| [1] | A. B. Djurišić, X. Chen, Y. H. Leung, and A. Man Ching Ng, “ZnO nanostructures: growth, properties and applications,” J. Mater. Chem., vol. 22, no. 14, p. 6526, 2012, doi: 10.1039/c2jm15548f. |
| [2] | V. Mariyappillaiet al., “Zr-modified ZnO nanoparticles: Optimized photocatalytic degradation and antibacterial efficiency for pollution control,” Ceram. Int., p. S0272884225010983, Feb. 2025, doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2025.02.402. |
| [3] | J. Rosowska, J. Kaszewski, B. Witkowski, Ł. Wachnicki, I. Kuryliszyn-Kudelska, and M. Godlewski, “The effect of iron content on properties of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by microwave hydrothermal method,” Opt. Mater., vol. 109, p. 110089, Nov. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2020.110089. |
| [4] | M. Carofiglio, S. Barui, V. Cauda, and M. Laurenti, “Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Potential Use in Nanomedicine,” Appl. Sci., vol. 10, no. 15, p. 5194, Jul. 2020, doi: 10.3390/app10155194. |
| [5] | L. Guerrini, R. A. Alvarez-Puebla, and N. Pazos-Perez, “Surface Modifications of Nanoparticles for Stability in Biological Fluids,” Materials, vol. 11, no. 7, p. 1154, Jul. 2018, doi: 10.3390/ma11071154. |
| [6] | R. Javed, M. Usman, S. Tabassum, and M. Zia, “Effect of capping agents: Structural, optical and biological properties of ZnO nanoparticles,” Appl. Surf. Sci., vol. 386, pp. 319–326, Nov. 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.06.042. |
| [7] | Z. Yang et al., “Glutathione: a naturally occurring tripeptide for functional metal nanomaterials,” Chem. Sci., vol. 16, no. 16, pp. 6542–6572, 2025, doi: 10.1039/D4SC08599J. |
| [8] | A. M. Alkilany and C. J. Murphy, “Toxicity and cellular uptake of gold nanoparticles: what we have learned so far?,” J. Nanoparticle Res., vol. 12, no. 7, pp. 2313–2333, Sep. 2010, doi: 10.1007/s11051-010-9911-8. |
| [9] | C. Fernández-Ponce et al., “Superficial Characteristics and Functionalization Effectiveness of Non-Toxic Glutathione-Capped Magnetic, Fluorescent, Metallic and Hybrid Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications,” Metals, vol. 11, no. 3, p. 383, Feb. 2021, doi: 10.3390/met11030383. |
| [10] | S. Kumar et al., “Effect of glutathione capping on the antibacterial activity of tin doped ZnO nanoparticles,” Phys. Scr., vol. 96, no. 12, p. 125807, Aug. 2021, doi: 10.1088/1402-4896/ac1eb3. |
| [11] | Kavita, K. Singh, S. Kumar, and H. S. Bhatti, “Glutathione-assisted synthesis of star-shaped zinc oxide nanostructures and their photoluminescence behavior,” J. Lumin., vol. 149, pp. 112–117, May 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2014.01.001. |
| [12] | M. Foyshal, M. F. Kabir, A. Islam, J. Ferdousy, M. R. Islam, and M. M. Rahman, “Enhanced Biocompatibility and Multifunctional Properties of Iron-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Applications,” Oct. 18, 2023. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3426239/v1. |
| [13] | A. C. Pierre, Introduction to Sol-Gel Processing. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2020. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-38144-8. |
| [14] | A. Vishwakarma, “Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle by Sol-Gel Method and Study its Characterization,” Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol., vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 1625–1627, Apr. 2020, doi: 10.22214/ijraset.2020.4265. |
| [15] | C.-Y. Tsay and T.-T. Huang, “Improvement of physical properties of IGZO thin films prepared by excimer laser annealing of sol–gel derived precursor films,” Mater. Chem. Phys., vol. 140, no. 1, pp. 365–372, Jun. 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2013.03.051. |
| [16] | Department of Physical and Biological Sciences, Murang’a University of Technology, PO BOX 75, Murang’a 10200, Kenya and J. Jepngetich, “Effects of Ag Doping Concentrations on Structural and Optical Properties of Citrus Reticulata Capped ZnO Nanoparticles,” J. Nanosci. Res. Rep., pp. 1–7, Apr. 2025, doi: 10.47363/JNSRR/2025(7)176. |
| [17] | M. Alagiri, C. Muthamizhchelvan, and S. Ponnusamy, “Structural and magnetic properties of iron, cobalt and nickel nanoparticles,” Synth. Met., vol. 161, no. 15–16, pp. 1776–1780, Aug. 2011, doi: 10.1016/j.synthmet.2011.05.030. |
| [18] | P. K. Sharma, R. K. Dutta, A. C. Pandey, S. Layek, and H. C. Verma, “Effect of iron doping concentration on magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater., vol. 321, no. 17, pp. 2587–2591, Sep. 2009, doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2009.03.043. |
| [19] | E. Moaseriet al., “Reversible Self-Assembly of Glutathione-Coated Gold Nanoparticle Clusters via pH-Tunable Interactions,” Langmuir, vol. 33, no. 43, pp. 12244–12253, Oct. 2017, doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b02446. |
| [20] | R. Iyer et al., “Glutathione-responsive biodegradable polyurethane nanoparticles for lung cancer treatment,” J. Controlled Release, vol. 321, pp. 363–371, May 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.02.021. |
| [21] | V. Mote, Y. Purushotham, and B. Dole, “Williamson-Hall analysis in estimation of lattice strain in nanometer-sized ZnO particles,” J. Theor. Appl. Phys., vol. 6, no. 1, p. 6, Dec. 2012, doi: 10.1186/2251-7235-6-6. |
| [22] | A. Singh et al., “Bandgap Modulation in ZnO Through Doping By Sol-Gel Method,” presented at the SOLID STATE PHYSICS, PROCEEDINGS OF THE 55TH DAE SOLID STATE PHYSICS SYMPOSIUM 2010, Manipal, (India), 2011, pp. 595–596. doi: 10.1063/1.3605998. |
| [23] | R. Jeyachitra, V. Senthilnathan, and T. S. Senthil, “Studies on electrical behavior of Fe doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared via co-precipitation approach for photo-catalytic application,” J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron., vol. 29, no. 2, pp. 1189–1197, Jan. 2018, doi: 10.1007/s10854-017-8021-0. |
| [24] | P. Jamdagni, P. Khatri, and J. S. Rana, “Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using flower extract of Nyctanthes arbor-tristis and their antifungal activity,” J. King Saud Univ. - Sci., vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 168–175, Apr. 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2016.10.002. |
| [25] | F. Sarf and H. Kızıl, “Defect Emission Energy and Particle Size Effects in Fe:ZnO Nanospheres Used in Li-Ion Batteries as Anode,” J. Electron. Mater., vol. 50, no. 11, pp. 6475–6481, Nov. 2021, doi: 10.1007/s11664-021-09191-1. |
| [26] | D. Verma, A. K. Kole, and P. Kumbhakar, “Red shift of the band-edge photoluminescence emission and effects of annealing and capping agent on structural and optical properties of ZnO nanoparticles,” J. Alloys Compd., vol. 625, pp. 122–130, Mar. 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.11.102. |
| [27] | Ma. D. L. Ruiz Peralta, U. Pal, and R. S. Zeferino, “Photoluminescence (PL) Quenching and Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Au-Decorated ZnO Nanorods Fabricated through Microwave-Assisted Chemical Synthesis,” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, vol. 4, no. 9, pp. 4807–4816, Sep. 2012, doi: 10.1021/am301155u. |
| [28] | Y. Sun, W. Zhang, Q. Li, H. Liu, and X. Wang, “Preparations and applications of zinc oxide based photocatalytic materials,” Adv. Sens. Energy Mater., vol. 2, no. 3, p. 100069, Sep. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.asems.2023.100069. |
| [29] | P. Sikam, P. Moontragoon, J. Jumpatam, S. Pinitsoontorn, P. Thongbai, and T. Kamwanna, “Structural, Optical, Electronic and Magnetic Properties of Fe-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized by Combustion Method and First-Principle Calculation,” J. Supercond. Nov. Magn., vol. 29, no. 12, pp. 3155–3166, Dec. 2016, doi: 10.1007/s10948-016-3690-0. |
| [30] | A. Sandmann, A. Kompch, V. Mackert, C. H. Liebscher, and M. Winterer, “Interaction of l -Cysteine with ZnO: Structure, Surface Chemistry, and Optical Properties,” Langmuir, vol. 31, no. 21, pp. 5701–5711, Jun. 2015, doi: 10.1021/la504968m. |
| [31] | Q. Fan, X. Cui, H. Guo, Y. Xu, G. Zhang, and B. Peng, “Application of rare earth-doped nanoparticles in biological imaging and tumor treatment,” J. Biomater. Appl., vol. 35, no. 2, pp. 237–263, Aug. 2020, doi: 10.1177/0885328220924540. |
| [32] | N. Madkhali, “Analysis of Structural, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of (Fe,Co) Co-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized under UV Light,” Condens. Matter, vol. 7, no. 4, p. 63, Nov. 2022, doi: 10.3390/condmat7040063. |
| [33] | X. Yu et al., “Enhanced photocatalytic activity of Fe-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized via a two-step sol–gel method,” J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron., vol. 25, no. 9, pp. 3920–3923, Sep. 2014, doi: 10.1007/s10854-014-2107-8. |
| [34] | B. Choudhury, S. Bayan, A. Choudhury, and P. Chakraborty, “Narrowing of band gap and effective charge carrier separation in oxygen deficient TiO 2 nanotubes with improved visible light photocatalytic activity,” J. Colloid Interface Sci., vol. 465, pp. 1–10, Mar. 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2015.11.050. |
| [35] | C. Liu, Y. Ding, Q. Li, and Y. Lin, “Photochemical synthesis of glutathione-stabilized silver nanoclusters for fluorometric determination of hydrogen peroxide,” Microchim. Acta, vol. 184, no. 7, pp. 2497–2503, Jul. 2017, doi: 10.1007/s00604-017-2302-4. |
| [36] | L. Rulíšek and Z. Havlas, “Theoretical Studies of Metal Ion Selectivity. 1. DFT Calculations of Interaction Energies of Amino Acid Side Chains with Selected Transition Metal Ions (Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, and Hg2+ ),” J. Am. Chem. Soc., vol. 122, no. 42, pp. 10428–10439, Oct. 2000, doi: 10.1021/ja001265g. |
| [37] | T. Janek, K. Sałek, J. Burger, Ż. Czyżnikowska, and S. R. Euston, “Investigating the biomolecular interactions between model proteins and glycine betaine surfactant with reference to the stabilization of emulsions and antimicrobial properties,” Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces, vol. 194, p. 111226, Oct. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.111226. |
| [38] | S. Munir, S. M. Shah, H. Hussain, and R. Ali Khan, “Effect of carrier concentration on the optical band gap of TiO2 nanoparticles,” Mater. Des., vol. 92, pp. 64–72, Feb. 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2015.12.022. |
| [39] | M. Julita, M. Shiddiq, and M. Khair, “Determination of Band Gap Energy of ZnO/Au Nanoparticles Resulting in Laser Ablation in Liquid,” Indo J Chem Res, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 83–87, Sep. 2022, doi: 10.30598//ijcr.2022.10-mar. |
| [40] | Y. Zheng, S. Gao, and J. Y. Ying, “Synthesis and Cell-Imaging Applications of Glutathione-Capped CdTe Quantum Dots,” Adv. Mater., vol. 19, no. 3, pp. 376–380, Feb. 2007, doi: 10.1002/adma.200600342. |
| [41] | A. G. Kaninginiet al., “Effect of Optimized Precursor Concentration, Temperature, and Doping on Optical Properties of ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized via a Green Route Using Bush Tea (Athrixiaphylicoides DC.) Leaf Extracts,” ACS Omega, vol. 7, no. 36, pp. 31658–31666, Sep. 2022, doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c00530. |
| [42] | W. Qi, Y. Tian, D. Lu, and B. Chen, “Detection of glutathione in dairy products based on surface-enhanced infrared absorption spectroscopy of silver nanoparticles,” Front. Nutr., vol. 9, p. 982228, Aug. 2022, doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.982228. |
| [43] | J. Andrade, C. G. Pereira, T. Ranquine, C. A. Azarias, M. J. V. Bell, and V. De Carvalho Dos Anjos, “Long-Term Ripening Evaluation of Ewes’ Cheeses by Fourier-Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy under Real Industrial Conditions,” J. Spectrosc., vol. 2018, pp. 1–9, 2018, doi: 10.1155/2018/1381864. |
| [44] | J.-J. Max and C. Chapados, “Infrared Spectroscopy of Aqueous Carboxylic Acids: Malic Acid,” J. Phys. Chem. A, vol. 106, no. 27, pp. 6452–6461, Jul. 2002, doi: 10.1021/jp014377i. |
| [45] | C. Battocchioet al., “Gold Nanoparticles Stabilized with Aromatic Thiols: Interaction at the Molecule–Metal Interface and Ligand Arrangement in the Molecular Shell Investigated by SR-XPS and NEXAFS,” J. Phys. Chem. C, vol. 118, no. 15, pp. 8159–8168, Apr. 2014, doi: 10.1021/jp4126057. |
| [46] | T. D. Kusworo, F. Dalanta, N. Aryanti, and N. H. Othman, “Intensifying separation and antifouling performance of PSf membrane incorporated by GO and ZnO nanoparticles for petroleum refinery wastewater treatment,” J. Water Process Eng., vol. 41, p. 102030, Jun. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102030. |
| [47] | S. V. Kaymaz, H. M. Nobar, H. Sarıgül, C. Soylukan, L. Akyüz, and M. Yüce, “Nanomaterial surface modification toolkit: Principles, components, recipes, and applications,” Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., vol. 322, p. 103035, Dec. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2023.103035. |


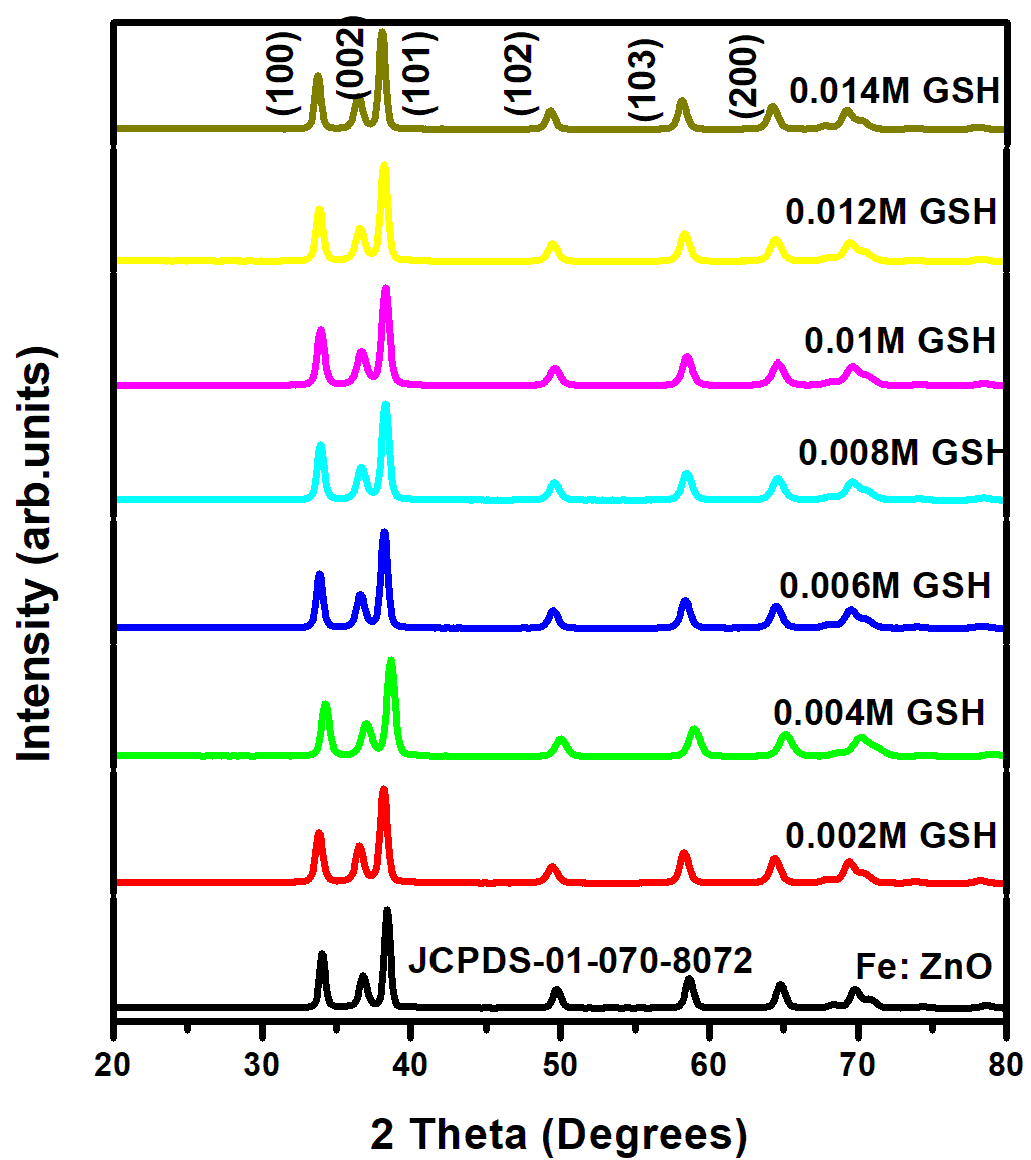
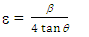
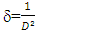
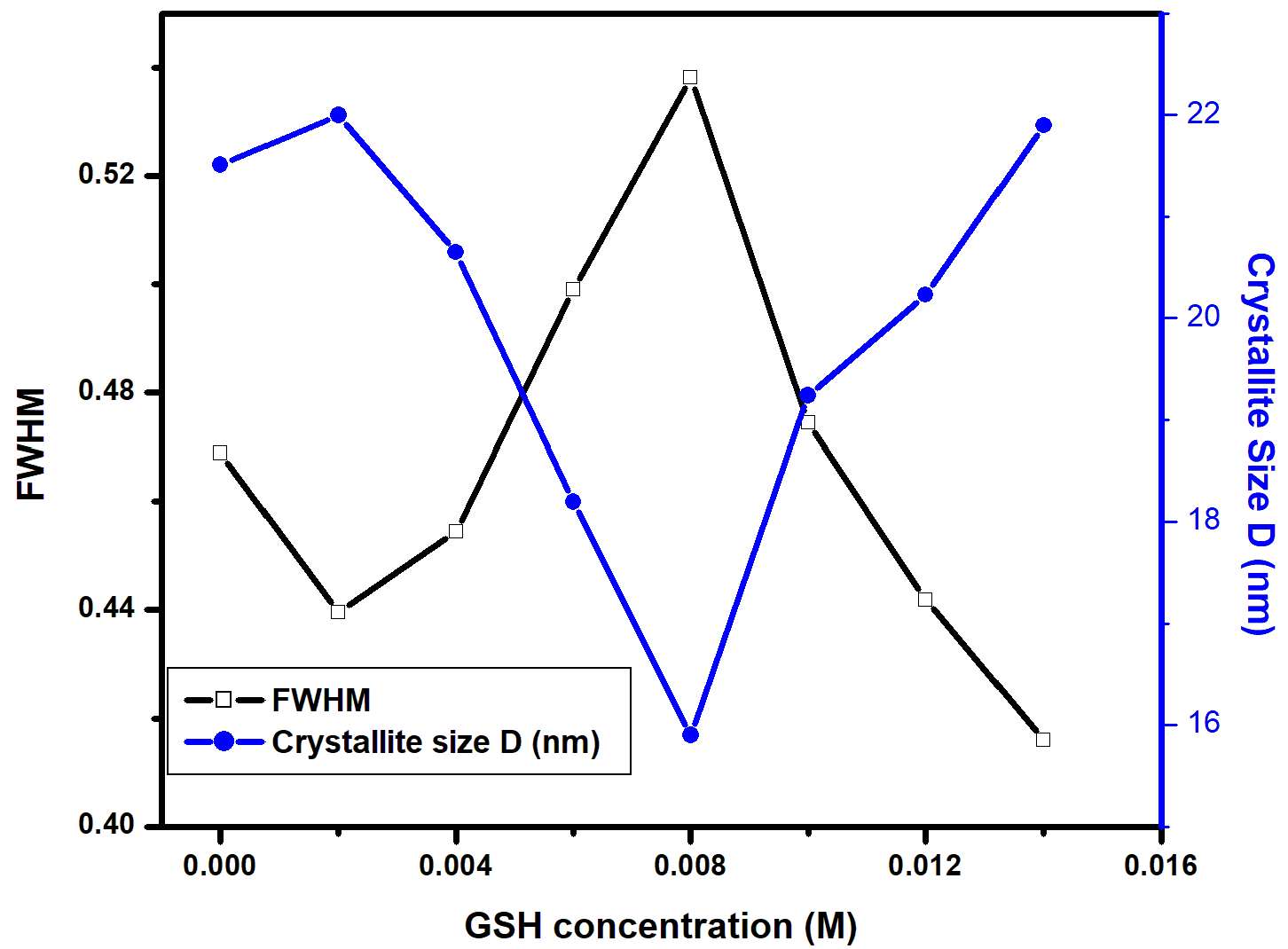
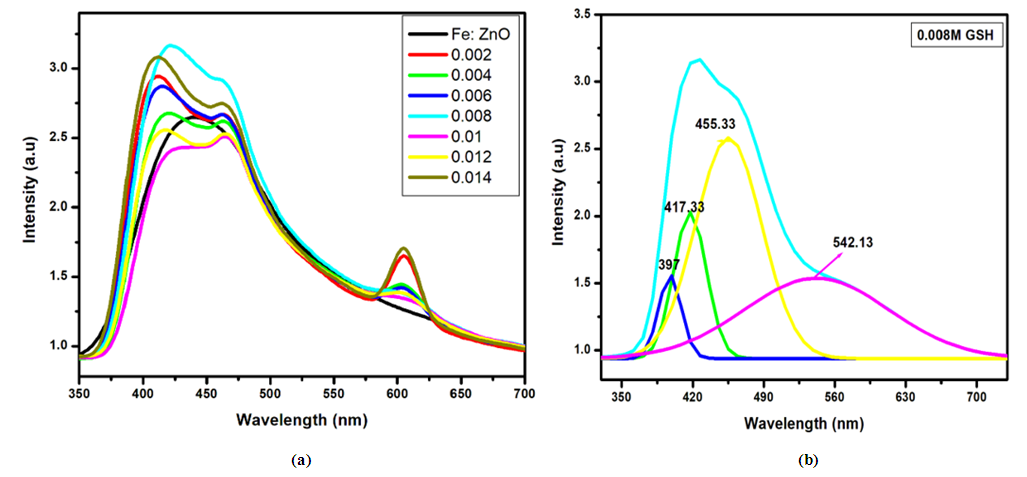
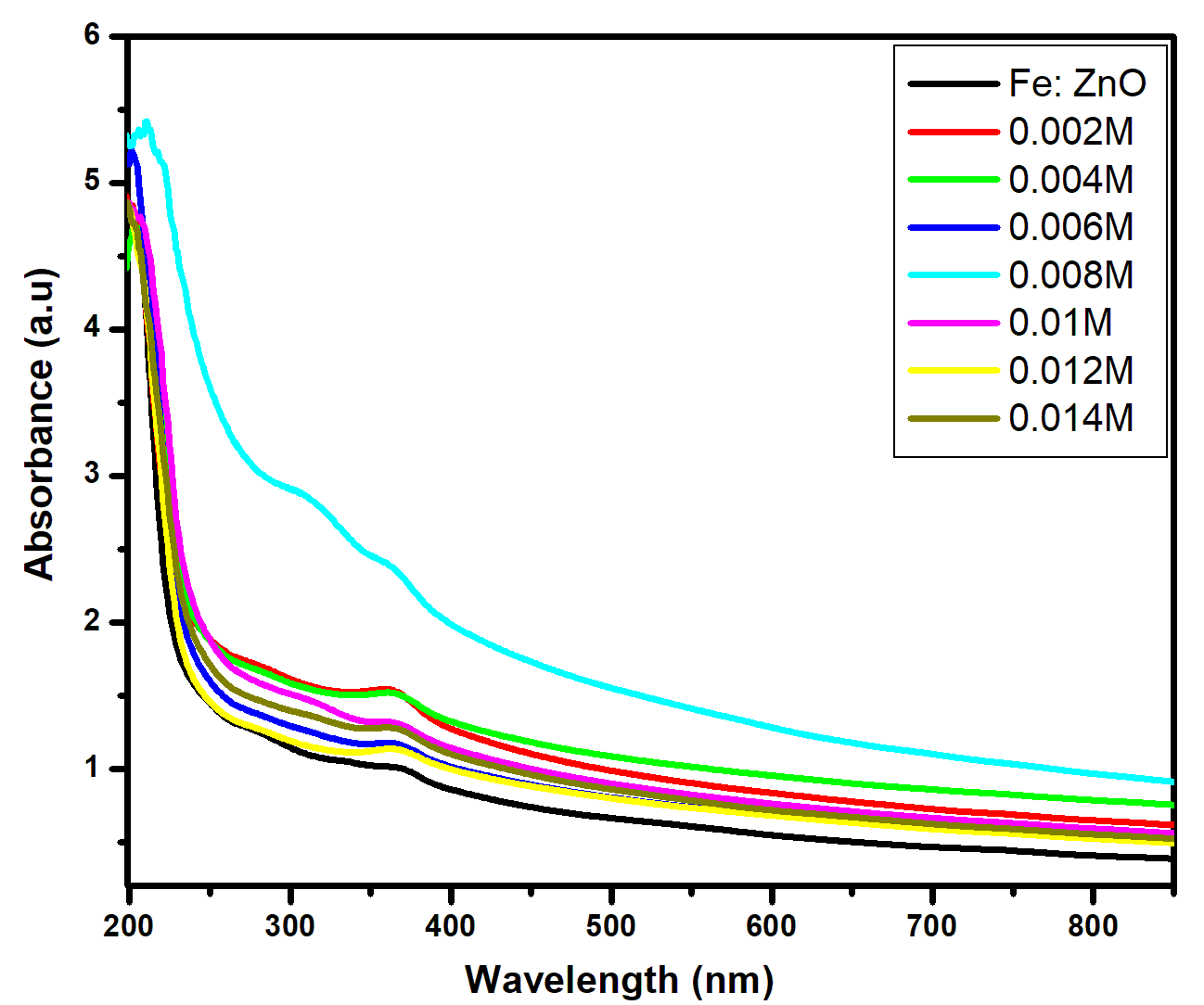
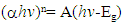
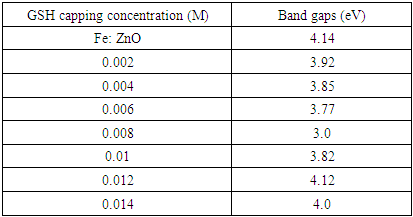
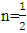 for direct allowed transitions, while n = 2 for indirect allowed transitions. Since ZnO is a direct bandgap semiconductor,
for direct allowed transitions, while n = 2 for indirect allowed transitions. Since ZnO is a direct bandgap semiconductor, 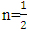 was used. The Tauc plot was obtained by plotting (αhv)2 against photon energy (hv), and the optical band gap was obtained by extrapolating the linear portion of the curve to the x-axis where (αhv)2 = 0. Figure 5 shows the optical band gaps obtained through extrapolation.
was used. The Tauc plot was obtained by plotting (αhv)2 against photon energy (hv), and the optical band gap was obtained by extrapolating the linear portion of the curve to the x-axis where (αhv)2 = 0. Figure 5 shows the optical band gaps obtained through extrapolation.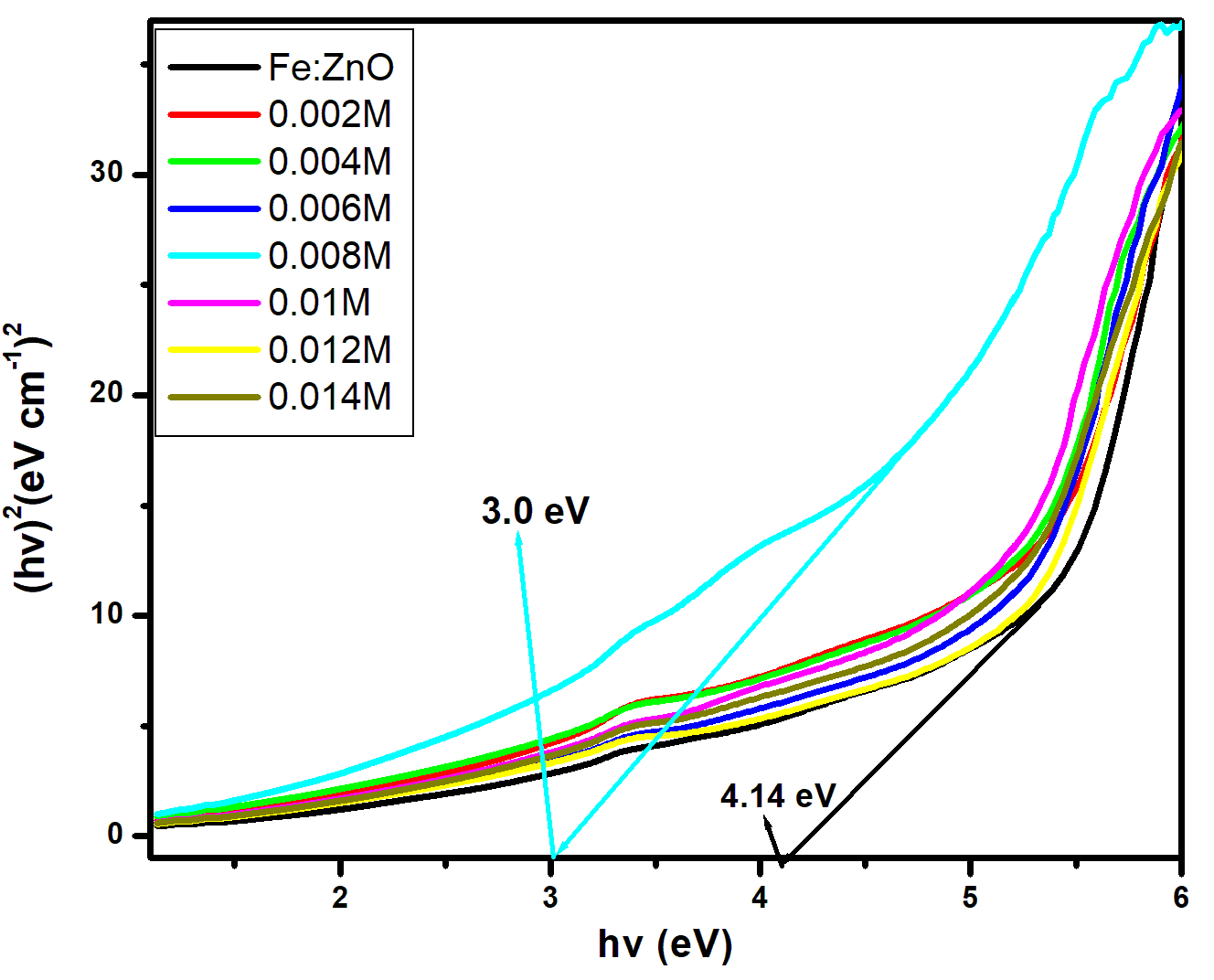
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML