-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics
p-ISSN: 2165-8935 e-ISSN: 2165-8943
2013; 3(1): 46-48
doi:10.5923/j.ajcam.20130301.08
Solution of Bratu’s Equation by He's Variational Iteration Method
M. Saravi1, M. Hermann2, D. Kaiser2
1Department of mathematics, Islamic Azad University, Nour Branch, Nour, Iran
2Fakultät für Mathematik und Informatic, Friedrich, Schiller, Universität Jena
Correspondence to: M. Saravi, Department of mathematics, Islamic Azad University, Nour Branch, Nour, Iran.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The purpose of this paper is to use He's variational iteration method for solving Bratu’s boundary value problem, using only three terms in series expansion of nonlinear part. The method converges rapidly and approximates the exact solution very accurately. Two special cases of the problem are illustrated by using two iterates of the recursive scheme and the numerical results and conclusions will be presented.
Keywords: Variational Iteration Method, Nonlinear Equations, Bratu’s Problem
Cite this paper: M. Saravi, M. Hermann, D. Kaiser, Solution of Bratu’s Equation by He's Variational Iteration Method, American Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, Vol. 3 No. 1, 2013, pp. 46-48. doi: 10.5923/j.ajcam.20130301.08.
1. Introduction
- One of the problems that had been attacked by several authors is Bratu’s boundary value problem which is given by
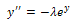 | (1) |
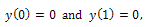 | (2) |
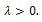 A typical example occurs in the theory of the electric charge around a hot wire and also in certain problems of solid mechanics. The Bratu’s problem in one-dimensional planner coordinates has two known, bifurcated solutions for values of
A typical example occurs in the theory of the electric charge around a hot wire and also in certain problems of solid mechanics. The Bratu’s problem in one-dimensional planner coordinates has two known, bifurcated solutions for values of 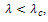 , no solution for
, no solution for 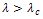 and a unique solution when
and a unique solution when 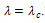 .The value of
.The value of 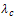 is related to the fixed point of hyperbolic contangent function and satisfies the equation
is related to the fixed point of hyperbolic contangent function and satisfies the equation 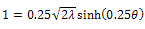 The exact solution of (1) and (2) is given by
The exact solution of (1) and (2) is given by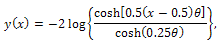 provided that
provided that 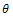 is the solution of
is the solution of 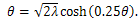 With given boundary conditions it is not possible to solve (1) by elementary methods.Various kinds of analytical methods and numerical methods were used to solve this equation[1-6]. For example, Bellman and Kalaba find substantial agreement of
With given boundary conditions it is not possible to solve (1) by elementary methods.Various kinds of analytical methods and numerical methods were used to solve this equation[1-6]. For example, Bellman and Kalaba find substantial agreement of  to exact solution by applying quasilinearization method [5] and S. A. Khuri used a Laplace transform numerical technique for solving this problem [3].It been shown that the variational iteration method is a very efficient tool for solving various kinds of nonlinear ordinary and partial differential equations[7-12]. Itbeen used to solve the Fokker Planck equation, the Lane-Emden differential equation, the Klein-Gordon partial differential equations, the Cauchy reaction-diffusion problem, the biological population model. For more applications of the method the interested reader is referred to [7]. It also is useful to solve integral equations [13-15].To illustrate the basic idea of the method, we consider the differential equation
to exact solution by applying quasilinearization method [5] and S. A. Khuri used a Laplace transform numerical technique for solving this problem [3].It been shown that the variational iteration method is a very efficient tool for solving various kinds of nonlinear ordinary and partial differential equations[7-12]. Itbeen used to solve the Fokker Planck equation, the Lane-Emden differential equation, the Klein-Gordon partial differential equations, the Cauchy reaction-diffusion problem, the biological population model. For more applications of the method the interested reader is referred to [7]. It also is useful to solve integral equations [13-15].To illustrate the basic idea of the method, we consider the differential equation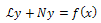 | (3) |
 is the source inhomogeneous term.The variational iteration method presents a correction functional for Eq. (3)in the form
is the source inhomogeneous term.The variational iteration method presents a correction functional for Eq. (3)in the form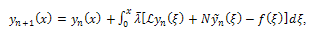 Where
Where 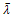 is a general Lagrange multiplier[3], which can be optimally found via variational theory and
is a general Lagrange multiplier[3], which can be optimally found via variational theory and 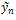 is a restricted variation which means,
is a restricted variation which means, 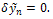
2. Procedure
- RecallBratu’s boundary value problem
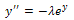 | (1) |
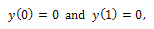 | (2) |
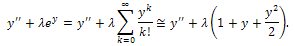 Thus
Thus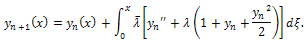 Impose
Impose 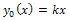 (one may use
(one may use 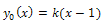 and apply
and apply 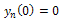 to find k), we obtainIntegrating by parts leads to
to find k), we obtainIntegrating by parts leads to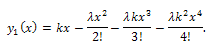 We have
We have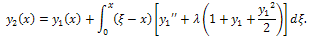 Therefore,
Therefore,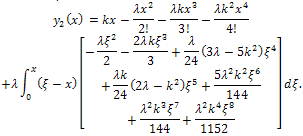 Again, we use integration by parts. We obtain
Again, we use integration by parts. We obtain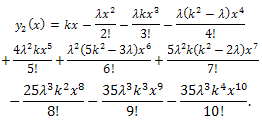 | (4) |
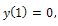 with a given value for
with a given value for 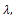 we can find four values for kWith appropriate choose of k,
we can find four values for kWith appropriate choose of k, 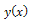 can be approximated for
can be approximated for 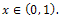
3. Examples
- In this section we examine the above procedure for
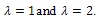 . Applying
. Applying 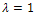 to Eq. (4) and simplify it, we come to
to Eq. (4) and simplify it, we come to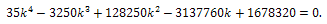 Solving this equation by a numerical method, gives
Solving this equation by a numerical method, gives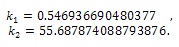 Since
Since 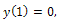 with two decimal points we may choose,
with two decimal points we may choose, 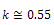 then
then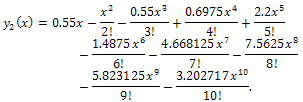 We tested it for values of
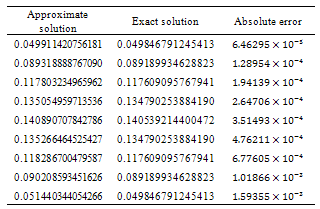
We tested it for values of 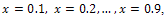 , respectively and the results are given in Table 1.For
, respectively and the results are given in Table 1.For 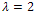 to Eq. (4), we come to
to Eq. (4), we come to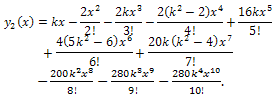 | (5) |
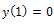 to Eq. (5), we obtain
to Eq. (5), we obtain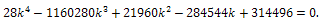 Roots of this equation are
Roots of this equation are Our appropriate choose will be
Our appropriate choose will be 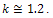 . We tested it similar to case of
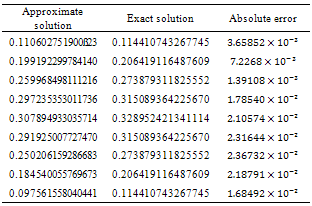
. We tested it similar to case of 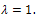 The results are given in Table 2.
The results are given in Table 2.
|
|
4. Conclusions
- Results in this paper show the efficiency of variational iterative method and is quite reliable.It can be observed that our approximations are accurate using only two iterates and avoid the much computation using Adomian polynomials[1, 3] or quasilinearization method [5]. There is no doubt, if more terms of Taylor series expansion, or more iterates were used, we obtain much better results. This approach also can be used for Poisson-Boltzman’s equation in one-dimensional planar coordinates if we choose
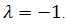 .
. Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML