-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Dermatology and Venereology
2014; 3(4): 75-79
doi:10.5923/j.ajdv.20140304.03
Treatment of Vitiligo with Topical 5% Tincture Iodine and UVA Light
Khalifa E. Sharquie1, Hayder R. Al-Hamamy2, Adil A. Noaimi1, Mosa H. Al-Obeidy3
1Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, University of Baghdad, Iraqi and Arab Board for Dermatology and Venereology, Baghdad Teaching Hospital, Medical City, Baghdad, Iraq
2Chairman of Scientific Council of Dermatology & Venereology-Iraqi Board for Medical Specializations, Baghdad, Iraq
3Department of Dermatology & Venereology, Baghdad Teaching Hospital, Baghdad, Iraq
Correspondence to: Khalifa E. Sharquie, Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, University of Baghdad, Iraqi and Arab Board for Dermatology and Venereology, Baghdad Teaching Hospital, Medical City, Baghdad, Iraq.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Background: There are many therapies for vitiligo like PUVA Sole, steroid, Narrow band UVB, 15 % lactic acid and 5%tincture iodine. Objective: To re-evaluate topical 5% tincture iodine action in vitiligo alone and in combination with UVA exposure in comparison with UVA exposure alone and tap water as placebo controlled in treatment of localized vitiligo. Patients and Methods: This single blind placebo controlled therapeutic trial where 20 patients with 80 patches of localized vitiligo were included. Patches were divided into 4 groups according to type of treatment: Group I: 20 patches treated with topical 5% tincture iodine solution alone. Group II: 20 patches treated with UVA exposure alone. Group III: 20 patches treated with topical 5% tincture iodine solution with UVA exposure. Group IV: 20 patches treated with application of tap water as a placebo control. All treatments were given on a twice weekly base. Patients were evaluated according to the grade of response to treatment. Results: After 6 months of treatment with 2 months follow up for each patient, the results were as follow: Group I: 85% (17 patches) patients showed re-pigmentation more than 75%of size of patches. Group II: 15% (3 patches) patients showed re-pigmentation more than 75% of size of patches. Group III: 95% (19 patches) patients showed re-pigmentation more than 75% of size of patches. Group IV: No response. Conclusions: Combination therapy of topical 5% tinctur iodine solution with UVA exposure was an effective mode of therapy for vitiligo and better than topical 5% tinctur iodine alone but did not reach the significant level.
Keywords: Topical 5% tinctur iodine, Vitiligo, UVA
Cite this paper: Khalifa E. Sharquie, Hayder R. Al-Hamamy, Adil A. Noaimi, Mosa H. Al-Obeidy, Treatment of Vitiligo with Topical 5% Tincture Iodine and UVA Light, American Journal of Dermatology and Venereology, Vol. 3 No. 4, 2014, pp. 75-79. doi: 10.5923/j.ajdv.20140304.03.
1. Introduction
- Vitiligo is a common pigmentry disfiguring disease but its etiopathogensis still has not well elucidated [1-4].There are many theories to explain the etiology but the most favorable one is the autoimmune reaction which is supported by the following observations: the disease might associated with other autoimmune diseases, the presence of circulating auto-antibodies [2], and the histopathological findings which are the lymphocytic infiltration of the epidermis forming Pauteriar's micro-abscess like with increase of CD8 in the early stage and CD4 in the late stage of the disease [1, 3, 4].The therapies of the disease could be successful especially in patient with localized type of vitiligo. Still there are two groups of patients according to their response to therapy: the 1st group responds quickly to any type of treatment whatever given drugs so, called rapid responder while the 2nd group, so called the non responder when the patients don't respond or refractory to any mode of therapy [4]. These observations could not be explained well but most probably related to the genetic elements that determine the response to treatments [1, 3-5]. There are many standard therapies for vitiligo like PUVA, PUVA Sole, steroid, Narrow Band UVB and 15% lactic acid, antioxidant (vitamins C and E). The response of therapies depends on severity of disease, location of the illness and time factor. Topical 5% tincture iodine has been used successfully for last 30 years especially in treatment of localized type of vitiligo [1-6]. Therefore, the present study was arranged to re-evaluate the effectiveness of topical 5% tincture iodine alone and in combination with UVA exposure in comparison with UVA exposure alone and tap water which was used as a placebo controlled group in treatment of localized vitiligo through this well established work.
2. Patients and Methods
- This single blind placebo controlled therapeutic trial was performed in the Department of Dermatology and Venerology-Baghdad Teaching Hospital, Baghdad, Iraq from November 2002 - June 2004. Twenty patients had localized vitiligo were included in this study. The total number was 80 patches with at least 4 patches per patient.Patients were fully interviewed regarding different medical aspects including: age, gender, duration, type, site, and examined under clear light. Wood's light examination was used when needed to confirm the diagnosis.The size of patches ranged from 0.20 cm2 – 10 cm2. Patients who had been recently treated in the last 3 months by other therapies, patients with systemic diseases like diabetes mellitus, or any immune compromised conditions and other severe illnesses were excluded. From each patient, formal consent was taken before the start the therapy, after full explanation about the goal and nature of the present study, the nature of the disease, course its complications, the method of treatment, duration, cost, side effects of therapy and duration of follow up, prognosis and the need for pre and post treatment photographs. Also, the ethical approval was carried out by the Scientific Council of Dermatology & Venereology-Iraqi Board for Medical Specializations.All patients were photographed by a digital camera as a baseline and then every two months, in the same place with fixed illumination and distance by using a digital camera (Sony: Cyber shoot with resolution 7 mega pixels). Patches were divided into 4 groups according to the mode of treatment in which each patch had the chance to be in any group:1. Group I: -Those patches treated with topical 5% tincture iodine alone twice weekly, (20 patches).2. Group II: -Those patches treated with UVA exposure twice weekly, (20 patches).3. Group III: -Those patches treated with topical 5% tincture iodine and UVA exposure twice weekly, (20 patches).4. Group IV: -Those patches treated by the application of tap water twice weekly, (20 patches).Procedures of therapy: Group I: - Topical tincture iodine 5% contains: 2.5% W/V of iodine and 2.5% W/V of potassium iodide according to the following formula:Iodine…………………..…..
 25 gmPotassium iodide……….
25 gmPotassium iodide………. 25 gmPurified water…………..
25 gmPurified water………….. 250 mlAlcohol 90% to…………
250 mlAlcohol 90% to………… 1000 mlIt was prepared by dissolving the potassium iodide and the iodine in the purified water and adding sufficient alcohol (90%) to produce 1000 ml, then used twice weekly over night in treatment of localized vitiligo [4].Group II: UVA machine for 10 minutes was used twice weekly in a way to be localized taking in consideration that no other patches could be exposed to UVA.The UV machine (AIRAM FINLAND) each 1 cm2 of patches exposed to 5 J.Group III: Topical tincture iodine 5% plus UVA was applied topically by the researcher using cotton tipped wood - stick to the affected patches, then after 30 minutes treatment, followed by exposure to UVA machine for 10 minutes twice weekly in a way to be localized, taking in consideration that no other patches could be exposed to UVA. Group IV: by the application of tap water twice weekly as a placebo controlled group.Follow up and assessment of response to treatment:The response to treatment was followed and assessed for 6 months, to be seen every 2 months of treatment and to record any local and systemic side effects. The outline and size of each lesion was drawn on a transperant paper and the surface area of each patch was calculated using graphic paper at every two months interval. The reduction in size of the patch was recorded on the same transperant paper and the percentage of reduction in surface area was caluculated.The patients were followed up for 2 months after the last session to record any relapse after stopping therapyThe responses to therapy were evaluated according to the following grading: [7]
1000 mlIt was prepared by dissolving the potassium iodide and the iodine in the purified water and adding sufficient alcohol (90%) to produce 1000 ml, then used twice weekly over night in treatment of localized vitiligo [4].Group II: UVA machine for 10 minutes was used twice weekly in a way to be localized taking in consideration that no other patches could be exposed to UVA.The UV machine (AIRAM FINLAND) each 1 cm2 of patches exposed to 5 J.Group III: Topical tincture iodine 5% plus UVA was applied topically by the researcher using cotton tipped wood - stick to the affected patches, then after 30 minutes treatment, followed by exposure to UVA machine for 10 minutes twice weekly in a way to be localized, taking in consideration that no other patches could be exposed to UVA. Group IV: by the application of tap water twice weekly as a placebo controlled group.Follow up and assessment of response to treatment:The response to treatment was followed and assessed for 6 months, to be seen every 2 months of treatment and to record any local and systemic side effects. The outline and size of each lesion was drawn on a transperant paper and the surface area of each patch was calculated using graphic paper at every two months interval. The reduction in size of the patch was recorded on the same transperant paper and the percentage of reduction in surface area was caluculated.The patients were followed up for 2 months after the last session to record any relapse after stopping therapyThe responses to therapy were evaluated according to the following grading: [7]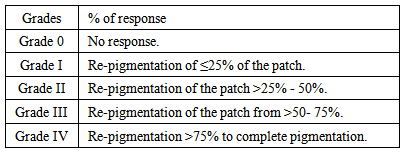 All data coded and computerized using SPSS 7.5 (statistic package for social science). All data arranged and tabulated in number, percentage, mean and standard division. Response to treatment was measured by using paired and a paired t-test, chi- square test and analysis of variance (ANOVA) test (p<0.05) was considered as level of significance.
All data coded and computerized using SPSS 7.5 (statistic package for social science). All data arranged and tabulated in number, percentage, mean and standard division. Response to treatment was measured by using paired and a paired t-test, chi- square test and analysis of variance (ANOVA) test (p<0.05) was considered as level of significance.3. Results
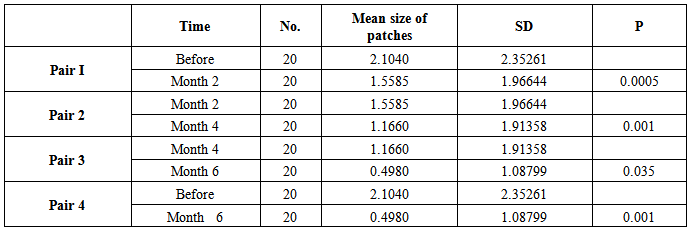
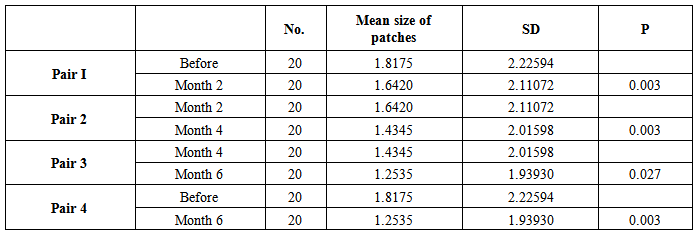
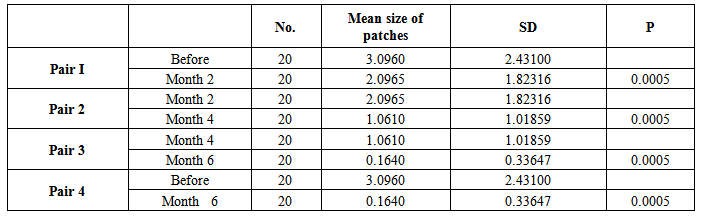
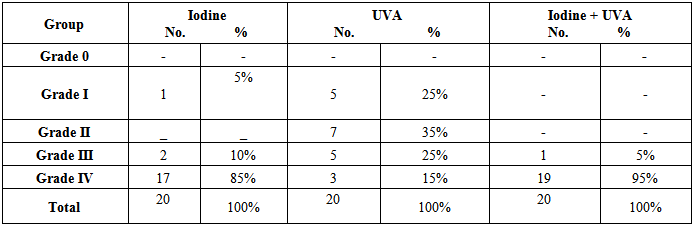
- Twenty patients with vitiligo enrolled in this study, 12 males and 8 females, their ages ranged from 3-43 years with a mean ± SD of 15.43± 9.44 years. The therapeutic results within 2 months interval follow up were as follow:-Group I: Treatment by topical 5% tincture iodineThe mean size of 20 patches before treatment was 2.10 ± 2.35 cm2, after 2 months became 1.55 ± 1.96 cm2, (p 0.0005),while after 4 months 1.16 ± 1.91 cm2 (p 0.0005). The mean size reached to 0.49 ± 1.08 cm2 after 6 months (p 0.001). According to the grading system of responses after 6 months the following grades were observed: Grade I (15%) 1 patch, Grade III (10%) 2 patches and Grade IV (85%) 17 patches (Table-1).
|
|
|
|
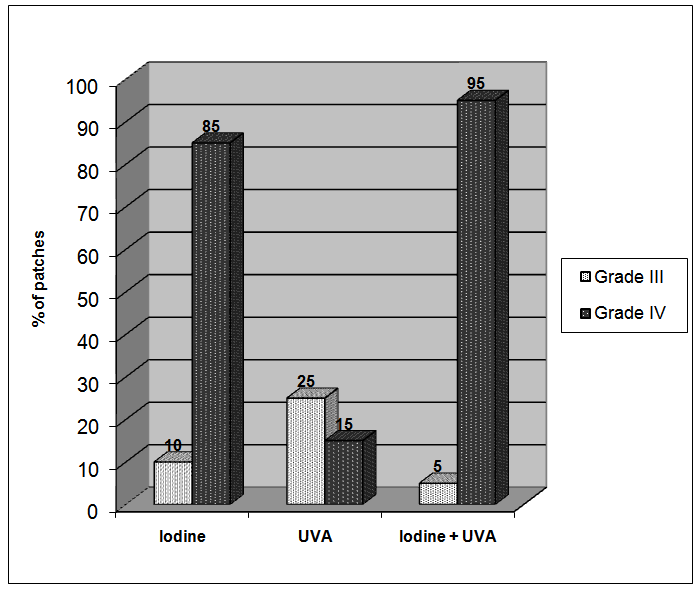 | Figure 1. Patients response to different modes of therapy after 6 months of treatment |
- No side effects were recorded after therapy apart from transient slight irritation that was noticed following iodine tincture application in some patients. Two months follow up after cessation of therapy showed no relapse of lesions in any group.
4. Discussion
- Vitiligo is a common dermatological disease encountered in daily practice and many modalities of therapy have been used for its treatment like phototherapy,photo-chemotherapy, immune modulators, steroids, Lactic acid 15%, ticture iodin 5%, calcipotriol, systemic antioxident, surgical procedures and cosmetics. Each has its advantages and limitations [1-8]. There are a number of patients who have localized vitiligo, where systemic therapy is not advised. In these cases often topical therapy might be enough. Therefore a number of topical therapies were evaluated [3-5]. Topical 5% tincture iodine has proved its effectiveness in the treatment of vitiligo, and is as effective as psoralen lotion [4].The aim of the present work is to re-evaluate its action in vitiligo alone and in combination with UVA therapy applying more extensively established study. The result was interesting as topical 5% tincture iodine was effective with marked response in 85% of patches. While combination of topical 5% tincture iodine with UVA gave 95% marked response. So, topical 5% tincture iodine and UVA was better than iodine alone, although the difference between them did not reach statistically significant level. A similar study using 15% lactic acid with UVA was more effective than lactic acid alone [3-5].The mechanism of action topical 5% tincture iodine, 15% lactic acid with or without UVA light is difficult to explain but we can speculate that these therapeutic agents work through the so called "irritant theory". [3-5] These therapies probably induce mild inflammation which stimulate keratinocytes to release inflammatory mediators, comparable to psoralen and UVA light, these mediators like basic fibroblast growth factor (BFGF) from keratinocytes which will stimulate melanocytes to hypertrophy and proliferate and by releasing other mediators from keratinocytes like interlukine-1(IL-1) which facilitates binding of α–MSH to the cells. Leukotrine C4 and D4 leads to melanocyte proliferation in vitro, leukotrine C4, transforming growth factor and α-(TGF-α) which cause melanocyte migration and lastly endotheline-1 causes melanocyte migration [9-12], so induce re-pigmentation. Topical calcipotriol has been used in treatment of vitiligo and also might work through stimulation of keratinocytes to release many mediators. Accordingly, we can imagine that any topical irritant agent that is used in treatment of vitiligo patch might induce re-pigmentation working through the so called "Irritant Theory".In conclusion, 5% iodine tincture with or without UVA light is recommended as an effective topical mode of therapy in treatment of vitiligo.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML