-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Condensed Matter Physics
p-ISSN: 2163-1115 e-ISSN: 2163-1123
2017; 7(1): 1-5
doi:10.5923/j.ajcmp.20170701.01

Pressure Induced Structural Phase Transition and Valence Change
Md. Tarek Hossain, Abdul Hannan
Department of Physics, Shahjalal University of Science and Technology, Sylhet, Bangladesh
Correspondence to: Md. Tarek Hossain, Department of Physics, Shahjalal University of Science and Technology, Sylhet, Bangladesh.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The application of hydrostatic pressure on a solid material has a direct effect on the extra-nuclear electronic states of the constituent atoms in the material. In this work, we have studied the effect of pressure on the various properties of the material, such as structural behavior, crystal lattice behavior, magnetic behaviors of magnetic material and transport behavior like electrical resistivity. We have calculated the Ce valency change in some compounds of cerium monochalcogenides CeX (X=O, S, Se and Te) and cerium monopnictides CeX (X=P, As, Sb and Bi). In doing this task, we have reproduced the reported experimental pressure-volume relationships of the compounds using the Birch equation of state. The corresponding pressure-volume relationships of these compounds for stable trivalent cerium have also been calculated using the same Birch equation. Clear effect of pressure on the cerium valency has been realized for each compound from the present calculation.
Keywords: Cerium monochalcogenides, Cerium monopnictide, Birch equation of state, Valency change
Cite this paper: Md. Tarek Hossain, Abdul Hannan, Pressure Induced Structural Phase Transition and Valence Change, American Journal of Condensed Matter Physics, Vol. 7 No. 1, 2017, pp. 1-5. doi: 10.5923/j.ajcmp.20170701.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
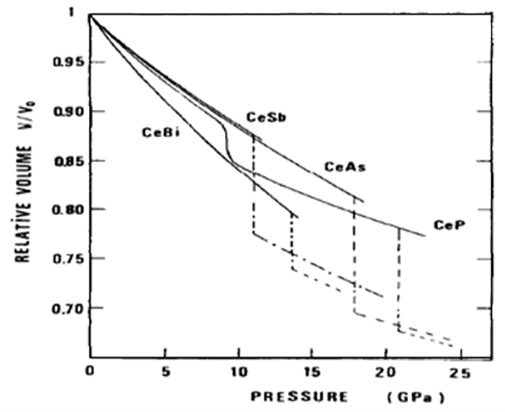
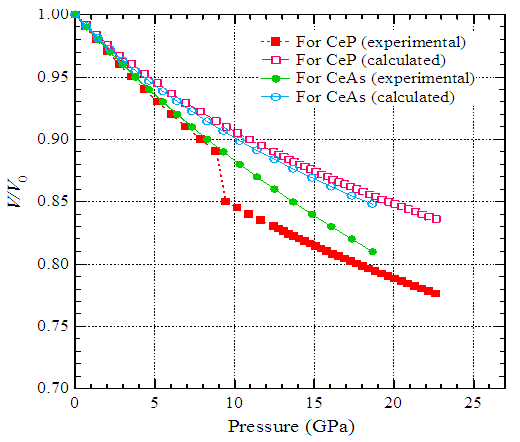
- Hydrostatic pressure on a solid material has direct effect material changes its properties due to the modification of the electronic states of the constituent atoms of the material. Various effects, such as structural phase transition, unusual crystal lattice behavior, unusual resistivity, appearance of complicated magnetic phase etc. of pressure have been reported earlier [1-4, 9-10, 15-24]. Some of these effects are highlighted blow. Two members of cerium monochalcogenides CeX (X=O, S, Se and Te), CeSe and CeTe change structure from NaCl-type to CsCl-type at about 20 GPa and 8 GPa, respectively with the increase of pressure [1]. There are also reported works on relative volume of cerium monopnictides CeX (X=P, As, Sb and Bi) as a function of pressure [1]. CeP shows isostructural discontinuous transition at around 10 GPa, and above 20 GPa it exhibits a structural transition from NaCl-type to CsCl-type structure [1, 2]. CeAs shows a sharp structural transition from NaCl–type to CsCl-type at about 18 GPa. CeSb exhibits a sharp structural transition from NaCl–type to body central tetragonal structure at 11 GPa. At 13 GPa, CeBi exhibits structural transition from NaCl–type to CsCl-type structure.The structural phase transition and unusual crystal lattice behavior are analyzed in the last few years [25-32]. There are reported relative volume of uranium monochalcogenides UX (X= S, Se and Te) as a function of pressure [1]. The volume of US decreases gradually up to 15 GPa. The data above this pressure scatter suggesting a transition, probably to an orthorhombic structure [3]. USe does not show any structural transition up to 20 GPa. UTe exhibits a NaCl to CsCl-type transition at 11 GPa with the increase of pressure. In uranium monopnictides, UAs and USb exhibit structural transitions from NaCl- to CsCl-type at 17 GPa and 9 GPa, respectively [1].If we apply high pressure on a material, its properties change due to the modification of the electronic states of the constituent atoms of the material. The structure of the material may be changed due to the application of the high pressure. Unusual crystal lattice behavior with temperature is also observed as a consequence of the application of pressure. The magnetic behaviors of magnetic material may be changed due to pressure. Transport behaviors like electrical resistivity, specific heat may also change due the effect of pressure.
2. Calculation of Valance Change Due to Pressure
2.1. Relative Volume of Monochalcogenides as a Function of Pressure
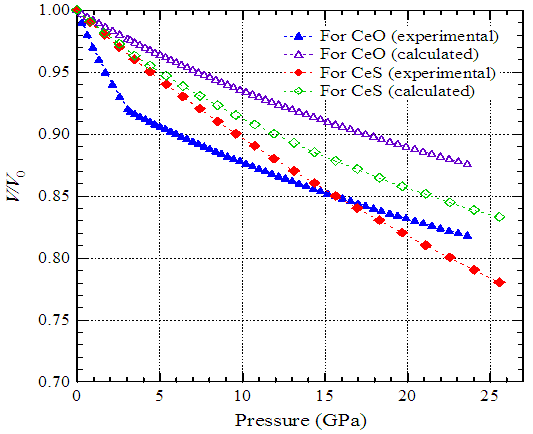
- Leger et al. investigated the pressure-volume relationship and the crystallographic phase changes of cerium monochalcogenides and monopnictides by X-ray diffraction in diamond anvil cells at room temperature [1, 11, 12]. Fig.1 shows the experimental change of relative volume of cerium monochalcogenides as a function of pressure [1]. The volume of CeO decreases very rapidly with pressure up to 3 GPa, above which the rate of change exhibits normal trend. The crystal structure of this compound up to 25 GPa remains the same (NaCl-type). The volume of CeS decreases smoothly up to the pressure of 27 GPa with exhibiting the NaCl-type structure. CeSe also shows the NaCl-type phase up to 25 GPa but above 20 GPa a phase of CsCl-type structure appears with a volume change of 9%. At 8 GPa, CeTe changes the structural phase from NaCl to CsCl-type.
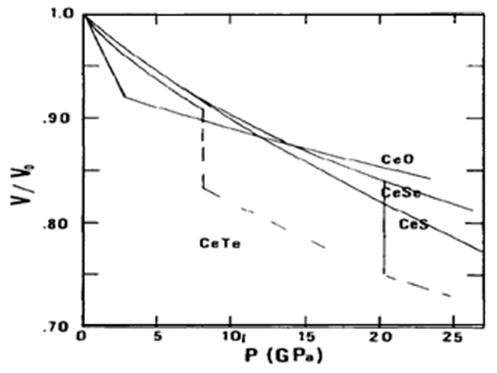 | Figure 1. Experimental change of relative volume of cerium monochalcogenides with pressure (solid line: NaCl- type structure, dashed line: CsCl-type structure) [1] |
2.2. Reproduction of Experimental Relative Volume
- The experimental pressure-volume relationship, as shown in Figs. 1 and 2, can be fitted using the Birch equation [13, 14] as written below:
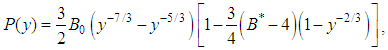 | (1) |
2.3. Theoretical Relative Volume for Stable Trivalent Cerium
- We have selected two compounds, CeO and CeS, from the category of cerium monochalcogenides. For trivalent stable cerium in CeO the parameters B0 and B* are 125 GPa and 5.4, respectively, and in CeS they are 85 GPa and 5.4, respectively [1]. Using these parameters, we have calculated (using Eq. (1)) the relative volumes of CeO and CeS as a function of pressure. The calculated relative volumes have been presented in Fig. 3 by open triangles and open diamonds.For trivalent stable cerium in CeP the parameters B0 and B* are 78 GPa and 5.4, respectively, and in CeAs they are 72.44 GPa and 5.4, respectively [1]. The relative volumes of CeP and CeAs as a function of pressure have been calculated using Eq. (1). The calculated relative volumes have been presented in Fig. 4 by open squares and open circles.
2.4. Calculation of Valence Change
- There is a linear variation of the cerium valency in the cerium monochalcogenide and cerium monopnictide compounds with the lattice parameter, a [1]. The increase of the valency, x, can be calculated from the following relation [1].
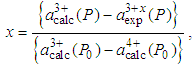 | (2) |
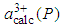 is the calculated lattice constant at pressure P with cerium valance 3+,
is the calculated lattice constant at pressure P with cerium valance 3+, 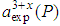 is the experimentally observed lattice constant at pressure P with cerium valance 3+x,
is the experimentally observed lattice constant at pressure P with cerium valance 3+x, 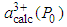 is the calculated lattice constant at ambient pressure with cerium valance 3+ and
is the calculated lattice constant at ambient pressure with cerium valance 3+ and 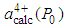 is the calculated lattice constant at ambient pressure with cerium valance 4+.In the calculation, the cerium coordination must be taken into account and the following cerium radii with a coordination of six, for fcc structure, are used:
is the calculated lattice constant at ambient pressure with cerium valance 4+.In the calculation, the cerium coordination must be taken into account and the following cerium radii with a coordination of six, for fcc structure, are used: 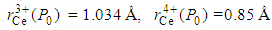 [1]. So, for NaCl-type cubic lattice we can write
[1]. So, for NaCl-type cubic lattice we can write 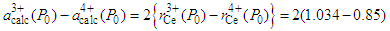 Ǻ=0.368 ǺSo, Eq. (2) becomes
Ǻ=0.368 ǺSo, Eq. (2) becomes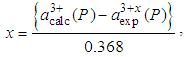 | (3) |
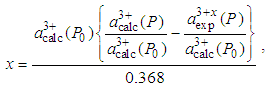 | (4) |
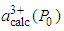 is the lattice parameter of the concerned fcc lattice at ambient pressure.
is the lattice parameter of the concerned fcc lattice at ambient pressure.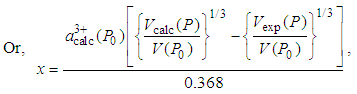 | (5) |
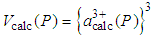 is the calculated volume of the unit cell at pressure P with cerium valance 3+,
is the calculated volume of the unit cell at pressure P with cerium valance 3+, 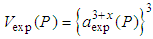 is the experimentally observed volume of the unit cell at pressure P with cerium valance 3+x and
is the experimentally observed volume of the unit cell at pressure P with cerium valance 3+x and 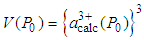 is the calculated volume of the unit cell at ambient pressure with cerium valance 3+.The valency of Ce at pressure P is calculated from the following relation:
is the calculated volume of the unit cell at ambient pressure with cerium valance 3+.The valency of Ce at pressure P is calculated from the following relation: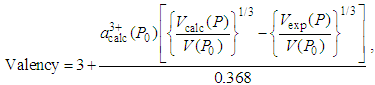 | (6) |
3. Results & Discussion
- In the present work we have studied the effect of pressure on the valency change of some compounds. Fig.5 shows the calculated valency of Ce, as calculated using Eq. (6), in CeO, CeS, CeP and CeAs as a function of pressure. For CeO, the valency of Ce rapidly increases with the increase of pressure, and at about 3 GPa the valency is 3.27+. Above 3 GPa the valency is almost pressure independent up to 23.5 GPa. The valency of Ce in CeS increases non-linearly with the increase of pressure, and at about 25.5 GPa the valency is 3.31+. For CeP the valency of Ce increases almost linearly with the increase of pressure, and at 9 GPa valency becomes 3.14+. Above this pressure, the valency suddenly increases to 3.35+ at about 9.5 GPa due to isostructural valence-phase transition, and then the valency is almost pressure independent up to 22.5 GPa. In the case of CeAs, a continuous non-linear increase of valency with the increase of pressure is found, and at 18.5 GPa the Ce valency is 3.23+.
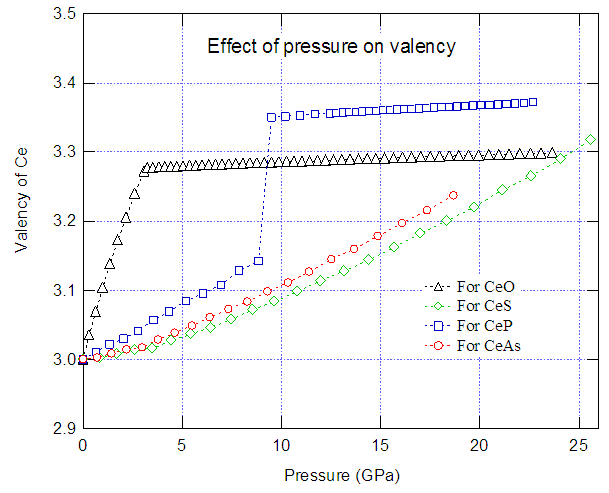 | Figure 5. Valency of Ce in CeO, CeS, CeP and CeAs |
4. Conclusions
- The pressure-dependent volume behaviors of cerium monochalcogenides and monopnictides have been studied in details. A method for the calculation of valency change of cerium in these compounds adopting the Birch equation of state has been introduced. Our calculation shows clear effect of pressure on the valency change. We interpreted that the environment around the Ce in a compound is solely responsible to drive how the valency of Ce in the compound will change.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML