for graphical user interface. It has a variety of extended library for most design. The main advantage of LabVIEW is the simplicity of code and leads for easier debugging of the program.In this design, face detection must be computed before identification and recognition. A sensor is implemented for motion detection. This has reduced the processing taskwhere only selected frames will be further processed. Algorithms were developed to detect face in a frame. This is done via background subtraction for every consecutive frame. Avideo processing is done to ease the real-time mode. Once face region is extracted from previous stage, person recognition is done by means of the designed network in neural network. Database were created, trained and tested accordingly with faces of a few people captured in different distance and angle. The result of the system is displayed in a GUI panel designed in LabVIEW. The objective of the paper is to design a face detection and recognition system in LabVIEW using Neural Network and to achieve a high accuracy result for a real-time implementation. This paper is organized as follows; Section 2 brieflydescribes the previous work that was done by other researches which is related to this research. The methodology of the system is explained in Section 3, followed by hardware development in Section 4. The software development done in LabVIEW is explained in detail in Section 5. Section 6 discusses the result obtained and a conclusion is done in Section 7.
2. Related Work
- This section discusses the study that has been conducted by other researchers related to the design. There are several methods to classify face detection; knowledge based, image based, feature based and also template matching method. Knowledge based method works on the rule of facial feature to know the relative distance and position but only suitable for frontal- image. Image based method have predefined standard face pattern. This method is used to match segments in an image to differentiate is it is a face or not. It uses training algorithms like Neural Network and Eigenfaces. This method is easy to be implemented but cannotdifferentiate different pose, scale and shape[4]. This technique has high detection rate because it depends on multi- resolution window but slower than feature based method[5]. Feature based method depends on extraction of facial feature from image[6][7]. Features on a face are located by determining the nearest neighbor classifier[8]. This technique needsinformation from face feature like skin color, face shape, eyes, nose and others. The advantage of this method is that it is not affected by lighting conditions and makes it suitable for rea l- time application. Facial features are difficult to be located when comes to non- frontal images. Skin color is suitable for detection of multiple faces in a frame but fails as different camera gives different pixel color[8]. Face tracking is done by locating the facial features and tracked in the image sequence frame. This method is only suitable forfrontal image tracking and high chance to fail if a large movement is detected[6]. Template matching method uses the correlation between the pattern in the input image and the original pattern of the face. This is done to find presence of a face or any other facial features[4].Background subtraction is very suitable to be used for video processing where few frames will be selected to observe the variation in the background. Foregrounddetection is done by comparing the input video frame with thebackground reference frame. It will then identify the foreground pixels from the input video that was fed in[9]. According to[10] detection of moving object can be done byimplementing background subtraction and CAMshift algorithm. Hand gestures are detected from each frame image from the sequence. Skin color was used to detect the face and hand region where face region were assumed to be static. Average filtering is applied to obtain the moving object clearly. In addition, applying filtering can remove noises that may appear from webcam. Problem arises when the face and hand overlaps as both gives the same threshold for skincolor[10][8].Morphological opening and closing is applied to group the pixels together to form a solid piece[9][11][8]. Updates are done for a few consecutive frames to adapt the changes with reference to the background. Mixture of Gaussian is used to cluster the objects together. Besides, Threshold value is used to mark the difference in two concurrent frames[12].Edge detection is applied at places where the image brightness changes a lot and has a sort of discontinuities. Sobel edge detector is more suitable to be used for an image that has a smaller size[13] while Prewitt edge detector is used to detect the vertical and horizontal edge[13][14]. The gradient for Canny edge detector is calculator through the derivation of Gaussian filter. This method use to detectstrong and weak edges. This causes Canny operator to be less likely to respond to noise[14].Neural network is made up of three layers which are the input layer, hidden layer and output layer. A neural network is made up of neurons built in various layer of network. These neurons of different layers are connected with each other through links called weights which stores information needed[15]. The sample image must have equal in size, clear and large enough[16][7]. Large sample of data is down sampled into a smaller size[7]. Training must be done a number of times but must not exceed the limit to avoid the system to memorize rather than learning[16]. The neural network is more suitable to be applied at the patternrecognition phase rather than the face detection phase to reduce complexity. Neural network can be very complex even for a small picture size and may lead to difficulties in training[3]. Neural Network is suitable for analysis of frontal and non- frontal image analysis[17]. The neural network is said to be efficient if it requires less training pattern, takes less time for training and able to recognize different type of patterns[15]. Besides, the recognition rate can be improved if the face region covers the most area in an extracted frame[17].[18] proposed a method to enhance the illumination using contrast stretching and image histogram equalization. Images were fed into Neural Network for analyzing by reducing the images into 1-D dimensional vector using Dicrete Cosine Transform (DCT) and Principal Component Anaysis (PCA).[7] proposed training algorithm; Volterra kernel for recognition. For training process, the size and order of the kernel is held constant which in return is similar as input for Neural Network. Images are in grayscale form to reduce processing complexity. Generally, faces close to the camera will appear larger than faces that are far away from the camera[14]. Tracking of the human face with an active motorized camera is necessary to keep the target in focus[2]. The face with the largest area is chosen as the region to track. In other words, the image that is closest to the camera is chosen to further processing[2][6]. If the scene is found to have more than one people, it is more likely that the face which is closer to the camera has an overall higher importance, and therefore will be selected for servoing[2]. Video processing can be converted into individual frames to find the possible skin region. This stage can reduce the search space. Human nature will have the least small amount if movements such as eye blinking and mouth or face movement. Facial feature search is done to check the face region using width and height of human face. Therefore, this method is only suitable for frontal image. Too muchmovement in a frame such as running and hand shaking can lead to the failure of system[19]. Database containing face images can be obtained from the available ones like XM2VTSDB[20] which has multiple pose. Other database are also commonly used like Yale A, CMU PIE, Extended Yale B, MERL Dome and CMUMultiPIE which were used for testing[7]. Available database can be used for experimental purposes if real-time application is not taken into account. Therefore, in order to test thereliability of the designed system in real-time, database is created with images of frontal and non- frontal[17].
3. Design Methodology
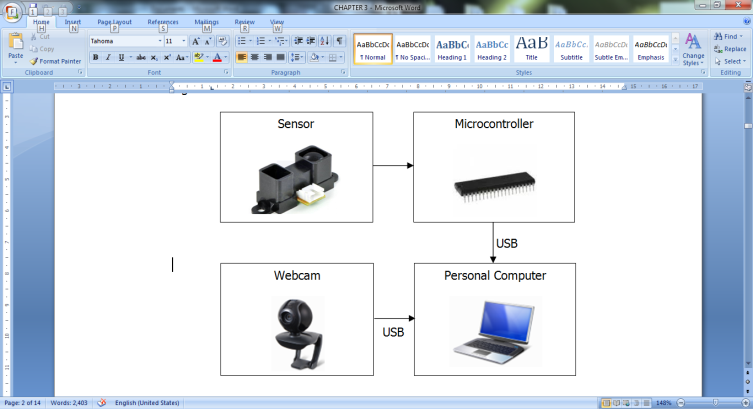 | Figure 1. Block Diagram of the Designed System |
 | Figure 2. Software Architecture |
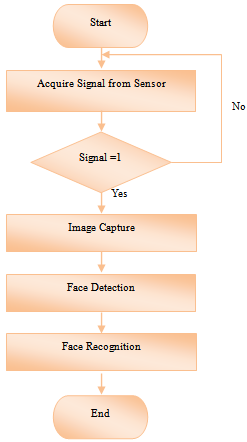 | Figure 3. Flowchart of the System |
4. Hardware Development
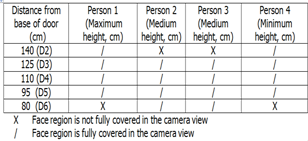
- This section discusses the hardware development for a real-time system for a single face detection and recognition. A system was designed for face detection and recognition in LabVIEW. It starts with the signal received from sensor with microcontroller programmed accordingly. The raw data that were received and extracted is displayed in LabVIEW GUI panel. This system detects and recognizes a person within the database in a pre- defined range of 1.4 meters from the base of the door depending on the person’s height. The variation in the height affects the camera view of focus.Microcontroller and camera is communicated to computer via a USB 2.0 connection. Figure 4 illustrates the top view of the designed system.
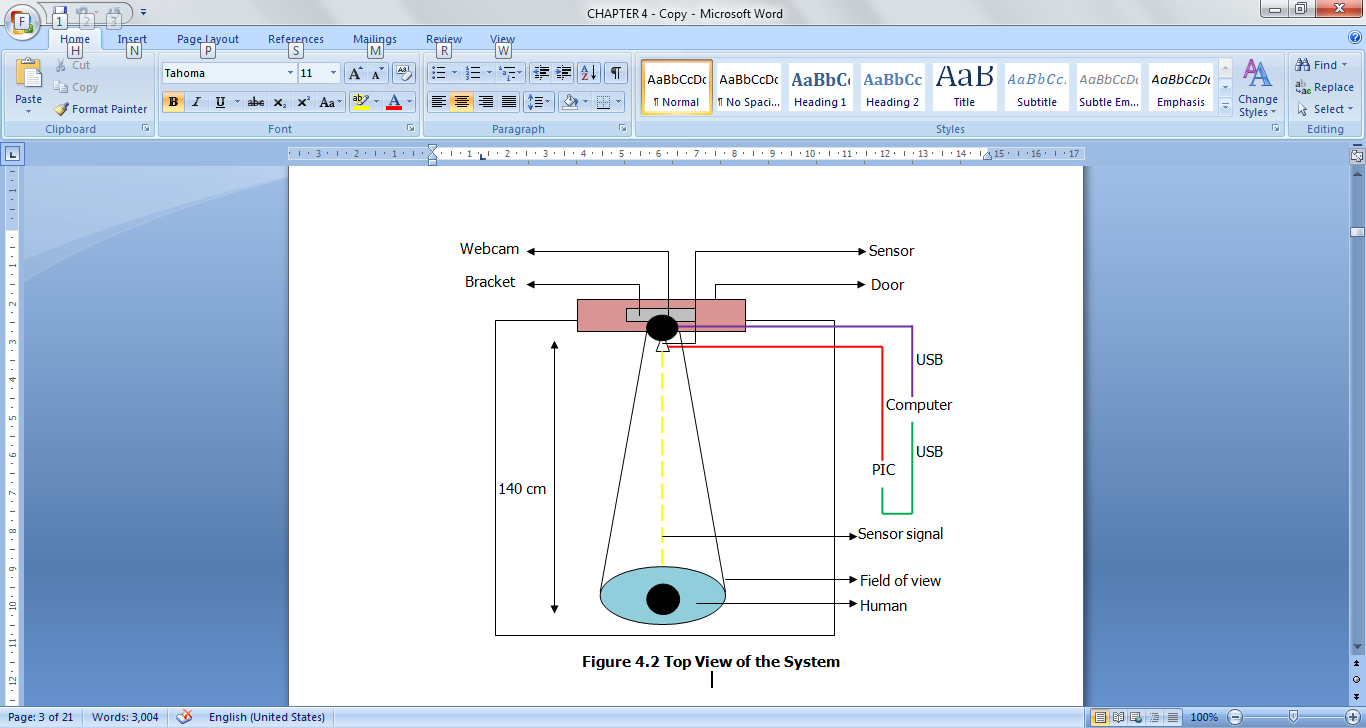 | Figure 4. Topview of the System |
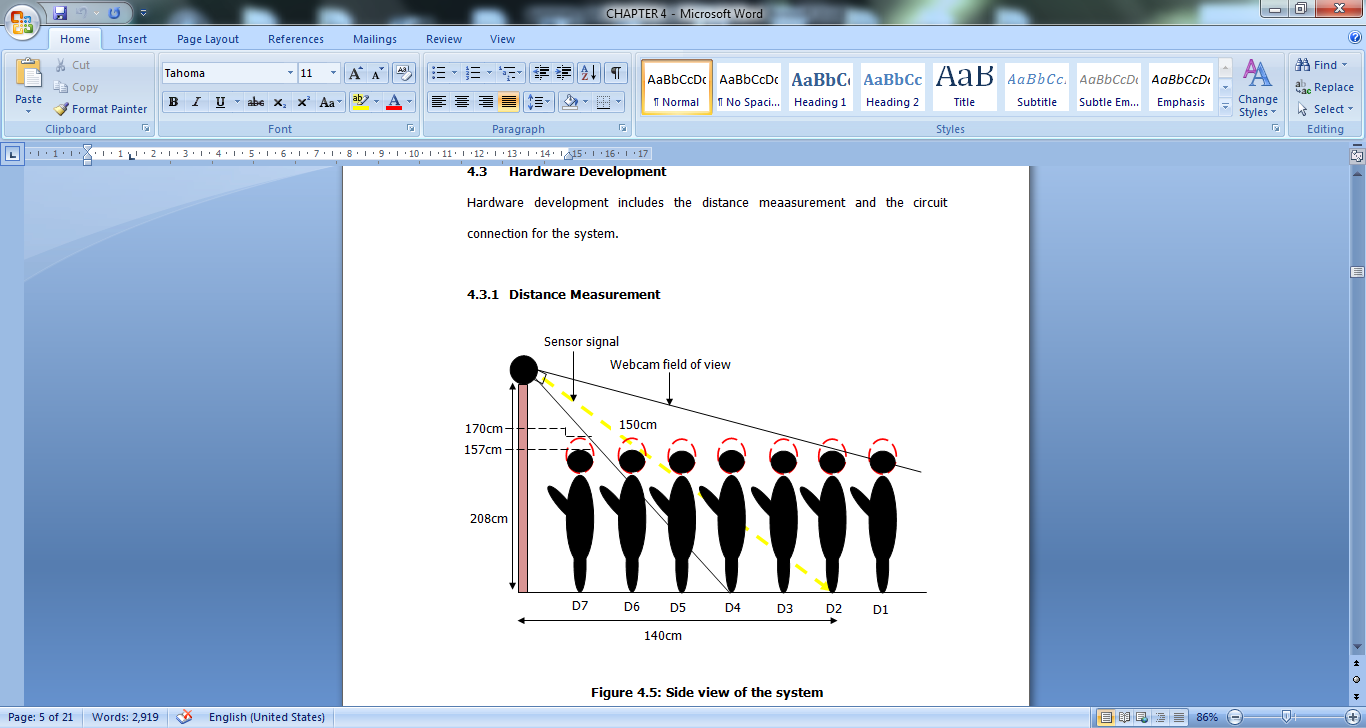 | Figure 5. Sideview of the System |
|
5. Software Development
- This section includes the serial port communication between PIC and computer, video acquisition and image processing. The algorithm developed for face detection and recognition is discussed in detail.
5.1. Serial Port Communication and Video Acquisition
- Serial port communication is the interface between a computer and microcontroller. This can be easily done via LabVIEW with VISA module. The analog data frommicrocontroller is converted to digital of ‘0’ and ‘1’. A LED indicator light will be on if a motion is detected where an array of ‘1’ will be displayed. Once data is received from microcontroller, a case structure is created. If ‘1’ is received, the webcam will be triggered to process the image in the frames. The images will be further processed for face detection and recognition. The captured images are in 32- bit RGB, PNG format.
5.2. Face Detection
- Algorithms were developed to extract the face region from a complex background. The captured image is in 640 X 480 pixel dimension. The background image is pre- loaded into the system and it is stored as buffer image. When a motion is detected, the background image is subtracted from the input image from webcam. This can be represented in Equation 1.
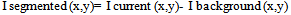 | (1) |
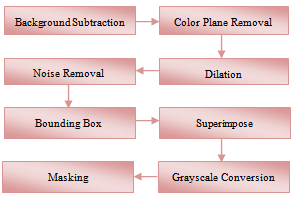 | Figure 6. Software Development for Face Detection |
5.3. Face Recognition
- A pre- processing stage is required to complete face recognition. Database was created with images of four people captured in different distance and angle as in Table 1. Capturing images in different distance will ensure that at least one image can be processed as the person walks. Images were captured in different angle as this system is designed for frontal and non- frontal face analysis. There are a total of 160 images in the database with 40 images per person. The advancement of Artificial Intelligence as added value where Neural Network had been employed this system. The input for this stage is the converted grayscale image which was reshaped and resized into 2500 rows with 128 and 160 columns for training and testing stage respectively. The output of the system is the face recognized which is 4. Feedforward backpropagation is applied as it is the most common algorithm used for pattern recognition. One hidden layer is enough to solve any complex problem. The input to the neural network is the grayscale face region from previous stage while the output is the person identified. Neural Network is used for face recognition to train and test the data. 80% of the database which is 128 images was fully trained following the target as set in Table 2. The network is trained until a 100% training accuracy is achieved. The database was randomized and tested for accuracy. The trained network was integrated in LABVIEW. The output from neural network is converted into array to display accordingly.
|
6. Results and Discussion
- This section describes the results obtained in this research and it is discussed in detail.
6.1. Microcontroller Data
- Figure 7 shows the string read from microcontroller in LabVIEW. When a motion is detected, which is a human in this case, the LED indicator will on and string of ‘1’ will be displayed while when no motion is detected, the LED will be off and string of ‘0’ will be displayed. The green light displayed in Figure 7 shows when a motion is detected.These data from microcontroller is extracted in LabVIEW.
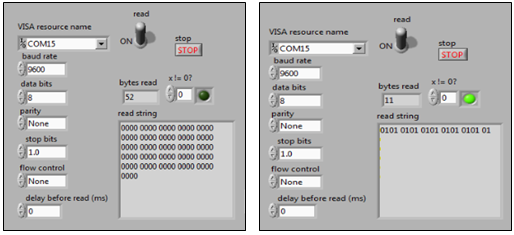 | Figure 7. Data from Microcontroller |
 | Figure 8. Face Detection |
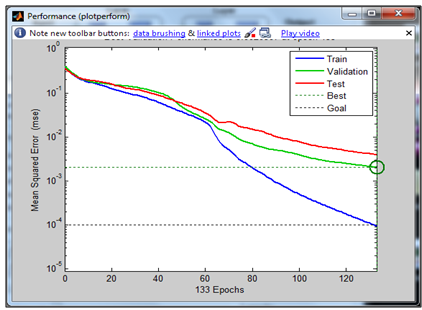 | Figure 9. Performance Plot for Training |
6.2. Face Detection
- Figure 8 displays the result of face detection designed in LabVIEW. The face region converted to grayscale is sent to neural network for face recognition. Background subtraction is done for every frame to extract the moving object. Vision Assistant in LabVIEW requires the image to be in 8 bit. By removing the color plane, a 32 bit image can beconverted to 8 bit for further processing. Particle analysis is done to extract the particle with the largest area in a frame. Therefore, background subtraction is needed to remove the non- moving object in a frame.
6.3. Face Recognition
- The trained network from MATLAB is integrated in LabVIEW. Parameters were set accordingly to obtain the maximum performance of the system. 100% trainingaccuracy will lead to an accurate result when the system is tested in real-time. Tansig was chosen as network layer as itconverges to reach the performance goal. Learning rate is set to be low so that the network learns completely instead of memorizing which is 0.01. Adding a momentum of 0.9 into a network will allow the network to recover back to training even if it falls into local minimum.From the study that was conducted, it was found that a 100% training accuracy was achieved. This is illustrated in the performance plot in Figure 9. All the images in database were tested. Before testing, the data was randomized. The testing result that was achieved is 96.8%. In order to achieve a better recognition rate, the face pixel must cover the most regions in a frame. The system was also tested with people in the database but with some changes in appearance it achieves almost 100% accuracy which shows the reliability of the system.
6.4. Real-Time Testing
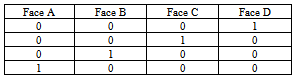
- Real-time testing includes face detection and recognition. A system was designed in LabVIEW with a Graphical User Interface (GUI) panel. When a motion is detected, the green LED indicator will be on with a signal of ‘1’ from the sensor. The recognition is displayed in array form as in Table 2. The overall system uses video processing as it suits for real- time testing. From the system designed, a face can be identifiedaccordingly in a range of 140 cm from the camera and sensor. A few frames were compared to verify the recognition result. Figure 10 to Figure 12 shows a continuous sequenceof frames. It begins when the system is initialized where no object is detected and followed by object detected at first and second distance. From the figures, it can be concluded that the system works well for face in all angle. The resultsobtained in every consecutive frames matches the target set as in Table 1 which is Face A. Figure 13 shows the testingconducted for frontal- image which gives the correct recognition which belongs to Face A. The reliability of the system is tested by testing it with images of the same people within the database but withdifferent appearance. These face images are not in the database. The system recognizes the faces correctly. This can be seen in Figure 13. Most research is done by using MATLAB. The current method developed by[10] for hand gesture which usesbackground subtraction and skin color segmentation yields an accuracy of 96.77%. System developed by[18] yields a high accuracy with Backpropagation Neural Network but it was not tested real- time.[7] tested the face detection system with the available database with more images to achieve highaccuracy. A method developed by[8] uses skin color to detect multiple faces gives an accuracy of 90%. A simple algorithm for face detection and recognition system is designed here for a real-time application which gives quite a high accuracy. The use of LabVIEW is found to generate an easier way of designing with a GUI panel. Besides, LabVIEW can be integrated with other design software like MATLAB and also for hardware interfacing which are a microcontroller and a webcam in this research.
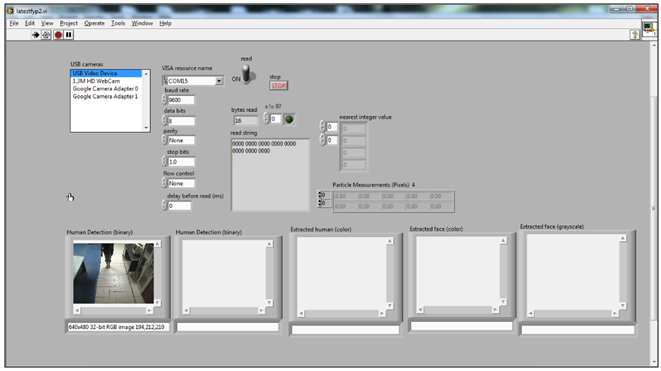 | Figure 10. System Initialized, No Object Detected |
 | Figure 11. Object Detected at First Distance, Non- Frontal |
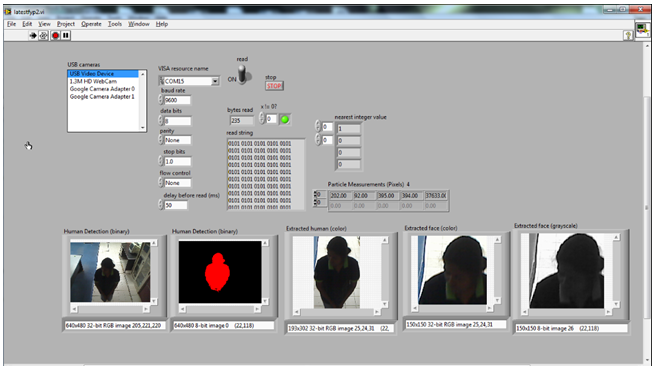 | Figure 12. Object Detected at Second Distance, Non Frontal |
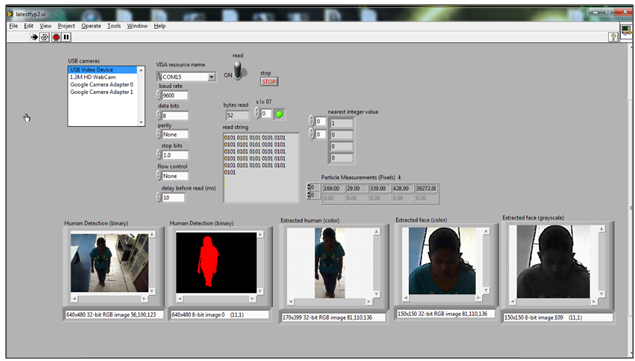 | Figure 13. Frontal Image with Changes in Appearance |
7. Conclusions
- This paper discusses the system designed for face detection and recognition in LabVIEW where it is the major platform. MATLAB were used for the training of Neural Network which was then integrated in LabVIEW. Sensor added to the system for motion detection to detect thepresence of moving object. The algorithm developed for facedetection was discussed in detail incorporating background subtraction and threshold setting as major processing as it suits for a real- time system. Background subtraction willallow the extraction of moving objects in a frame which allows reduces processing task where only frames with faces were further processed. Artificial Intelligence, Neural Network has also added value where training the images in different distance and angle allows the system to work well for frontal and non- frontal face recognition which gives an accuracy of 96.8%. The system gives a high accuracy when it was tested with faces with difference appearance. In order for the system accurate result, the recognition was tested for every frame that contains face images. This system can be further developed for face tracking with person identification. In addition to that, different algorithm can be improved to get a higher accuracy of the overall system.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors would like to thank the Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia for the research grant RAG0004 – TK - 2012.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML