-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Dermatology and Venereology
p-ISSN: 2332-8479 e-ISSN: 2332-8487
2024; 13(1): 1-11
doi:10.5923/j.ajdv.20241301.01
Received: May 25, 2024; Accepted: Jul. 3, 2024; Published: Jul. 9, 2024

Premature Aging Skin Manifestations in Down's Syndrome – Trisomy 21
Marwa A. H. Adam1, Khalid O. Alfarouk2, Gamal O. Elhassan3, Adil H. H. Bashir2
1Department of Dermatology and Venereology, SMSB, Khartoum, Sudan
2Institute of Endemic Diseases, University of Khartoum, Sudan
3Qassim University, Buraydah, KSA
Correspondence to: Marwa A. H. Adam, Department of Dermatology and Venereology, SMSB, Khartoum, Sudan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Down syndrome (DS) is the most frequently occurring chromosomal abnormality in humans and affecting between 1 in 400-1500 babies born in different populations.The study aimed to explore the various dermatological manifestations of premature aging in DS people.Site of the study was a school for DS students, named Sudan center for Down syndrome (SCDS), which was the only specified place for DS in Sudan. Out of 60 students, only 24 students applied to the study. A control of 21 of normal population was set. I Used the Score for Intrinsic and Down syndrome adolescent. Extrinsic Skin Aging (SCINEXA) (modified) for assessing the aging process, Modified Fitzpatrick scaling system for assessing the facial wrinkling and the Busso scale for hands. The results showed obvious acceleration of premature aging signs. The most dermatological findings in DS group were: Miliaria 45.8%, nail ridging 37.5%, Subungual hyperkeratosis 25%, Chelitis 25%, Palmoplantar keratoderma (PPK) 20.8%, followed by impetigo 16.7% and Dermatophagia 16.7%. There was significant association between having a child with DS and an older mother age. Paternal diabetes and hypertension were remarkable in DS group, but less significant than maternal age at birth. In conclusion, there was a true accelerated aging process in DS group. Paternal diabetes and hypertension obviously had a role for having a baby with DS, but less significant than the maternal age.
Keywords: Down syndrome, Alzheimer disease, Dysmorphic features, Genodermatosis, Progeria, Intrinsic aging, Photoaging, Extrinsic aging, Skin aging
Cite this paper: Marwa A. H. Adam, Khalid O. Alfarouk, Gamal O. Elhassan, Adil H. H. Bashir, Premature Aging Skin Manifestations in Down's Syndrome – Trisomy 21, American Journal of Dermatology and Venereology, Vol. 13 No. 1, 2024, pp. 1-11. doi: 10.5923/j.ajdv.20241301.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
- Down syndrome (DS) is the most frequently occurring chromosomal abnormality in humans and affecting between 1 in 400-1500 babies born, dependent on different populations. DS people have various health issues, including heart defects, hematopoietic disorder, and early-onset Alzheimer disease. It is coupled with intellectual disability, gastrointestinal anomalies, weak neuromuscular tone, dysmorphic features of the head, neck and airways, audio vestibular and visual impairment, characteristic facial and physical features. [1]Cytogenetics (Genotypes) of DS: DS is caused by trisomy of chromosome 21. Mainly there are three cytogenetic forms of DS:1. Standard (Free) Trisomy 21 (95%). Consists of a supplementary chromosome 21 in all cells. 2. Mosaic Trisomy 21 (3-5%). Means that there are two cell lineages, one with the normal number of chromosomes and another one with an extra number of chromosome 21. 3. Robertsonian Translocation Trisomy 21 (4%). Occurs only in 2-4% of the cases. Around 90% of free trisomy 21 is due to a maternal meiotic error and only a small fraction is due to paternal errors.4. Other forms of trisomy 21 (1%):a) A terminal rearrangement of chromosome 21 around the telomeric region, the final chromosome having two centromeres and satellites on both ends.b) As a component of a double aneuploidy (for example, 48, XYY, +21 or 46,X, +21) [2].Clinical phenotype: The clinical phenotype in all types of DS is similar, with subtle differences in mosaic DS which depends on the extent of the trisomy 21 cell population. [3]People with DS have smaller brain volume but with atypically thicker cortex in the frontal and occipitoparietal cortices and thinner motor cortex and temporal pole compared to normal people. DS people also have disproportionately larger putamina and smaller hippocampi, likely a result of abnormal brain development and maturation. [4]
1.2. What is AGING?
- Historical background:Every society has had a concept of old age. Older people in various nations and cultures experience aging quite differently. The age at which old age is thought to start varies in different cultures. In Samoa, old age is usually defined as starting at 50; at 60 in Japan and Thailand, at 65 to 70 years in most western industrial countries. Whilst the term old or elderly appears a near universal social category recognized throughout recorded history, the twentieth century has seen a radical rethinking of what being old means. The pension and retirement policies that emerged during the first decades of the last century provided a new indicator of what it was to become an old person. Demographic change, state retirement policies and the emergence of Gerontology and Geriatrics as empirical disciplines studying old age produced a revolutionary shift in thinking about old age throughout most of the developed world rendering the physical determinacy of aging problematic. Being old is something that happens on an individual basis, the criteria for old age tend to be flexible, and transition may occur over a long period of time. People age differently within their personal life contexts according to individual characteristics and histories that bring to the older adulthood. [5]A research on Italian people observed the mortality rate curves, revealed that age-related risk of death plateaus after age 105. Death rates that increased exponentially up to about age 80, decelerated thereafter and interestingly reached or closely approached a plateau after age 105. [6] The maximum human lifespan is suggested to be 115 years. The oldest reliably recorded human was Jeanne Calment, she died in 1997 at 122. [7]
1.3. Definition of Aging
- Nowadays, the aging society is increasing and concerns about aging sequence have started to receive special attention. The primary target of an aging study is to increase the quality of elderly life and to prevent age related diseases. Especially, aged skin is more interesting because the skin is the most noticeable sign of the aging mechanism and demonstrative of human health, as it seems to prognosticate the systemic illness and prognosis. [8]WHO defines Healthy Aging “as the process of developing and maintaining the functional ability that enables well-being in older age.” [9]A study defined aging as a process of time-dependent persistent change in functionality and reproducibility (of all higher organisms) related to an increased probability of morbidity and mortality. [10]
1.4. Theories and Mechanism of Aging
- There are hundreds of concepts that tried to understand the aging mechanism and its discussion is beyond the scope of this study, but we will share some interesting data.Telomere theory:Telomeres are repetitive nucleotide sequences that cap and save the ends of chromosomes from degradation and abnormal recombination. They become shorter with each cell division and ultimately result in cellular senescence and limited numbers of cell division. [11]Advanced Glycation End Product Accumulation:Advanced glycation end (AGE) products are formed by a non-enzymatic process called glycation, during which proteins, lipids, or nucleic acids are covalently bound by sugar molecules such as glucose or fructose, resulting in the inhibition of normal function of target molecules. [12] This is quite different from normal glycosylation, which occurs at defined sites under mediation of enzymes and is necessary for target molecules to fulfill their functions. Glycation is involved in both intrinsic and extrinsic aging. Long-lived proteins in the dermal matrix and cytoskeleton are particularly susceptible to glycation, resulting in tissue stiffening and reduced elasticity. [13]
1.5. Aging and Down Syndrome
- While life expectancy of Down syndrome population has greatly increased over the last decades, mortality rates are still high and subjects are facing prematurely a phenomenon of atypical and accelerated aging. The presence of an immune impairment in Down syndrome subjects is suggested for a long time by the existence of an increased incidence of infections, the incomplete efficacy of vaccinations, and a high prevalence of autoimmunity.DS has long been considered as a progeroid syndrome, as individuals with trisomy 21 start to age prematurely and present precociously conditions usually characteristic of the geriatric population. The aging process in DS subjects not only seems to be premature/accelerated but also appears to be atypical and segmental, as it recapitulates many, but not all, of the classical signs and symptoms of aging. Clinically, DS subjects present signs of early aging affecting particularly the neurological system, with an extremely high prevalence of dementia of Alzheimer’s type. Aging affects also prematurely the dermatological, sensory, endocrine, and musculoskeletal systems, leading to high levels of mortality and multi-morbidity in this population. Increased incidence of infections, failure of vaccination, and the high prevalence of autoantibodies that can be observed in older people of the general population, all support the concept of DS as an accelerated aging syndrome. [14] The dysregulation of immune responses and the inflammatory state are likely to greatly contribute to age related diseases and especially to neurodegeneration which is highly prevalent in this specific population. [15]The immune dysregulation in DS is caused by multiple dysfunctional layers acting in both thymic epithelial cells and thymocytes. Telomere damage, increased senescent process induced by mitochondrial dysfunction and accumulation of Radicals all contribute to premature thymic involution with consequent alterations in thymocytes maturation kinetics and egression of exhausted lymphocytes. [16]
1.6. Skin Aging
- Skin aging, like aging of the other organs, is characterized by a progressive loss of functionality and regenerative potential. It is a multi-factorial process that affects nearly every aspect of its biology and function.The skin, our mechanically protective and flexible barrier organ, is the most visible organ, where all changes, including aging, are very noticeable. The aging process of skin can be described as intrinsic and extrinsic.Intrinsic or chronological skin aging is an inevitable chronological or time dependent process, due to genetic and hormonal factors. [17]The clinical signs corresponding to intrinsic skin aging are fine lines, xerosis (dry skin) and laxity. [18]The other type is the extrinsic skin aging predominantly manifested as coarse wrinkles, irregular pigmentation and lentigines (or age spots), and is restricted mostly to exposed sites, such as the face, neck and hands. The factors contributing to extrinsic skin aging involves sunlight, air pollution, cigarette smoke, nutritional factors, temperature, stress and lack of sleep. [19]Aging of the skin is characterized by slower regeneration and eventual erosion of skin structure and functionality. Skin aging is associated with a compromised protective role – specifically impaired wound healing and barrier function, increased inflammation, impaired water and thermal homeostasis for the organism, and susceptibility to various skin disorders including cancer. [20]Chronic exposure to UVR induces accelerated skin aging and results in photoaging (dermaheliosis) and increased photocarcinogensis. [21]Chronologic age and solar damage are the most important intrinsic and extrinsic factors associated with skin aging. Skin aging characteristics vary ethnically among races. No one is spared from skin wrinkling, sunspots, uneven skin color, vascular abnormality, benign tumor, and skin cancer; yet, these symptoms manifest differently according to one’s ethnic origin. Among the races, Caucasians manifest signs of photo-damage earlier than other races because of their relatively low melanin content. [22]Notably, long-term exposure to solar ultraviolet (UV) radiation is the primary factor of extrinsic skin aging and is referred to as photoaging.Changes in Skin Aging:Exposed directly to the air, skin is not only subject to intrinsic aging but also superimposed by extrinsic aging.These aging processes are accompanied by phenotypic changes in cutaneous cells as well as structural and functional changes in extracellular matrix components such as collagens, elastin, and proteoglycans that are required to provide tensile strength, elasticity, and hydration to the skin, respectively.Recent research has found that photo-aging makes the N-terminal and central parts of the tropo-elastin molecules more susceptible to enzymatic cleavage and, hence, accelerates the age-related degradation of elastin. [23]Pollution and cigarette smoke are well-known external factors that accelerate skin aging; however, the most significant extrinsic aging factor is still UV radiation (known as photo-aging), which causes DNA damage and oxidative damage, inducing cellular senescence. [24,25]Aging appears to affect all skin layers, and is manifested as alterations in terms of their structure and function. [26]Increasing evidence suggests that senescent cells accumulate in chronologically aged skin, as well as prematurely aged skin, and may contribute to age-related skin changes and pathologies. [27]Cutaneous immunosenescence:Aging of the body is characterized by a decline in the competence of the immune system. This progressive alteration, called immunosenescence, is associated with an increase in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, described as inflammaging. It occurs in conditions of multi-morbidity and potentially harmful environmental factors (stressful events, infections, etc.), and thus increases the risk of frailty in the elderly. Certain chronic infections or nutritional deficiencies contribute to the decline of the immune response in older people. In these subjects, immunosenescence is characterized by an alteration of the innate immune response, particularly the defense capacity, particularly against bacteria, by a reduction in the phagocytic activity of macrophages. It thus promotes an increase in the incidence of bacterial or viral infections in these people, but also an increase in certain autoimmune pathologies or cancers (Figure 2A). Adaptive immunity is also impaired in older people, with an immune response found to be less effective. [28]
2. Patients & Methods
2.1. Objectives
- General objective: to determine the various dermatological manifestations of premature aging in DS people during the period from 2019 to 2020.Specific objectives: ο To detect the most common dermatological condition among DS, e.g.: atopic dermatitis, lentigines, and rhytids, etc.ο To determine the prevalence of dermatological premature aging manifestations among people with DS.
2.2. Methods
- Study design: this was observational, descriptive, and cross sectional study.Study area: SCDS, located in al-Faiha square 8, east-Nile. 60 students with DS are accepted annually with different activities. After obtaining the consent, 24 students or their parents agreed to participate in the study and a control of 21 students of normal population were chosen randomly. Study duration: started from: 15th February -2019 to 15th September -2020.Study population: all DS students and attendants of the mentioned setting, including male and female.Inclusion criteria: all Sudanese students with DS.Sampling: the number of Genodermatosis among DS was rare (limited). No data of prevalence in Sudan. The only school in Sudan for DS is the one mentioned above and it was the area of this study. These school attendees were 60 students.Methods of data collections: Tools of data collection: Questionnaire that include patient's information from history to general and dermatological examination, interview guided. Hospital- based. For assessing the aging process clinically, I applied SCINEXA (modified) scoring system, the total SCINEXA scores range from 0 to 69, the intrinsic from 0 to 15, and extrinsic from 0 to 54. [29] The modified Fitzpatrick scaling system [30], for assessing the facial wrinkling, also the Busso hand volume severity scale [31], guided by photos taken by cell phone camera with 12 megapixel- dual. Data was assessed and analyzed using SPSS version 22.0. Both descriptive and analytical statistics were carried.
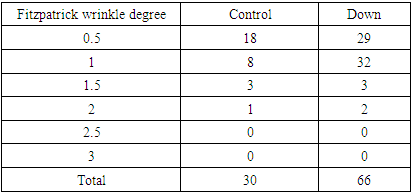
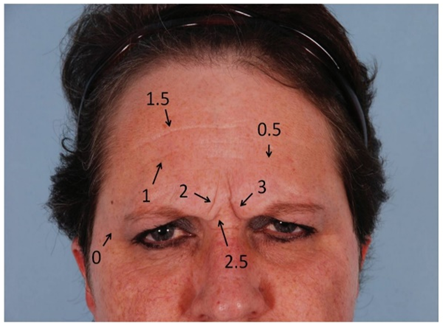 Modified Fitzpatrick wrinkle grading scale.Grade 0: absence of wrinkles;Grade 0.5: very shallow yet visible wrinkle;Grade 1: visible wrinkle with slight indentation;Grade 1.5: visible wrinkle and clear indentation less than 1mm in depth;Grade 2: clearly visible wrinkle 1 to 2 mm in depth;Grade 2.5: prominent and visible wrinkle more than 2 mm & up to 3 mm in depth;Grade 3: deep furrow appearing to measure more than 3 mm in depth.
Modified Fitzpatrick wrinkle grading scale.Grade 0: absence of wrinkles;Grade 0.5: very shallow yet visible wrinkle;Grade 1: visible wrinkle with slight indentation;Grade 1.5: visible wrinkle and clear indentation less than 1mm in depth;Grade 2: clearly visible wrinkle 1 to 2 mm in depth;Grade 2.5: prominent and visible wrinkle more than 2 mm & up to 3 mm in depth;Grade 3: deep furrow appearing to measure more than 3 mm in depth.3. Results
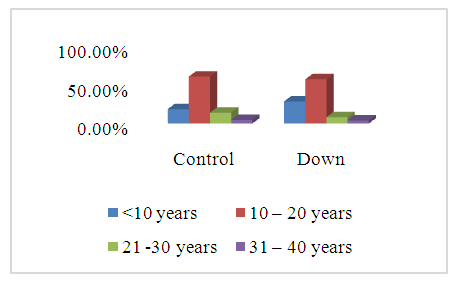
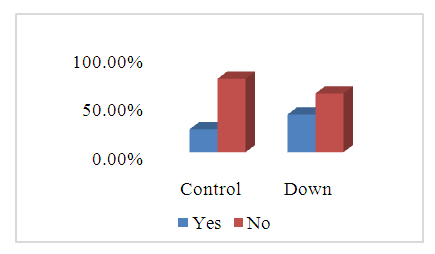
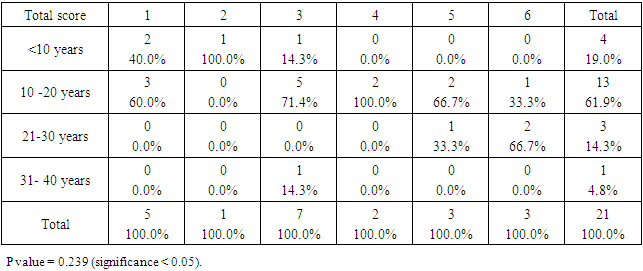
- The ages of the 45 participants were somewhat similar. The most frequent age group was between 10 and 20 years: control = (13) 61.9%, DS = (14) 58.3%, as showed in Figure 1.
3.1. Skin, Hair, and Nail Examination
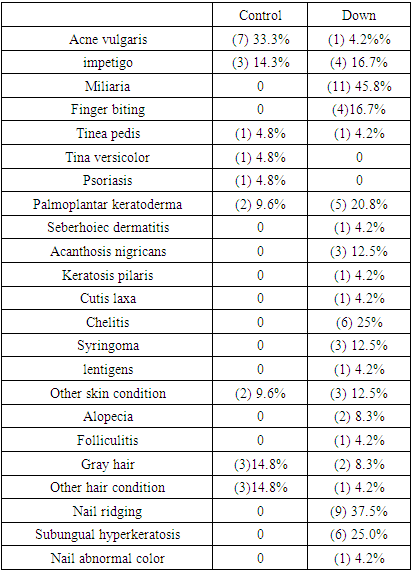
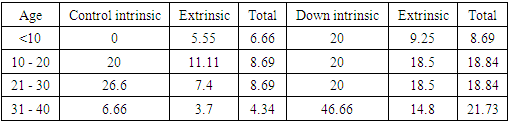
- Revealed sharp differences, particularly the Miliaria in DS (11)45.8%, followed by nail ridging (9)37.5%, Subungual hyperkeratosis (6)25%, and Chelitis (6)25%. The acne vulgaris was the most clinical finding in control group (7)33.3%, detailed in Table 1.
|
3.2. The SCINEXA Score
- Control group:
|
|
|
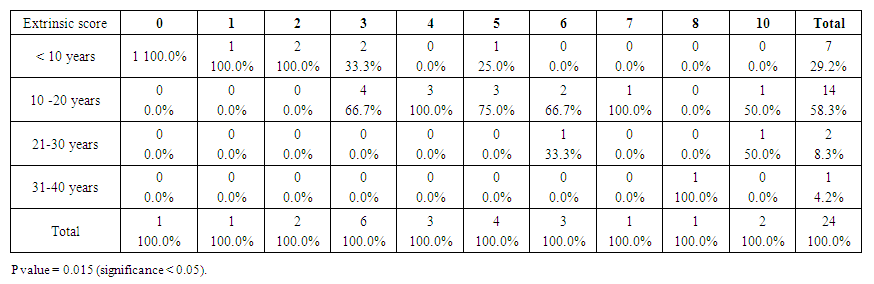 | Table 6. Showed the extrinsic score for the Down group. The top score was 10 (compare to 6 for control group). Premature aging skin manifestations in down syndrome –Trisomy 21, 2019-2020. (n = 24) |
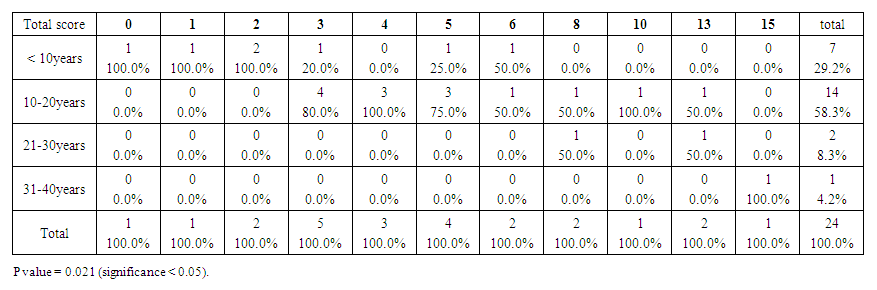 | Table 7. Showed the total SCINEXA score for Down group, the top score was 15 (compare to 6 for control group). Premature aging skin manifestations in down syndrome –Trisomy 21, 2019-2020. (n = 24) |
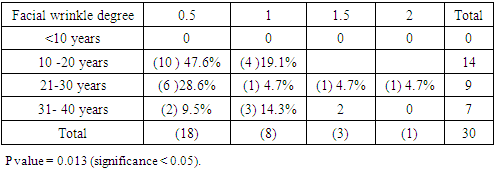
3.3. Facial Wrinkling
- Control group:
|
|
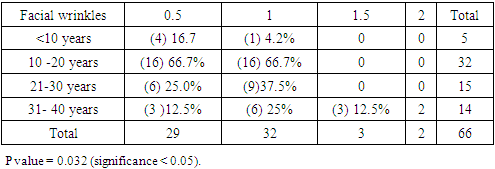
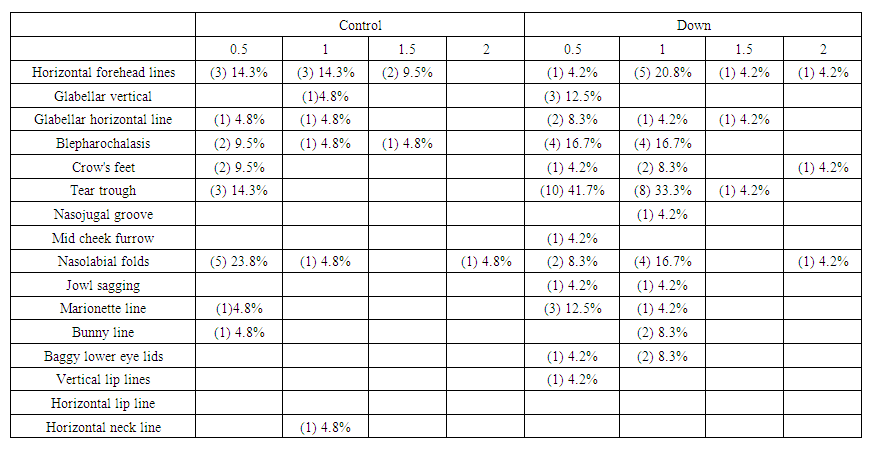 | Table 10. Showed the distribution of facial wrinkles among groups. Premature aging skin manifestations in Down syndrome -Trisomy 21, 2019-2020. (n = 45: DS = 24, Control = 21) |
4. Disscusion
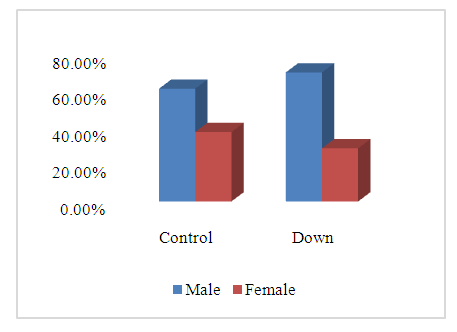
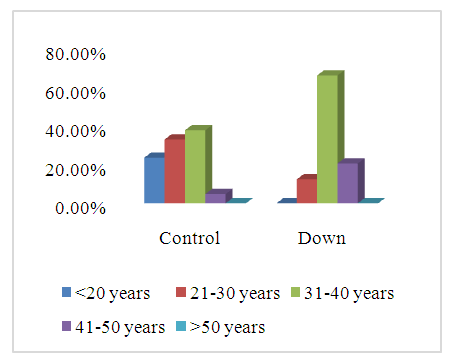
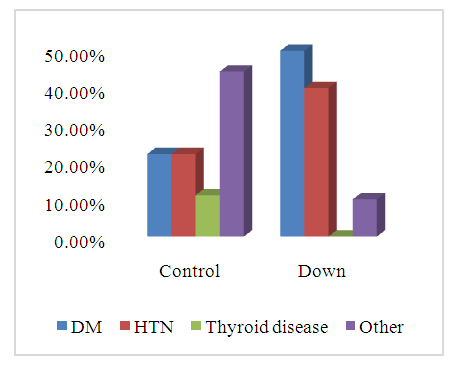
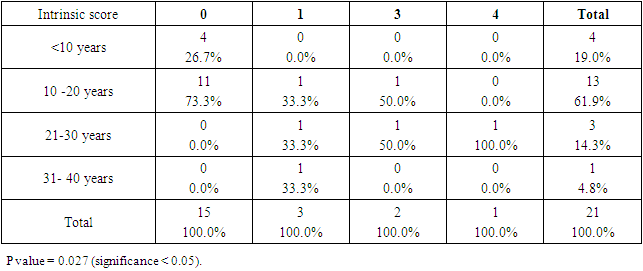
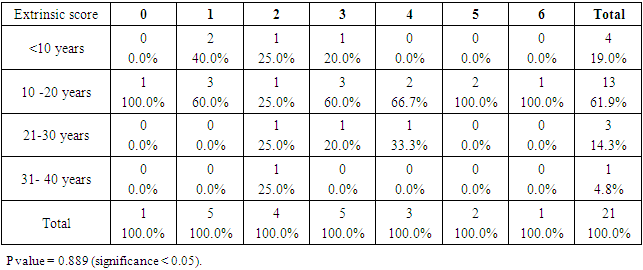
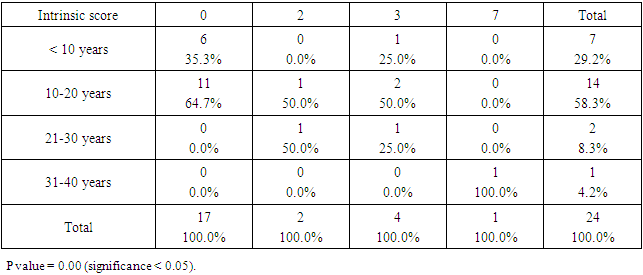
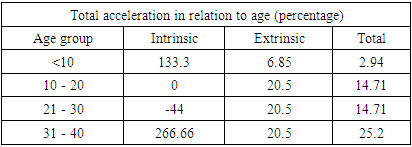
- SCDS was a peace of heaven, when I entered through the entrance, the door was opened by a handsome down adolescent with a welcoming smile. I handled the workup plan with the administrator and thereafter conducted the days of meeting with the parents and students of DS. Regarding the parents or guardians, although, it was a descent social connection, the majority didn’t confirm for the study and some refused. There is still a significant ignorance or nescience in concern to DS and generally for the intellectual disabilities may be due to illiteracy or other cultural causes.The ages were a bit younger for DS groups as a starting ages but older in relation to parallel grades due to delayed learning process and/or delayed entrance to school. None of the DS students continued to secondary educational level, as people of DS are mentally retarded. Males participants were dominant for both groups especially for DS group, may be for cultural restrictions. The majority of DS students were born after the third child 58.3%.Mothers ages between 31 – 40 years had the highest DS birth prevalences, in similar context with Kazemi et al 2016 [1]. Concerning the father risk for having a baby with DS, it was not on the spot in researches and studies done like the maternal factor for decades. But in the last years, paternal side had the attention and still needs more studies. In our study, paternal diabetes and hypertension raised a concern.Cardiac disease was the most associated morbidity in DS students in the study 45.8%.Fitzpatrick skin type 5 had the major part for both groups.The most significant P value was the intrinsic aging in DS group 0.00 followed by education level of the participants 0.006, this confirms accelerated true aging and mental intellectual defect for DS. Assessment of the aging process and its progression was done by using SCINEXA scoring system, Vierkötter. et al. 2009 [29]. Top scores were all achieved by DS students: intrinsic 7, extrinsic 10 and total 15, in comparison to 4, 6, and 6 respectively for control students. This explains the accelerated aging process in DS students. Now look at the Table 11:
|
|
|
5. Conclusions
- 1. There was a true accelerated aging process in DS group.2. The most common dermatological findings in DS were: Miliaria, nail ridging, Subungual hyper keratosis, Chelitis, PPK, followed by impetigo and Dermatophagia. 3. Older mother age at birth increases the chance for having a child with DS.4. Paternal diabetes and hypertension were remarkable in DS group, but less significant than maternal age at birth.5. The lowest P value was for the intrinsic aging in DS group 0.00, followed by educational level of the participants 0.006 (Significant).6. Busso hand severity scale did not show any significant difference or relationship between groups.
6. Recommendations
- 1. The society needs more social workup to help DS reach a comprehensive concept, in order to give people of DS a better way of living situations.2. Strongly recommends building well equalized schools with a well trained staff.3. Further studies are needed to investigate the paternal risk factors for having a baby with DS.4. Encouragement of the importance of sun protection use in our society.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The completion of this work could not have been possible without the participation and assistance of so many people whose names may not all be enumerated. Their contributions are sincerely appreciated and gratefully acknowledged. However, I would like to express my deep appreciation and indebtedness to my colleagues in dermatology, my friends and others for their support and kind sharing of their experiences.Above all, to the Great Almighty Allah, the source of knowledge and wisdom, for his countless love, I thank you.
References
| [1] | Mohammad Kazemi, Mansoor Salehi, Majid Kheirollahi. Down Syndrome: Current Status, Challenges and Future Perspectives. Int J Mol Cell Med.2016 Summer; 5(3): 125-133. |
| [2] | Vasilica PLAIASU. Down Syndrome – Genetics and Cardiogenetics MAEDICA – a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 12(3): 208-213. |
| [3] | Ngan V, Writer S, et al. Dermatological manifestations of Down syndrome.www.dermanetnz.org .2018. |
| [4] | Tiina Annus, Liam R. Wilson, Julio Acosta-Cabronero, Arturo Cardenas-Blanco, Young T. Hong, Tim D. Fryer, Jonathan P. Coles, David K. Menon, Shahid H. Zaman, Anthony J. Holland, Peter J. Nestor, The Down syndrome brain in the presence and absence of fibrillar β-amyloidosis, Neurobiology of Aging, Volume 53, 2017, Pages 11-19, ISSN 0197-4580, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.01.009. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0197458017300179). |
| [5] | Pathath AW. Theories of Aging. The International Journal of Indian Psychology. July 2017; 4(4): 15-22. |
| [6] | Barbi et al., The plateau of human mortality: Demography of longevity pioneers. Science. 29 June 2018; 360 (6396), 1459–1461. |
| [7] | Dong X, Milholland B, et al. "Evidence for a limit to human lifespan". Nature. October 2016; 538 (7624): 257–259. |
| [8] | Panich U, Sittithumcharee G, Rathviboon N, Jirawatnotai S. Ultraviolet radiation-induced skin aging: The role of DNA damage and oxidative stress in epidermal stem cell damage mediated skin aging. Stem Cells Int. 2016; 2016: 7370642. |
| [9] | Kyriazis M. Aging as "Time-Related Dysfunction": A Perspective. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Jul 27; 7: 371. doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.00371. PMID: 32850891; PMCID: PMC7397818. |
| [10] | Höhn, A.; Weber, D.; Jung, T.; Ott, C.; Hugo, M.; Kochlik, B.; Kehm, R.; König, J.; Grune, T.; Castro, J.P. Happily (n)ever after: Aging in the context of oxidative stress, proteostasis loss and cellular senescence. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 482–501. |
| [11] | Panich U, Sittithumcharee G, Rathviboon N, Jirawatnotai S. Ultraviolet radiation-induced skin aging: The role of DNA damage and oxidative stress in epidermal stem cell damage mediated skin aging. Stem Cells Int. 2016; 2016: 7370642. |
| [12] | Danby FW. Nutrition and aging skin: sugar and glycation. Clin Dermatol. 2010; 28(4): 409–411. |
| [13] | Farrar MD. Advanced glycation end products in skin ageing and photoageing: what are the implications for epidermal function? Exp Dermatol. 2016; 25(12): 947–948. |
| [14] | Gensous N, Bacalini MG, Franceschi C, Garagnani P: Down syndrome, accelerated aging and immunosenescence. Semin Immunopathol. 2020 Oct; 42(5): 635-645. doi: 10.1007/s00281-020-00804-1. Epub 2020 Jul 23. PMID: 32705346; PMCID: PMC7666319. |
| [15] | Ballard C, Mobley W, Hardy J, Williams G, Corbett A (2016) Dementia in Down’s syndrome. Lancet Neurol 15:622–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(16)00063-6. |
| [16] | Marcovecchio GE, Ferrua F, Fontana E, Beretta S, Genua M, Bortolomai l, Conti A, Montin D, Cascarano MT, Bergante S, D'Oria V, Giamberti A, Amodio D, Cancrini C, Carotti A, Di Micco R, Merelli I, Bosticardo M, Villa A. Premature Senescence and Increased Oxidative Stress in the Thymus of Down Syndrome Patients. Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 1;12: 669893. doi:10.3389/fmmu.2021.669893. PMID: 34140950; PMCID: PMC8204718. |
| [17] | Hensley, K.; Floyd, R.A. Reactive oxygen species and protein oxidation in aging: A look back, a look ahead. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2002, 397, 377–383. [CrossRef] [PubMed] |
| [18] | Krutmann, J.; Schikowski, T.; Morita, A.; Berneburg, M. Environmentally-Induced (Extrinsic) Skin Aging: Exposomal Factors and Underlying Mechanisms. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 1096–1103. [CrossRef] |
| [19] | Krutmann, J.; Bouloc, A.; Sore, G.; Bernard, B.A.; Passeron, T. The skin aging exposome. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 85, 152–161. [CrossRef] [PubMed] |
| [20] | Velarde, M.C., Demaria, M., 2016. Targeting senescent cells: possible implications for delaying skin aging: a mini-review. Gerontology 62, 513–518. |
| [21] | Panich, U., Sittithumcharee, G., Rathviboon, N., Jirawatnotai, S., 2016. Ultraviolet radiation-induced skin aging: the role of DNA damage and oxidative stress in epidermal stem cell damage mediated skin aging. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 7370642. |
| [22] | Vashi NA, de Castro Maymone MB, Kundu RV. Aging differences in ethnic skin. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2016; 9: 31–8. |
| [23] | Mora Huertas AC, Schmelzer CE, Hoehenwarter W, Heyroth F, Heinz A. Molecular-level insights into aging processes of skin elastin. Biochimie 2016; 128–129: 163–173. |
| [24] | Wang, A.S.; Dreesen, O. Biomarkers of cellular senescence and skin aging. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 247. [CrossRef] [PubMed] |
| [25] | Farage, M.A.; Miller, K.W.; Elsner, P.; Maibach, H.I. Intrinsic and extrinsic factors in skin ageing: A review. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2008, 30, 87–95. [CrossRef] [PubMed] |
| [26] | Blume-Peytavi, U.; Kottner, J.; Sterry, W.; Hodin, M.W.; Griffiths, T.W.; Watson, R.E.B.; Hay, R.J.; Griffiths, C.E.M. Age-Associated Skin Conditions and Diseases: Current Perspectives and Future Options. Gerontologist 2016, 56, S230–S242. [CrossRef] |
| [27] | Campisi, J. The biology of replicative senescence. Eur. J. Cancer 1997, 33, 703–709. [CrossRef] |
| [28] | Boismal F, Serror K, Dobos G, Zuelgaray E, Bensussan A, Michel L. Vieillissement cutané Physiopathologie et thérapies innovantes [Skin aging: Pathophysiology and innovative therapies]. Med Sci (Paris). 2020 Dec; 36(12): 1163-1172. French. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2020232. Epub 2020 Dec9 PMID: 33296633. |
| [29] | Vierkötter A, Ranft U, Krämer U, Sugiri D, Reimann V, et al. The SCINEXA: a novel, validated score to simultaneously asses and differentiate between intrinsic and extrinsic skin ageing. Journal of dermatological science.2009; 53(3): 207-211. |
| [30] | Shoshani D, Markovitz E, Monstrey SJ, Narins DJ., The Modified Fitzpatrick Wrinkle Scale: A Clinical Validated Measurement Tool for Nasolabial Wrinkle Severity Assessment. Dermatologic Surgery. 2008; 34 (1): S85-S91. |
| [31] | Busso M, et al. Dermatol Surg.2010; 36(1):790-797. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML