-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Environmental Engineering
p-ISSN: 2166-4633 e-ISSN: 2166-465X
2017; 7(1): 1-9
doi:10.5923/j.ajee.20170701.01

Development of Manual Drive Thrasher Plastic Cup
Darwin R. B. Syaka, Ahmad Kholil, Aam Aminingsih, Afri Siswaldi, Imam Gunandi
Department of Mechanical Engineering Education, State University of Jakarta, Indonesia
Correspondence to: Darwin R. B. Syaka, Department of Mechanical Engineering Education, State University of Jakarta, Indonesia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The aim of research to design thrasher plastic cup with a manual drive, as well as test performance. This study uses the Deutcher Ingeneure Verein (VDI) in 2221 which is the method to solve problems and optimize the use of materials, technology and economic conditions. The conclusion of this study is the researchers succeeded in designing a chopper machine plastic cups with optimal shape and minimalist, cutting speed (0,012 m/s) and flattens speed (0.01 m/s). Shaft diameter is determined by the shear stress flattens (5.09 Kg/mm2) and shear blades (18.8 Kg/mm2) to obtain the results of 12 mm. Power is required on this engine of 0.05 kW and transmissions used in this machine is the use of gears connected chain. The test results plastic glass cutting machines weighing 3 grams in 4.2 seconds with a maximum noise of only 70.3 db, where the results of flake size ranging from size 4 mm x 4 mm, the size of which can be sold in plastic recycling company.
Keywords: Thrasher, Plastic Cup, VDI, Manual Drive
Cite this paper: Darwin R. B. Syaka, Ahmad Kholil, Aam Aminingsih, Afri Siswaldi, Imam Gunandi, Development of Manual Drive Thrasher Plastic Cup, American Journal of Environmental Engineering, Vol. 7 No. 1, 2017, pp. 1-9. doi: 10.5923/j.ajee.20170701.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Population and economic growth are high in developing countries in Asia that is not balance with caring concern for industrial waste management resulted in the environment, one of the which is the high use of plastic packaging products. Packaging products with plastic material has some drawbacks which are not biodegradable itself, therefore it is necessary for the management of plastic waste. The main obstacle in most developing countries Including Indonesia are weak organization and the budget allocation to deal with plastic waste, while the alternative solution of handling plastic waste is to use the social and technical approach [1]. Based on research conducted in the area of Bali, the model of waste management that is based on social and cultural development is done adaptively, can provide economic benefits, a accommodate local labor and other social benefits such as health and aesthetics, and self-actualization in social and cultural activities [2].Processing of plastic waste in Jakarta is still focused on the place - certain places, for example: at the site of Bantar Gebang. Plastic packaging products that we see most often are garbage cups or bottles of fresh water because the pattern of an increasing number of people are very practical or because of the unavailability of fresh water like in the Thousand Islands, many residents rely on fresh water packing for daily needs. Besides dikepulauan also be interesting sights that attract tourists to visit and bring plastic waste mineral water. Handling waste water glass packaging nothing directly by consumers home. Garbage is usually collected scavengers then do the chopping to pieces in the processing in final waste disposal (landfill). The existence of the landfill itself has limited land because of the difficulty of obtaining proper space and with distance from the city center, as well as the need for large funds for land acquisition landfill, are the external factors that influence the waste problem [3]. As If sold, the plastic cups of the former will be appreciated much cheaper when compared with the price of chips. Plastic cups if it had been crushed into small pieces price could reach twice as compared to its original value. The added value is the main attraction of waste plastics processing industry by utilizing scavengers and garbage collectors.Increased recycling waste trade involving Asian countries may be a better choice, but the corresponding capacity, backed by the expertise and techniques necessary to build a model of modern waste management and environmentally friendly [4].In this regard, it is necessary to waste management to an integrated management system, with a total ergonomic approach of integration between the micro and macro ergonomics. The integration of both bringing the framework in order to optimize the fit between people, technology and organizational [5]. The solution of that is providing technology that is suitable for the smallest organizations in waste management, namely households.Processing waste of plastic cups that are now using a large capacity engine because the engine is in the market is the industrial scale and expensive. The large capacity makes it impossible to process the garbage discarded plastic cups of household. One home or office does not produce a lot of garbage plastic cups unless there is an event or activity that invites a lot of people. Based on this there needs to be the development of portable machine and cheap.The study of the design thrasher trash has been done by Yamin et al. devoted to handle organic waste [6], as for the design of plastic chopper made by Rajagukguk, has a dimension which is not suitable for the micro scale [7], while Tushar Sane et al. recently conducted a study on the design and computational analysis [8]. Several studies discussing the plastic thrasher them done by Qomaruddin and Darmanto making machine just to cut the top of a plastic bottle [9]. While plastic chopper made by Nur. et al and Napitupulu. et al, all of which still uses an electric motor with a power greater than 2 kW that this makes these machines are not suitable for household or remote areas that are not contained electrical power [10, 11]. Studies on the mechanism of operation and type of crusher knife cut its noise making it unsuitable for use in dense residential neighborhood [12]. Mechanical model studies shredder plastic actuated manually by manpower conducted by Senthil Kannan. N, while at the design stage [13]. In this case the design and manufacture of plastic waste shredder is driven manually by human power and quite quiet so it can be operated dense environment is a suitable technology for the smallest organizations in waste management, namely households.Anticipate problems of lack of space and the amount of plastic cups processing machines, then the solution offered is to innovate by creating a simple thrasher of plastic cups. Making the thrasher plastic cups machine, is expected to minimize the amount of plastic waste in Jakarta, especially in the thousand islands. In addition, with the thrasher plastic cups machine can be prospective opportunities for households to increase the yield of production waste recycling of plastic cups, without having to incur huge costs for investasi.
2. Method
- The method used to this design is the method VDI 2221 (Verein Deutcher Ingeneure). The method VDI 2221 is one method to solve problems and optimize the use of materials, technology and economic conditions. This method is expected to facilitate designers to master the system design without knowing in detail [14]. The method VDI 2221 divided into several phases as follows:1. Classification of the Task; This stage is the stage of gathering information and parse them into similar shapes and forms the basis of the specification, and identify constraints - constraints faced in order to achieve optimal solutions. Things to consider in making a distinction between the requirements specification list is whether demand or wishes. Demand is all the requirements to be met in the design and wishes a requirement in the form of desire and can be inserted through considerations - considerations. To help facilitate the preparation of specifications, use a checklist.2. Conceptual Design. This phase contains a discussion of the problems of abstraction, making the structure function, then do a search matching problem solving principles and the combination of the principle of solving the problem (the concept of variance). The results of this phase in the form of basic troubleshooting or concept.3. Embodiment Design. This stage contains a sketch of a combination of solutions that have created a form of the initial layout, then have qualified according to the specifications and good according to the criteria, both from the technical and economic aspects. Selected first layout will be developed into a layout so the (definitive) which is a form of design that suits your needs and expectations. Layout definitive includes some of the following:Ÿ The shape of the elements of a product.Ÿ The calculation techniques.Ÿ Selection of shapes and sizes.4. Detail Design. This stage is the final stage in the design. Detail design results in the form of documents covering machine image, detail drawing machine, parts lists, material specifications, operating system, tolerance and other documents which constitute one unit. Then do a re-evaluation of the product, whether it is true - it already meets the specifications given.Metode desain mesin pencacah gelas plastik digunakan metode VDI 2221. Secara umum, metode ini dapat dibuat diagram alir dari desain sebagai berikut:Further testing, where test objects directly conducted on of plastic cups litter with the same thickness and aims to determine the output chopped good results. Some measuring devices, such as stopwacth to calculate the cutting speed, decibel meter to measure the noise of the engine used for calculating the performance of this of plastic cups thrasher.
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Design and Manufacture
- Based on the method VDI 2221, the process of design and manufacture of plastic cups thrasher with manual drive divided into several phases as follows:
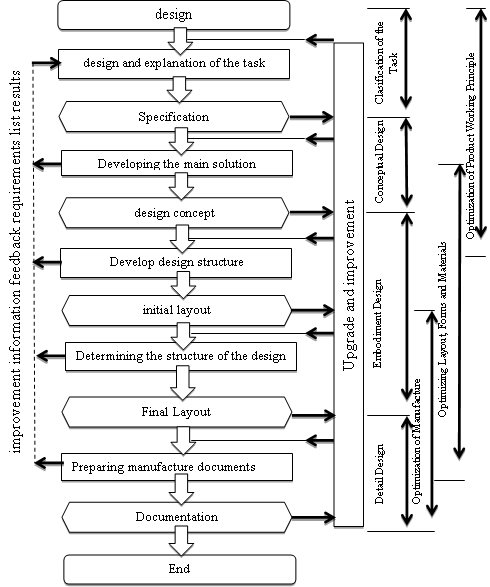 | Figure 1. The Flow chart Process Design of the VDI 2221 Method |
3.1.1. Clasification of the Task
- This stage is the stage of gathering information and parse them into similar shapes and forms the basis of the specification. Early stage in the design of this, the initial specification set by taking into account the requirements of whether demand or wishes as shown in Table 1.
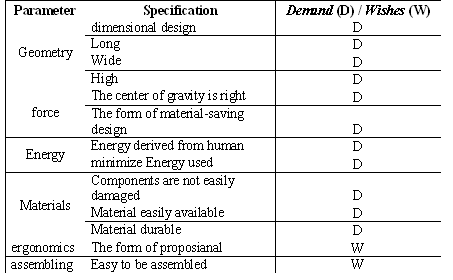 | Table 1. The initial specifications |
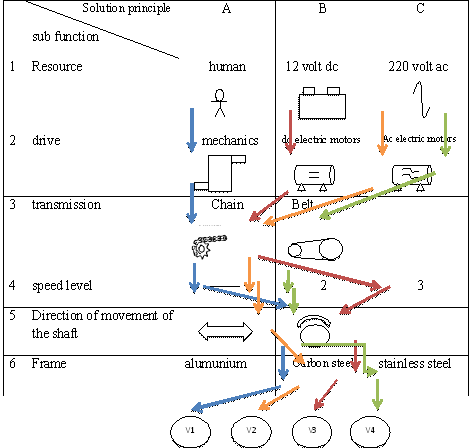 | Table 2. Combination of Principle Solutions Sub Function |
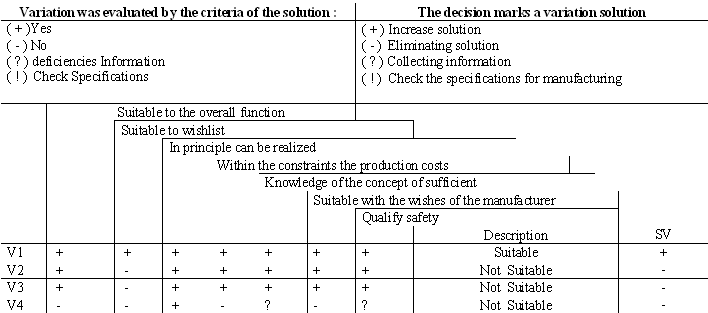 | Table 3. Variation solution |
3.1.2. Conceptual Design
- The concept stage to discuss about issues of abstraction, making the structure function, then do a search matching problem solving principles and the combination of the principle of solving the problem (the concept of variance).Design details include power calculations, calculation and selection of components - components for machinery, construction design and assembly. In planning this of plastic cups thrasher predetermined capacity of 2 kg/h, the initial capacity is needed as a basis for planning calculation.• Cutting speed- The density of plastic, = 1370 kg/m3- The length of the blade arc, p = 2 mm = 0.002 m- High-blade, T = 3 mm = 0.003 m- Thickness of blade, b = 4 mm = 0.004 m- Theoretical capacity, assuming Q = 2 kg/h- cutting speed
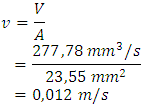 Ÿ Flatter speed
Ÿ Flatter speed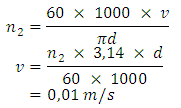
3.1.3. Embodiment Design
- This stage contains a sketch of a combination of solutions that have created a form of the initial layout, then have qualified according to the specifications and good according to the criteria, both from the technical and economic aspects. Selected first layout will be developed into a layout so the (definitive) which is a form of design that suits your needs and expectations. Layout definitive includes some of the following:• The shape of the elements of a product.• The calculation techniques.• Selection of shapes and sizes.Packaging plastic cups is a very soft material. Based on the character of the material on the cutting tool planning must be extremely sharp, strong and selecting appropriate cutting angle so that the plastic does not slip in between the blade and easily sharpened. Also based on the purpose of designing this machine for household then design the cutting tool to be minimalist and economical.The following is design thrasher blade of plastic cups for the household scale that has gone through the stages of planning design the most appropriate blade to smash plastic cups and minimize the components in the engine unit (fig. 2).
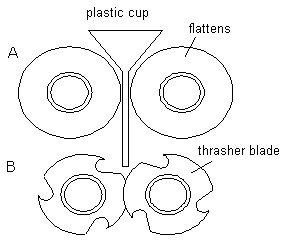 | Figure 2. A. flattens; B. thrasher blade |
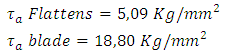 T1= 1413 Kg.mm (the torque shaft of flatten)Kt= 1, CB = 1,2T2= 1695,6 Kg.mm (the torque shaft of blade)Kt= 1,5, CB = 1,8
T1= 1413 Kg.mm (the torque shaft of flatten)Kt= 1, CB = 1,2T2= 1695,6 Kg.mm (the torque shaft of blade)Kt= 1,5, CB = 1,8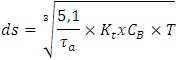 Then to find diameter shaft of flatten is:
Then to find diameter shaft of flatten is: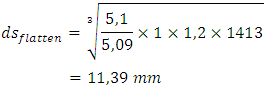 Then to find diameter shaft of blade is:
Then to find diameter shaft of blade is: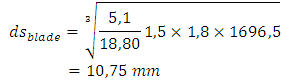 Having known diameter of the shaft in the above calculation, which is 11.93 mm and 10.75 mm. So in the design of this machine, will be made all the size of the shaft with the same diameter, ds = 12 mm. the goal of uniformity shaft size, simplify the procurement of spare parts and reduce τa desired.• Comparison of rotation gear (ratio)
Having known diameter of the shaft in the above calculation, which is 11.93 mm and 10.75 mm. So in the design of this machine, will be made all the size of the shaft with the same diameter, ds = 12 mm. the goal of uniformity shaft size, simplify the procurement of spare parts and reduce τa desired.• Comparison of rotation gear (ratio)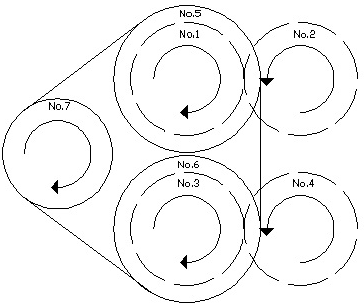 | Figure 3. Schemes direction of rotation of the transmission gear |
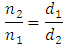 As :n1 = drive rotationn2 = driven rotationd1 = diameter gear drived2 = diameter gear drivenComparison rotation gear sprockets on the shaft No. 7 and gear sprocket no. 5 to find for a rotation on the gear No. 7
As :n1 = drive rotationn2 = driven rotationd1 = diameter gear drived2 = diameter gear drivenComparison rotation gear sprockets on the shaft No. 7 and gear sprocket no. 5 to find for a rotation on the gear No. 7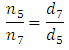 So,
So, 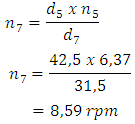
 | Table 4. Results of calculation rpm |
3.1.4. Detail Design
- Detail design results in the form of documents covering machine image, detail drawing machine, parts lists, material specifications, operating system, tolerance and other documents which constitute one unit. Based on the design and results of calculations for thrasher plastic cups obtained some data as a reference in designing the machine. The process of design and calculation greatly affects the power and engine efficiency. In design these machines have to adjust from purpose of design. purpose of this study, thrasher earmarked in the household, then the design should be minimalist and attractive views.Ÿ Assembling ProcessAssembly process thrasher plastic cups containers for household scale, ie:1. Assembling shaft flattens and shaft blade thrasher.2. Install four bearing rolling on the holes for the shaft flattens on the mounting components.3. Install the 2 bearings rolling in the holes on the blade shaft on a side of the body frame.4. Place the gear on the shaft blade and then given a stake.5. Attach shaft blade and shaft flattens on the mounting components have been mounted rolling bearings simultaneously.6. Attach the opposite side of the framework and adjust the shaft blade and shaft flattens.7. Attach the cleanser comb shredded results8. Install two other rolling bearings for shaft blade.9. Place the gear on the shaft flattens.10. Install the adjusting screw shaft blade.11. Install the rolling bearings for the crankshaft (driving).12. Install the shaft for driving.13. Install the gear sprockets on the shaft flattens, the blade and the crankshaft (driving).14. Attach the chain to connect the third-gear sprocket.15. install the drive lever.16. Install sump thrasher results.17. Set the tip of the blade assembly of the shaft with the other.18. Set the gap between the blade shaft bolt setter using loopholes to get the maximum thrasher.
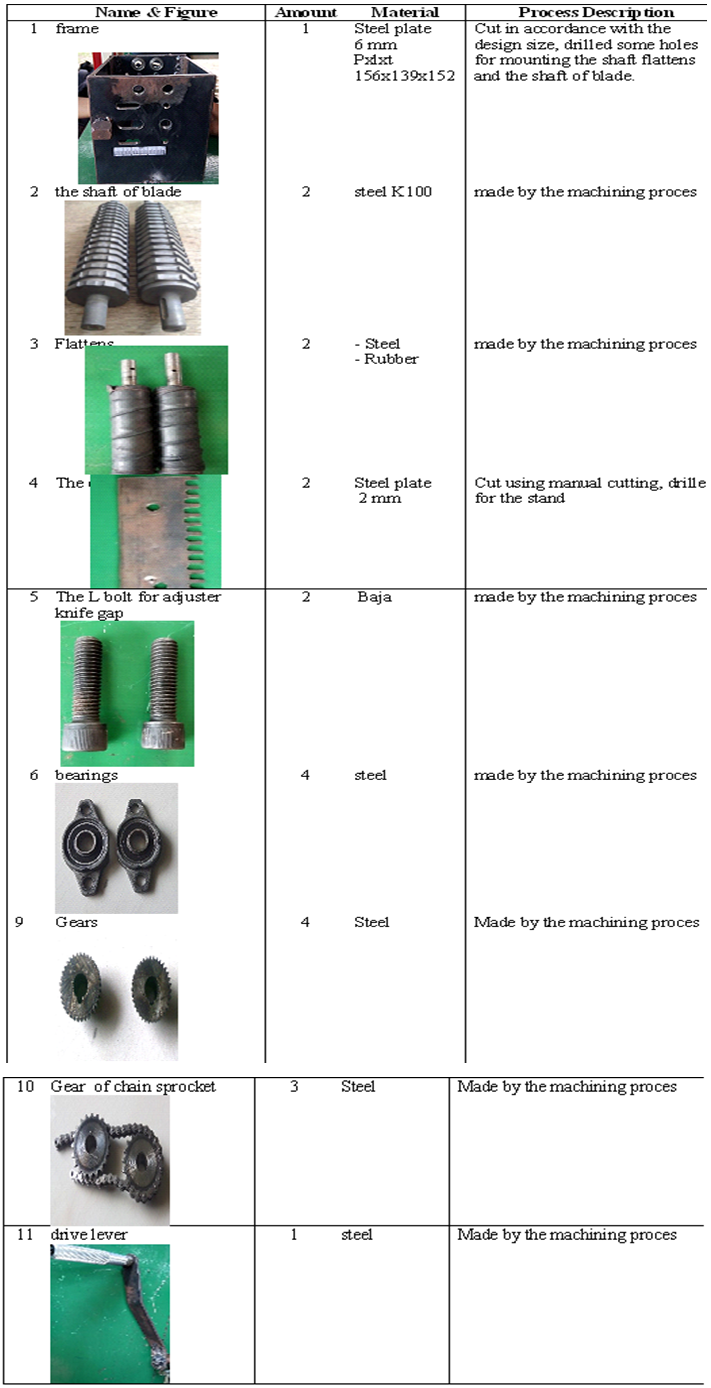 | Table 5. Parts of manual drive thrasher plastic cu |
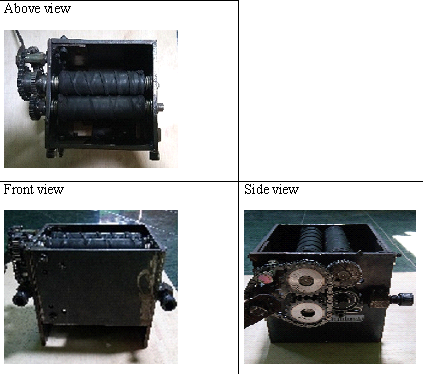 | Figure 4. Manufacture Results |
3.2. Testing
- Test results for capacity and cutting speed using a machine with garbage cups packaging drinking water. Cutting time is calculated when the glass packaging plastics have been entered into hoper and will be associated with the shaft ends flatten to pack the plastic cups go into the tank a plastic flake.Based on the results of tests performed it turned out to cut 1 package weighing 3 grams requires time for 4.2 seconds, with a loadest of 6 kg is the crank.In connection with the target machine that will be aimed at micro-enterprises or household businesses, then the noise factor these tools become essential in order not to disturb the environment when it is operated. Based on the standardization of engines, the noise level allowed in db is < 80 with a distance of 1 m from the test equipment or operator [15], this means that this machine must be able to operate below the noise level.As shown fig. 5, For a distance of 1 meter from the machine (as required by the standards), the noise level is below 70 db engine, even for the shorter distance of 0.5 m, a maximum noise level of this machine is 70.3 db, still below the 80 db. This means that the thrasher plastic cups is feasible to operate in the environment as micro or household without disrupting the environment or cause noise.
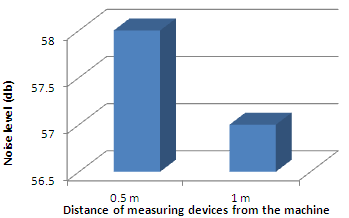 | Figure 5. Noise level of thrasher plastic cups |
 | Figure 6. Results shredded of plastic cups |
4. Conclusions
- This study successfully design thrasher plastic cups to optimal form and minimalist. Transmissions used in this machine use gear connected chain, which results from the count is 4 mm x 4 mm, it is in accordance with the standards to be sold in plastic recycling company. Results noise is still below the threshold limits, this means thrasher plastic cups is feasible to operate in the environment as micro or household without disrupting the environment or cause noise.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This research was support by Hibah Penelitian Fundamental Tahun Anggaran 2016, Direktorat Jenderal Pendidikan Tinggi.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML