-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Dermatology and Venereology
2013; 2(3): 23-26
doi:10.5923/j.ajdv.20130203.02
Topical Adapalene 0.1% Gel versus Topical Combination of (Tretinoin 0.025% and Erythromycin 4%) Gel in Treatment of AcneVulgaris(A Split Face Comparative Study)
Hayder R. Al-Hamamy1, Adil A. Noaimi1, Husam Ali Salman1, Nawar A. Abdul Jabbar2
1Department of Dermatology & Venereology, College of Medicine- University of Baghdad, Baghdad, Iraq
2Department of Dermatology & Venereology-Baghdad Teaching Hospital, Baghdad, Iraq
Correspondence to: Husam Ali Salman, Department of Dermatology & Venereology, College of Medicine- University of Baghdad, Baghdad, Iraq.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This study was conducted to compare the efficacy of topical adapalene 0.1% gel versus a combined formula of topical tretinoin 0.025% and erythromycin 4% gel in the treatment of mild to moderate inflammatory acne vulgaris. Thirty six patients with inflammatory acne vulgaris (papules and pustules) were enrolled in the study. A split face method was used inwhich each patient was instructed to use a combined gel formula (tretinoin 0.025% and erythromycin 4%) on the right side of the face and adapalene 0.1% gel on the left side. Each patient was instructed to use the same amount of both gels at night. The duration of therapy was 6 weeks.Only 30 patients completed the study, 23 females and 7males, their ages ranged from 14-33 (20.66±4.79) years. After 3 weeks of treatment the mean percent of reduction of lesions of the right and left sides was 67.86% and 50.41% respectively. The difference was statistically significant p-value <0.0001. After 6 weeks it reduced to 91.69% and 87.36% respectively. The difference was not significant p-value = 0.065. Few patients had mild erythema and dryness at both sides.In conclusion, both formulae have comparable efficacy.
Keywords: Acne, Adapalene, Tretinoin, Topical Erythromycin
Cite this paper: Hayder R. Al-Hamamy, Adil A. Noaimi, Husam Ali Salman, Nawar A. Abdul Jabbar, Topical Adapalene 0.1% Gel versus Topical Combination of (Tretinoin 0.025% and Erythromycin 4%) Gel in Treatment of AcneVulgaris(A Split Face Comparative Study), American Journal of Dermatology and Venereology, Vol. 2 No. 3, 2013, pp. 23-26. doi: 10.5923/j.ajdv.20130203.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Acne vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory disease of pilosebaceous units. Propionobacterium acnes proliferate in sebum and the follicular epithelium becomes altered and form plugs called comedons[1].There are many therapies for acne. Adapalene, a naphthoic acid derivative with retinoid-like activity, it reduces the number of non inflammatory and inflammatory lesions in patients with mild to moderate acne[2]. Erythromycin acts both as antibacterial agent suppressing Propionibacterium acnes and as anti-inflammatory agents[3].Topical tretinoin acts against comedones andmicrocomedones and have direct anti - inflammatory effects[4].Many studies showed that adapalene gel 0.1% is as effective as 0.025% tretinoin gel[5, 6] and other study revealed that it has equivalent efficacy and was significantly better tolerated than tretinoin cream 0.05% in patients with mild to moderate acne vulgaris[7]. Also tretinoin enhances the penetration of topical antibiotics with synergistic effect[1]. For the above conflicting results and to verify if a combined tretinoin - antibiotic has better effect than monotherapy; this study was conducted.
2. Patients and Methods
- This was a single – blind comparative split face therapeutic study, conducted at the Department of Dermatology - Baghdad Teaching Hospital during October 2009 to October 2010. A total of 36 patients with mild to moderate acne vulgaris were enrolled in the study. Their ages range from 14-33 years with a mean SD, 20.58 4.81. Twenty five (69.4%) patients were females and eleven (30.6%) patients were males.All patients were without any systemic and / or topical treatment for at least 2 months before starting the study.Full history was taken from each patient regarding age, sex, duration of the disease and previous treatment.Physical examination was done to evaluate the severity of acne.Scoring the severity of acne was done according to the following method.[1].1-Mild acne in which the count of pustules is less than 20 and the count of papules is less than 10. 2-Moderate acne in which the count of pustules is ranging from (20 – 40) and the count of papules is ranging from (10-30). 3-Severe acne, in which the count of pustules is more than 40 pustules and the count of papules, is more than 30.Patients excluded from the study were those with severe acne, nodulocystic acne, patients with systemic diseases, pregnant and lactating women.A split face method for application of treatment was used in which each patient was instructed to use a combined gel formula of tretinoin 0.025% and erythromycin 4% on the right side of the face and adapalene 0.1% gel on the left side.The drugs were bought from the market. The trade name of adapalene is sure cure made by Jamjoom pharmaceuticals, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. The trade name of the combined gel (tertinoin and erythromycin) is retinomycin made by Mediphar Laboratories Dbaya – Lebanon.A formal consent was obtained from each patient. Ethical approval was granted from the ethical committee.Each patient was instructed to use the same amount of both gels (finger tip method), ½ hour in the 1st night then wash and increase the time by ½ hour in the successive nights till reach 8 hours; thereafter to keep the applications till morning.The duration of therapy was 6 weeks and follow up for another 6weeks.The clinical evaluation was done every 3 weeks by 2 dermatologists; the assessment was carried out by counting the inflammatory lesions (papules and pustules) and watching any local side effects.The satisfaction of the patients to the treatment is classified into:1- Full satisfaction.2- Partial satisfaction.3 - No satisfaction.Statistical analysis was done by using EPI version 6. Both descriptive and analytic data used. P-value equal or less than 0.05 was considered significant.Photographs were taken by Sony digital camera (dsc-w150), 8.1 mega pixels, with a fixed illumination and at the same place.
3. Results
- Thirty patients completed the study, 23 females and 7 males, their ages ranged from 14-33 with a mean ± SD, 20.66±4.79 years.
3.1. Right Side
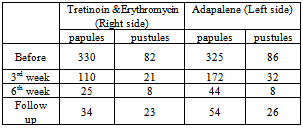
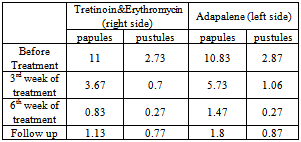
- The total number of papules before the treatment was 330. At 3rd and 6th weeks of treatment it was reduced to 110 and 25 respectively (Table 1). This reduction was statistically significant, F statistic = 141.7, P- value < 0.0001. The mean ± SD number of papules per patient before the treatment was 11± 4.59. At 3rd and 6th weeks of treatment it was reduced to 3.67 and 0.83 respectively (Table 2).
|
|
3.2. Left Side
- The total number of papules before the treatment was 325. At 3rd and 6th weeks of treatment it was reduced to 172 and 44 respectively (Table 1). This reduction was statistically significant, F statistic = 142.8, P value < 0.0001.The mean ± SD number of papules per patient before the treatment was 10.83±17. At 3rd and 6th weeks of treatment it was reduced to 5.73 and 1.47 respectively (Table 2).The total number of pustules before treatment was 86. At 3rd and 6th weeks of treatment it was reduced to 32 and 8 respectively (Table 1). This reduction was statistically significant, F statistic = 11.83, P value < 0.0001. The mean ± SD number of pustules per patient before the treatment was 2.87 ± 1.8. It was reduced to 1.06 at 3rd and 0.27 at 6th weeks of treatment (Table 2).After 3 weeks of treatment, the mean percent reduction of inflammatory lesions (papules and pustules) at the right side was 67.86 %. It was higher than the mean percent of reduction at the left side which was 50.41%. This difference was statistically significant, F statistic = 35.24, P value < 0.0001 After 6th week of treatment, the mean percent reduction at the right side was 91.69 % (Figure 1), while at the left side it was 87.36% (Figure 2). This difference was not significant. F statistic = 3.57, P value = 0.065.
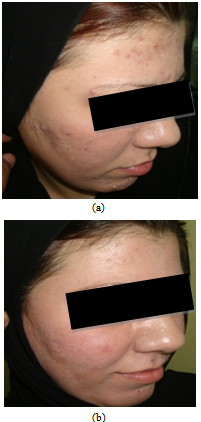 | Figure 1. (a) A twenty two years old female with three years history of acne vulgaris treated with tretinoin and erythromycin gel (right side). (b) After 6 weeks of treatment |
3.3. Side Effects
- Mild erythema and dryness were observed in 25 (83.33%) patients in both sides, which were disappeared in few days and did not necessitate cessation of therapy.
3.4. Patients’ Satisfaction
- At the adapalene side 86% of patients were fully satisfied and 90% were fully satisfied at the combined formula side.
3.5. Follow up
- Six weeks after stopping treatment, the recurrence rates for the adapalene and the combined formula were 5% and 4.5% respectively.
4. Discussion
- Acne is a major problem in young people ,which has both physical and psychological impacts on patients life .There are many therapies for acne ranging from topical agents such as retinoic acid, benzoyl peroxide, clindamycin solution, erythromycin and azelaic acid. Systemic agents such as antibiotics (doxycyclin, erythromycin), retinoid and hormonal agents are also used. Both types of treatment are not free of side effects. Combination regimens that include an antibiotic and a retinoid to reduce follicular plugging are the mainstay of topical treatment[1].
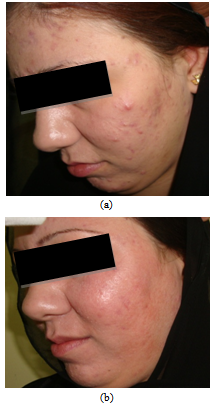 | Figure 2. (a) The same patient treated with adapalene gel (left side). (b) After 6 weeks of treatment |
5. Conclusions
- 1- Both topical adapalene 0.1% and a topical combination of (tretinoin 0.025% and erythromycin 4%) have comparable efficacy in treatment of mild to moderate inflammatory acne vulgaris.2- If we consider that the combined formula has synergistic effect; then we can conclude that adapalene 0.1% has better efficacy than tretinoin 0.025 and erythromycin 4% alone. 3- A topical combination of (tretinoin 0.025% and erythromycin 4%) acts faster than adapalene 0.1%.4- We recommend doing a similar study with a longer duration of treatment and following up in moderate to severe acne to show which has more efficacy and sustained effect.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML