-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Geographic Information System
p-ISSN: 2163-1131 e-ISSN: 2163-114X
2012; 1(3): 72-99
doi:10.5923/j.ajgis.20120103.05
Algorithms for the Characterisation of Plant Strategy Patterns on a Global Scale
James Furze 1, Jennifer Hill 1, Quan Min Zhu 1, Feng Qiao 2
1Faculty of Environment and Technology, University of the West of England, Frenchay Campus, Coldharbour Lane, Bristol, BS16 1QY, UK
2Faculty of Information and Control Engineering, Shenyang Jianzhu University, 9 Hunnan East Road, Hunnan New District, Shenyang, 110168, China
Correspondence to: James Furze , Faculty of Environment and Technology, University of the West of England, Frenchay Campus, Coldharbour Lane, Bristol, BS16 1QY, UK.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Plant species, primary producers are in a constant process of evolution due to biotic and abiotic pressures. Climate and topographical variables are principal, large-scale factors dictating plant distribution over space and time. In this study, fuzzy algorithms were used to show the relationship between plant species presence, topology and the water-energy dynamic at seven example locations thereby inferring plant strategy on a global scale. Species locality records were obtained from the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) and climatic data was sourced from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Plant life history strategies were ordered from ruderal, through competitive, to stress tolerant types with increasing severity of the environment. Abundance of species within each strategy was illustrated in contour levels in a conceptual diagram. Future developments include the use of local finer spatial resolution data in order to offer more detailed characterisation of plant species by life-form categories, metabolism and morphology, which may enhance modelling and prediction of climatic changes.
Keywords: Fuzzy Algorithm, Contour, Plant Strategy, Characterisation
Cite this paper: James Furze , Jennifer Hill , Quan Min Zhu , Feng Qiao , Algorithms for the Characterisation of Plant Strategy Patterns on a Global Scale, American Journal of Geographic Information System, Vol. 1 No. 3, 2012, pp. 72-99. doi: 10.5923/j.ajgis.20120103.05.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Plant strategies are based on plant life history descriptions[1],[2]. As reference[2] states ‘A plant strategy may be defined as a grouping of similar or analogous genetic characteristics which recurs widely among species or populations, such that they show similarities in ecology’ page 3,[2], meaning that species of the same strategy display similar growth patterns and form the same relational place in habitats with respect to surrounding species and conditions. The main strategy categories are: Competitor (C), Stress-tolerating (S) and Ruderal (R) species.Competitive species (C) are fast growing, often aggressive species with rapid nutrient absorbtion plus rapid root and leaf growth. They develop a consolidated growth form with vigorous lateral spread above and below ground, thriving in high nutrient soils. Stress-tolerating species (S) are slow growing species, capturing and retaining scarce resources in a continuously hostile environment. Their leaves are long-lived and often heavily defended against predation. Ruderal species (R) have a potentially high growth rate within the seedling phase and display early onset of the reproductive phase. The early allocation of resources to flowers and seeds is suited neither to development of extensive root and shoot systems needed for dominance of habitats, nor to highly stressed environments dependent on conservative patterns of resource use. Species may combine the above strategies (e.g. C-R, S-R, S-C and C-S-R), integrating different growth forms to suit the environment. Environment infers the strategy and vice versa[3], “Understanding the distribution of plant species across environmental gradients requires bringing theories together regarding the construction of plants, as well as their interactions with the environment, and the assembly of communities” page 1041,[4]. However the principal drawbacks of strategies in the classical form resides in the difficulty/complexity with which plants are ordinated into different types, making categorisation sometimes time-consuming and impractical when applied to large numbers of species. For example,[2] list 20 characteristics of the three strategies that have proven useful in classifying plants: main groups include types of morphology (including life-forms), elements of specific life history, physiological descriptions of growth rate (including photosynthetic mechanisms) and miscellaneous elements (such as litter description, palatability to unspecialized herbivores and DNA amount). These 4 may form key elements of plant strategies to be individually researched at a later scale. Application of Grime’s strategies was made in relation to Quercus cerris L. var. cerris woodland in Samsun, northern Turkey. Categorisation was considered appropriate as habitat diversity and environmental factors present in different combinations equated to various functional modifications in plants. Plant species conformed to definite strategies, supporting the contention that plant traits are subject to the dominant factors of competition and disturbance in their selection. The classical predictor values described by[3] proved to be inappropriate for Ruscus aculeatus due to the stem being the photosynthetic organ as opposed to the leaf (used in the calculation). Furthermore it was shown that species storing large amounts of water in their leaves may be mis-classified as the categorisation requires calculation of specific leaf area and leaf dry matter. Mis-classification also occurs in species adapted to live in very shaded conditions or high salt environments. It is recommended that future applications of strategies should be done through more robust calculation[5], which is what this paper sets out to do via the application of the fuzzy rule base.In a study of the evolution of model plant populations in computer simulated environments, nitrogen availability and disturbance frequency were used, and evolution of plant strategies and patterns consistent with previously described theoretical and field evidence were shown[1],[6].Illustration of plant strategies in computer simulated systems supported the existence of patterns on all scales, ultimately these may be modelled in real space and time. In simulation the species of 7 environments, linearly spaced across the rK (‘Kp’) continuum, were clearly set out[7]. From low to high Kp value, plants of ruderal (R) strategy were isolated in places of high disturbance and productivity, stress tolerant-ruderal plants (S-R) were seen in lightly disturbed habitats with low productivity, competitive-ruderal plants (C-R) were present in habitats where disturbance brought moderated competition by a relatively low level of stress, competitive plants (C) were found in environments with low disturbance and high productivity, competitive-stress tolerant-ruderal plants (C-S-R) were found in environments where there was a moderate intensity of stress and disturbance, competitive-stress tolerating plants (C-S) were found in environments where a moderate intensity of stress and a situation of relative-non-disturbance existed and stress tolerating plants (S) were found in environments where there was low productivity and low disturbance. An algorithm was combined with the technique for order preference and similarity to ideal situation[7],[8], which effectively reconciled both rK and C-S-R theories[1],[9].Ruderal plants exhibit low maturity, and in response to frequent disturbance early seed production takes place. Low seed biomass allows production of many seeds. Ruderals evolve with high growth rates, selection favouring high resource use, and accelerated life cycle. The collection of traits of ruderals are in common with the life history strategies of r-selected plants[10]. Stress tolerators have the longest life span, with slow growth and reproduction due to few soil resources. Computer simulated systems have been used in illustration of plant strategies with a more complex suite of input variables[7],[11].Considering large numbers of species in virtual or real-life situations, there are various methods that can be used to show clustering or grouping patterns. The recent work on L-systems[12], makes use of multi-variate principle component analysis. In reality, use of principle component analysis and detrended correspondance analysis may be difficult due to the nature of data being analysed and / or due to the ‘arching effect’ of continuous variables. In such situations, it may be more pertinent to make use of basic clustering methods, such as those used in modelling and algorithm development[11] - fuzzy logic is one method by which algorithms may be developed. The process of fuzzy logic starts with the linguistic construction of a fuzzy rule base and fuzzy consequences (undefined) and proceeds to higher numerical definition of the rule base and consequences[13].In using fuzzy techniques in classification, approximated summarised data is sufficient to be used[14], as fuzzy logic is a process of approximate reasoning which gives mathematical strength to perceptual and linguistic elements of patterns. An inference mechanism is provided under uncertainty, allowing networks to be learnt and adapted with tolerance to errors or changes in the variables[13].
1.1. Aim / Objectives
- The aim of this paper is to show the effectiveness of engineering data modelling techniques over those previously used in less flexible analyses for basic characterisation of plant life-history strategies. Fuzzy algorithms are formed to characterise plant strategies and are demonstrated through the use of climatic data and species numbers. The overall objective was to answer whether concise algorithmic statements of climatic conditions and species numbers may be used to infer finite classes of plant strategies / ‘environments’. Further an attempt to make the conceptual illustration of the model will be made.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Stages of Model Construction
- The stages of characterisation of plant species variation were carried out in the fuzzy rule based algorithms[13] as follows:1. Data were selected to define model parameters.2. The spread of numerical data and the total number of variables were defined.3. The minimum number of key parameters required to build the model was determined.4. Units and partitions within the data used were identified and concise linguistic description was made.5. Linguistic description of the data to give fuzzy description of each variable and the fuzzy consequences for each plant strategy/environment (E1 to E7) were defined.
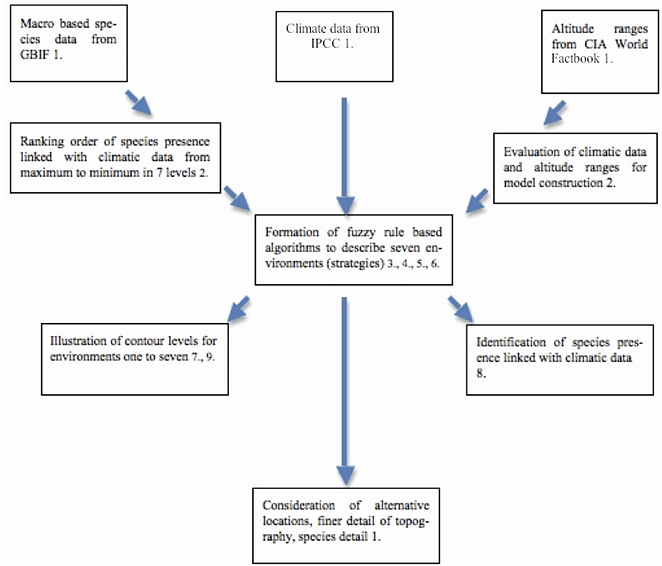 | Figure 1. Block diagram to show stages of methodology for the formation of fuzzy based algorithms to quantify plant life-history strategies on a global scale |
2.2. Selection of Sources
- The climatic model parameters (1960-90) were identified from the Intergovernmental Panel for Climate Change[17]. Altitude ranges for the chosen example locations were sourced and borders of the locations defined by the CIA World Factbook. Multiple expeditions were carried out by numerous research institutes across each location (citations available in supplementary information on request). Species identities and imprecise location details data were logged into the GBIF[18]. The final species presence data obtained in each case were used in this study were validated[19]. The predominant plant life history based strategy was approximated in conjunction with the IPCC and altitude data used to model them.
2.3. Numerical and Graphical Model Input Data
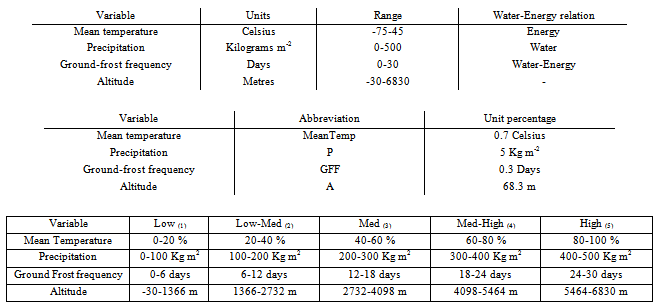
- Numerical data for water and energy related factors were sourced from[20] and may be graphically shown using software available from the IPCC. Maps displaying the data for the variables used were constructed. Nine variables in total were considered in accordance with the water-energy dynamic[21] as shown in Table 1. Altitude was considered as an essential element of the model due to the variable effects of climate (water and energy related factors) at different heights.
2.4. Minimisation of Variables
- The variables shown in Table 1 were reduced to four key variables in order to facilitate modelling of strategies. These variables were ground frost frequency (chosen for its effect in terms of disturbance), precipitation (chosen as the key water related variable), mean temperature (chosen as the key energy related variable) and altitude. Altitude was used, as it was key in the water-energy modelling of plant species, altitude varying the effect of different levels of water and energy related climatic variables[21],[22].
2.5. Units and Parameters
- Each variable was described in the units of the source documents. The ranges covered were defined and the unit percentage of each variable was calculated as shown in Table 2. The full description of variables is available in supplementary information on request.
|
2.6. Linguistic Description of Data
- The 5 linguistic terms were equally partitioned across each range of the variables in terms of percentage, quantifying the graphical description of the data shown in Figures 2-4. (The example locations are available with the fuzzy linguistic description in supplementary information on request).
2.7. Estimation of Number of Species in Chosen Examples
- In total seven estimates of the total number of individual plant occurrences were made, one for each of the example locations that were chosen randomly from areas containing more than 3000 plant species per 10000 km2 - diversity zones (DZ) 8-10[15], GBIF recorded number of individuals in each location were summed (citations available in supplementary information on request). The resultant total numbers of individuals were ranked in decreasing order from one to seven. After modelling water-energy and altitude variables to infer extremity of the environments’ plant life history based strategy, each number is allocated to an environment.
2.8. Construction of Algorithms
- The numerical data for each of the variables of Table 1 were considered in each of the seven example environments. Using the maximum and minimum inference of each variable’s linguistic definition (A1,…, n), the fuzzy rule-based algorithms were constructed such that each variable was expressed in terms of the number of species (B1,…, n) of each geographic location (E1, …, E7).Mean temperature was given as A1(1,…,n), precipitation was given as A2(1,…n), ground frost frequency was given as A3(1,…n), altitude was given as A4(1,…n), the number of species was given as B(1,…, n).The linguistic connections ‘IF’, ‘AND’ and ‘THEN’ were used to construct the conditional fuzzy rule base:
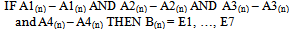 | (1) |
2.9. Illustration of Plant Strategies with Respect to Species Presence
- The technical computing platform MATLAB (version 2010a ©) Contour Plot function was used to display conceptual levels of the seven plant strategies with respect to the total individual numbers of plants within each of the seven environments. Numbers of individuals were entered into MATLAB to form a 2x2 matrix and a Z matrix of numbers was calculated (using a numerical space of 700 to reflect the seven plant strategies) from the 2x2 data. The magnitude of the number of individuals in each environment was used to reflect the difference between contour levels. The contours were plotted diagrammatically on a 700x700 axis using the ‘contour’ command in MATLAB.
3. Results
- Mexico was used as the example location to display graphical results.
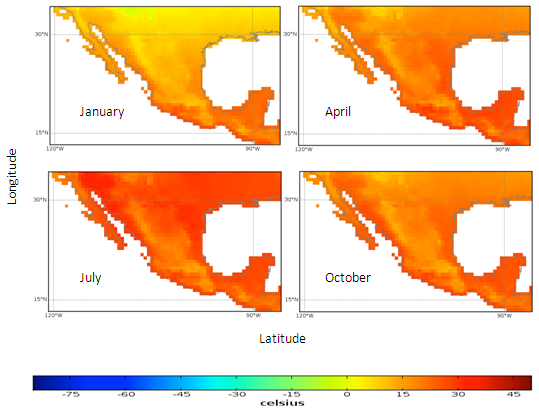 | Figure 2. Mexico quarterly temperature (1960-1990) mean |
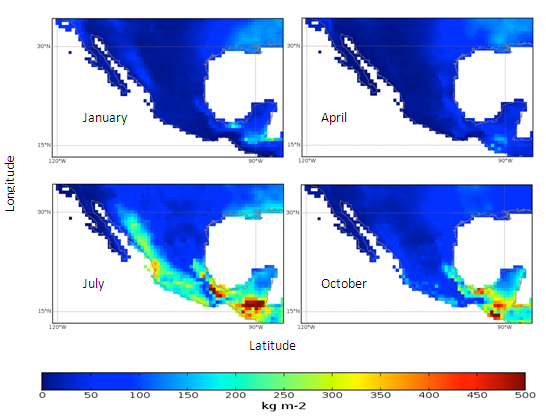 | Figure 3. Mexico quarterly observed precipitation (1960-90) mean |
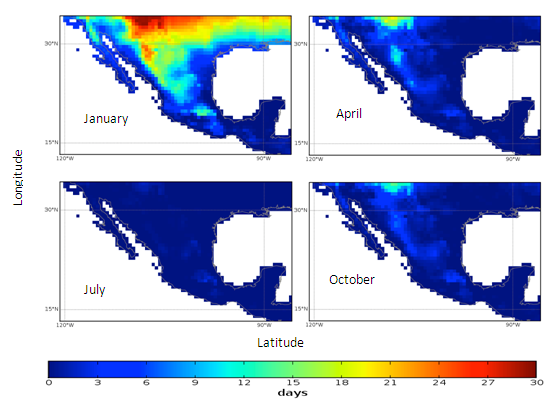 | Figure 4. Mexico quarterly observed ground frost frequency (1960-90) mean |
3.1. Fuzzy Rule Base for the Seven Environments
- The conditional fuzzy rule base for E1 is shown using the example environment of Mexico:IF A1(4) - A1(5) AND 0.5A2(1) - A2(3), 0.5A2(1) - A2(5) AND 0.25A3(1) - A3(5), 0.5A3(1) - A3(3), 0.25A3(1) IS ≤ A3(1) AND A4(1) - A4(5) THEN B(65535)=E1The above algorithm translated into the following conditions:IF Variables (A) =- Temperature = 40-60 % to 80-100 %- Precipitation = 0.5 x 0-100 Kg m2 to 200-300 Kg m2, 0.5 x 0-100 Kg m2 to 400-500 Kg m2- Ground Frost frequency = 0.25 x 0-6 days to 24-30 days, 0.5 x 0-6 days to 12-18 days, 0.25 x 0-6 days to 0-6 days- Altitude = -30-1366 m to 5464-6830 mTHEN Environment 1 (B) = 51847-65535 individual plant occurrences.Coefficients are used to concisely partition the inferential variable data (A), to give reasoning for the consequential data (B). Totals of individual plant occurrences from the collecting institutes were characterized in the following environments:Environment 1 (Ruderal) 51847-65535 (e.g. Mexico, Central America).Environment 2 (Stress-tolerant to Ruderal) 50700-51847 (e.g. Guyana, South America)Environment 3 (Stress-tolerant to Ruderal, Competitive to Ruderal) 33356-50700 (e.g. Cuba)Environment 4 (Competitive to Ruderal, Competitive) 11355-33356 (e.g. Democratic Republic of the Congo, Africa)Environment 5(Competitive to Stress-tolerant to Ruderal, Competitive to Stress-tolerant) 8805-11355 (e.g. Georgia, Eastern Europe)Environment 6 (Competitive to Stress-tolerant) 2203-8805 (e.g. Guinea, Africa)Environment 7 (Stress tolerant) 0-2023 (e.g. Macedonia, Southern Europe).
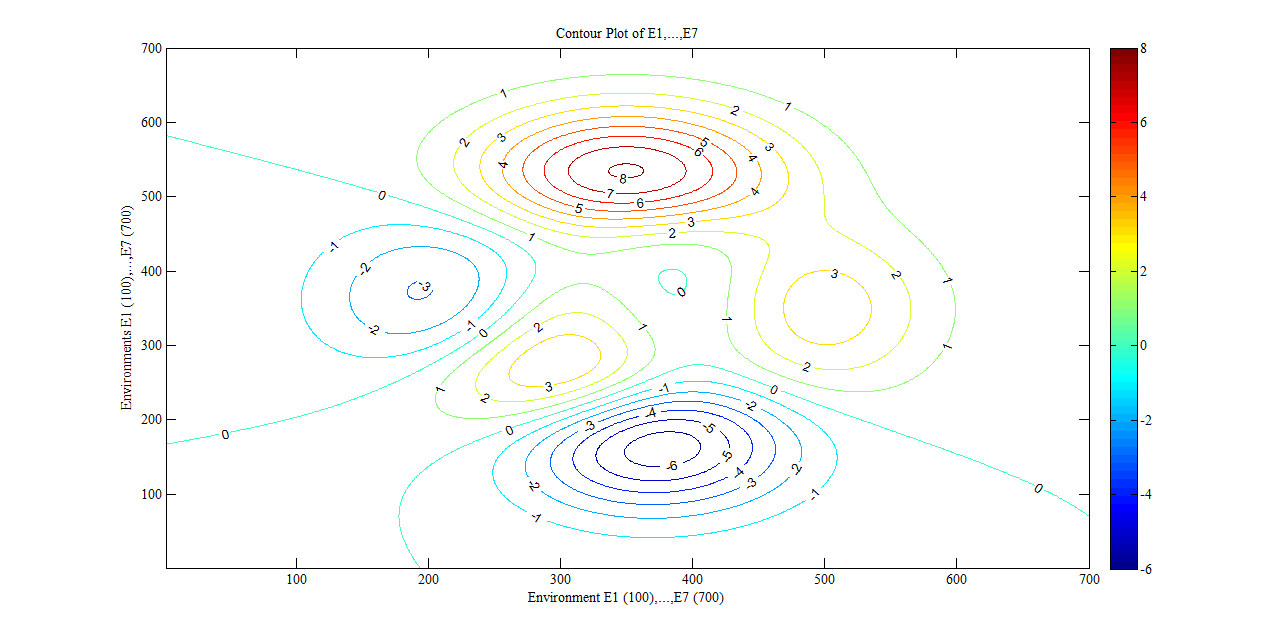 | Figure 5. Conceptual diagram showing contour level plot of environments one to seven |
4. Discussion
- Preserving the relationship between plant species presence and climatic and topographic variability requires the application of cooperatively controlled multi-agent systems. The use of a fuzzy-logic rule base is especially appropriate with respect to species presence as numbers of the latter involve mathematical dispersion based on the levels of water, energy and topographic dynamics. This paper clearly shows the relevance of a mathematical approach with respect to water and energy dynamics and furthers the information rich patterning of plant species based on life-history strategy characterisation[23]. The ecological relevance of the concept of plant strategies as derived from individual plant numbers is that the plant strategy patterns are shown in macro scale space. Topology has been simplified to discrete value ranges for the example locations given in this initial mathematical approach in order to show the validity of the modelling procedure. Precise detail of the locations was not available though will be explored in later studies. Feeding location-specific data into the models will validate their application at finer spatial resolution and enhance regional interpretation of biodiversity patterns. Greater understanding may direct conservation management at local and national level, especially pertinent in future dynamic climatic scenarios. The mathematical approach detailed is superior to other previously shown methods[1],[3],[9],[21] as it enables simple quantification of many different elements and expression through specific algorithms. The methods used in this paper are not Boolean which may be distorted by uneven data sampling but make use of the normal distribution of variables as may be used to describe dynamic patterns with greater accuracy[14]. These methods are suggested above historical approaches as they resort in minimal error[23], this is of great use in describing natural systems as the sensitivity of ecosystems with change can be eloquently stated.The application of the fuzzy rule base was shown along with the appropriate use of contour levels in order to reflect the numerical distribution of dimensionality between plant strategy groups. The information rich ordering of plant strategies shows the least severe environment to contain the highest numbers of individuals (ruderal plants) through competitive to the least number of individuals (stress tolerant plants) in the most severe environment.
5. Conclusions
- The patterning of plant species presence may be broken down into the seven life-history based strategies in the following way: The occurrence of a high water-energy dynamic results in the highest level of plant species diversity reflected in the greatest numbers of plant species presence. The highest plant species presence numbers reflects the dominant ruderal plant species. The effect of water and energy (mean rainfall and temperature) on plant distribution shown in this study may also be used to suggest application of more accurate modelling variables with the changing conditions within global warming / cooling cyles. Patterning of plant species in this and later studies may be used to increase the accuracy of climatic modelling.Decreasing numbers of individuals in each algorithmically described environment reflects the transition through competitive to stress tolerant species, which are present in the more extreme (hotter, dryer) environments.Future work will make use of the increased application of the mathematical methods shown in this paper with more highly detailed use of the climatic variables and region-specific topographic data which is available in order to specify more detailed characterisation of plant species at finer spatial and temporal resolutions. It is proposed that the more detailed characterisation may be carried out with use of field based species data and climatic / topographic data, which is available through online sources linked through the technical computing modelling platform Matlab (version 2010a ©) and subsequent versions. Such work will characterise plant species within categories of life form, metabolism and through to the different morphologies which are reflected in variation of the primary producers and their adaptive radiation[9],[24]. This will greatly enhance modelling of climatic scenarios available and provide valuable understanding of diversity patterns of local and national importance under the changing climate. Further implications of this study may provide contribution towards improved policy formation on a national scale of relevance in sustainability of global economies in line with plant species diversity, which may be seen within them. This is of increasing importance with increased pressures on natural resources.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Thanks go to the IPCC for the use of climatic data and to Prof. Holger Kreft for inspiration for this paper.
Appendix
- Partitions/Units for Model Parameters
 Guyana quarterly mean temperature (1960-1990) mean.
Guyana quarterly mean temperature (1960-1990) mean.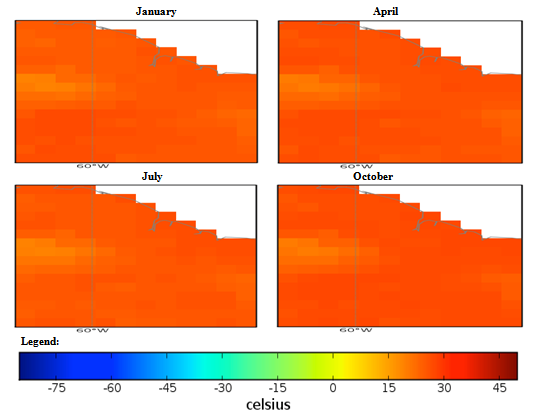 Guyana quarterly observed precipitation (1960-90) mean.
Guyana quarterly observed precipitation (1960-90) mean.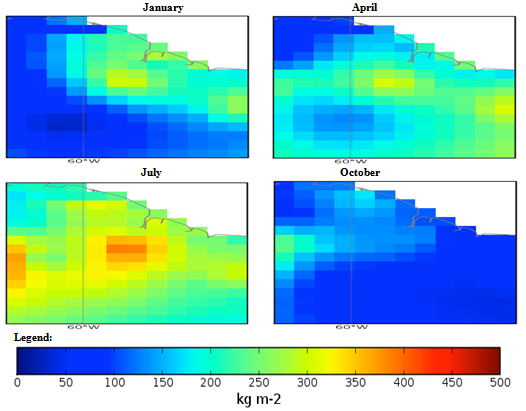 Guyana quarterly observed ground frost frequency (1960-90) mean.
Guyana quarterly observed ground frost frequency (1960-90) mean.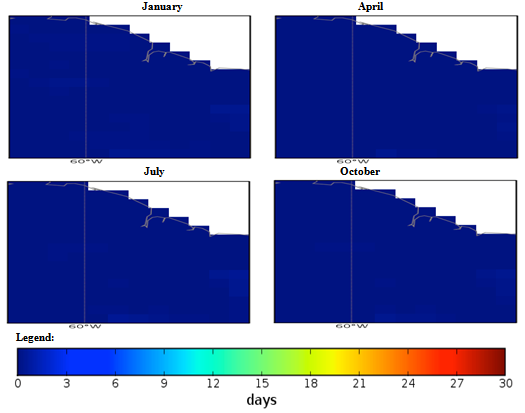 Cuba quarterly mean temperature (1960-1990) mean.
Cuba quarterly mean temperature (1960-1990) mean.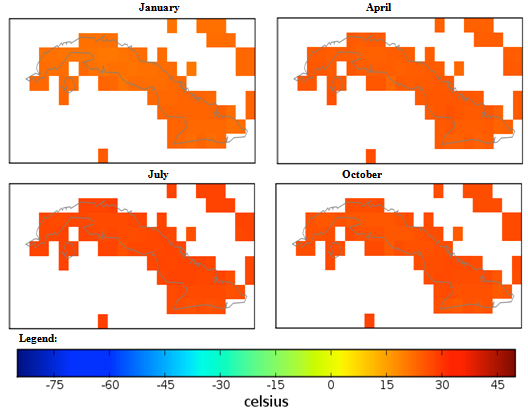 Cuba quarterly observed precipitation (1960-90) mean.
Cuba quarterly observed precipitation (1960-90) mean.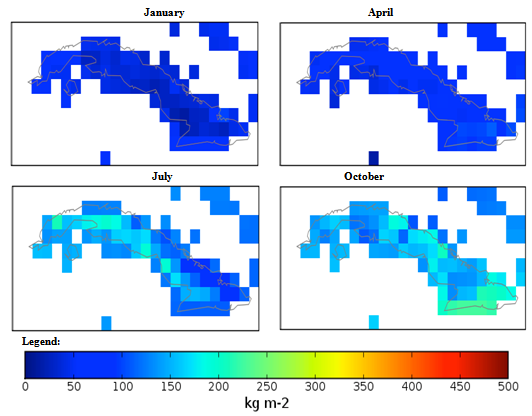 Cuba quarterly observed ground frost frequency (1960-90) mean.
Cuba quarterly observed ground frost frequency (1960-90) mean.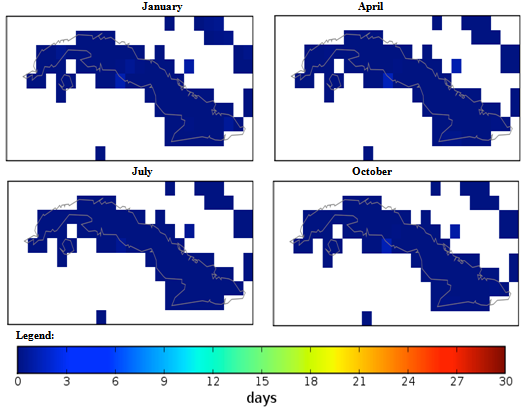 Democratic Republic of the Congo, Africa quarterly mean temperature (1960-1990) mean.
Democratic Republic of the Congo, Africa quarterly mean temperature (1960-1990) mean.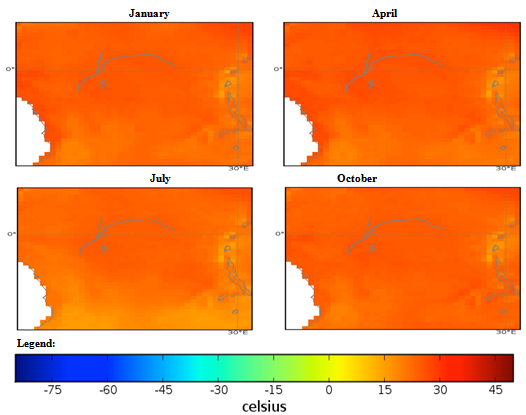 Democratic Republic of the Congo, Africa quarterly observed precipitation (1960-90) mean.
Democratic Republic of the Congo, Africa quarterly observed precipitation (1960-90) mean.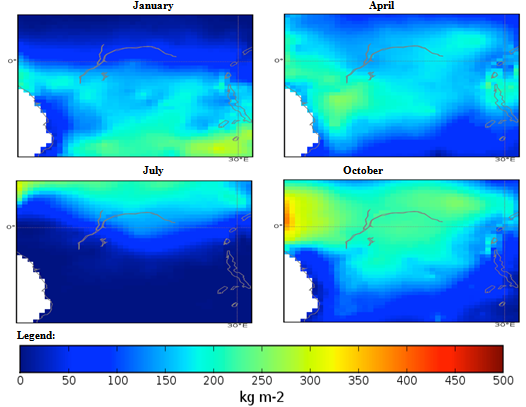 Democratic Republic of the Congo, Africa quarterly observed ground frost frequency (1960-90) mean.
Democratic Republic of the Congo, Africa quarterly observed ground frost frequency (1960-90) mean. Georgia, Eastern Europe quarterly mean temperature (1960-1990) mean.
Georgia, Eastern Europe quarterly mean temperature (1960-1990) mean.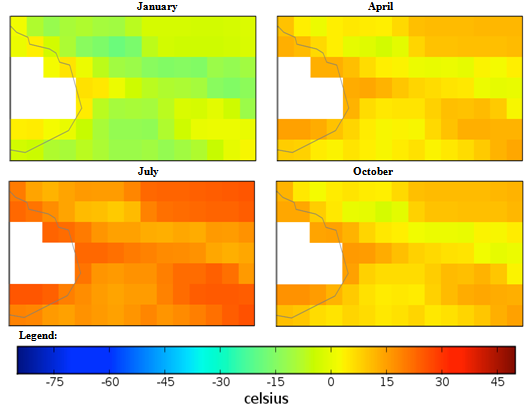 Georgia, Eastern Europe quarterly observed precipitation (1960-90) mean.
Georgia, Eastern Europe quarterly observed precipitation (1960-90) mean.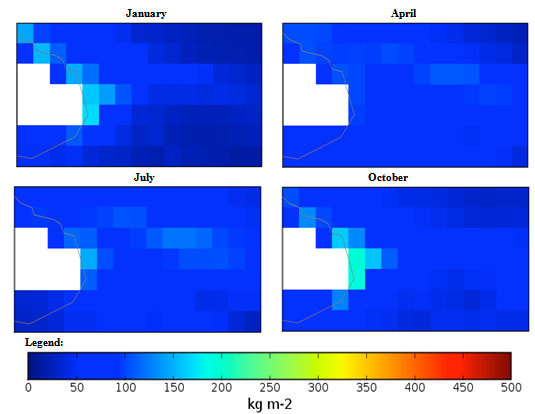 Georgia, Eastern Europe quarterly observed ground frost frequency (1960-90) mean.
Georgia, Eastern Europe quarterly observed ground frost frequency (1960-90) mean.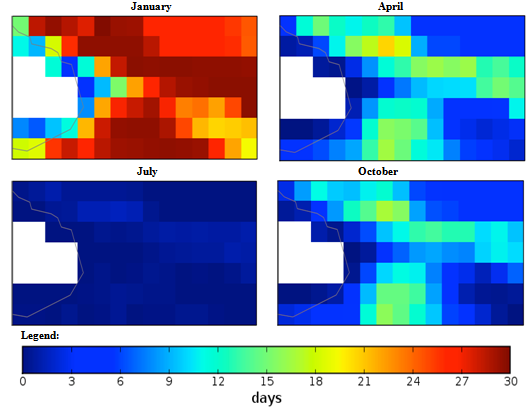 Guinea, Africa quarterly mean temperature (1960-1990) mean.
Guinea, Africa quarterly mean temperature (1960-1990) mean. Guinea, Africa quarterly observed precipitation (1960-90) mean.
Guinea, Africa quarterly observed precipitation (1960-90) mean.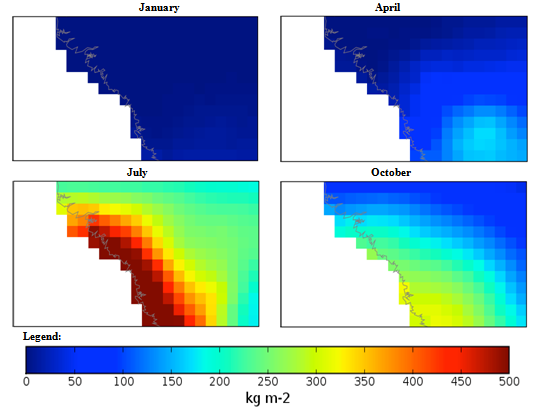 Guinea, Africa quarterly observed ground frost frequency (1960-90) mean.
Guinea, Africa quarterly observed ground frost frequency (1960-90) mean.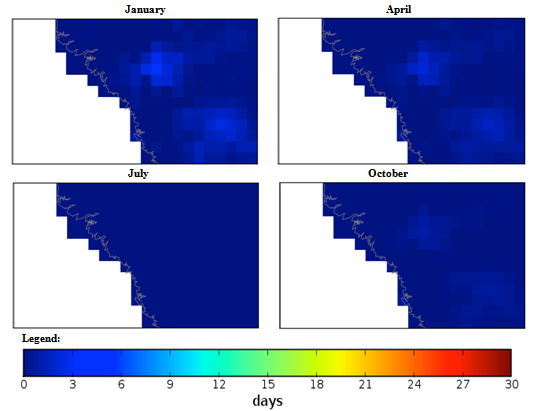 Macedonia, Southern Europe quarterly mean temperature (1960-1990) mean.
Macedonia, Southern Europe quarterly mean temperature (1960-1990) mean.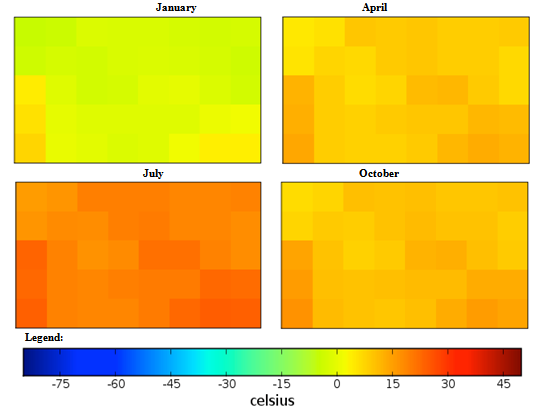 Macedonia, Southern Europe quarterly observed precipitation (1960-90) mean.
Macedonia, Southern Europe quarterly observed precipitation (1960-90) mean.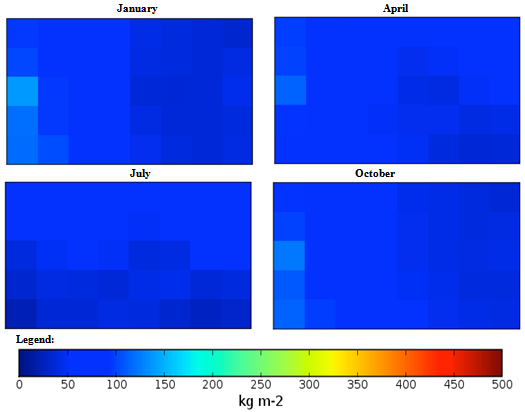 Macedonia, Southern Europe quarterly observed ground frost frequency (1960-90) mean.
Macedonia, Southern Europe quarterly observed ground frost frequency (1960-90) mean.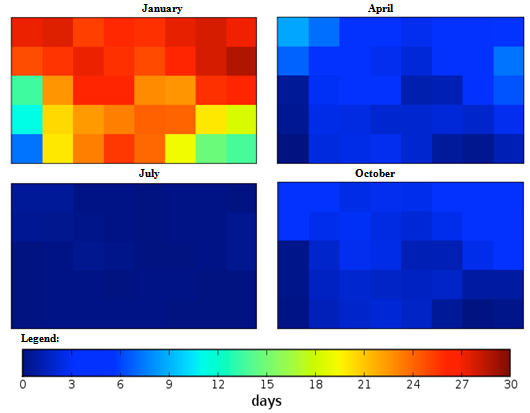 GBIF Citation sources:Mexico (DZ 8-9):(accessed through GBIF data portal, Type herbarium, Gottingen (GOET),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1494)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Bryophyte herbarium, Gottingen (GOET),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1492)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Vascular Plant Collection - University of Washington Herbarium (WTU), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/126)(accessed through GBIF data portal, herbario, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/566)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Paleobiology Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/563)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Flora of Japan Specimen Database,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/586)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Algae Collection of National Museum of Nature and Science,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/595)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Tropicos Specimen Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/621)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/629)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Arizona State University Vascular Plant Herbarium,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/676)(accessed through GBIF data portal, EURISCO, The European Genetic Resources Search Catalogue,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1905)(accessed through GBIF data portal, University of Copenhagen's Arboretum,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/702)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CGN-PGR, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1102)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Database Schema for UC Davis[Herbarium Labels],http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/734)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Database Schema for UC Davis[TGRC],http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/735)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UCD BOTANICAL CONSERVATORY, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/739)(accessed through GBIF data portal, California State University, Chico,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/737)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UA Herbarium, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/7900)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium (UNA), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/775)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Frutos y Semillas, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/778)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Plantas Vasculares, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/780)Guyana (DZ 8):Please cite this data as follows:(accessed through GBIF data portal, Bryophyte herbarium, Gottingen (GOET),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1492)(accessed through GBIF data portal, herbario, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/566)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Tropicos Specimen Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/621)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/629)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Arizona State University Vascular Plant Herbarium,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/676)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium (UNA), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/775)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Plantas Vasculares, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/780)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Fungi (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1038)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Mosses (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1040)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Algaterra Types, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1084)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Lichen Herbarium Berlin, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1097)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CGN-PGR, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1102)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbier de la Guyane, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1436)(accessed through GBIF data portal, HBGSpermatophyta - Herbarium Hamburgense,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1604)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium GZU, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1491)(accessed through GBIF data portal, The System-wide Information Network for Genetic Resources (SINGER), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1430)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium W, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1479)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Harvard University Herbaria, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1827)(accessed through GBIF data portal, National Herbarium of The Netherlands (NL) - Main collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11520)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium WU, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1496)(accessed through GBIF data portal, United States National Plant Germplasm System Collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1429)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Type herbarium, Gottingen (GOET),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1494)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Australian National Herbarium (CANB),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/47)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Berolinense, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1095)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Vascular Plant Collection - University of Washington Herbarium (WTU), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/126)(accessed through GBIF data portal, The AAU Herbarium Database,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/224)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico (Madrid), Vascular Plant Herbarium (MA),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/240)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbario de la Universidad de Sevilla, SEV-Historico,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/284)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CABI Bioscience Genetic Resource Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/166)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico, Madrid: MA-Musci,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/235)(accessed through GBIF data portal, BoGART, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1087)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Gothenburg Herbarium - Types (GBIF:IH:GB:Herbarium),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1766)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UCBG TAPIR Provider, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1412)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Coleccion de Briofitas, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/784)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamie, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1506)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Canadian Museum of Nature Herbarium,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/123)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Fairchild Tropical Botanic Garden Virtual Herbarium Darwin Core format, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/202)(accessed through GBIF data portal, SysTax, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1875)(accessed through GBIF data portal, NSW herbarium collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/968)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CABI Bioscience Fungus Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/167)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Zurich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1903)(accessed through GBIF data portal, EURISCO, The European Genetic Resources Search Catalogue, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1905)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Oxford University Herbaria, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/2020)(accessed through GBIF data portal, NMNH Botany Collections, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1874)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UA Herbarium, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/7900)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Specimens of Museum of Nature and Human Activities, Hyogo Prefecture, Japan,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1958)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Rapid Assessment Program (RAP) Biodiversity Survey Database,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8076)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamic Botanical Collections (S),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8113)(accessed through GBIF data portal, DUKE Bryophyte Collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8104)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium WRSL, Main Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8182)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Senckenbergianum (FR),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8311)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Instituto de Ciencias Naturales, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/2559)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium of The New York Botanical Garden,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8967)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Coleccion de Plantas Acuaticas,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8047)(accessed through GBIF data portal, RBGE Living Collections, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/9167)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Zurich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11516)(accessed through GBIF data portal, DAO Herbarium Type Specimens, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/527)(accessed through GBIF data portal, University of Alberta Museums, Vascular Plant Herbarium, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11612)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CONN GBIF data, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/7857)(accessed through GBIF data portal, RBGE Herbarium (E), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8402)Cuba (DZ 8):Please cite this data as follows:(accessed through GBIF data portal, Type herbarium, Gottingen (GOET),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1494)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Bryophyte herbarium, Gottingen (GOET),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1492)(accessed through GBIF data portal, herbario, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/566)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Paleobiology Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/563)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Tropicos Specimen Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/621)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/629)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Arizona State University Vascular Plant Herbarium,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/676)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Database Schema for UC Davis[TGRC],http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/735)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UCD BOTANICAL CONSERVATORY, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/739)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium (UNA), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/775)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Plantas Vasculares, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/780)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Mosses (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1040)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Lund Botanical Museum (LD), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1028)(accessed through GBIF data portal, BoGART, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1087)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Lichen Herbarium Berlin, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1097)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CGN-PGR, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1102)(accessed through GBIF data portal, HBGBryophyta - Herbarium Hamburgense,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1603)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbier de la Guyane, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1436)(accessed through GBIF data portal, HBGSpermatophyta - Herbarium Hamburgense,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1604)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium GZU, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1491)(accessed through GBIF data portal, The System-wide Information Network for Genetic Resources (SINGER), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1430)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium W, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1479)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Harvard University Herbaria, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1827)(accessed through GBIF data portal, National Herbarium of The Netherlands (NL) - Main collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11520)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium WU, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1496)(accessed through GBIF data portal, United States National Plant Germplasm System Collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1429)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Bishop Museum Natural Sciences Data,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/54)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Programa de repatriacion de datos de ejemplares mexicanos, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/2488)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Australian National Herbarium (CANB),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/47)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Berolinense, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1095)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CBS fungi strains, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/69)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Australian Antarctic Division Herbarium,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/76)(accessed through GBIF data portal,Sukkulentensammlung Zurich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8135)(accessed through GBIF data portal, BCCM/MUCL - (Agro)Industrial Fungi and Yeasts Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/103)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Vascular Plant Collection - University of Washington Herbarium (WTU), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/126)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico, Madrid: MA-Algae,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/234)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico, Madrid: MA-Musci,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/235)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico, Madrid: MA-Hepat,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/236)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Botanic Garden of Finnish Museum of Natural History,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/2406)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico (Madrid), Vascular Plant Herbarium (MA),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/240)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Jardin Botanico de Cordoba: Herbarium COA,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/247)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Botany (UPS), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1045)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CIBIO,Alicante:ABH-GBIF, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/251)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico, Madrid: MA-Funhist,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/256)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Escuela Tecnica Superior de Ingenieros de Montes, UPM: EMMA, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/278)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Universidad de Malaga: MGC-Cormof,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8105)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbario de la Universidad de Sevilla, SEV-Historico,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/284)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CUBA: Herbario de la Academia de Ciencias, La Habana, Cuba:HAC-Pteridophyta, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/296)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CUBA:Herbario del Jardin de los Helechos, Centro Oriental de Ecosistemas y Biodiversidad, Santiago de Cuba: BSC-Pteridophyta, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/297)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CUBA:Herbario del Jardin Botanico Nacional, La Habana, Cuba:HAJB-Pteridophyta, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/298)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CABI Bioscience Genetic Resource Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/166)(accessed through GBIF data portal, The AAU Herbarium Database,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/224)(accessed through GBIF data portal, The Myxomycetes Collection at the V. L. Komarov Botanical Institute, St. Petersburg, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1751)(accessed through GBIF data portal, IPK Genebank, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1851)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Algaterra Types, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1084)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Gothenburg Herbarium - General (GBIF:IH:GB:Herbarium),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1765)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Gothenburg Herbarium - Types (GBIF:IH:GB:Herbarium),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1766)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Fairchild Tropical Botanic Garden Virtual Herbarium Darwin Core format, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/202)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Institut Botanic de Barcelona, BC-Historico,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1523)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UCBG TAPIR Provider, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1412)(accessed through GBIF data portal, DAO Herbarium Type Specimens, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/527)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Planetary Biodiversity Inventory Eumycetozoan Databank,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1515)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Canadian Museum of Nature Herbarium,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/123)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Coleccion de Briofitas, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/784)(accessed through GBIF data portal, NSW herbarium collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/968)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamie, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1506)(accessed through GBIF data portal, NMNH Botany Collections, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1874)(accessed through GBIF data portal, USU-UTC Specimen Database,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1508)(accessed through GBIF data portal, SysTax, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1875)(accessed through GBIF data portal, DUKE Bryophyte Collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8104)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CABI Bioscience Fungus Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/167)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Zurich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1903)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Database Schema for UC Davis[Herbarium Labels],http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/734)(accessed through GBIF data portal, EURISCO, The European Genetic Resources Search Catalogue,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1905)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbario del Instituto de Ecologia, A.C., Mexico (IE-XAL), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1597)(accessed through GBIF data portal, TestCollection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/2397)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UCMP TAPIR Provider, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1414)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Instituto de Ciencias Naturales, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/2559)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CONN GBIF data, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/7857)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UA Herbarium, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/7900)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Botany Vascular Plant Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/7915)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Specimens of Museum of Nature and Human Activities, Hyogo Prefecture, Japan,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1958)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CeDoc de Biodiversitat Vegetal: BCN-Phycophyta,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1760)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamic Botanical Collections (S),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8113)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Peabody Paleobotany DiGIR Service,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8141)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium WRSL, Main Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8182)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Peabody Paleoportal DiGIR Service (PB),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8176)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Senckenbergianum (FR),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8311)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Algae (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1039)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Universidad de Oviedo. Departamento de Biologia de Organismos y Sistemas: FCO-Algae,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8403)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Bridel Herbar, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1088)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Universitat de Valencia, Colecciones de Criptogamas: VAL_Algae, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/2509)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium of The New York Botanical Garden,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8967)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Tipos de plantas vasculares,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/782)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Coleccion de Plantas Acuaticas,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8047)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Agavaceae, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8391)(accessed through GBIF data portal, RBGE Living Collections, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/9167)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbario XAL del Instituto de Ecologia, A.C., Mexico (IE-XAL), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/10980)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Coleccion de Monocotiledoneas Mexicanas (UAM-I),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11109)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Zurich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11516)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Nordic Genetic Resources, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1487)(accessed through GBIF data portal, University of Alberta Museums, Vascular Plant Herbarium,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11612)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Natural Geography In Shore Areas (NaGISA) Dataset,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/327)(accessed through GBIF data portal, RBGE Herbarium (E), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8402)Democratic Republic of the Congo, Africa (DZ 8):Please cite this data as follows:(accessed through GBIF data portal, Paleobiology Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/563)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Tropicos Specimen Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/621)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/629)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Pteridophytes (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1037)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Mosses (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1040)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Algaterra Types, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1084)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Staatliches Museum fur Naturkunde Stuttgart, Herbarium,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1100)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CGN-PGR, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1102)(accessed through GBIF data portal, HBGSpermatophyta - Herbarium Hamburgense,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1604)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/7943)(accessed through GBIF data portal, The System-wide Information Network for Genetic Resources (SINGER), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1430)(accessed through GBIF data portal, National Herbarium of The Netherlands (NL) - Main collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11520)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Bryophyte herbarium, Gottingen (GOET),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1492)(accessed through GBIF data portal, United States National Plant Germplasm System Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1429)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Central African Plants, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8377)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Bishop Museum Natural Sciences Data,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/54)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Australian National Herbarium (CANB),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/47)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Berolinense, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1095)(accessed through GBIF data portal, National Botanic Garden Belgium - Albertian Rift Rubiaceae (ENBI wp13), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/90)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Royal Museum of Central Africa - Metafro-Infosys - Prelude,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/96)(accessed through GBIF data portal, BCCM/MUCL - (Agro)Industrial Fungi and Yeasts Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/103)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Zurich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1903)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Botany (UPS), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1045)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Botanic Garden of Finnish Museum of Natural History,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/2406)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UCMP TAPIR Provider, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1414)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Harvard University Herbaria, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1827)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UCBG TAPIR Provider, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1412)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Coleccion de Briofitas, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/784)(accessed through GBIF data portal, NSW herbarium collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/968)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamie, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1506)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Ichtyologie, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1507)(accessed through GBIF data portal, SysTax, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1875)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CABI Bioscience Fungus Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/167)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UA Herbarium, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/7900)(accessed through GBIF data portal, EURISCO, The European Genetic Resources Search Catalogue,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1905)(accessed through GBIF data portal, NHT_flora, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8350)(accessed through GBIF data portal, NMNH Botany Collections, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1874)(accessed through GBIF data portal, DUKE Bryophyte Collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8104)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Specimens of Museum of Nature and Human Activities, Hyogo Prefecture, Japan,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1958)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Rapid Assessment Program (RAP) Biodiversity Survey Database,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8076)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamic Botanical Collections (S),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8113)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Database Schema for UC Davis[Herbarium Labels],http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/734)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Peabody Paleobotany DiGIR Service,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8141)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Peabody Paleoportal DiGIR Service (PB),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8176)(accessed through GBIF data portal,Sukkulentensammlung Zurich, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8135)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium of The New York Botanical Garden,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8967)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium of the Universite Libre de Bruxelles,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/9102)(accessed through GBIF data portal, IICT Herb√°rio LISC, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/10840)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Zurich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11516)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Flora of tanzania, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/10860)(accessed through GBIF data portal, RBGE Herbarium (E), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8402)(accessed through GBIF data portal, The Vascular Plant Collection at the Botanische Staatssammlung Munchen, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11996)Georgia (DZ 8):Please cite this data as follows:(accessed through GBIF data portal, Paleobiology Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/563)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Tropicos Specimen Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/621)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/629)(accessed through GBIF data portal, EURISCO, The European Genetic Resources Search Catalogue, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1905)(accessed through GBIF data portal, University of Copenhagen's Arboretum,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/702)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium of Oskarshamn (OHN),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1024)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Lund Botanical Museum (LD), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1028)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Pteridophytes (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1037)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Mosses (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1040)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Staatliches Museum fur Naturkunde Stuttgart, Herbarium,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1100)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CGN-PGR, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1102)(accessed through GBIF data portal, HBGBryophyta - Herbarium Hamburgense,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1603)(accessed through GBIF data portal, The System-wide Information Network for Genetic Resources (SINGER), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1430)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium W, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1479)(accessed through GBIF data portal, National Herbarium of The Netherlands (NL) - Main collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11520)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium WU, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1496)(accessed through GBIF data portal, United States National Plant Germplasm System Collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1429)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Polish gene bank ‚Äì passport data of plants accessions which are important in human life, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8332)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Australian National Herbarium (CANB),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/47)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Berolinense, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1095)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico, Madrid: MA-Musci,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/235)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Universidad del Pais Vasco/EHU, Bilbao: Herbario BIO,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/242)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico (Madrid), Vascular Plant Herbarium (MA),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/240)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Jardin Botanic de Valencia: VAL, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/238)(accessed through GBIF data portal, IPK Genebank, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1851)(accessed through GBIF data portal, BoGART, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1087)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Harvard University Herbaria, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1827)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Universidad Politecnica de Madrid, Biologia Vegetal, Banco de Germoplasma, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1521)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamie, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1506)(accessed through GBIF data portal, DUKE Bryophyte Collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8104)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CABI Bioscience Fungus Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/167)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Aranzadi Zientzi Elkartea, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/248)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Zurich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1903)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Bryophyte herbarium, Bergen (BG),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1073)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium GZU, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1491)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbario de la Universidad de Salamanca: SALA,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/239)(accessed through GBIF data portal, HBGSpermatophyta - Herbarium Hamburgense,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1604)(accessed through GBIF data portal, NMNH Botany Collections, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1874)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Nordic Genetic Resources, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1487)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbario de la Universidad de Sevilla, SEV,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/283)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamic Botanical Collections (S),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8113)(accessed through GBIF data portal, RBGE Living Collections, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/9167)(accessed through GBIF data portal,Sukkulentensammlung Zurich, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8135)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium of The New York Botanical Garden,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8967)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Z√ºrich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11516)(accessed through GBIF data portal, RBGE Herbarium (E), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8402)Guinea, Africa (DZ 8):Please cite this data as follows:(accessed through GBIF data portal, Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/629)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Tropicos Specimen Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/621)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UCD BOTANICAL CONSERVATORY, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/739)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Pteridophytes (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1037)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Mosses (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1040)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Lund Botanical Museum (LD), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1028)(accessed through GBIF data portal, HBGBryophyta - Herbarium Hamburgense,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1603)(accessed through GBIF data portal, The System-wide Information Network for Genetic Resources (SINGER), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1430)(accessed through GBIF data portal, National Herbarium of The Netherlands (NL) - Main collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11520)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Bryophyte herbarium, Gottingen (GOET),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1492)(accessed through GBIF data portal, United States National Plant Germplasm System Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1429)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Berolinense, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1095)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico, Madrid: MA-Musci,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/235)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico (Madrid), Vascular Plant Herbarium (MA),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/240)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Jardin Botannico de Cordoba: Herbarium COA,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/247)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CABI Bioscience Genetic Resource Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/166)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Harvard University Herbaria, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1827)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UCBG TAPIR Provider, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1412)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamie, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1506)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CABI Bioscience Fungus Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/167)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Zurich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1903)(accessed through GBIF data portal, EURISCO, The European Genetic Resources Search Catalogue,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1905)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium W, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1479)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbario de la Universidad de Salamanca: SALA,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/239)(accessed through GBIF data portal, NMNH Botany Collections, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1874)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Rapid Assessment Program (RAP) Biodiversity Survey Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8076)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamic Botanical Collections (S),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8113)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Senckenbergianum (FR),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8311)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium of The New York Botanical Garden,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8967)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Colecci√≥n de Plantas Acu√°ticas,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8047)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium of Namur, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11286)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Z√ºrich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11516)(accessed through GBIF data portal, RBGE Herbarium (E), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8402)Macedonia (DZ 8):Please cite this data as follows:(accessed through GBIF data portal, EURISCO, The European Genetic Resources Search Catalogue,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1905)(accessed through GBIF data portal, University of Copenhagen's Arboretum,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/702)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Pteridophytes (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1037)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Lund Botanical Museum (LD), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1028)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Fungi (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1038)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Mosses (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1040)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Algaterra Types, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1084)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Staatliches Museum fur Naturkunde Stuttgart, Herbarium,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1100)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CGN-PGR, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1102)(accessed through GBIF data portal, HBGSpermatophyta - Herbarium Hamburgense,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1604)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium W, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1479)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium GJO, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1484)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium WU, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1496)(accessed through GBIF data portal, United States National Plant Germplasm System Collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1429)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Type herbarium, Gottingen (GOET),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1494)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Berolinense, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1095)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico (Madrid), Vascular Plant Herbarium (MA),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/240)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Australian National Herbarium (CANB),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/47)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbario de la Universidad de Sevilla, SEV,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/283)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Jardi Botanic de Valencia: VAL, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/238)(accessed through GBIF data portal, IPK Genebank, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1851)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Gothenburg Herbarium - Types (GBIF:IH:GB:Herbarium),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1766)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Polish seed gene bank ‚Äì historical passport data of accessions, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8333)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Harvard University Herbaria, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1827)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Institut Botanic de Barcelona, BC, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/299)(accessed through GBIF data portal, USU-UTC Specimen Database,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1508)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Zurich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1903)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium GZU, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1491)(accessed through GBIF data portal, FloVegSI - Floristical and fitocenological database of ZRC SAZU, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/2585)(accessed through GBIF data portal, NMNH Botany Collections, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1874)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamic Botanical Collections (S),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8113)(accessed through GBIF data portal, DUKE Bryophyte Collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8104)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Senckenbergianum (FR),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8311)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbario de la Universidad de Salamanca: SALA,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/239)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium of The New York Botanical Garden,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8967)(accessed through GBIF data portal, RBGE Living Collections, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/9167)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/629)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Z√ºrich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11516)(accessed through GBIF data portal, National Herbarium of The Netherlands (NL) - Main collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11520)(accessed through GBIF data portal, RBGE Herbarium (E), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8402)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamie, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1506)IF-Then rules for 7 environmentsUsing Max-Min inference (A1,n) MeanTemp (Mean Temperature, Energy), P (Precipitation, Water), GFF (Ground frost frequency), A (Altitude) equal to E1 (Number of species (B1,n) is High, minimum competitive strategy) to E7 (Number of species (B1,n) is ≥ 1, Low, maximum stress tolerating strategy)(1)=0-20%, (2)=20-40%, (3)=40-60%, (4)=60-80%, (5)=80-100%Algorithms to be read over the course of a year (10 year mean)IF A… THEN B… Variables = A Environments = BMeanTemp is A1(1,n)Precipitation is A2(1,n)Ground frost frequency is A3(1,n)Altitude is A4(1,n)Number of species is B(1,n)1. E1 (R)Example: MexicoE1 Temp is med-high - highE1 P is 0.5low - med 0.5low - highE1 GFF is 0.25low – high 0.5low – med 0.25 low – lowE1 A is low - HighIF A1(4) - A1(5) AND 0.5A2(1) - A2(3), 0.5A2(1) - A2(5) AND 0.25A3(1) - A3(5), 0.5A3(1) - A3(3), 0.25A3(1) IS ≤ A3(1) AND A4(1) - A4(5) THEN B(65535)=E1IF Variables (A) =- Temperature = 40-60 % to 80-100 %- Precipitation = 0.5 x 0-100 Kg m2 to 200-300 Kg m2, 0.5 x 0-100 Kg m2 to 400-500 Kg m2- Ground Frost frequency = 0.25 x 0-6 days to 24-30 days, 0.5 x 0-6 days to 12-18 days, 0.25 x 0-6 days to 0-6 days- Altitude = -30-1366 m to 5464-6830 mTHEN Environment 1 (B) = 51847-655352. E2 (S-R)Example GuyanaE2 Temp is high – high E2 P is 0.75low - med 0.25 low – med-highE2 GFF ≥0 low - lowE2 A is low – med-highIF A1(5)≤ A1(5) AND 0.75A2(1) - A2(3), 0.25A2(1) - A2(4) AND A3(1) IS ≤ A3(1) AND A4(1) to A4(4) THEN B(51847)=E2IF Variables A =- Temperature = 80-100 % to 80-100 %- Precipitation = 0.75 x 0-100 Kg m2 to 200-300 Kg m2, 0.25 x 0-100 Kg m2 to 300-400 Kg m2- Ground Frost frequency = 0-6 days to 0-6 days- Altitude = -30-1366 m to 4098-5464 mTHEN Environment 2 (B) = 50700-518473. E2/3 (S-R – C-R)Example CubaE3 Temp is 0.25med-high – high 0.75high-highE3 P is 0.5low – low 0.25low - med 0.25low-med – medE3 GFF ≥0 low-lowE3 A is low – low-medIF 0.25A1(4) - A1(5), 0.75A1(5) IS ≤ A1(5) AND 0.5A2(1) ≤ A2(1), 0.25A2(1) - A2(3), 0.25A2(2) - A2(3) AND A3(1) IS ≤ A3(1) AND A4(1) - A4(2) THEN B(50700)=E3IF Variables (A) = Temperature = 0.25 x 60-80 % to 80-100 %, 0.75 80-100 % - 80-100 %Precipitation = 0.5 x 0-100 Kg m2 to 0-100 Kg m2, 0.25 x 0-100 Kg m2 to 200-300 Kg m2, 0.25 x 100-200 Kg m2 to 200-300 Kg mGround Frost frequency = 0-6 days to 0-6 daysAltitude = -30-1366 m to 1366-2732 mTHEN Environment (B) = 33356-507004. E3/4 (C-R - C)Example Congo (DRC)E4 Temp is med-high – highE4 P is 0.5low – med-high 0.5low – medE4 GFF is 0.5low – low-med 0.5low – lowE4 A is low – med-highIF A1(4) - A1(5) AND 0.5A2(1) - A2(4), 0.5A2(1) - A2(3) AND 0.5A3(1) - A3(2), 0.5A3(1) IS ≤ A3(1) AND A4(1) - A4(4) THEN B(33356)=E4IF Variables (A) = Temperature = 60-80 % to 80-100 %Precipitation = 0.5 x 0-100 Kg m2 to 300-400 Kg m2, 0.5 x 0-100 Kg m2 to 200-300 Kg m2Ground Frost frequency = 0.5 x 0-6 days to 6-12 days, 0.5 x 0-6 days to 0-6 daysAltitude = -30-1366 m to 4098-5464 mTHEN Environment (B) = 113555-333565. E5/6 (C-S-R – C-S)Example GeorgiaE5 Temp is 0.75med – med-high 0.25med-high - highE5 P is 0.75low – low-med 0.25low – medE5 GFF is 0.25low-med – high 0.5low – med-high 0.25low – low-medE5 A is low – med-highIF 0.75A1(3) - A1(4), 0.25A1(4) - A1(5) AND 0.75A2(1) - A2(2), 0.25A2(1) - A2(3) AND 0.25A3(2) - A3(5), 0.5A3(1) - A3(4), 0.25A3(1) - A3(2) AND A4(1) - A4(4) THEN B(11355)=E5IF Variables (A) = Temperature = 0.75 x 40-60 % to 60-80 %, 0.25 x 60-80 % to 80-100%Precipitation = 0.75 0-100 Kg m2 to 100-200 Kg m2, 0.25 x 0-100 Kg m2 to 200-300 Kg m2Ground Frost frequency = 0.25 x 6-12 days – 24-30 days, 0.5 0-6 days to 18-24 days, 0.25 x 0-6 days to 6-12 daysAltitude = -30-1366 m to 4098-5464 mTHEN Environment (B) = 8805-11355 6. E6 (C-S)Example AzerbaijanE6 Temp is 0.25med – med-high 0.5med-high – med-high 0.25med-high - highE6 P is low – low-medE6 GFF is 0.25med – high 0.5low – med 0.25low – low-medE6 A is low – med-highIF 0.25A1(3) - A1(4), 0.5A1(4) IS ≤ A1(4), 0.25A1(4) - A1(5) AND A2(1) - A2(2) AND 0.25A3(3) - A3(5), 0.5A3(1) - A3(3), 0.25A3(1) - A3(2) AND A4(1) - A4(4) THEN B(8805)=E6IF Variables (A) = Temperature = 0.25 x 40-60 % to 60-80 %, 0.5 60-80 % to 60-80%, 0.25 60-80 % to 80-100%Precipitation = 0-100 Kg m2 to 100-200 Kg m2Ground Frost frequency = 0.25 x 12-18 days to 24-30 days, 0.5 0-6 days to 12-18 days, 0.25 x 0-6 days to 6-12 daysAltitude = -30-1366 m to 4098-5464 mTHEN Environment (B) = 2023-88057. E7 (S)Example data not available though E6 Macedonia as a potential candidateE6 Temp is 0.75med-high – med-high 0.25med-high – highE6 P is low – low-medE6 GFF is 0.25low-med – high 0.5low - low-med 0.25low – lowE6 A is low – medIF 0.75A1(4) IS ≤ A1(4), 0.25A1(4) - A1(5) AND A2(1) - A2(2) AND 0.25A3(2) - A3(5), 0.5A3(1) - A3(2), 0.25A3(1) IS ≤ A3(1) AND A4(1) - A4(3) THEN B(2023)=E7IF Variables (A) = Temperature = 0.75 x 60-80 % to 60-80%, 0.25 60-80 % to 80-100%Precipitation = 0-100 Kg m2 to 100-200 Kg m2Ground Frost frequency = 0.25 6-12 days to 24-30 days, 0.5 0-6 days to 6-12 days, 0.25 0-6 days to 0-6 daysAltitude = -30-1366 m to 2732-4098 mTHEN Environment (B) = 0-2023Environment 1 (Ruderal) 51847-65535 (e. g. Mexico, Central America)Environment 2 (Stress-tolerant to Ruderal) 50700-51847 (e. g. Guyana, South America)Environment 3 (Stress-tolerant to Ruderal , Competitive to Ruderal) 33356-50700 (e. g. Cuba)Environment 4 (Competitive to Ruderal, Competitive) 11355-33356 (e. g. Democratic Republic of the Congo, Africa)Environment 5(Competitive to Stress-tolerant to Ruderal, Competitive to Stress-tolerant) 8805-11355 (e. g. Georgia, Eastern Europe)Environment 6 (Competitive to Stress-tolerant) 2203-8805 (e. g. Guinea, Africa)Environment 7 (Stress tolerant) 0-2023 (e. g. Macedonia, Southern Europe)
GBIF Citation sources:Mexico (DZ 8-9):(accessed through GBIF data portal, Type herbarium, Gottingen (GOET),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1494)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Bryophyte herbarium, Gottingen (GOET),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1492)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Vascular Plant Collection - University of Washington Herbarium (WTU), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/126)(accessed through GBIF data portal, herbario, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/566)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Paleobiology Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/563)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Flora of Japan Specimen Database,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/586)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Algae Collection of National Museum of Nature and Science,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/595)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Tropicos Specimen Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/621)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/629)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Arizona State University Vascular Plant Herbarium,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/676)(accessed through GBIF data portal, EURISCO, The European Genetic Resources Search Catalogue,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1905)(accessed through GBIF data portal, University of Copenhagen's Arboretum,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/702)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CGN-PGR, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1102)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Database Schema for UC Davis[Herbarium Labels],http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/734)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Database Schema for UC Davis[TGRC],http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/735)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UCD BOTANICAL CONSERVATORY, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/739)(accessed through GBIF data portal, California State University, Chico,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/737)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UA Herbarium, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/7900)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium (UNA), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/775)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Frutos y Semillas, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/778)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Plantas Vasculares, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/780)Guyana (DZ 8):Please cite this data as follows:(accessed through GBIF data portal, Bryophyte herbarium, Gottingen (GOET),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1492)(accessed through GBIF data portal, herbario, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/566)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Tropicos Specimen Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/621)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/629)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Arizona State University Vascular Plant Herbarium,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/676)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium (UNA), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/775)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Plantas Vasculares, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/780)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Fungi (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1038)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Mosses (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1040)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Algaterra Types, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1084)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Lichen Herbarium Berlin, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1097)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CGN-PGR, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1102)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbier de la Guyane, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1436)(accessed through GBIF data portal, HBGSpermatophyta - Herbarium Hamburgense,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1604)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium GZU, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1491)(accessed through GBIF data portal, The System-wide Information Network for Genetic Resources (SINGER), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1430)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium W, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1479)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Harvard University Herbaria, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1827)(accessed through GBIF data portal, National Herbarium of The Netherlands (NL) - Main collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11520)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium WU, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1496)(accessed through GBIF data portal, United States National Plant Germplasm System Collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1429)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Type herbarium, Gottingen (GOET),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1494)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Australian National Herbarium (CANB),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/47)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Berolinense, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1095)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Vascular Plant Collection - University of Washington Herbarium (WTU), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/126)(accessed through GBIF data portal, The AAU Herbarium Database,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/224)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico (Madrid), Vascular Plant Herbarium (MA),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/240)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbario de la Universidad de Sevilla, SEV-Historico,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/284)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CABI Bioscience Genetic Resource Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/166)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico, Madrid: MA-Musci,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/235)(accessed through GBIF data portal, BoGART, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1087)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Gothenburg Herbarium - Types (GBIF:IH:GB:Herbarium),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1766)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UCBG TAPIR Provider, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1412)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Coleccion de Briofitas, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/784)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamie, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1506)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Canadian Museum of Nature Herbarium,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/123)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Fairchild Tropical Botanic Garden Virtual Herbarium Darwin Core format, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/202)(accessed through GBIF data portal, SysTax, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1875)(accessed through GBIF data portal, NSW herbarium collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/968)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CABI Bioscience Fungus Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/167)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Zurich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1903)(accessed through GBIF data portal, EURISCO, The European Genetic Resources Search Catalogue, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1905)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Oxford University Herbaria, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/2020)(accessed through GBIF data portal, NMNH Botany Collections, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1874)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UA Herbarium, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/7900)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Specimens of Museum of Nature and Human Activities, Hyogo Prefecture, Japan,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1958)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Rapid Assessment Program (RAP) Biodiversity Survey Database,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8076)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamic Botanical Collections (S),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8113)(accessed through GBIF data portal, DUKE Bryophyte Collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8104)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium WRSL, Main Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8182)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Senckenbergianum (FR),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8311)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Instituto de Ciencias Naturales, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/2559)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium of The New York Botanical Garden,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8967)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Coleccion de Plantas Acuaticas,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8047)(accessed through GBIF data portal, RBGE Living Collections, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/9167)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Zurich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11516)(accessed through GBIF data portal, DAO Herbarium Type Specimens, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/527)(accessed through GBIF data portal, University of Alberta Museums, Vascular Plant Herbarium, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11612)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CONN GBIF data, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/7857)(accessed through GBIF data portal, RBGE Herbarium (E), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8402)Cuba (DZ 8):Please cite this data as follows:(accessed through GBIF data portal, Type herbarium, Gottingen (GOET),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1494)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Bryophyte herbarium, Gottingen (GOET),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1492)(accessed through GBIF data portal, herbario, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/566)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Paleobiology Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/563)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Tropicos Specimen Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/621)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/629)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Arizona State University Vascular Plant Herbarium,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/676)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Database Schema for UC Davis[TGRC],http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/735)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UCD BOTANICAL CONSERVATORY, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/739)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium (UNA), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/775)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Plantas Vasculares, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/780)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Mosses (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1040)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Lund Botanical Museum (LD), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1028)(accessed through GBIF data portal, BoGART, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1087)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Lichen Herbarium Berlin, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1097)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CGN-PGR, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1102)(accessed through GBIF data portal, HBGBryophyta - Herbarium Hamburgense,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1603)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbier de la Guyane, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1436)(accessed through GBIF data portal, HBGSpermatophyta - Herbarium Hamburgense,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1604)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium GZU, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1491)(accessed through GBIF data portal, The System-wide Information Network for Genetic Resources (SINGER), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1430)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium W, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1479)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Harvard University Herbaria, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1827)(accessed through GBIF data portal, National Herbarium of The Netherlands (NL) - Main collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11520)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium WU, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1496)(accessed through GBIF data portal, United States National Plant Germplasm System Collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1429)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Bishop Museum Natural Sciences Data,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/54)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Programa de repatriacion de datos de ejemplares mexicanos, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/2488)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Australian National Herbarium (CANB),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/47)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Berolinense, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1095)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CBS fungi strains, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/69)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Australian Antarctic Division Herbarium,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/76)(accessed through GBIF data portal,Sukkulentensammlung Zurich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8135)(accessed through GBIF data portal, BCCM/MUCL - (Agro)Industrial Fungi and Yeasts Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/103)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Vascular Plant Collection - University of Washington Herbarium (WTU), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/126)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico, Madrid: MA-Algae,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/234)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico, Madrid: MA-Musci,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/235)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico, Madrid: MA-Hepat,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/236)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Botanic Garden of Finnish Museum of Natural History,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/2406)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico (Madrid), Vascular Plant Herbarium (MA),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/240)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Jardin Botanico de Cordoba: Herbarium COA,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/247)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Botany (UPS), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1045)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CIBIO,Alicante:ABH-GBIF, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/251)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico, Madrid: MA-Funhist,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/256)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Escuela Tecnica Superior de Ingenieros de Montes, UPM: EMMA, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/278)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Universidad de Malaga: MGC-Cormof,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8105)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbario de la Universidad de Sevilla, SEV-Historico,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/284)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CUBA: Herbario de la Academia de Ciencias, La Habana, Cuba:HAC-Pteridophyta, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/296)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CUBA:Herbario del Jardin de los Helechos, Centro Oriental de Ecosistemas y Biodiversidad, Santiago de Cuba: BSC-Pteridophyta, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/297)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CUBA:Herbario del Jardin Botanico Nacional, La Habana, Cuba:HAJB-Pteridophyta, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/298)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CABI Bioscience Genetic Resource Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/166)(accessed through GBIF data portal, The AAU Herbarium Database,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/224)(accessed through GBIF data portal, The Myxomycetes Collection at the V. L. Komarov Botanical Institute, St. Petersburg, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1751)(accessed through GBIF data portal, IPK Genebank, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1851)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Algaterra Types, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1084)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Gothenburg Herbarium - General (GBIF:IH:GB:Herbarium),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1765)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Gothenburg Herbarium - Types (GBIF:IH:GB:Herbarium),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1766)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Fairchild Tropical Botanic Garden Virtual Herbarium Darwin Core format, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/202)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Institut Botanic de Barcelona, BC-Historico,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1523)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UCBG TAPIR Provider, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1412)(accessed through GBIF data portal, DAO Herbarium Type Specimens, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/527)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Planetary Biodiversity Inventory Eumycetozoan Databank,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1515)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Canadian Museum of Nature Herbarium,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/123)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Coleccion de Briofitas, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/784)(accessed through GBIF data portal, NSW herbarium collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/968)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamie, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1506)(accessed through GBIF data portal, NMNH Botany Collections, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1874)(accessed through GBIF data portal, USU-UTC Specimen Database,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1508)(accessed through GBIF data portal, SysTax, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1875)(accessed through GBIF data portal, DUKE Bryophyte Collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8104)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CABI Bioscience Fungus Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/167)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Zurich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1903)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Database Schema for UC Davis[Herbarium Labels],http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/734)(accessed through GBIF data portal, EURISCO, The European Genetic Resources Search Catalogue,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1905)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbario del Instituto de Ecologia, A.C., Mexico (IE-XAL), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1597)(accessed through GBIF data portal, TestCollection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/2397)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UCMP TAPIR Provider, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1414)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Instituto de Ciencias Naturales, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/2559)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CONN GBIF data, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/7857)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UA Herbarium, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/7900)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Botany Vascular Plant Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/7915)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Specimens of Museum of Nature and Human Activities, Hyogo Prefecture, Japan,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1958)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CeDoc de Biodiversitat Vegetal: BCN-Phycophyta,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1760)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamic Botanical Collections (S),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8113)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Peabody Paleobotany DiGIR Service,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8141)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium WRSL, Main Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8182)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Peabody Paleoportal DiGIR Service (PB),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8176)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Senckenbergianum (FR),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8311)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Algae (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1039)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Universidad de Oviedo. Departamento de Biologia de Organismos y Sistemas: FCO-Algae,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8403)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Bridel Herbar, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1088)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Universitat de Valencia, Colecciones de Criptogamas: VAL_Algae, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/2509)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium of The New York Botanical Garden,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8967)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Tipos de plantas vasculares,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/782)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Coleccion de Plantas Acuaticas,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8047)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Agavaceae, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8391)(accessed through GBIF data portal, RBGE Living Collections, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/9167)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbario XAL del Instituto de Ecologia, A.C., Mexico (IE-XAL), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/10980)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Coleccion de Monocotiledoneas Mexicanas (UAM-I),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11109)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Zurich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11516)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Nordic Genetic Resources, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1487)(accessed through GBIF data portal, University of Alberta Museums, Vascular Plant Herbarium,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11612)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Natural Geography In Shore Areas (NaGISA) Dataset,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/327)(accessed through GBIF data portal, RBGE Herbarium (E), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8402)Democratic Republic of the Congo, Africa (DZ 8):Please cite this data as follows:(accessed through GBIF data portal, Paleobiology Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/563)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Tropicos Specimen Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/621)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/629)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Pteridophytes (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1037)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Mosses (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1040)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Algaterra Types, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1084)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Staatliches Museum fur Naturkunde Stuttgart, Herbarium,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1100)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CGN-PGR, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1102)(accessed through GBIF data portal, HBGSpermatophyta - Herbarium Hamburgense,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1604)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/7943)(accessed through GBIF data portal, The System-wide Information Network for Genetic Resources (SINGER), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1430)(accessed through GBIF data portal, National Herbarium of The Netherlands (NL) - Main collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11520)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Bryophyte herbarium, Gottingen (GOET),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1492)(accessed through GBIF data portal, United States National Plant Germplasm System Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1429)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Central African Plants, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8377)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Bishop Museum Natural Sciences Data,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/54)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Australian National Herbarium (CANB),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/47)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Berolinense, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1095)(accessed through GBIF data portal, National Botanic Garden Belgium - Albertian Rift Rubiaceae (ENBI wp13), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/90)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Royal Museum of Central Africa - Metafro-Infosys - Prelude,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/96)(accessed through GBIF data portal, BCCM/MUCL - (Agro)Industrial Fungi and Yeasts Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/103)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Zurich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1903)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Botany (UPS), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1045)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Botanic Garden of Finnish Museum of Natural History,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/2406)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UCMP TAPIR Provider, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1414)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Harvard University Herbaria, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1827)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UCBG TAPIR Provider, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1412)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Coleccion de Briofitas, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/784)(accessed through GBIF data portal, NSW herbarium collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/968)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamie, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1506)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Ichtyologie, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1507)(accessed through GBIF data portal, SysTax, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1875)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CABI Bioscience Fungus Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/167)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UA Herbarium, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/7900)(accessed through GBIF data portal, EURISCO, The European Genetic Resources Search Catalogue,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1905)(accessed through GBIF data portal, NHT_flora, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8350)(accessed through GBIF data portal, NMNH Botany Collections, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1874)(accessed through GBIF data portal, DUKE Bryophyte Collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8104)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Specimens of Museum of Nature and Human Activities, Hyogo Prefecture, Japan,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1958)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Rapid Assessment Program (RAP) Biodiversity Survey Database,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8076)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamic Botanical Collections (S),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8113)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Database Schema for UC Davis[Herbarium Labels],http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/734)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Peabody Paleobotany DiGIR Service,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8141)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Peabody Paleoportal DiGIR Service (PB),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8176)(accessed through GBIF data portal,Sukkulentensammlung Zurich, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8135)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium of The New York Botanical Garden,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8967)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium of the Universite Libre de Bruxelles,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/9102)(accessed through GBIF data portal, IICT Herb√°rio LISC, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/10840)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Zurich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11516)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Flora of tanzania, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/10860)(accessed through GBIF data portal, RBGE Herbarium (E), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8402)(accessed through GBIF data portal, The Vascular Plant Collection at the Botanische Staatssammlung Munchen, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11996)Georgia (DZ 8):Please cite this data as follows:(accessed through GBIF data portal, Paleobiology Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/563)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Tropicos Specimen Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/621)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/629)(accessed through GBIF data portal, EURISCO, The European Genetic Resources Search Catalogue, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1905)(accessed through GBIF data portal, University of Copenhagen's Arboretum,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/702)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium of Oskarshamn (OHN),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1024)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Lund Botanical Museum (LD), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1028)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Pteridophytes (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1037)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Mosses (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1040)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Staatliches Museum fur Naturkunde Stuttgart, Herbarium,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1100)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CGN-PGR, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1102)(accessed through GBIF data portal, HBGBryophyta - Herbarium Hamburgense,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1603)(accessed through GBIF data portal, The System-wide Information Network for Genetic Resources (SINGER), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1430)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium W, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1479)(accessed through GBIF data portal, National Herbarium of The Netherlands (NL) - Main collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11520)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium WU, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1496)(accessed through GBIF data portal, United States National Plant Germplasm System Collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1429)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Polish gene bank ‚Äì passport data of plants accessions which are important in human life, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8332)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Australian National Herbarium (CANB),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/47)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Berolinense, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1095)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico, Madrid: MA-Musci,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/235)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Universidad del Pais Vasco/EHU, Bilbao: Herbario BIO,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/242)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico (Madrid), Vascular Plant Herbarium (MA),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/240)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Jardin Botanic de Valencia: VAL, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/238)(accessed through GBIF data portal, IPK Genebank, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1851)(accessed through GBIF data portal, BoGART, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1087)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Harvard University Herbaria, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1827)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Universidad Politecnica de Madrid, Biologia Vegetal, Banco de Germoplasma, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1521)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamie, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1506)(accessed through GBIF data portal, DUKE Bryophyte Collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8104)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CABI Bioscience Fungus Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/167)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Aranzadi Zientzi Elkartea, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/248)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Zurich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1903)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Bryophyte herbarium, Bergen (BG),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1073)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium GZU, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1491)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbario de la Universidad de Salamanca: SALA,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/239)(accessed through GBIF data portal, HBGSpermatophyta - Herbarium Hamburgense,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1604)(accessed through GBIF data portal, NMNH Botany Collections, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1874)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Nordic Genetic Resources, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1487)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbario de la Universidad de Sevilla, SEV,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/283)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamic Botanical Collections (S),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8113)(accessed through GBIF data portal, RBGE Living Collections, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/9167)(accessed through GBIF data portal,Sukkulentensammlung Zurich, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8135)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium of The New York Botanical Garden,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8967)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Z√ºrich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11516)(accessed through GBIF data portal, RBGE Herbarium (E), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8402)Guinea, Africa (DZ 8):Please cite this data as follows:(accessed through GBIF data portal, Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/629)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Tropicos Specimen Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/621)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UCD BOTANICAL CONSERVATORY, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/739)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Pteridophytes (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1037)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Mosses (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1040)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Lund Botanical Museum (LD), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1028)(accessed through GBIF data portal, HBGBryophyta - Herbarium Hamburgense,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1603)(accessed through GBIF data portal, The System-wide Information Network for Genetic Resources (SINGER), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1430)(accessed through GBIF data portal, National Herbarium of The Netherlands (NL) - Main collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11520)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Bryophyte herbarium, Gottingen (GOET),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1492)(accessed through GBIF data portal, United States National Plant Germplasm System Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1429)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Berolinense, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1095)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico, Madrid: MA-Musci,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/235)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico (Madrid), Vascular Plant Herbarium (MA),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/240)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Jardin Botannico de Cordoba: Herbarium COA,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/247)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CABI Bioscience Genetic Resource Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/166)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Harvard University Herbaria, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1827)(accessed through GBIF data portal, UCBG TAPIR Provider, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1412)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamie, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1506)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CABI Bioscience Fungus Collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/167)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Zurich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1903)(accessed through GBIF data portal, EURISCO, The European Genetic Resources Search Catalogue,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1905)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium W, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1479)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbario de la Universidad de Salamanca: SALA,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/239)(accessed through GBIF data portal, NMNH Botany Collections, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1874)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Rapid Assessment Program (RAP) Biodiversity Survey Database, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8076)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamic Botanical Collections (S),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8113)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Senckenbergianum (FR),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8311)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium of The New York Botanical Garden,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8967)(accessed through GBIF data portal, MEXU/Colecci√≥n de Plantas Acu√°ticas,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8047)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium of Namur, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11286)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Z√ºrich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11516)(accessed through GBIF data portal, RBGE Herbarium (E), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8402)Macedonia (DZ 8):Please cite this data as follows:(accessed through GBIF data portal, EURISCO, The European Genetic Resources Search Catalogue,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1905)(accessed through GBIF data portal, University of Copenhagen's Arboretum,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/702)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Pteridophytes (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1037)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Lund Botanical Museum (LD), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1028)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Fungi (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1038)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Mosses (S), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1040)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Algaterra Types, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1084)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Staatliches Museum fur Naturkunde Stuttgart, Herbarium,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1100)(accessed through GBIF data portal, CGN-PGR, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1102)(accessed through GBIF data portal, HBGSpermatophyta - Herbarium Hamburgense,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1604)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium W, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1479)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium GJO, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1484)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium WU, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1496)(accessed through GBIF data portal, United States National Plant Germplasm System Collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1429)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Type herbarium, Gottingen (GOET),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1494)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Berolinense, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1095)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Real Jardin Botanico (Madrid), Vascular Plant Herbarium (MA),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/240)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Australian National Herbarium (CANB),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/47)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbario de la Universidad de Sevilla, SEV,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/283)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Jardi Botanic de Valencia: VAL, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/238)(accessed through GBIF data portal, IPK Genebank, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1851)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Gothenburg Herbarium - Types (GBIF:IH:GB:Herbarium),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1766)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Polish seed gene bank ‚Äì historical passport data of accessions, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8333)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Harvard University Herbaria, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1827)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Institut Botanic de Barcelona, BC, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/299)(accessed through GBIF data portal, USU-UTC Specimen Database,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1508)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Zurich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1903)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium GZU, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1491)(accessed through GBIF data portal, FloVegSI - Floristical and fitocenological database of ZRC SAZU, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/2585)(accessed through GBIF data portal, NMNH Botany Collections, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1874)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamic Botanical Collections (S),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8113)(accessed through GBIF data portal, DUKE Bryophyte Collection, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8104)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium Senckenbergianum (FR),http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8311)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbario de la Universidad de Salamanca: SALA,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/239)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbarium of The New York Botanical Garden,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8967)(accessed through GBIF data portal, RBGE Living Collections, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/9167)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/629)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Herbaria of the University and ETH Z√ºrich,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11516)(accessed through GBIF data portal, National Herbarium of The Netherlands (NL) - Main collection,http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/11520)(accessed through GBIF data portal, RBGE Herbarium (E), http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/8402)(accessed through GBIF data portal, Phanerogamie, http://data.gbif.org/datasets/resource/1506)IF-Then rules for 7 environmentsUsing Max-Min inference (A1,n) MeanTemp (Mean Temperature, Energy), P (Precipitation, Water), GFF (Ground frost frequency), A (Altitude) equal to E1 (Number of species (B1,n) is High, minimum competitive strategy) to E7 (Number of species (B1,n) is ≥ 1, Low, maximum stress tolerating strategy)(1)=0-20%, (2)=20-40%, (3)=40-60%, (4)=60-80%, (5)=80-100%Algorithms to be read over the course of a year (10 year mean)IF A… THEN B… Variables = A Environments = BMeanTemp is A1(1,n)Precipitation is A2(1,n)Ground frost frequency is A3(1,n)Altitude is A4(1,n)Number of species is B(1,n)1. E1 (R)Example: MexicoE1 Temp is med-high - highE1 P is 0.5low - med 0.5low - highE1 GFF is 0.25low – high 0.5low – med 0.25 low – lowE1 A is low - HighIF A1(4) - A1(5) AND 0.5A2(1) - A2(3), 0.5A2(1) - A2(5) AND 0.25A3(1) - A3(5), 0.5A3(1) - A3(3), 0.25A3(1) IS ≤ A3(1) AND A4(1) - A4(5) THEN B(65535)=E1IF Variables (A) =- Temperature = 40-60 % to 80-100 %- Precipitation = 0.5 x 0-100 Kg m2 to 200-300 Kg m2, 0.5 x 0-100 Kg m2 to 400-500 Kg m2- Ground Frost frequency = 0.25 x 0-6 days to 24-30 days, 0.5 x 0-6 days to 12-18 days, 0.25 x 0-6 days to 0-6 days- Altitude = -30-1366 m to 5464-6830 mTHEN Environment 1 (B) = 51847-655352. E2 (S-R)Example GuyanaE2 Temp is high – high E2 P is 0.75low - med 0.25 low – med-highE2 GFF ≥0 low - lowE2 A is low – med-highIF A1(5)≤ A1(5) AND 0.75A2(1) - A2(3), 0.25A2(1) - A2(4) AND A3(1) IS ≤ A3(1) AND A4(1) to A4(4) THEN B(51847)=E2IF Variables A =- Temperature = 80-100 % to 80-100 %- Precipitation = 0.75 x 0-100 Kg m2 to 200-300 Kg m2, 0.25 x 0-100 Kg m2 to 300-400 Kg m2- Ground Frost frequency = 0-6 days to 0-6 days- Altitude = -30-1366 m to 4098-5464 mTHEN Environment 2 (B) = 50700-518473. E2/3 (S-R – C-R)Example CubaE3 Temp is 0.25med-high – high 0.75high-highE3 P is 0.5low – low 0.25low - med 0.25low-med – medE3 GFF ≥0 low-lowE3 A is low – low-medIF 0.25A1(4) - A1(5), 0.75A1(5) IS ≤ A1(5) AND 0.5A2(1) ≤ A2(1), 0.25A2(1) - A2(3), 0.25A2(2) - A2(3) AND A3(1) IS ≤ A3(1) AND A4(1) - A4(2) THEN B(50700)=E3IF Variables (A) = Temperature = 0.25 x 60-80 % to 80-100 %, 0.75 80-100 % - 80-100 %Precipitation = 0.5 x 0-100 Kg m2 to 0-100 Kg m2, 0.25 x 0-100 Kg m2 to 200-300 Kg m2, 0.25 x 100-200 Kg m2 to 200-300 Kg mGround Frost frequency = 0-6 days to 0-6 daysAltitude = -30-1366 m to 1366-2732 mTHEN Environment (B) = 33356-507004. E3/4 (C-R - C)Example Congo (DRC)E4 Temp is med-high – highE4 P is 0.5low – med-high 0.5low – medE4 GFF is 0.5low – low-med 0.5low – lowE4 A is low – med-highIF A1(4) - A1(5) AND 0.5A2(1) - A2(4), 0.5A2(1) - A2(3) AND 0.5A3(1) - A3(2), 0.5A3(1) IS ≤ A3(1) AND A4(1) - A4(4) THEN B(33356)=E4IF Variables (A) = Temperature = 60-80 % to 80-100 %Precipitation = 0.5 x 0-100 Kg m2 to 300-400 Kg m2, 0.5 x 0-100 Kg m2 to 200-300 Kg m2Ground Frost frequency = 0.5 x 0-6 days to 6-12 days, 0.5 x 0-6 days to 0-6 daysAltitude = -30-1366 m to 4098-5464 mTHEN Environment (B) = 113555-333565. E5/6 (C-S-R – C-S)Example GeorgiaE5 Temp is 0.75med – med-high 0.25med-high - highE5 P is 0.75low – low-med 0.25low – medE5 GFF is 0.25low-med – high 0.5low – med-high 0.25low – low-medE5 A is low – med-highIF 0.75A1(3) - A1(4), 0.25A1(4) - A1(5) AND 0.75A2(1) - A2(2), 0.25A2(1) - A2(3) AND 0.25A3(2) - A3(5), 0.5A3(1) - A3(4), 0.25A3(1) - A3(2) AND A4(1) - A4(4) THEN B(11355)=E5IF Variables (A) = Temperature = 0.75 x 40-60 % to 60-80 %, 0.25 x 60-80 % to 80-100%Precipitation = 0.75 0-100 Kg m2 to 100-200 Kg m2, 0.25 x 0-100 Kg m2 to 200-300 Kg m2Ground Frost frequency = 0.25 x 6-12 days – 24-30 days, 0.5 0-6 days to 18-24 days, 0.25 x 0-6 days to 6-12 daysAltitude = -30-1366 m to 4098-5464 mTHEN Environment (B) = 8805-11355 6. E6 (C-S)Example AzerbaijanE6 Temp is 0.25med – med-high 0.5med-high – med-high 0.25med-high - highE6 P is low – low-medE6 GFF is 0.25med – high 0.5low – med 0.25low – low-medE6 A is low – med-highIF 0.25A1(3) - A1(4), 0.5A1(4) IS ≤ A1(4), 0.25A1(4) - A1(5) AND A2(1) - A2(2) AND 0.25A3(3) - A3(5), 0.5A3(1) - A3(3), 0.25A3(1) - A3(2) AND A4(1) - A4(4) THEN B(8805)=E6IF Variables (A) = Temperature = 0.25 x 40-60 % to 60-80 %, 0.5 60-80 % to 60-80%, 0.25 60-80 % to 80-100%Precipitation = 0-100 Kg m2 to 100-200 Kg m2Ground Frost frequency = 0.25 x 12-18 days to 24-30 days, 0.5 0-6 days to 12-18 days, 0.25 x 0-6 days to 6-12 daysAltitude = -30-1366 m to 4098-5464 mTHEN Environment (B) = 2023-88057. E7 (S)Example data not available though E6 Macedonia as a potential candidateE6 Temp is 0.75med-high – med-high 0.25med-high – highE6 P is low – low-medE6 GFF is 0.25low-med – high 0.5low - low-med 0.25low – lowE6 A is low – medIF 0.75A1(4) IS ≤ A1(4), 0.25A1(4) - A1(5) AND A2(1) - A2(2) AND 0.25A3(2) - A3(5), 0.5A3(1) - A3(2), 0.25A3(1) IS ≤ A3(1) AND A4(1) - A4(3) THEN B(2023)=E7IF Variables (A) = Temperature = 0.75 x 60-80 % to 60-80%, 0.25 60-80 % to 80-100%Precipitation = 0-100 Kg m2 to 100-200 Kg m2Ground Frost frequency = 0.25 6-12 days to 24-30 days, 0.5 0-6 days to 6-12 days, 0.25 0-6 days to 0-6 daysAltitude = -30-1366 m to 2732-4098 mTHEN Environment (B) = 0-2023Environment 1 (Ruderal) 51847-65535 (e. g. Mexico, Central America)Environment 2 (Stress-tolerant to Ruderal) 50700-51847 (e. g. Guyana, South America)Environment 3 (Stress-tolerant to Ruderal , Competitive to Ruderal) 33356-50700 (e. g. Cuba)Environment 4 (Competitive to Ruderal, Competitive) 11355-33356 (e. g. Democratic Republic of the Congo, Africa)Environment 5(Competitive to Stress-tolerant to Ruderal, Competitive to Stress-tolerant) 8805-11355 (e. g. Georgia, Eastern Europe)Environment 6 (Competitive to Stress-tolerant) 2203-8805 (e. g. Guinea, Africa)Environment 7 (Stress tolerant) 0-2023 (e. g. Macedonia, Southern Europe)
References
| [1] | Grime, J P, “Plant Strategies and Vegetation Processes”. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester, 1979. |
| [2] | Grime J P, Hodgson J G, Hunt R, “The abridged comparative plant ecology”, Chapman & Hall, 1995. |
| [3] | Hodgson J G, Wilson P J, Hunt R, Grime J P, Thompson K, “Allocating C-S-R plant functional types: a soft approach to a hard problem”, Oikos, vol.85, pp.282–294, 1999. |
| [4] | Craine J M, “Reconciling plant strategy theories of Grime and Tilman”, Journal of Ecology, vol. 93, pp.1041-1052, 2005. |
| [5] | Kilinç M, Karavin N, Kutbay H G, (2010). “Classification of some plant species according to Grime’s strategies in a Quercus cerris L. var. cerris woodland in Samsun, northern Turkey”, Turk. J. Bot., vol.34, pp.521-529, 2010. |
| [6] | Mustard J M, Standing D B, Aitkenhead M J, Robinson S, McDonald J S, “The emergence of primary strategies in evolving virtual-plant populations”, Evolutionary Ecology Research, vol.5, pp.1067-1081, 2003. |
| [7] | Barreto L S, “The reconciliation of the r-K, and C-S-R-models for life history strategies”, Silva Lusitana, vol.16, pp.97-103, 2008. |
| [8] | Hung C C, Chen L H, “A fuzzy TOPSIS decision making model with entropy weight under intuiutionistic fuzzy environment”, in Proceedings of the International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists 2009, vol.1, pp.13-16, 2009. |
| [9] | Raunkier C, “The Life Forms of Plants and Statistical Plant Geography”, Oxford University Press, 1934. |
| [10] | Pianka E, “On r and k selection”, American Naturalist, vol.104, pp.592-597, 1970. |
| [11] | Bornhofen S, Lattaud C, “Evolving CSR Strategies in Virtual Plant Communities”. in Artificial Life XI, Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on the Simulation and Synthesis of Living Systems, pp.64-71, 2008. |
| [12] | Bornhofen S, Barot S, Lattaud C, “The evolution of CSR life-history strategies in a plant model with explicit physiology and architecture, Ecological Modelling, vol.222, pp.1-10, 2011. |
| [13] | Sivanandam S N, Sumathi S, Deepa S N, “Introduction to fuzzy logic using matlab”, Springer-Verlag, 2007. |
| [14] | Zadeh L S, “Fuzzy sets”, Information and Control, vol.8, pp.338-353, 1965. |
| [15] | Barthlott W, Mutke J, Rafiqpoor D, Kier G, Kreft H, “Global Centers of Vascular Plant Diversity”, Nova Acta Leopoldina NF, vol.16, no.1, pp.97-103, 2005. |
| [16] | Sommer J H, Kreft H, Kier G, Jetz W, Mutke J, Barthlott, W, “Projected impacts of climate change on regional capacities for global plant species richness”, Proc. R. Soc. B, vol.277, pp.2271-80, 2010. |
| [17] | Online Available: http://www.ipcc-data.org/ |
| [18] | Online Available: http://www.gbif.org/ |
| [19] | Yesson C, Brewer P W, Sutton T, Caithness N, Pahwa J S, Burgess M, et al., “How global is the global biodiversity information facility?”, Plos One, vol.11, pp.1-10, 2007. |
| [20] | New M, Hulme M, Jones P, “Representing twentieth century space-time climate variability. Part I- Development of a 1961-90 mean monthly terrestrial climatology”, J. Climate, vol.12, pp.829-856, 1999. |
| [21] | Hawkins B A, Field R, Cornell H V, Currie D J, Guégan J F, Kaufman D M, Kerr J T, Mittelbach G G, Oberdorff T, O’Brien E M, Porter E E, Turner J R G, “Energy, water, and broad-scale geographic patterns of species richness”, Ecology, vol.84, no.12, pp.3105-3117, 2003. |
| [22] | Vetaas O R, “Comparing species temperature response curves: population density versus second-hand data”, Journal of Vegetation Science, vol.11, pp.659–666, 2000. |
| [23] | Furze J N, Zhu Q, Qiao F, Hill J, “Species area relations and information rich modelling of plant species variation” in 17th International Conference on Automation and Computing (ICAC), 2011, pp.63-68, 2011. Online:http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6084902&isnumber=6084889 |
| [24] | Silvera K, Santiago L S, Cushman J S, Winter K, “Crassulacean acid metabolism and epiphytism linked to adaptive radiations in the orchidaceae”, Plant Physiol., vol.149, pp.1838-1847, 2009. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML