-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Environmental Engineering
p-ISSN: 2166-4633 e-ISSN: 2166-465X
2013; 3(2): 85-94
doi:10.5923/j.ajee.20130302.01
Soil Washing Remediation of Soil Artificially Contaminated with Naphthalene: Evaluation of Palm Kernel Oil, Coconut Oil and Waste Cooking Oil as Solubilization Agents
Samuel E. Agarry, Mujidat O. Aremu, Olufunmilayo A. Aworanti
Biochemical Engineering and Biotechnology Laboratory, Department of Chemical Engineering, Ladoke Akintola University of Technology, Ogbomoso, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Samuel E. Agarry, Biochemical Engineering and Biotechnology Laboratory, Department of Chemical Engineering, Ladoke Akintola University of Technology, Ogbomoso, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This study investigated the feasibility of naphthalene contaminated soil remediation using vegetable oil. Batch experiments were performed to test the desorption efficiency of palm kernel oil, coconut oil and used cooking oil in naphthalene removal from contaminated soil, the effect of initial naphthalene concentration on desorption efficiency of the oils and to test the mass transfer behaviour of naphthalene from soil to oil. An empirical model was employed to describe the kinetics of naphthalene desorption and to predict equilibrium concentrations of naphthalene in oil. Naphthalene containing oil was regenerated using coconut shell-derived activated carbon. The results showed that between 87.3% and 99% of naphthalene was respectively removed by palm kernel oil, coconut oil and used cooking oil from 50 to 150 mg kg-1 naphthalene contaminated soils in 6 h. The mass transfer rate coefficient for desorption of naphthalene from contaminated soil generally increased with increase in the initial naphthalene concentration in the soil. The feasibility of oil regeneration showed that more than 60% naphthalene was removed by coconut shell derived-activated carbon. These results indicated that the palm kernel oil, coconut oil and used cooking oil has a promising solubilization capacity for the remediation of naphthalene contaminated soils.
Keywords: Naphthalene, Soil Remediation, Solubilization, Vegetable Oil, Mass Transfer
Cite this paper: Samuel E. Agarry, Mujidat O. Aremu, Olufunmilayo A. Aworanti, Soil Washing Remediation of Soil Artificially Contaminated with Naphthalene: Evaluation of Palm Kernel Oil, Coconut Oil and Waste Cooking Oil as Solubilization Agents, American Journal of Environmental Engineering, Vol. 3 No. 2, 2013, pp. 85-94. doi: 10.5923/j.ajee.20130302.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Contamination of soils and groundwater by toxic or hazardous pollutants is a widespread environmental problem and the removal of hydrophobic organic compounds (HOCs) such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHS) from soils has become a major concern. PAHs are a class of organic compounds consisting of over 100 individual moieties composed of 2 or more fused aromatic rings. PAHs are released into the environment by incomplete combustion of fossil fuels or organic matter or by accidental discharge of petroleum products during transport, use and disposal[1]. The US Environmental Protection Agency has listed 16 PAHs as priority pollutants, which are distributed ubiquitously in soils and they are of concern because of their toxic, carcinogenic, and mutagenic effects[2]. Most PAHs are hydrophobic in nature because of their low water solubility, electrochemical stability and high octanol–water partition coefficient[3], and thus, can exist as well as accumulate in soils for ages[4]. Multifarious physical and chemical remediation techniques for PAHs removal from contaminated soil have been proposed and have been demonstrated to have varying degrees of success[5, 6, 7, 8]. These methods include surfactant solubilization, solvent extraction, supercritical fluid extraction, hot water extraction, and some other leaching remediation techniques[9, 10, 11, 12]. Most often, PAHS especially those with high molecular weights are not as efficiently removed as expected from contaminated soil or other form of ecosystem due to their low bioavailability, high hydrophobicity and slow desorption[13]. However, because of the extremely hydrophobic nature of PAHs that may hinder their recovery from soil as the contaminants bind tightly to, or become entrapped within, the soil particles[14], a solubilization or washing agents may be utilized to promote mass transfer[15]. Therefore, in-situ flushing and ex-situ washing of PAH-contaminated soils may be feasible soil cleanup techniques[5, 16]. In the late 1970s, the technology of soil flushing developed by the U.S. EPA was primarily used to treat the soil and groundwater contaminated with hydrophobic organic compounds[17]; and this soil-washing process has been used widely in the USA to remediate Superfund sites contaminated by petroleum hydrocarbon by-products[18]. With this process, the washing solution extracts and separates the contaminants from the soil, thereby reducing the quantity of contaminant for further treatment.The use of surfactants (synthetic surfactant and biosurfactant), which could enhance PAH solubility, and organic solvents like alcohols has successfully been applied to remove PAHs from contaminated soils[17, 19, 20, 21], and the application of cyclodextrins in several soil remediation technologies has been increasingly studied[3, 22, 23]. However, it has been found that both organic solvents and synthetic surfactants have some limitations for soil remediation applications. Synthetic surfactants form high-viscosity emulsions that are difficult to remove from the soils[24] and inhibit microbial activity in soils thereby reducing their natural bioremediation capability[25]. While the difficulties or limitations associated with organic solvents lie with their recovery, re-use and high cost. Solvents present in soil are often removed by flushing the soil with water followed by chemical/thermal treatment to isolate contaminants and separate liquid fractions[26]. Hence, contaminant transport and solubility-enhancing additives that do not adsorb or retain in the soil, and also do not inhibit natural soil microbial activity are desired. In response to these limitations, we tried to find an environment-friendly solvent, which can rapidly and efficiently remove hydrophobic organic compounds (HOC) from contaminated soils. It has been demonstrated that vegetable oil which has the advantage of being readily available, non-toxic, biodegradable and cost-effective can be used as an alternative to these conventional solvents and surfactants to effectively extract organic contaminants from soils for a remediation purpose[3, 11, 27, 28]. Both Pannu et al.[28] and Gong et al.[11] also suggested that the remaining oil in the soil may aid in bioavailability and act as a growth substrate for PAH degrading microorganisms. Thus, biodegradation of contaminants in soil is further stimulated by the residual oil. Peanut, sunflower and rapeseed oils have been found to be efficient in solubilising and extracting PAH from contaminated soils[28, 29]. These solubilization potential of vegetable oil prompted us to study the potential of some vegetable oil that has not been used in ex-situ washing of naphthalene-contaminated soils. Thus, the primary objective of the present study is to evaluate and compare the desorption efficiencies or potential of used cooking oil, coconut oil and palm kernel oil (PKO) in the soil-washing of naphthalene contaminated soil. Additionally, the effects of initial naphthalene concentration on the efficiency of PAH dissolution into these oils was investigated and the mass transfer coefficients of naphthalene desorption from soil-bound naphthalene was also determined.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Samples and Soil Characterization
- The soil sample for the experiment was collected from the agricultural farm of Ladoke Akintola University of Technology, Ogbomoso, Nigeria. The soil was sandy loam allowing soil washing procedure, as it is known that soil washing is not directly applicable in treatment of fine-grained soils due to the low permeability and high resistance to hydraulic flow through these types of porous media (Gong et al., 2010). It was kept in a polyethylene bag and stored in the laboratory prior to use. The soil sample was characterized for total carbon (TC), total nitrogen (N), total phosphorus (P), total potassium (K), moisture content and pH using the Standard Methods[30]. The organic matter content was determined by mass loss on ignition on a dry weight basis. Soil pH was determined by rotating 5 g of dry soil with 5 mL of deionized water for 1 d and measuring the pH of the suspension. The physical–chemical characteristics of the soil are listed in Table 1. Activated carbon (AC) used in this study was derived from coconut shells with BET surface area 765 m2-1 g, porosity 0.27, and diameter of carbon pore 1.9 nm.
|
2.2. Preparation of Naphthalene-Contaminated Soil
- The soil was artificially spiked with naphthalene dissolved in methanol. The target concentrations of naphthalene in the spiked soils were 50, 75, 100, 125, and 150 mg/kg. The spiked soil was completely stirred and blended to ensure homogeneity. Finally, the contaminated soil was laid in a fume hood for about 4 to 6 days until the methanol was completely evaporated and the artificially contaminated soil was dry. During the ventilation, the spiked soil was stirred each day. All mixing processes were carried out in glass containers. The spiked soil was moisturized with deionized water to keep water content of 10%, and aged for 2 weeks before use.
2.3. Soil Washing of Soil-Bound Naphthalene
- Removal of naphthalene from the artificially contaminated LAUTECH agricultural farm soil using the oils was investigated in batch experiments. Naphthalene contaminated soils were washed by putting 200 g samples into glass bottles (500 mL) and thereafter, 200 mL of oils was added. These treatments ensured pure washing agent to soil ratio of 1:1. The bottles were sealed with the caps and and mechanically shaken vigorously on a magnetic stirrer for 6 h at room temperature (28 ± 2oC). At intervals of 1 h, an aliquot of the mixture in the bottle was taken and centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 15 min to separate the eluting agent and the soil. The supernatant was taken and the naphthalene concentrations of the supernatant were analyzed spectrophotometrically using a UV-visiblespectrophotometer () at an absorbance wavelength of 279 nm. Soil washing was performed in duplicate at the same condition.
2.4. Modelling the Desorption Kinetics of Naphthalene
- The empirical first order model proposed by Woolgar and Jones[31] was employed to describe the kinetics of naphthalene mass transfer rates from soil to the oils. This model can be used when dissolution (or desorption) arises out of equilibrium partitioning and mass transfer phenomena take place between two phases, one of which is a liquid phase and the other is a solid phase[32]. The theoretical basis of this model is that at equilibrium, there is no net transfer between two phases and partition coefficients was used to represent the ratio of the concentration of the same chemical species in two phases. Relative concentrations of naphthalene between two distinct phases provide an explicit measure of the propensity of naphthalene to exist in each phase.
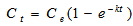 | (1) |
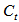 is the naphthalene concentration of the oil phase at time
is the naphthalene concentration of the oil phase at time 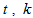 is the lumped mass transfer coefficient,
is the lumped mass transfer coefficient, 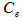 is the equilibrium oil-phase concentration and
is the equilibrium oil-phase concentration and 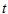 is the contact time with oil. In this study, mass transfer theory was used to derive first-order mass transfer coefficients and equilibrium oil phase concentration by fitting the data to Eq. (1). Fitting of the data to the equation was achieved using a non linear curve fitting of MATLAB 7.0 software package.
is the contact time with oil. In this study, mass transfer theory was used to derive first-order mass transfer coefficients and equilibrium oil phase concentration by fitting the data to Eq. (1). Fitting of the data to the equation was achieved using a non linear curve fitting of MATLAB 7.0 software package.2.5. Oil Regeneration Feasibility
- The feasibility of the oils (PKO, coconut oil and used cooking oil) regeneration were investigated using coconut shell derived-activated carbon to adsorb naphthalene from used oil by means of a batch experiment in a 250 ml- Erlenmeyer flask. A total of 90 mL used oil was poured into a 250 mL- Erlenmeyer flask, to which 20 g activated carbon derived from coconut shell was added, while a flask without activated carbon served as control. The Erlenmeyer flask was placed on a magnetic stirrer for 6 h. The suspensions were settled and oil samples were taken and filtered through glass membrane for naphthalene analysis.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
- Mean of naphthalene removal by the different oil was compared using one way analysis of variance and least significance difference of a statistical software, SPSS 11.5, at 95% confidence. The homogeneity of the variances was tested with Levene’s test.
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Desorption of Naphthalene from Contaminated Soil
- Transport and mass transfers of naphthalene from the contaminated soil might be key processes responsible for reducing naphthalene of the soil. To achieve maximum polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (e.g. naphthalene) removal, a specific period of time is required. Many studies on solvent agent remediation of organic chemicals contaminated soils tried to reduce the time required for the process[33, 34]. Our results demonstrated a rapid dissolution of naphthalene contaminated soil within 6 hours. The percentages of naphthalene removal or desorption efficiencies from the artificially contaminated soils by the individual washing or solubilization agents are shown in Figure 1. Generally, the naphthalene DE for PKO, coconut oil and used cooking oil in all cases were greater than 80 %. This showed that PKO, coconut oil and used cooking oil respectively enhanced the apparent solubility of naphthalene, which was spiked in the soils at a concentration of 50 to 150 mg/kg. When PKO was used as a washing or solubilization agent, 96.91%, 98.60%, 99%, 98.36% and 93.33% of naphthalene removal from the soil with naphthalene concentration of 50, 75, 100, 125 and 150 mg/kg were observed, respectively; while 93.16%, 93.40%, 95.50%, 93.88% and 87.30% of naphthalene removal from the soil with coconut oil as eluting agent were respectively achieved. In addition, 95.60%, 96.67%, 98.45%, 97.80%, and 91.50% of naphthalene removal from the contaminated soil were also obtained when used cooking oil was used as the solubilization agent. This demonstrated that the desorption efficiencies of the oils in naphthalene removal increased with increasing initial naphthalene concentration from 50 to 125 mg/kg and thereafter decreased at 150 mg/kg.
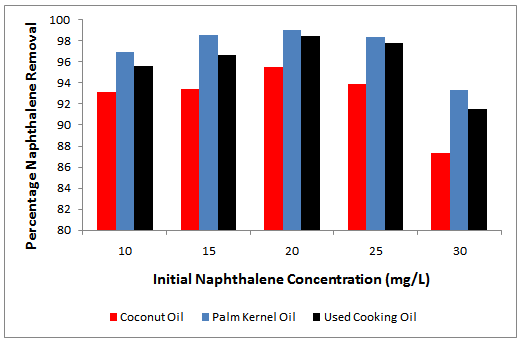 | Figure 1. Percentage removal of naphthalene by vegetable oil as a function of initial naphthalene concentration |
- Maximum desorption efficiencies of 99 %, 95.50 % and 98.45 % were attained at 125 mg/kg initial naphthalene concentration using PKO, coconut oil and used cooking oil, respectively. A solubility limitation might be the reason for this difference, as the solubilization of naphthalene from the spiked soil was rather significant. The difference in naphthalene removal by PKO and used cooking oil was not quite pronounced while both showed a higher efficiency than that observed in using coconut oil. Lau et al.[35] have observed that the desorption efficiency of phenanthrene increased with increased phenanthrene concentration from 200 ppm to 1000 ppm using PKO as eluting agent, while Chi et al.[17] observed that anthracene removal efficiency decreased with increase in initial anthracene concentration from 200 mg/kg to 400 mg/kg when soybean oil was used as eluting agent. More also, Pannu et al.[36] showed that the DE of anthracene increased from 50 to 92% when using peanut oil for a soil contaminated with 50 – 100 ppm anthracene and it dropped to 16 %. The discrepancies that exists between different researches is probably due to the content of organic matter, concentration of PAH, moisture, and the characteristics of soil. It was observed that after dissolution of naphthalene from contaminated soil, the PKO, coconut oil and the used cooking oil turned dark brown in color, apparently containing a large amount of co-extracted soil organic materials. A similar observation has been reported for the use of sunflower in the dissolution of anthracene, phenanthrene and fluoranthene present in contaminated soil [32]. In the soils with organic material content greater than 0.1%, hydrophobic organic pollutant (HOC) partitioning into the soil organic material has been found to be the dominant process [37]. Dissolution of soil organic material by the PKO, coconut oil and used cooking oil will as well make the naphthalene bound-soil organic material to be dissolved into PKO, coconut oil and used cooking oil. This further enhances the capacity of PKO, coconut oil and used cooking oil to extract naphthalene from the contaminated soil.
3.2. Kinetics of Naphthalene Desorption/Dissolution
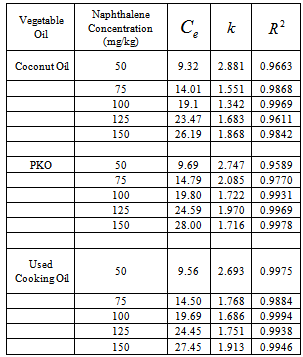
- Kinetics of naphthalene desorption or dissolution from soil /oil slurry were plotted for PKO, coconut oil and used cooking oil at naphthalene initial concentration of 10 to 50 mg/L corresponding to 50 – 150 mg/kg soil as shown in Figure 2 to Figure 4. During the initial phase (0 – 6 h), desorption or dissolution was rapid, which was followed by a phase of slower dissolution. For the naphthalene, equilibrium could be approached within 6 h. The empirical model proposed by Woolgar and Jones [31] suitably describe the kinetics of naphthalene desorption or dissolution in palm kernel oil, coconut oil and used cooking oil, respectively. Using this model, equilibrium naphthalene concentrations (
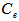 ) and mass transfer coefficients (
) and mass transfer coefficients (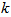 ) at different initial naphthalene concentrations were obtained. The mass transfer rate coefficients of naphthalene desorption and the oil phase equilibrium concentration of naphthalene are presented in Table 2. The correlation coefficient of naphthalene (
) at different initial naphthalene concentrations were obtained. The mass transfer rate coefficients of naphthalene desorption and the oil phase equilibrium concentration of naphthalene are presented in Table 2. The correlation coefficient of naphthalene (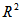 ) at different initial concentration is highly significant and varied between 0.95 and 0.99 (Table 2). The results in Table 2 showed that mass transfer rate coefficient generally decreases and the oil phase equilibrium concentration increases with increased initial naphthalene concentration in the soil. Gong et al. [32] have reported a decrease in mass transfer coefficient in the dissolution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (anthracene, phenanthrene and fluoranthene) by sunflower oil when oil/soil ratio was increased from 1:1 to 2:1.
) at different initial concentration is highly significant and varied between 0.95 and 0.99 (Table 2). The results in Table 2 showed that mass transfer rate coefficient generally decreases and the oil phase equilibrium concentration increases with increased initial naphthalene concentration in the soil. Gong et al. [32] have reported a decrease in mass transfer coefficient in the dissolution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (anthracene, phenanthrene and fluoranthene) by sunflower oil when oil/soil ratio was increased from 1:1 to 2:1. | Figure 2. Dissolution rates and first-order model fitted curves of naphthalene in coconut oil. The circles denote the experimental data and the solid lines are the model fitting curves |
 | Figure 3. Dissolution rates and first-order model fitted curves of naphthalene in palm kernel oil, The circles denote the experimental data and the solid lines are the model fitting curves |
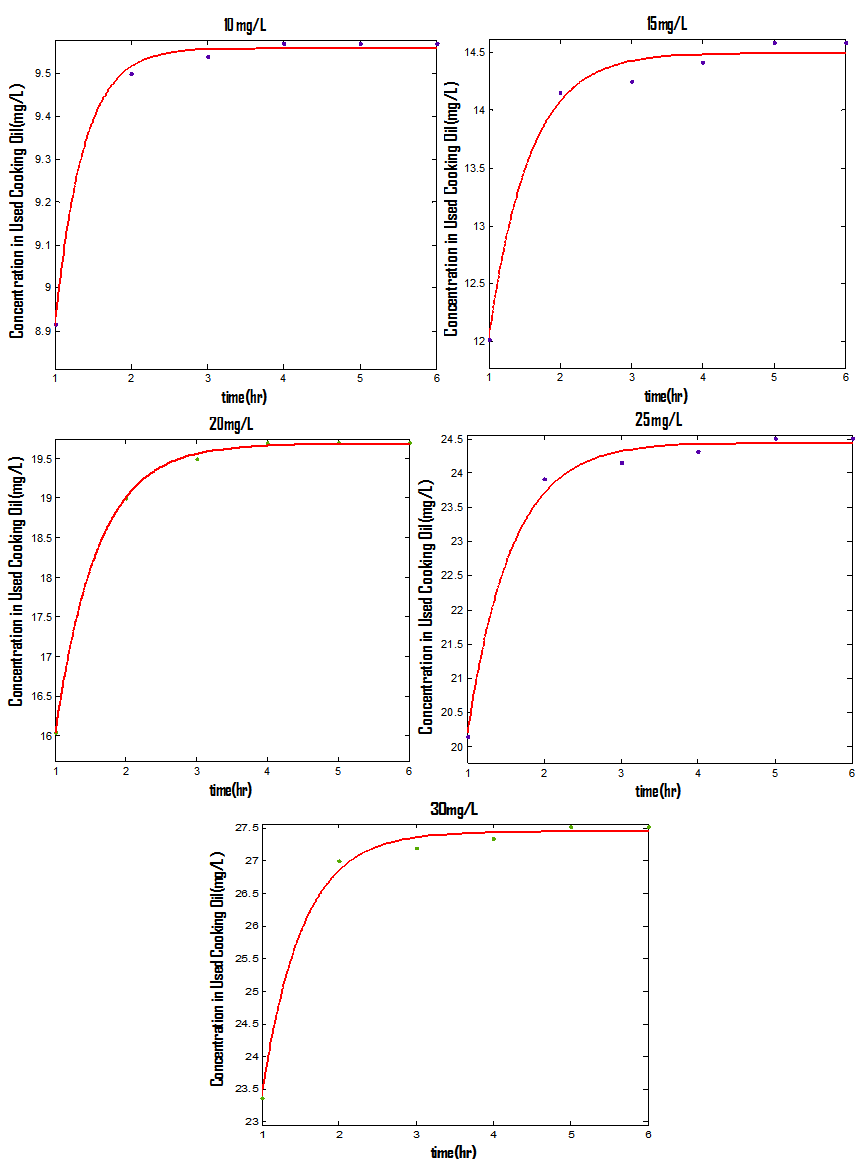 | Figure 4. Dissolution rates and first-order model fitted curves of naphthalene in used cooking oil, The circles denote the experimental data and the solid lines are the model fitting curves |
|
3.3. Regeneration of the Oils
- Regeneration of the oils is a vital step for the successful development of the remediation process with Coconut oil, PKO and Used Cooking Oil as a solvent. Activated carbon was considered as a sorbent for the application in batch experiment. The overall efficiency of sorption process to achieve oil regeneration was determined based on concentrations of naphthalene in oils before and after the activated carbon treatment as shown in Figure 5. Figure 5 shows that the naphthalene concentration at t = 0 is the total naphthalene left in the oil after remediation while the concentration at t = 1-6 h is the naphthalene left in the oil after the recovery. For PKO after the remediation, a total of 35.99 mg/L naphthalene concentration remained in the soil/oil slurry with initial naphthalene concentration ranging from 50-150 mg/kg and after the recovery; 13.77 mg/L naphthalene concentration was left indicating an activated carbon efficiency of 62%. While for coconut oil, 68.64 mg/L of naphthalene concentration was left after soil washing remediation and 17.12 mg/L concentration of naphthalene remained after the oil recovery indicating an effectiveness of 75%; and also for waste cooking oil, a total of 44.21 mg/L concentration of naphthalene remained after remediation and 11.54 mg/L naphthalene was left after oil regeneration indicating 75% efficiency of the activated carbon. These results indicated that activated carbon is a good matrix to remove naphthalene from the oils. Nevertheless, further study is required to optimize the regeneration process.
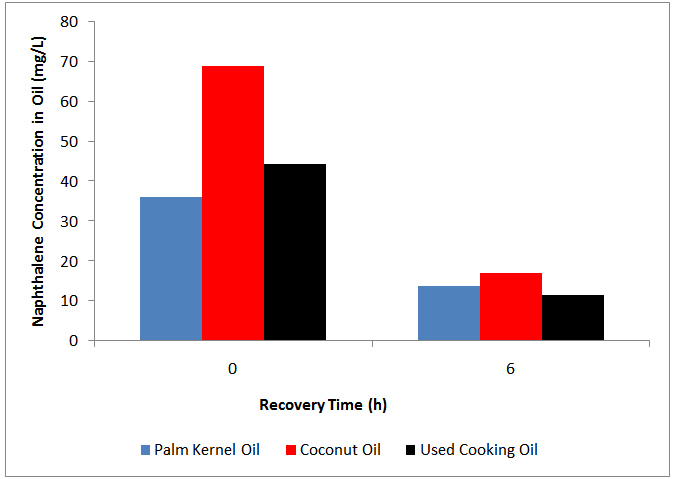 | Figure 5. Naphthalene regeneration from palm kernel oil, coconut oil and used cooking oil |
4. Conclusions
- The study has revealed that the removal or desorption efficiency for 50 to 150 mg/kg naphthalene-contaminated soils ranges from 85 - 99 % with the use of PKO, coconut oil and used cooking oil as washing or solubilization agents. The solubilization or removal of naphthalene from soils using PKO, coconut oil and waste cooking oil was also dependent on naphthalene concentrations. Coconut shell-derived activated carbon efficiently removed the naphthalene in PKO, coconut oil and waste cooking oil and the adsorption efficiency reached 63-75%. Further investigations into remediating naphthalene-contaminated soil with various combinations of silt and clay fractions will be conducted to understand the effects of organic carbon content and particulate size on the soil washing process.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML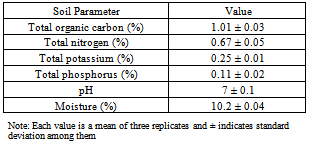
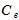 ) and mass transfer coefficients (
) and mass transfer coefficients (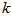 ) derived from first-order model fitted to naphthalene soil washing data
) derived from first-order model fitted to naphthalene soil washing data