-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Environmental Engineering
p-ISSN: 2166-4633 e-ISSN: 2166-465X
2012; 2(3): 54-57
doi: 10.5923/j.ajee.20120203.03
Gibbs Free Energies, Enthalpies and Entropies of Transfer for Reference Ions Ph4 As+ and Ph4 B- in Mixed DMFA-H2O Solvents at Different Temperatures
Esam A. Gomaa
Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Mansoura University, Mansoura, 35516, Egypt
Correspondence to: Esam A. Gomaa , Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Mansoura University, Mansoura, 35516, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The thermodynamic data (Gt , Ht and TSt ) of transfer for tetraphenylarsonium-tetraphenylborate (Ph4AsBPh4) from water to mixed dimethylformamide (DMFA)-H2O solvents were estimated from the experimental solubility and calorimeter measurements. The experiments were done at three different temperatures 288.15, 298.15 and 308.15 K. Also the thermodynamic parameters were divided into reference anion and cation following the asymmetric deviation and their values, were discussed. Dividing all the thermodynamic functions between the cation and anion by using 1.064 factors we obtain their individual functions. The reference ion values can be easily used for evaluating the different thermodynamic parameters of any ion that contains in its counterion tetraphenyl cation or anion . By using the data given here the thermodynamic parameters for some single ion can be estimated for following their behaviour in environment. The single ion thermodynamics are helpful for predicting, explaining and mechanisms suggesting. Theoretical and engineering chemistry are in need for experimental single ion parameters for the comparison with that calculated by different solvation theories.
Keywords: Gibbs Free Energies, Enthalpies, Entropies, Tetraphenylarsonium-Tetraphenyl Borate, Dimethylformamide
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Single ion transfer Gibbs energies, entropies and enthalpies play an important role in many areas of chemistry, such as the estimation of solubilities, electrochemical potentials, distribution ratio and complex formation constants[1]. Extra thermodynamic models must be used for the determination of single ion thermodynamic quantities[2,3].As one of the extrathermodynamic assumptions, the refrence electrolytes such as tetrphenylphosphonium , tetraphenylarsonium and triso – amyl -n- butylammonium – tetra phenyl borate have been used for the partition of thermodynamic quantities of electrolytes into values of individual ions[4 -6] . Also thermodynamics of ion association are in need to the single ion parameters[7]. The reference electrolyte Ph4AsBPh4 with its caution and anion of different sizes and large tetrahedral structure in which the central ion is buried in four phenyl rings, provide the possibility of evaluating single ion thermodynamic quantities in different solvents[8].This reference electrolyte assumption has been studied experimentally as well as theoretically in many pure solvents[9], and mixed solvents[10]. Here in this work the Gibbs energies, enthalpies and entropies of transfer for Ph4 As BPh4 from water to mixed DMFA-H2O solvents were experimentally determined at 288.15, 298.15 & 308.15 K and their values were discussed. The aim of the work is to give data about the solvation of very important reference electrolyte Ph4AsBPh4 in mixed DMFA-H2O solvents and its ions, necessary for the evaluating other single ion thermodynamic parameters. These data can help the analyst for further evaluation and discussion about ion properties in solutions.
2. Experimental
- The DMFA used was of spectroscopic purity (Uvasol) from Merck and used directly without purification.Ph4AsBPh4 was prepared by the condensation of aqueous solutions of Ph4AsPh4B and NaBPh4 followed by crystallization in acetonitrile as described in ref. 15. The effect of temperature was studied by shaking samples put in closed test tubes in a shaking water bath of the types "Assistant" till saturation for one week at the studied temperatures 288.15, 298.15 and 308.15 K. The solubilities were determined as explained before in ref. 12. Calorimeter like thermos shape (RMG) type 489/10 was used for measuring the enthalpies of solvation at the used temperature. The solubility were determines conductometically and gravimetrically as explained before which are ease, reproducible and cheap methods . Also it consumes little time and accurate data.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Gibbs Free Energies
- The calculated
 Gt and their transfer values (
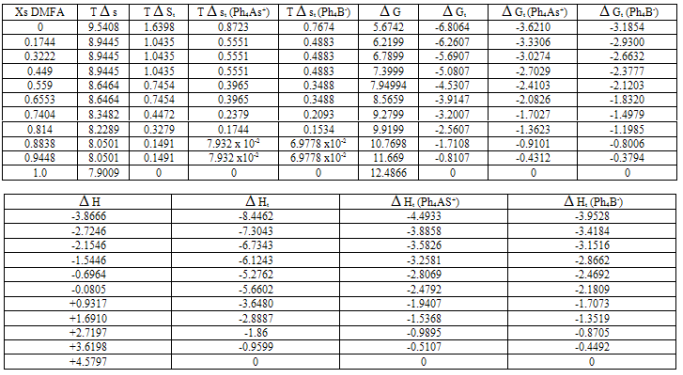
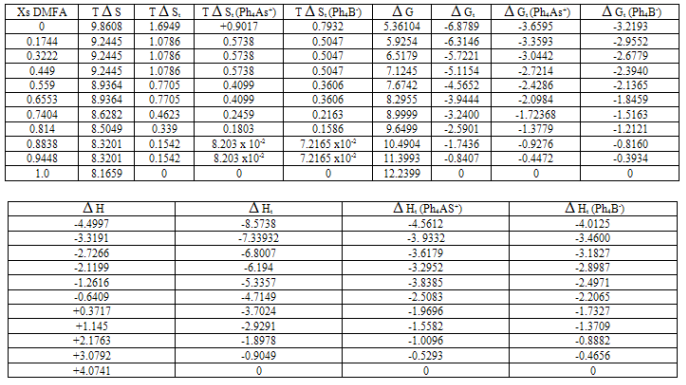
Gt and their transfer values ( Gt) for Ph4AsBPh4 at 288.15, 298.15 and 308.15 K were evaluated as explained in ref. 12 and their values are listed in Tables1-3 with standard deviation of ±0.3 KJ/mole.
Gt) for Ph4AsBPh4 at 288.15, 298.15 and 308.15 K were evaluated as explained in ref. 12 and their values are listed in Tables1-3 with standard deviation of ±0.3 KJ/mole. 3.2. Enthalpies and Entropies
- The enthalpies
 Ht from water to mixed DMFA-H2O solvents for the reference electrolyte (RE) Ph4 As B Ph4 were estimated calorimetrically at 288.15, 298.15 and 308.15 K and their values are given in Tables 1-3 also. The entropies T
Ht from water to mixed DMFA-H2O solvents for the reference electrolyte (RE) Ph4 As B Ph4 were estimated calorimetrically at 288.15, 298.15 and 308.15 K and their values are given in Tables 1-3 also. The entropies T S and entropies of transfer T
S and entropies of transfer T St for Ph4AsBPh4 were obtained by applying equation 1, and their values are also presented in Tables 1-3[13 - 18].
St for Ph4AsBPh4 were obtained by applying equation 1, and their values are also presented in Tables 1-3[13 - 18]. 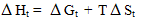 | (1) |
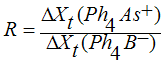 | (2) |
4. Conclusions
- This work is to give data about the solvation of very important reference electrolyte Ph4AsBPh4 in mixed DMFA-H2O solvents and its ions, Ph4 As+ , Ph4B- necessary for the evaluating other single ion thermodynamic parameters. These data can help the analyst for further evaluation and discussion about ion properties in solutions.
|
|
|
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML