-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Geographic Information System
p-ISSN: 2163-1131 e-ISSN: 2163-114X
2013; 2(3): 37-46
doi:10.5923/j.ajgis.20130203.02
A Visual Aided DSS Prototype Development to Mitigate the Flood Hazards
Nasly M. A., Faisal Nadeem Saher
Faculty of Civil Engineering & Earth Resources, University Malaysia Pahang, Malaysia
Correspondence to: Nasly M. A., Faculty of Civil Engineering & Earth Resources, University Malaysia Pahang, Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Flood hazards caused by extreme rain events or unplanned watersheds is a problem and it has become a growing concern under impact of climate change. There is a dire need to develop new paradigm to combat flood hazards and operational decision-making process. Effective decision is a challenge, in a context to select best-suited option for mitigation. The general objective of this paper is to propose a visual aided decision support platform providing an ease but acceptable level of strategy. Presented prototype includes modelling and GIS based visual aids. A study of Pahang River in Malaysia conducted, to explain the applications of the prototype. This study affirms two major conclusions: First, there is great potential to adopt the proposed methodology at a level of decision-making authorities, leading to selection of actual measures for flood mitigation. Second, integration of model, Water Evaluation and Planning (WEAP), Global Mapper and GIS proved as a salient feature of Decision Support System as visual aided scenario generation. This paper has given an account of and the reasons for the use of prototype for flood hazards.
Keywords: Visual Aided DSS, WEAP, Pahang River, Scenarios Generation, Flood Mitigation
Cite this paper: Nasly M. A., Faisal Nadeem Saher, A Visual Aided DSS Prototype Development to Mitigate the Flood Hazards, American Journal of Geographic Information System, Vol. 2 No. 3, 2013, pp. 37-46. doi: 10.5923/j.ajgis.20130203.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- A decision support system (DSS) helps the users to resolve the complex problems interactively for reliable decision development[1]. However, the complexity of the problems can simplify to come up with understandable action plan. The professional community has put considerable efforts to develop more sophisticated DSS through an attempt of integrating different models with GIS. Under similar case, a hybrid approach for flood risk zones mapping and impact of flood occurrences by integrating GIS and HEC-RAS testified with reliable outputs[2]. It is becoming difficult to ignore the current systems of decision analysis, which consider policy concerns. A web based DSS prototype tool developed by[3] is an example of, to focus on consequences of relevant policies for river management. Another leading cause is a shift from flood protection towards flood risk management. This shift is a progressive change to avoid uncertainties in different decision situations [4].In recent years, there has been discussed a methodology at improving the interactions between the professionals and other stakeholders for decision-making processes in water management[5]. Keeping in view all the participants concerned with decision, it shows the importance of a system capable to depict the datasets with visual aids.During study of flood behaviour of rivers, the impact of tidal would not spare, as it becomes necessary to predict the routing of floods under tidal influence. This issue highlighted by[6]. The problem is to include these factors at one platform to forecast flood risk and accordingly preparation of mitigation plan. The present study designed to determine the problem solution: as to adopt more sophisticated decision-making tools. In future, the risk of floods to our lives is dependant to the existing flood measures[7]. As a policy for future planning, a system of water monitoring would be required to improve the decision support systems, as an effective source of planning[8]. Several attempts made to develop user-friendly system of DSS at windows environment with a capacity to select the appropriate model for analysis[6, 9]. The limitation of these systems is the demonstration of the decision options as dynamic views. This dynamic visualization would enhance the mapping features[10]. Some other researcher uses the concept of dynamic graphing tools and dynamic 3D flood information[11, 12]. Simultaneously, use of the integration concept is stimulated through the growing tendency of visual enhancement processes. In decision sciences, the decision process involves different tools such as artificial intelligence, data mining, online analytical processing, and knowledge management[13]. The DSS may focus into four categories: i) on data ii) on improving the user interface iii) models and iv) development of web-based applications[14]. The current study has considered the enhancement of user interface with dynamic display of data and results.Malaysia has been subjecting to the hazard of flooding due heavy rainfall during monsoon. In Malaysia maximum rainfall occurs during the months of November, December and January, while June and July are the driest months[15]. Excessive rainfall during monsoon and other development activities results heavy soil erosion and landslides causing siltation of rivers which makes floods severe in magnitude [16]. During floods, evacuation to minimize life losses is a good strategy at the time of hazard.In this paper, we will describe the conceptual design of the visual aided DSS. To demonstrate the potential of adopting the proposed prototype elaborated and integration of WEAP model, Global Mapper and GIS proved as a salient feature of DSS as visual aided scenario generation. This paper has discussed the reasons for the use of prototype for flood hazards.
2. Integration of Model with Visuals
- The reliable of the identified mitigation measure for flood depends upon the accuracy of input datasets and method of analysis. Keeping in view this fact spatial data layers were acquired from secondary source (Department of Irrigation and Drainage, Malaysia) and get verified through collecting GPS field data. After collection and preparation of all datasets, layers were exported to geodatabase format of ArcGIS.The relationship between decision making and interactive graphics was investigated by[17]. Under this study, an interactive graphics based problem was structured and cognitive psychology incorporated into a decision support system. It confirmed that understanding complex problems influenced by visual-thinking, verbal, and logical reasoning skills. The general prototype design presents to brief the structure of proposed DSS and to define some terms used in the DSS as shown in figure 1.
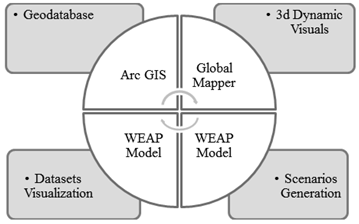 | Figure 1. General schematic structure of Visual aided DSS |
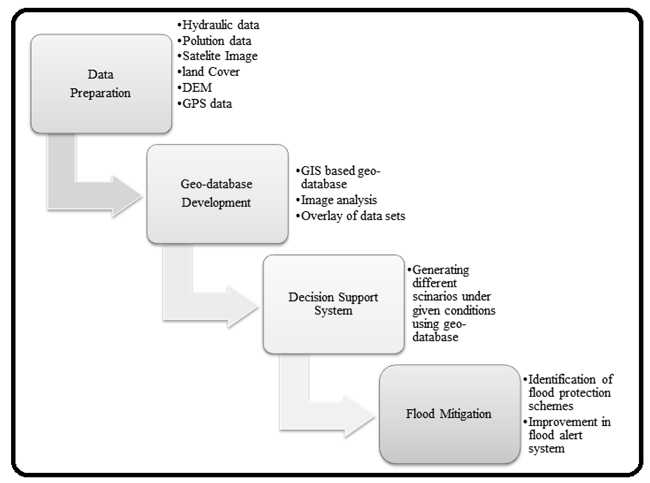 | Figure 2. Flow diagram for development of DSS |
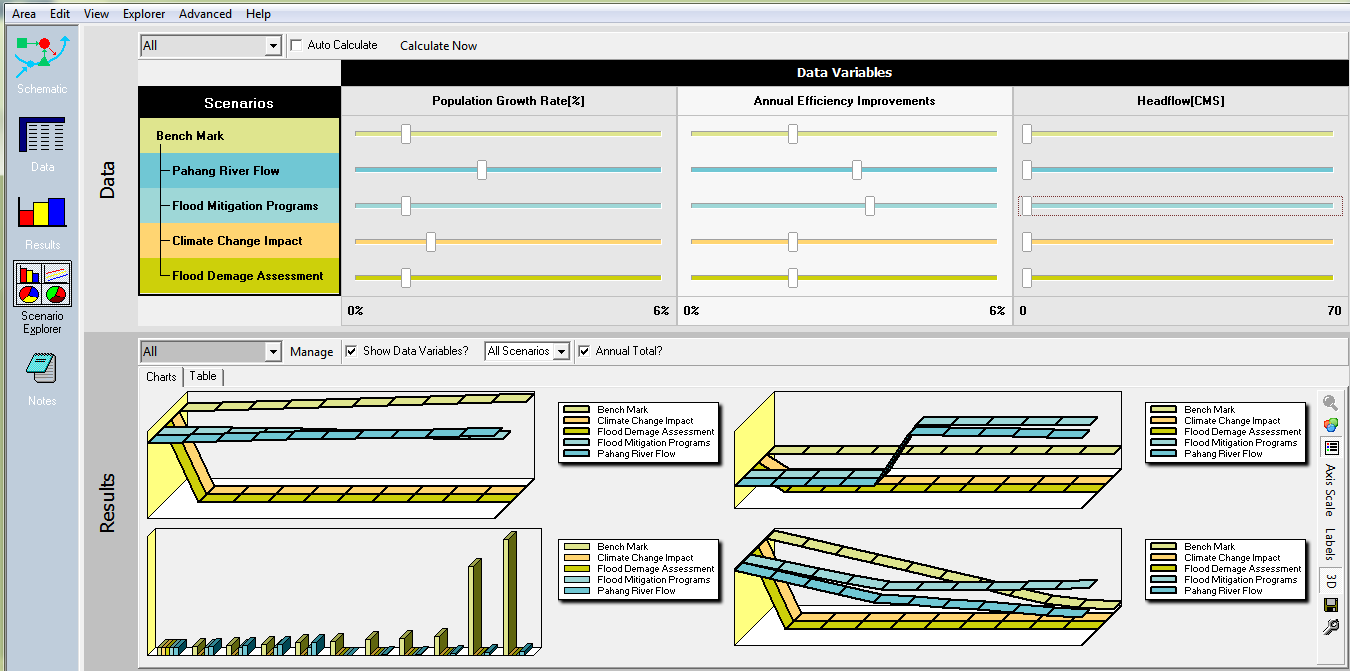 | Figure 3. Scenarios generation module with data visuals |
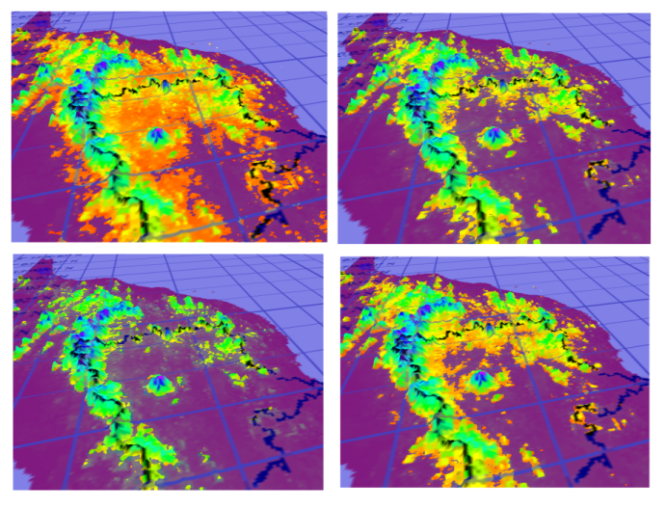 | Figure 4. Flood inundation as 3D dynamic visuals |
3. Visual Aided DSS Prototype
- Dynamically display of terrain parameters discussed in earlier section. Other important aspect is to simulate the datasets and results visualization. Figure 5 gives the simulated results for the Pahang River flows under impact of flood mitigation programs. This simulation testified using WEAP model and results as shown in figure 5.As a comparative, other study demonstrated that combining with GIS outputs and XP-SWMM for hydrodynamic simulation, the obtained results would prove to be more sophisticated as a tool for flood forecasting and flood warning system[18]. In this case, we may consider these facts, to involve the flexibility in proposed prototype so that users would be able to use different models. This situation will lead to more adoptive system of integration for improved DSS process.
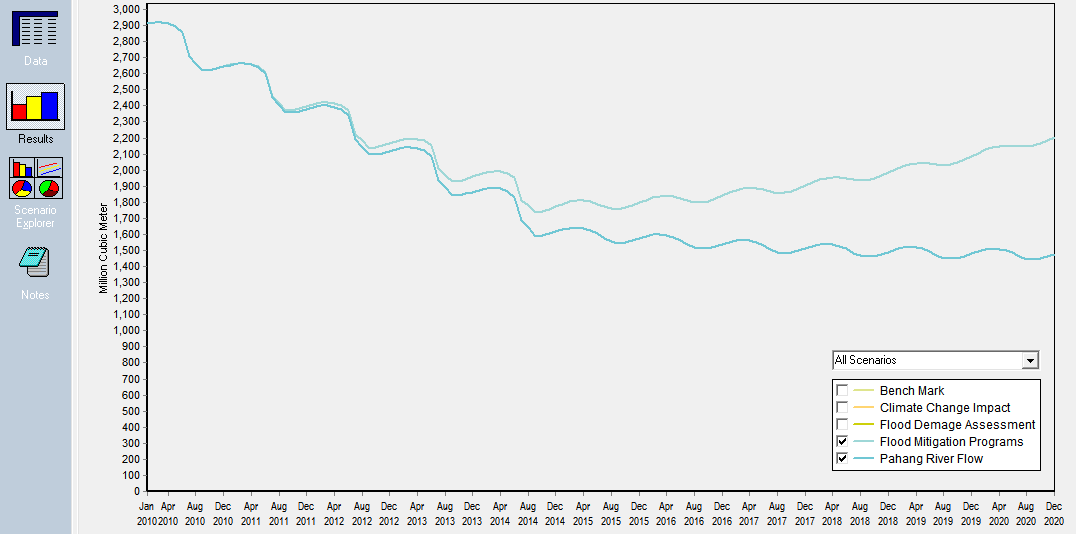 | Figure 5. Simulated results for Pahang River flow predictions under Impact of flood mitigation |
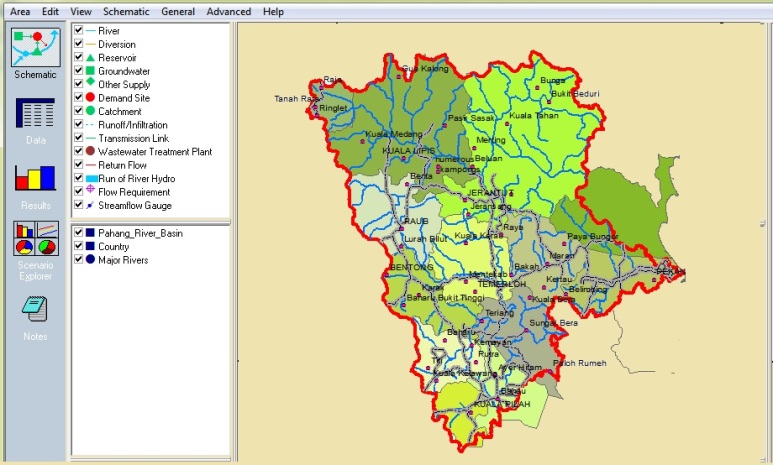 | Figure 6. Integrated Interface of WEAP modules with arc GIS display |
4. Application Potential of Prototype
- This section will show the proposed design and interface of DSS prototype. An example of application described below in figure 6. This integrated interface has been design to propose prototype display arrangement, under user - friendly environment.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
- There would be several possible modifications in the design of prototype as proposed. These changes truly suggested for localized validation of models for better output result. However, the concept of dynamic visual aided DSS would remain same. For a case of flood risk simulations for major events expose the people to higher vulnerability. To make the system sustainable and more resilient to natural disasters, it requires proper decisions for floodplains as a planning process[2]. In general, it can concluded, that an inappropriate model selection leads, towards satisfactory foundations to decide over best of the available options. In this study, an underestimation of the quantitative results based on the secondary data of hydrology and river flows. It also observed that the accuracy and validation of the generated scenarios is directly dependent on the accuracy of DEM. The improved development of 3D visual user interface attempted by[19], which facilitates users to participate actively in the process of visualizing flood forecasting. Current study added an aspect of DSS through integrating the 3D visuals. This study affirms that there is great potential to adopt the proposed methodology at a level of decision-making and integrated approach for DSS prototype including WEAP model, Global Mapper and GIS. This system provides users to take advantage to review the scenarios for post processing simulations. This provides a mean to fine-tune results, required to manage rivers and preparation plans prior to flood occurrences. The study concept would be adopted for the regions having similar climate, however, parameters of hydrological calculations may vary from basin to basin.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- University Malaysia Pahang funded this work under research grant GRS 110334 and provision of modelling software supported by Department of Irrigation and Drainage Malaysia. The authors would like to thank these both institutions and indebted to Centre for Earth Resources Research & Management (CERRM) for providing the facilities during field verifications.
Appendix
- MAPPING LAYERS OF GEODATABASE
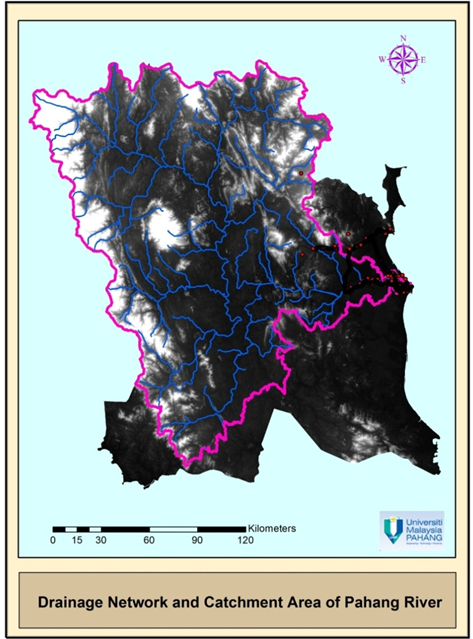 | Drainage Network and Catchment Area of Pahang River |
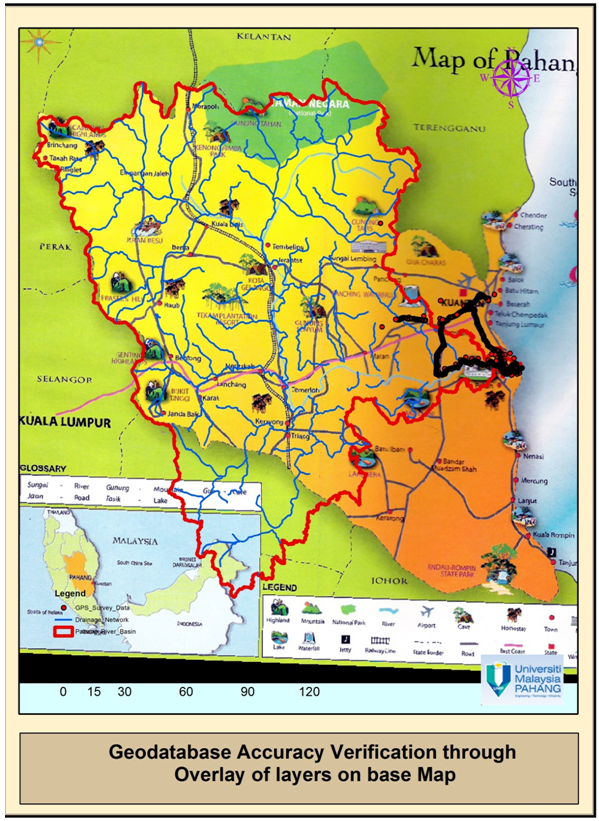 | Geodatabase Accuracy Verification through Overlay of layers on base Map |
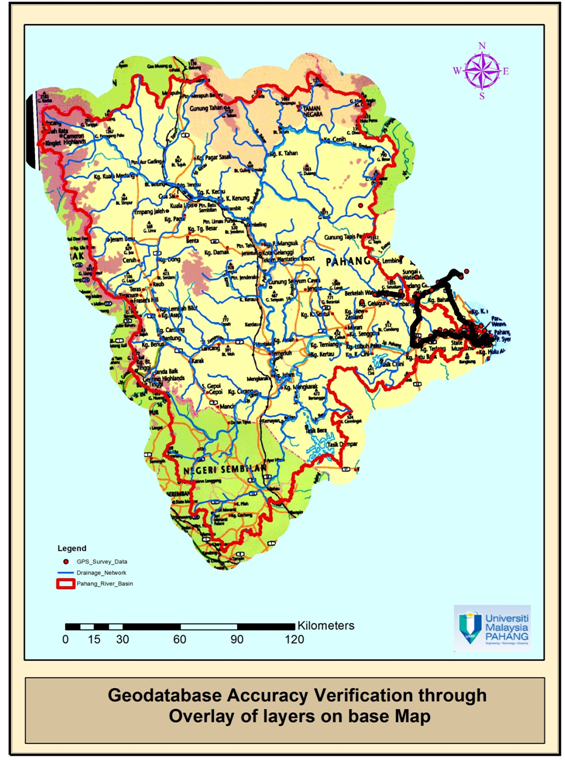 | Geodatabase Accuracy Verification through Overlay of layers on base Map |
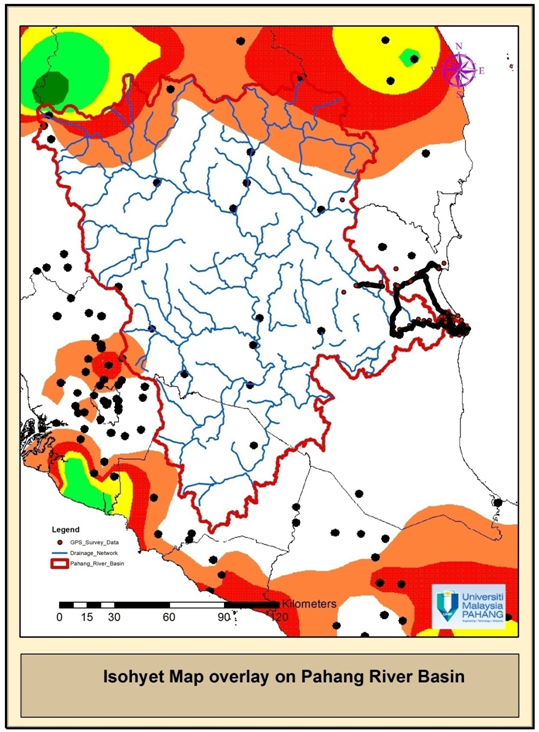 | Isohyet Map overlay on Pahang River Basin |
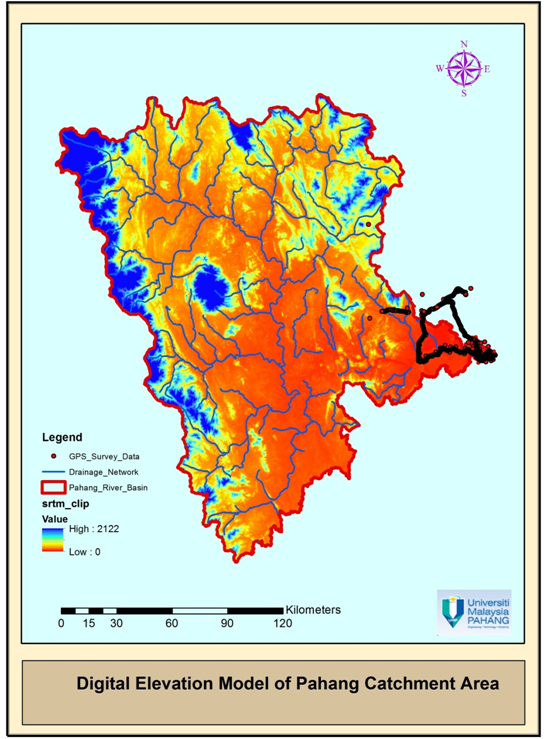 | Digital Elevation Model of Pahang Catchment Area |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML