-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Environmental Engineering
p-ISSN: 2166-4633 e-ISSN: 2166-465X
2011; 1(1): 1-9
doi: 10.5923/j.ajee.20110101.01
Removal of Orange 7 Dye from Wastewater Used by Natural Adsorbent of Moringa Oleifera Seeds
Reza Marandi , Seyedeh Marjan Bakhtiar Sepehr
Department of Environmental Engineering, Islamic Azad University, North Tehran Branch, Tehran, Iran
Correspondence to: Reza Marandi , Department of Environmental Engineering, Islamic Azad University, North Tehran Branch, Tehran, Iran.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Removal of Orange 7 from wastewater using natural adsorbent of Moringa Oleifera seeds were investigated. The effects of some operational parameters such as pH, the amount of biosorbent, initial dye concentration and temperature were examined. The present study revealed optimum conditions for the removal process which included dose of biosorbent (0.4 g), initial dye concentration (20 mg/L), initial pH (6) and temperature (25°C). The Langmuir and Freundich isotherms were applied for describing the biosorption equilibrium. The process was represented by the Freundich isotherm with a correlation coefficient of 0.94. The first-order, second-order and intra-particle diffusion kinetic models were implemented for demonstrating the biosorption mechanism and, as a result, intra-particle diffusion kinetics fitted best to the experimental data.
Keywords: Wastewater, Orange 7, Moringa Oleifera, Biosorption
Cite this paper: Reza Marandi , Seyedeh Marjan Bakhtiar Sepehr , "Removal of Orange 7 Dye from Wastewater Used by Natural Adsorbent of Moringa Oleifera Seeds", American Journal of Environmental Engineering, Vol. 1 No. 1, 2011, pp. 1-9. doi: 10.5923/j.ajee.20110101.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Among waters, dye wastewater from dyestuff and textile industries is one the most difficult ones to be treated[1]. By absorbing sunlight, dyes can prevent photosynthesis in aqueous ecosystems. Sulfur dyes are harmful to aqueous organisms, since they can rapidly reduce the oxygen content of water[2]. Many studies have been done on physico-chemical methods in order to remove color from textile effluent. These methods include coagulation, oxidization, ultra filtration, electro-chemical, adsorption and combined electro-chemical and adsorption techniques[1-16].Generally speaking, synthetic dyes’ complex aromatic structures make them stable and difficult to biodegrade[17]. Adsorption has some specific benefits, which include treating high-flow wastewaters with good final quality and without producing any harmful substances[2].Acid Orange 7 [p-(2-hydroxy-1-naphthylazo) benzene sulfonic acid, as a popular water-soluble dye, is used for dyeing a variety of materials such as nylon, aluminum, detergents, cosmetics, wool and silk. Similar to other azo dyes, it is usually disposed in industrial wastewater, which can be considered a serious health threat to humans. It is highly toxic; thus its ingestion can irritate eye, skin, mucous membrane and upper respiratory tract; severe headaches, nausea, water-borne diseases such as dermatitis and loss of bone marrow leading to anemia are also among its harmful consequences. Since it is carcinogenic in nature and leads totumors, it can be fatal to consume it. Current research has found that the electron-with drawing character of the azo group is the main cause of its chronic toxicity, which develops an electron deficiency and is reduced to carcinogenic amino compounds[12].Since Acid Orange 7 is toxic and carcinogenic by nature, its removal has been attempted by biodegradation and photosensitization on TiO2 particles. Unfortunately, metabolic intermediates produced after its biodegradation are carcinogenic and photosensitization produces 1,2 - naphthoquinone and phthalic acid during degradation, which are also harmful. Additionally, Biofilm systems have been applied for aerobic nitrification, anoxic denitrification and anaerobic digestionin order to decolorize Acid Orange7[12].Therefore, it can be concluded that despite its high toxicity, thus far, few attempts have been made to remove Acid Orange 7 from aqueous solutions. Even common chemical/physical methods such as coagulation, flocculation, ozonation, reverse osmosis, electrolysis, ultra-chemical filtration and chemical treatments have not been attempted, which can be attributed to either high solubility of the dye in water or possibility of generating toxic intermediates/products during the process. Furthermore, adsorption, which is influenced by the chemical properties and structure of the dye and also do not produce any toxic products, is deliberately used for the eradication of Acid Orange 7 from waste wate[12]. One of the natural coagulants is the water -soluble extract of the dry seeds of Moringa oleifera, which is a tropical plant from the family of Moringaceae. So far, up to fourteen different species have been identified for it. Moringa oleifera is the most widespread species and grows quickly at low altitudes of the whole tropical belt including arid zones[18].It is drought-tolerant, has nutritional, medicinal and water cleaning attributes and its leaves, flowers, fruits and roots are locally used as food articles. Because of its medical and therapeutic properties, it is applied as a cure for different ailments and diseases and physiological disorders in eastern allopathic medicine.The present investigation aims at examining the sorption potential of SMOS in order to remove organics from aquous media[19].
|
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instruments
- 1-METTLER balance with accuracy 0.0001 g2-EDT Instruments pH meter3-Sigma 301 centrifuge4-GFL 3005 Shaker 5- Heidolph unimax 1010 Shaker Incubator 6- unico 4802 UV-Vis spectrophotometer
2.2. Preparing Acid Orange 7 and Biosorption Capacity
- The Acid Orange 7 used in this study was obtained from Merck and Stock AO7 solution (500 mg/L) was prepared by dissolving 0.05 g of AO7 in 10 mL of double-distilled water and diluting quantitatively to 100 mL. AO7 solutions of different concentrations (2.5–50mg/L) were prepared by the adequate dilution of the stock solution to 250 mL. The applied glassware was rinsed several times with double-distilled water before being used. The absorbance of standard AO7solutions was measured and plotted against the concentration.In brief, batch experiments were carried out as functions of biomass dose (0.05–1.0g), dye concentration (2.5–50 mg/L), pH (3.0–9.0), temperature (10–30℃) and contact time (1–60 min). Known solutions of AO7 were poured into separate 100ml Erlenmeyer flasks. After pH adjustment, a known quantity of biosorbent was added and, at last, dye bearing suspensions were kept on the shaker (250 RPM) for 60 minutes at the temperature. The samples were taken from 0 to 60 minutes and the biomass was separated from the solutions by centrifuge and was subjected to dye estimation by UV/Vis spectrophotometry. Dye concentrations were recorded before and after biosorption. Removal efficiency was computed by the following equation[19]:
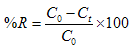 | (1) |
2.3. Analytical Methods
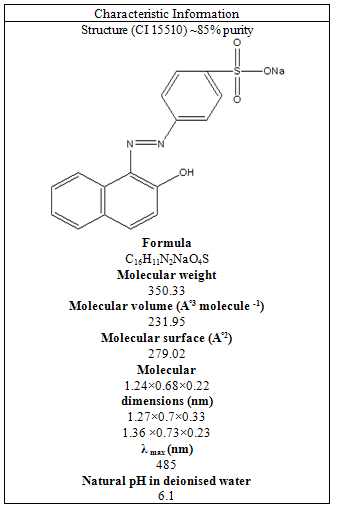
- Maximum absorbance wavelength of AO7 was determined experimentally. The concentration of AO7 in the solutions before and after the equilibrium was determined by UV/Vis spectrophotometry at a λmax of 485 nm, using a unico 4802 UV/Vis spectrophotometer. pH of the solutions was measured by a EDT Instruments pH meter.NaOH and HCl were obtained from Merck, Germany. Dilute solutions of NaOH and HCl were prepared and used for adjusting the pH.All the chemicals used in this study were of analytical reagent grade.
3. Results and Discussion
- To acquire a comprehensive understanding of biosorption of AO7 onto SMOS, a meticulous investigation of effective parameters was carried out. Prior knowledge on the optimal conditions provides a better design and modeling which are, therefore, of vital importance for exploiting the potentiality of the SMOS biosorbent[19]. The biosorption of AO7 onto SMOS is influenced by the sorbent dose, concentration of sorbate, initial pH, reaction temperature and contact time.
3.1. Effect of Biosorbent Dose
- A number of investigations were carried out by varying the amount of SMOS from 0.05 to 1.0 g at the fixed initial dye concentration of 20 mg/L, pH of 7 and room temperature of 25±1 ℃. These studies showed an increase in biosorption with the increase in the dose of biosorbent (Fig.3-1). Optimum biosorbent dose was found to be 0.4 g.
3.2. Effect of Initial Dye Concentration
- Fig.3-2, show the results of experiments conducted in the range of dye concentration (2.5–50mg/L) at the constant biosorbent dose (0.2 g), pH (7) and temperature (25℃). The obtained results reveal that percent removal of dye depends on the initial dye concentration. The obtained optimum dye concentration was 20 mg/L. These observations can be explained by the fact that sufficient biosorption sites are available for accommodating an increasing number of dye molecules. In other words, the number of molecules available for sorbing onto the sorbent surface is relatively lower in comparison with the ones available for biosorption sites[19,24]. Higher dye concentrations are capable of affecting the chemical equilibrium between dye molecules in the liquid phase and the ones adsorbed onto the biosorbent surface resulting in a further biosorption process. Moreover, this sorption behavior can be attributed to higher chance of effective interaction between adsorbate molecules and biosorbent surface as the concentration of dye increases. These findings demonstrate the applicability and efficacy of SMOS for the removal of AO7 dye from the aqueous media.
3.3. Effect of Initial pH
- Effect of initial pH on the biosorption process was monitored in the pH range of 3 and 9 at the biosorbent dose of 0.20 g, initial dye concentration of 20 mg/L and temperature of 25±1 ℃ (Fig.3-3). The most appreciable biosorption was found in pH 6. Variation in the removal of AO7 with respect to pH can be explained by considering surface properties of biosorbent material and ionization state of AO7[24]. Protaineous amino acids are mainly considered as the active functional compounds present in shelled Moringa Oleifera seeds. These amino acids have a variety of structurally pH-dependent properties and the ability to generate negatively charged atmosphere.
3.4. Effect of Temperature
- Effect of temperature over the ranges 10, 25and 30℃ on AO7 biosorption was examined under the conditions of 0.20 g biosorbent dose, 20 mg/L dye concentration and the initial pH of 7. The biosorption was fast at the beginning of the experiment. The sensitivity of biosorption process toward temperature is presented in Fig.3-4. This figure exhibits a small fluctuation in the percent sorption of dye as temperature increases from 10℃ to 25℃ and decreases from 25℃ to 30℃.
3.5. Effect of Contact Time
- The variation in the sorption of AO7 as a function of contact time is presented in Fig. 3-5. The results obtained under constant conditions of 0.20 g biosorbent dose, 20 mg/L initial dye concentration, pH of 7 and room temperature of 25±1 ℃ reveal that the percent removal of AO7 rises as time proceeds. The sorption is quite rapid initially, then slows down gradually and, finally, levels out and reaches a maximum dye removal. This trend may be attributed to the elevation of contact between the sorbate and sorbent during the experiment. Interestingly, near 60% of the ultimate biosorption occurred within first 5 minutes of contact. Bearing in mind the time restraints in the practice, it is recommended that SMOS be capable of being used as an effective pretreatment technology in the dye wastewater treatment.
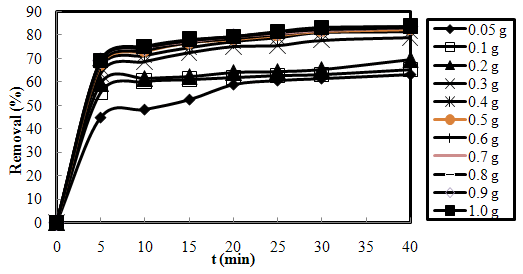 | Figure 3-1. Effect of biosorbent dose on the removal of AO7 using SMOS at C0=20 mg/L, pH=7 and T=25 ℃ |
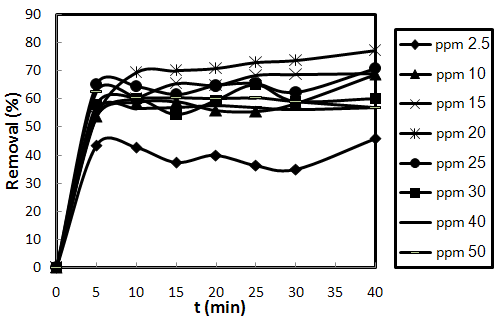 | Figure 3-2. Effect of initial dye concentration on the biosorption behavior of AO7 on SMOS at m=0.2g, pH=7 and T=25 ℃ |
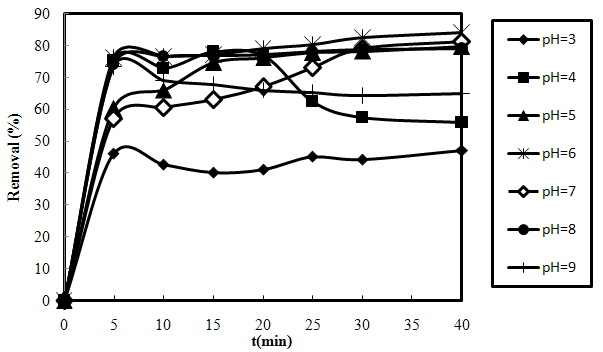 | Figure 3-3. Effect of varying initial pH on the removal of AO7 by SMOS at m=0.20 g, C0=20 mg/L and T=25 ℃ |
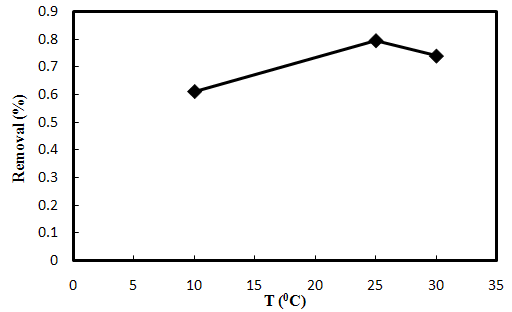 | Figure 3-4. Effect of different temperatures on the biosorption of AO7 by SMOS at m=0.20 g, C0=20 mg/L and pH=7 |
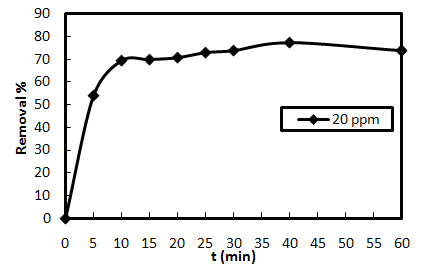 | Figure 3-5. Effect of contact time on the removal of AB9 using SMOS at m=0.40 g, C0=20 mg/L, pH=7 and T= 25 ℃ |
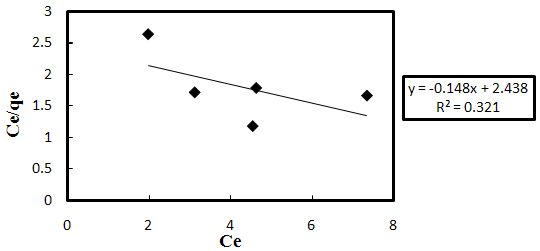 | Figure 3-6. Langmuir isotherm chart. |
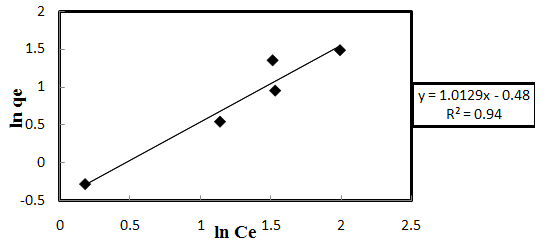 | Figure 3-7. The Freundlich isotherm’s chart |
3.6. Adsorption Isotherm
- In order to understand the adsorption process, the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms, Figs. 3-6 and 3-7, respectively, were used to represent the equilibrium relationship for different initial Acid Orange 7 concentrations’ experiments. The Langmuir equation assumes that adsorption is limited to monolayer; its linearized form can be represented as:
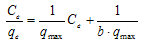 | (2) |
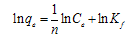 | (3) |
|
|
|
3.7. Kinetic Studies
- In order to evaluate the kinetics of AO7 biosorption onto SMOS, three models were applied, i.e. first-order model, second-order model and intra-particle diffusion model. The linear form of the first-order model can be formulated as:
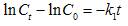 | (4) |
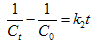 | (5) |
 | (6) |
 | (7) |
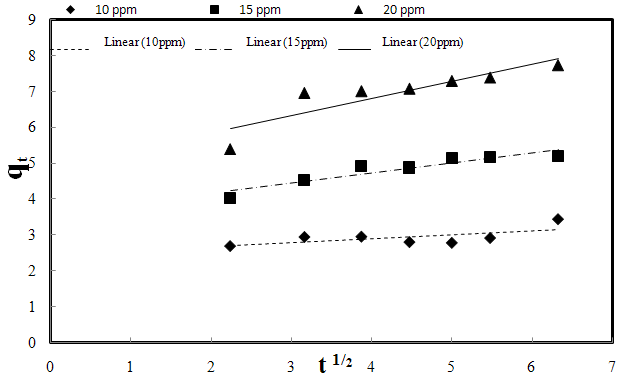 | Figure 3-8. The intra-particle diffusion kinetic plots for the biosorption of AO7 dye by SMOS at different initial dye concentrations, 0.2 g biosorbent dose, pH 7 and 25℃ |
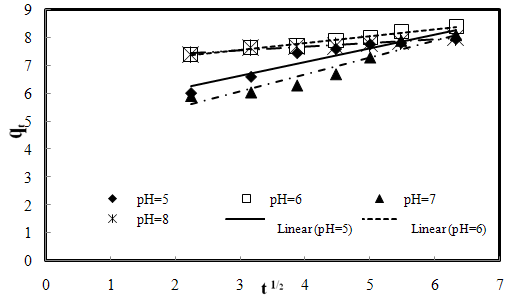 | Figure 3-9. The intra-particle diffusion kinetic plots for the biosorption of AO7 dye by SMOS at different initial pH, 20 mg/L initial dye concentration, 0.2 g biosorbent dose and 25 ℃ |
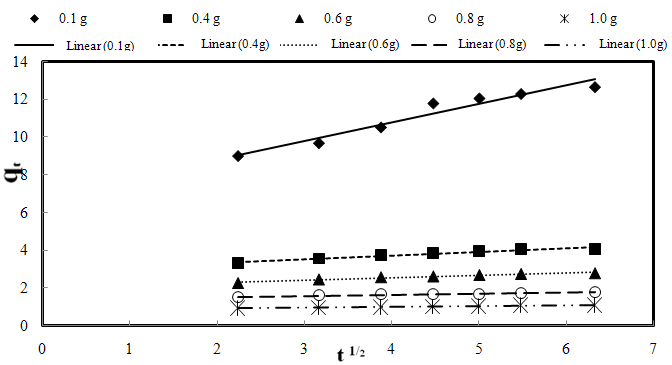 | Figure 3-10. The intra-particle diffusion kinetic plots for biosorption of AO7 dye by SMOS at different biosorbent doses, 20 mg/L initial dye concentration, pH 7 and 25 ℃ |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4. Conclusions
- Successful application of shelled Moringa Oleifera Lamarck seeds as a biosorbent at the laboratory scale introduces an effective, feasible and environmentally-friendly method for removing C.I. Acid Orange 7 from the aqueous systems. The biosorption process was found to be dependent on biosorbent dose, initial dye concentration, initial pH, temperature and contact time. Under the studied conditions, biosorption equilibrium data followed Freundlich isotherm more favorably than Langmuir isotherm. The values of 1/n and Kf from Freundlich and Langmuir isotherms confirmed the effectiveness of SMOS biosorbent for removing AO7 dye at low concentrations. Batch biosorption capacity tests have shown that intra-particle diffusion kinetics can be applied for describing the biosorption mechanism in certain conditions, whereas the first-order and second-order models with little differences did not fit the experimental data. The removal of Acid Orange 7 was observed to be rapid at the primary stages of biosorption process. The main conclusion is that the shelled Moringa Oleifera seeds demonstrate an adequate potential for being exploited as an economically viable and indigenous pretreatment approach in modern technology of wastewater treatment. Future investigations should be conducted with a view to selectively separating the present dye contaminants, regenerating the exhausted biomass, recovering the sorbed dye and designing to continuous dye treatment systems. These studies can further ameliorate the economic aspects of dye wastewater treatment.
References
| [1] | Padmesh, T.V.N., Vijayaraghavan, K., Sekaran, G., Velan, M., 2005, Batch and column studies on biosorption of acid dyes on fresh water macro alga Azolla filiculoides, J. Haz. Mat., B125, PP.121-129 |
| [2] | Aber, S., Daneshvar , N., Soroureddin, S.M., 2007, Study of acid orange 7 removal from aqueous by powered activated carbon of experimental results by artificial neural network, Desalination, 211, PP.87-95 |
| [3] | Gupta, V.K., Suhas, 2009, Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal – A review, Journal of Enviromental Management, 90, PP.2313-2342 |
| [4] | Aksu, Z., 2005, Application of biosorption for the removal of organic pollutant: a review, Process Biochemistry, 40, PP.997-1026 |
| [5] | Ozer, A., Gonul, A., Turabik, M, 2006, The removal of Acid Red 274 from wastewater: Combined biosorption and biocoagulation with Spirogyra rhizopus, Dyes and Pigments, 71, pp.83-89 |
| [6] | Gao, J., Zhang, Q., Chen, R., Peng, Y., 2009, Biosorption of Acid Yellow 17 from aqueous solution by non-living aerobic granular sludge, Jounal of Hazardous Materials, 10612, No. of Pages 11 |
| [7] | Al-Degs, Y., El-Barghouthi, m., El-Sheikh, A.H., Walker, G., 2008, Effect of solution pH, ionic strength, and temperature on adsorption behavior of reactive dyes on activated carbon, Dyes and Pigments, 77, PP.16-23 |
| [8] | Moussavi, Gh., Mahmoudi, M., 2009, Removal of azo and anthraquinon reactive dyes from industrial wastewaters using MgO nanoparticles, Jounal of Hazardous Materials, 168, pp.806-812 |
| [9] | Silva, J. P., Sousa, S., Rodrigues, J., 2004, Adsorption of acid orange 7 dye in aqueous solution by spent grains, Separation and Purification Technology, 40, PP.309-315 |
| [10] | Cheung, W. H., Szeto, Y. S., Mckey, G., 2009, Enhancing the adsorption capacities of acid dyes by chitosan nano particles, Bioresource Technology, 100, PP.1143-1148 |
| [11] | Ji, P., Zhang, J., Chen, feng, Anpo, M., 2009, Study of adsorption and degradation of acid orang 7 on the surface of CeO2 under visibile light irradiation, Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 85, PP.148-154 |
| [12] | Gupta, V. K., Mittal, A., Gajbe , V., Mittal, J., 2006, Removal and Recovery of the Hazardous Azo Dye Acid Orange 7 through Adsorption over Waste Materials: Bottom Ash and De-Oiled Soya, Ind. Eng. Chem., 45, PP.1446-1453 |
| [13] | Tung Lin, Y., Huang Weng, Ch., Ying Chen, F., 2008, Effective removal of AB24 dye by nano/micro-size zero-valent iron, Separation and Purification Technology, 64, PP. 26–30 |
| [14] | Gonzalez, M. P. E., Montoya, V. H., 2009, Removal of acid orange 7 by guava seed carbon: A four parameter optimization study, J. Haz. Mat., 168, PP.515-522 |
| [15] | Silva, J. P., Sousa, S., Rodrigues, J., Antunes, H., 2004, Adsorption of acid orange 7 dye in aqueous solutions by spent brewery grains, Separation and Purification Technology, 40, PP.309–315 |
| [16] | Mahony, T. O., Guibal, E., Tobin, J. M., 2002, Reactive dye biosorption by Rhizopus arrhizus biomass, Enzayme and Technology, 31, PP.456-463 |
| [17] | Meia, H. Ch., Chienb, Ch. T., Dec, P. S., Lungd, Ch. H., 2009, Adsorption characteristics of Orange II and Chrysophenine on sludge adsorbent and activated carbon fibers, Journal of Hazardous Materials 161, PP.1384–1390 |
| [18] | Ndabigengesere, A, Narasiah, S, 1998 Quality of water treated by coagulation using Moringa Oleifera Seeds,Wat. Res,Vol 32,NO 3,PP.781-791 |
| [19] | Akhtar, M, Hasany, S. M., Bhanger, M.I., Iqbal,Sh, 2007, Sorption potential of Moringa oleifera pods for the removal of organic pollutants from aqueous solutions, Journal of Hazardous Materials,141, PP.546-556 |
| [20] | Krishna Prasad, R, 2009, Color removal from distillery spent wash through coagulation using Moringa oleifera seeds: Use of optimum response surface methodology, Journal of Hazardous Materials 165, PP. 804–811 |
| [21] | Sharma, P, Kumari,P, Srivastava, M. M., Srivastava, Sh, 2006, Removal of cadmium from aqueous system by shelledMoringa oleifera Lam. seed powder, Bioresource Technology 97,PP.299–305 |
| [22] | Gupta, V. K., Mittal, A., Krishnan, L., Mittal, J.,2006, Adsorption treatment and recovery of the hazardous dye, Brilliant Blue FCF, over bottom ash and de-oiled soya, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 293, PP.16–26. |
| [23] | Bhatti,H, N, Mumtaz, B, M Asif Hanif, M, Nadeem, R, 2007, Removal of Zn(II) ions from aqueous solution using Moringa oleifera Lam. (horseradish tree) biomass, Process Biochemistry 42 ,PP.547–553 |
| [24] | A. Mittal, 2006, Use of hen feathers as potential adsorbent for the removal of a hazardous dye, Brilliant Blue FCF, from wastewater, J. Hazard. Mater. B 128, PP.233–239 |
| [25] | M. Nadeem, A. Mahmooda, S. A. Shahid, S. S. Shah, A. M. Khalid, G. McKay,2006, Sorption of lead from aqueous solution by chemically modified carbon adsorbents, J. Hazard. Mater. B 138 ,PP.604–613 |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML