-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics
p-ISSN: 2165-8935 e-ISSN: 2165-8943
2012; 2(5): 206-217
doi: 10.5923/j.ajcam.20120205.02
Modelling the Effects of Competing Toxin Producing Phytoplankton on a Zooplankton Population: Role of Holling Type-II Functional Response with Time-Lag
O. P. Misra 1, Chhatrapal Singh Sikarwar 1, Poonam Sinha 2
1School of Mathematics and Allied Sciences, Jiwaji University, Gwalior-474 011, India
2Department of Mathematics, S.M.S.Govt Model Science College, Gwalior-474 011, India
Correspondence to: Chhatrapal Singh Sikarwar , School of Mathematics and Allied Sciences, Jiwaji University, Gwalior-474 011, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
In this paper, a system consisting of two competing harmful phytoplankton and a zooplankton with Holling type-II functional response and discrete time lag is considered. A stable co-existence of all the species has been observed for the system without delay and the Hopf-bifurcation phenomenon is observed for the interior equilibrium point. The Hopf-bifurcating solution is obtained for the critical values of parameters like predation rates and half saturation constants. Further, using the normal form theory, we have determined the direction and the stability of the Hopf-bifurcation solution. The introduction of time delay in the system also shows the Hopf-bifurcation as the delay parameter passes through a critical value. Finally, the numerical simulation is carried out to support the theoretical results.
Keywords: Harmful Phytoplankton, Zooplankton, Delay, Stability , Hopf-Bifurcation
Cite this paper: O. P. Misra , Chhatrapal Singh Sikarwar , Poonam Sinha , "Modelling the Effects of Competing Toxin Producing Phytoplankton on a Zooplankton Population: Role of Holling Type-II Functional Response with Time-Lag", American Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics , Vol. 2 No. 5, 2012, pp. 206-217. doi: 10.5923/j.ajcam.20120205.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- There has been a global increase in harmful plankton blooms in last three decades[1-3]. Recently, there has been increasing interest in investigating the dynamics of harmful algal bloom (HAB) and its control[4 -7]. Plankton model is a kind of ecological model and different plankton models have been established and studied, previously[8, 9]. There are several papers in which attempts have been made to establish the role of different hydrological parameters in the formation of plankton blooms and then look for a suitable form of functional response to describe the reduction of zooplankton population due to toxin producing phytoplankton (TPP), for example, see[1, 2, 10, 11]. Reduction of grazing pressure of zooplankton due to release of toxic substances by phytoplankton is one of the most vital parameter in this context[12, 13]. Areas rich in some phytoplankton organisms e.g., Phaeocystis, Coscinodiscus, Rhizosolenia etc. are unaccepted/avoided by zooplankton due to dense concentration of phytoplankton or the production of some toxic as well as unpleasant factors by them and this phenomena is well explained by the exclusion principle[14, 15]. Buskey and Stockwell[16] have demonstrated in their field studies that micro and meso zooplankton population are reduced during the bloom of a chrysophyte Aureococcus nophagefferens in the southern Texas coast. These observations indicate that the toxic substance as well as toxic phytoplankton plays an important role on the growth of the zooplankton and have a great impact on phytoplankton zooplankton interactions. However, all the above studies do not explain several key features, such as, allelopathic interactions on the co-existence and persistence of phytoplankton species and its immediate effect on predators, control of recurring harmful algal bloom or oscillations and the effect of time lag required to release toxic substances.In this stage, we would like to mention that various combinations of predational functional response and toxin liberation process give rise to several interesting dynamics of the system . In this study, we are mainly interested to present a mechanism for planktonic bloom in which the liberation of toxic substance or the effect of toxic phytoplankton is not an instantaneous process but is mediated by some time lag and can be helpful to reduce oscillations in the population and in turn, it is useful to maintain a stable co-existence of the species. The study of biological systems with time delays have been of considerable interest for a long time. There are also several reports that the zooplankton mortality due to the toxic phytoplankton bloom occurs after some time lapse (see, www.mote.org, www.mdsg.umd.edu). Our mathematical and field observations[17] also suggest that the abundance of Paracalanus (zooplankton) population reduces after some time lapse of the bloom of toxic phytoplankton Noctiluca scintillans and this allows us some considerable freedom for considering the delay factor in the model construction. Sarkar et al.[18] studied the role of two toxin producing plankton and their effect on phytoplankton zooplankton system. They considered the predational functional response as a linear and distribution of toxic substances as Holling type II functions. They suggested in this paper that the role of time lag and environmental fluctuations in the two harmful phytoplankton-zooplankton dynamics may give some interesting results and needs further investigation. Therefore, in this paper we have studied a mathematical model for a phytoplankton-zooplankton system considering both the Holling type II predational functional response and Holling type II functional form with time lag for the distribution of toxic substances.
2. Model Formulation and Basic Assumptions
- The current study has been originated from the theoretical as well as experimental results on the interaction of harmful algal bloom and different types of phytoplankton zooplankton interactions[10, 16-20]. Motivated from the literature and the field observations[18, 20], a dynamical model consisting of two competing phytoplankton harmful to zooplankton has been proposed and the role of time lag in the underlying system is studied. Let P1(t) and P2(t) are the concentrations of the two kinds of harmful phytoplankton and Z(t) is the concentration of zooplankton at time t. Let r1 and r2 are the growth rates of the harmful phytoplankton, respectively, and k is the carrying capacity, which is assumed to be common for both the phytoplankton species. Let ρ1 and ρ2 are the rates of predation of both phytoplankton by zooplankton and γ1 and γ2 are the corresponding conversion rates of zooplankton, where the predator functional response is assumed to follow the Holling type-II functional response[21, 22], with h1 and h2 as half saturation constants. Let d is the natural death rate of zooplankton; α1 and α2 are the inhibitory effects of the two competing harmful phytoplankton.
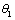 (γ1 >
(γ1 >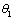 ) and
) and 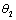 (γ2 >
(γ2 >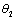 ) are the rates of toxin liberation by the harmful phytoplankton reducing the growth of zooplankton. The discrete time lag τ is assumed to follow[23] and it is taken in the term describing the mortality of zooplankton due to liberation of toxic substances by two harmful phytoplankton P1, P2. The mathematical model is thus given by the following system of eSquations:
) are the rates of toxin liberation by the harmful phytoplankton reducing the growth of zooplankton. The discrete time lag τ is assumed to follow[23] and it is taken in the term describing the mortality of zooplankton due to liberation of toxic substances by two harmful phytoplankton P1, P2. The mathematical model is thus given by the following system of eSquations: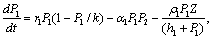 | (1) |
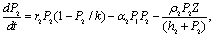 | (2) |
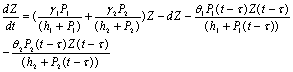 | (3) |
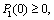
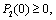
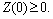
3. Model Without Delay
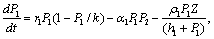 | (4) |
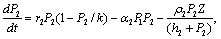 | (5) |
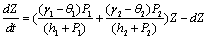 | (6) |
3.1. Equlibria of the System
- The equilibrium points of the system of Equations (4)-(6) are1. The trivial equilibrium point: ET ≡(0, 0, 0),2. The axial equilibrium points:
 ≡ (0, k, 0)and
≡ (0, k, 0)and 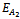 ≡ (k, 0, 0)3. The boundary equilibrium points:
≡ (k, 0, 0)3. The boundary equilibrium points: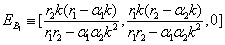
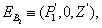 Where
Where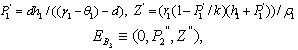 Where
Where 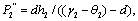
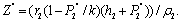 Now, we observe that the boundary equilibrium point
Now, we observe that the boundary equilibrium point  exists if the inhibitory effects of both the harmful phytoplankton are less than certain thresholds, that is, if α1< r1/k, α2< r2/k. The equilibrium points
exists if the inhibitory effects of both the harmful phytoplankton are less than certain thresholds, that is, if α1< r1/k, α2< r2/k. The equilibrium points  and
and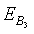 exist if d< (γ1-θ1) and d< (γ2-θ2).4. The unique interior equilibrium point:
exist if d< (γ1-θ1) and d< (γ2-θ2).4. The unique interior equilibrium point: 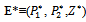 ,where
,where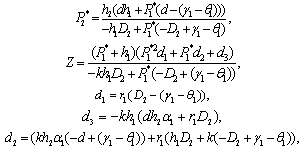 The unique interior equilibrium point
The unique interior equilibrium point 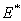 exist if
exist if 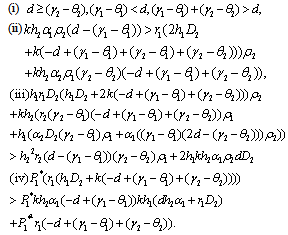
3.2. Dynamic Behaviour and Hopf-Bifurcation
- Eigen value analysis to establish local asymptotic stability: By computing the variational matrix around the respective biological feasible equilibria, one can easily deduce the following lemmas:Lemma 3.2.1 The steady state ET (0, 0, 0) of system of Equations (4)-(6) is a saddle point.Lemma 3.2.2 There exists two steady states
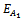 (0, k, 0) and
(0, k, 0) and 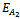 (k, 0, 0) which are feasible (one harmful phytoplankton and zooplankton free state) and are unstable saddle.Lemma 3.2.3 There exists a zooplankton free steady state
(k, 0, 0) which are feasible (one harmful phytoplankton and zooplankton free state) and are unstable saddle.Lemma 3.2.3 There exists a zooplankton free steady state 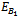 which is unstable saddle if
which is unstable saddle if 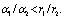 Lemma 3.2.4 There exists a steady state
Lemma 3.2.4 There exists a steady state 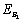 which is unstable if
which is unstable if 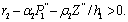 Lemma 3.2.5 There exists a steady state
Lemma 3.2.5 There exists a steady state 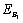 which is unstable if
which is unstable if 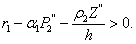 Next, we perform a stability study of the interior equilibrium point E*. For the sake of simplicity, the equilibrium point (
Next, we perform a stability study of the interior equilibrium point E*. For the sake of simplicity, the equilibrium point (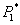 ,
,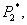 Z*) of the system of Equations (4)-(6) is shifted to a new point (x1, x2, x3) through transformations
Z*) of the system of Equations (4)-(6) is shifted to a new point (x1, x2, x3) through transformations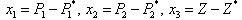 In terms of the new variables, the dynamical equations can be written in the matrix form as
In terms of the new variables, the dynamical equations can be written in the matrix form as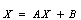 | (7) |
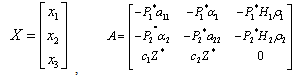 And
And 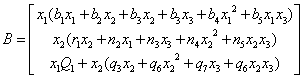 The characteristic equation of the community matrix corresponding to the linearized version of system of Equations (4)-(6) at E* is
The characteristic equation of the community matrix corresponding to the linearized version of system of Equations (4)-(6) at E* is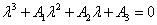 | (8) |
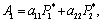
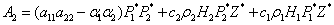
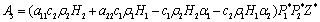 Using the Routh-Hurwitz criteria[22, 24], E* is locally asymptotically stable, if
Using the Routh-Hurwitz criteria[22, 24], E* is locally asymptotically stable, if 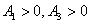 and
and 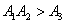 . Here the conditions A1 >0, A3 >0 and A1 A2 >A3 requires,
. Here the conditions A1 >0, A3 >0 and A1 A2 >A3 requires,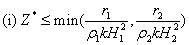
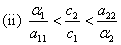 If one of the above mentioned conditions is violated then the system would become unstable around the positive interior equilibrium E*.and (iii) the eigenvalues of the characteristic equation should be of the form λi = ui+
If one of the above mentioned conditions is violated then the system would become unstable around the positive interior equilibrium E*.and (iii) the eigenvalues of the characteristic equation should be of the form λi = ui+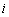 vi, and
vi, and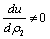 , i=1, 2, 3. After substituting the values, the condition C = A1A2-A3 becomes
, i=1, 2, 3. After substituting the values, the condition C = A1A2-A3 becomes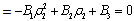 | (9) |
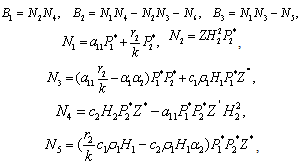
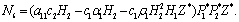 The Equation (9) has at least one positive root say
The Equation (9) has at least one positive root say 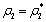 .Therefore, one pair of eigen values of the characteristic Equation (8) at
.Therefore, one pair of eigen values of the characteristic Equation (8) at 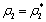 .are of the form
.are of the form 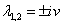 , where v is positive real number.Now, we will verify the Hopf-bifurcation condition (iii), putting λi = ui+ivi, in Equation (8), we get
, where v is positive real number.Now, we will verify the Hopf-bifurcation condition (iii), putting λi = ui+ivi, in Equation (8), we get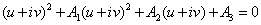 | (10) |
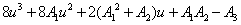 | (11) |
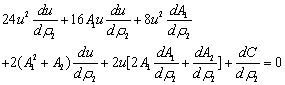 Now, since at
Now, since at 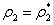 ,
,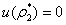 we get
we get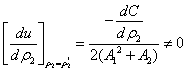 | (12) |
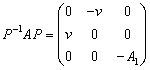 where the non-singular matrix P is given as
where the non-singular matrix P is given as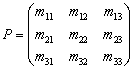 Where
Where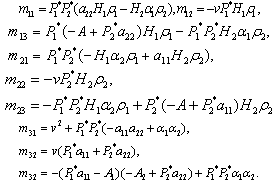 To achieve normal form of the Equation (7), we make another change of variable i.e. X =PY, where
To achieve normal form of the Equation (7), we make another change of variable i.e. X =PY, where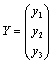 Through some algebraic manipulations, Equation (7) takes the form
Through some algebraic manipulations, Equation (7) takes the form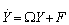 | (13) |
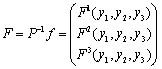 f is given by
f is given by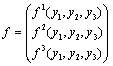
 Equation (13) is the normal form of Equation (7) from which the stability and direction of the Hopf bifurcation can be computed. In Equation (13), on the right hand side of the first term is linear and the second is non-linear in y’s. From these non-linear terms the stability and direction of the Hopf bifurcation is obtained[25].
Equation (13) is the normal form of Equation (7) from which the stability and direction of the Hopf bifurcation can be computed. In Equation (13), on the right hand side of the first term is linear and the second is non-linear in y’s. From these non-linear terms the stability and direction of the Hopf bifurcation is obtained[25].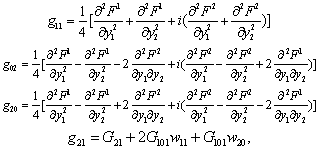 where,
where,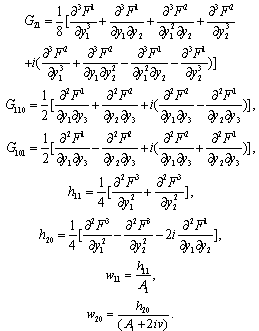 All these partial derivatives are determined at the Hopf bifurcation point ρ2 as well as at the origin. Based on the above analysis, we can see that each
All these partial derivatives are determined at the Hopf bifurcation point ρ2 as well as at the origin. Based on the above analysis, we can see that each 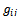 can be determined by the parameters. Thus we can compute the following quantities:
can be determined by the parameters. Thus we can compute the following quantities: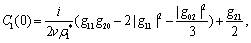
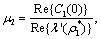 | (14) |
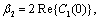
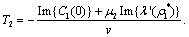 Theorem 3.1. μ2 determines the direction of the Hopf bifurcation: if μ2>0 (μ2<0), then the Hopf bifurcation is supercritical (subcritical) and the bifurcating periodic solutions exist for ρ2 > ρ2* (ρ2 < ρ2*); β2 determines the stability of bifurcating periodic solutions. and T2 determines the period of the bifurcating periodic solutions, the period increases (decreases) if T2 > 0 (T2 < 0). Now we will study the Hopf-bifurcation[25, 11, 26] of the system without delay taking ρ1 as the bifurcation parameter. The necessary and sufficient conditions for the existence of the Hopf-bifurcation for ρ1 = ρ1*, if it exist are (i) Ai(ρ1*) > 0, i=1, 2, 3 (ii) A1(ρ1*) A2(ρ1*) – A3(ρ1*) = 0 and (iii) the eigenvalues of the characteristic Equation should be of the form λi = ui+ivi, and
Theorem 3.1. μ2 determines the direction of the Hopf bifurcation: if μ2>0 (μ2<0), then the Hopf bifurcation is supercritical (subcritical) and the bifurcating periodic solutions exist for ρ2 > ρ2* (ρ2 < ρ2*); β2 determines the stability of bifurcating periodic solutions. and T2 determines the period of the bifurcating periodic solutions, the period increases (decreases) if T2 > 0 (T2 < 0). Now we will study the Hopf-bifurcation[25, 11, 26] of the system without delay taking ρ1 as the bifurcation parameter. The necessary and sufficient conditions for the existence of the Hopf-bifurcation for ρ1 = ρ1*, if it exist are (i) Ai(ρ1*) > 0, i=1, 2, 3 (ii) A1(ρ1*) A2(ρ1*) – A3(ρ1*) = 0 and (iii) the eigenvalues of the characteristic Equation should be of the form λi = ui+ivi, and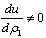 , i=1, 2, 3. After substituting the values, the condition C = A1A2-A3 becomes
, i=1, 2, 3. After substituting the values, the condition C = A1A2-A3 becomes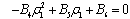 | (15) |
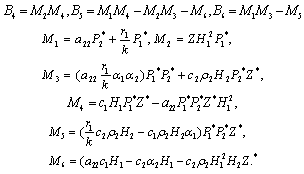 The Equation (15) has at least one positive root say ρ1 = ρ1* Therefore, one pair of eigenvalues of the characteristic Equation (8) at ρ1 = ρ1* are of the form
The Equation (15) has at least one positive root say ρ1 = ρ1* Therefore, one pair of eigenvalues of the characteristic Equation (8) at ρ1 = ρ1* are of the form 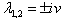 , where v is positive real number. Now, we will verify the Hopf-bifurcation condition (iii), putting λ = u+iv in (8), we get
, where v is positive real number. Now, we will verify the Hopf-bifurcation condition (iii), putting λ = u+iv in (8), we get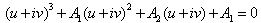 | (16) |
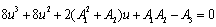 | (17) |
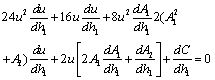 Now, since at
Now, since at 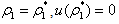 we get
we get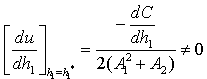 This ensures that the above system has a Hopf-bifurcation around the positive interior equilibrium E*.As above, similarly we have computed C1(0), μ2, β2 and T2 for studying the direction and stability of Hopf-bifurcating solution for the parameter ρ1 and obtain,
This ensures that the above system has a Hopf-bifurcation around the positive interior equilibrium E*.As above, similarly we have computed C1(0), μ2, β2 and T2 for studying the direction and stability of Hopf-bifurcating solution for the parameter ρ1 and obtain,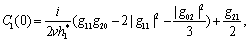
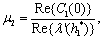 | (18) |
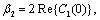
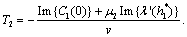 Theorem 3.2. μ2 determines the direction of the Hopf bifurcation: if μ2>0 (μ2<0), then the Hopf bifurcation is supercritical (subcritical) and the bifurcating periodic solutions exist for ρ1 > ρ1* (ρ1 < ρ1*); β2 determines the stability of bifurcating periodic solutions. and T2 determines the period of the bifurcating periodic solutions, the period increases (decreases) if T2 > 0 (T2 < 0).Now we will study the Hopf-bifurcation[25, 11, 26] of the system without delay taking h1 as the bifurcation parameter. The necessary and sufficient conditions for the existence of the Hopf-bifurcation for h1 =
Theorem 3.2. μ2 determines the direction of the Hopf bifurcation: if μ2>0 (μ2<0), then the Hopf bifurcation is supercritical (subcritical) and the bifurcating periodic solutions exist for ρ1 > ρ1* (ρ1 < ρ1*); β2 determines the stability of bifurcating periodic solutions. and T2 determines the period of the bifurcating periodic solutions, the period increases (decreases) if T2 > 0 (T2 < 0).Now we will study the Hopf-bifurcation[25, 11, 26] of the system without delay taking h1 as the bifurcation parameter. The necessary and sufficient conditions for the existence of the Hopf-bifurcation for h1 = 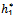 , if it exist are (i) Ai(
, if it exist are (i) Ai(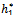 )> 0, i=1, 2, 3 (ii) A1(
)> 0, i=1, 2, 3 (ii) A1(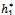 )A2(
)A2(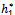 )-A3(
)-A3(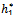 )= 0 and (iii) the eigenvalues of the characteristic equation should be of the form λi = ui+ivi and du/dh1 ≠0, i=1, 2, 3. After substituting the values, the condition C = A1A2-A3 becomes
)= 0 and (iii) the eigenvalues of the characteristic equation should be of the form λi = ui+ivi and du/dh1 ≠0, i=1, 2, 3. After substituting the values, the condition C = A1A2-A3 becomes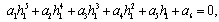 | (19) |
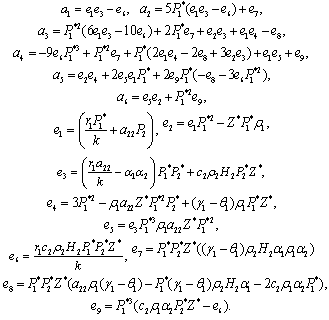 The Equation (19) has at least one positive root say h1 =
The Equation (19) has at least one positive root say h1 = 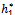 Therefore, one pair of eigenvalues of the characteristic Equation (8) at h1 =
Therefore, one pair of eigenvalues of the characteristic Equation (8) at h1 = 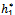 are of the form λ1,2 = ≠± iv, where v is positive real number. Now, we will verify the Hopf-bifurcation condition (iii), putting λ= u+iv in (8), we get
are of the form λ1,2 = ≠± iv, where v is positive real number. Now, we will verify the Hopf-bifurcation condition (iii), putting λ= u+iv in (8), we get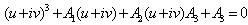 | (20) |
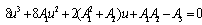 | (21) |
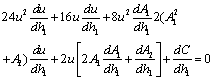 Now, since at h1 =
Now, since at h1 = 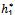 , u(
, u(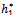 ,) = 0 we get
,) = 0 we get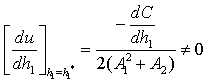 This ensures that the above system has a Hopf-bifurcation around the positive interior equilibrium E*.As above, similarly we have computed C1(0), μ2, β2 and T2 for studying the direction and stability of Hopf-bifurcating solution for the parameter h1 and obtain,
This ensures that the above system has a Hopf-bifurcation around the positive interior equilibrium E*.As above, similarly we have computed C1(0), μ2, β2 and T2 for studying the direction and stability of Hopf-bifurcating solution for the parameter h1 and obtain,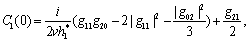
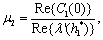 | (22) |
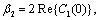
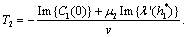 Theorem 3.3. μ2 determines the direction of the Hopf bifurcation: if μ2>0 (μ2<0), then the Hopf bifurcation is supercritical (subcritical) and the bifurcating periodic solutions exist for h1 >
Theorem 3.3. μ2 determines the direction of the Hopf bifurcation: if μ2>0 (μ2<0), then the Hopf bifurcation is supercritical (subcritical) and the bifurcating periodic solutions exist for h1 > 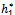 (h1 <
(h1 <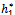 ); β2 determines the stability of bifurcating periodic solutions. and T2 determines the period of the bifurcating periodic solutions, the period increases (decreases) if T2 > 0 (T2 < 0).Similarly if we take h2 as the bifurcation parameter. The necessary and sufficient conditions for the existence of the Hopf-bifurcation for h2 = h2*, if it exist are (i)Ai(h2* ) > 0, i=1, 2, 3 (ii) A1(h2*)A2(h2*)-A3(h2*) = 0 and (iii) the eigenvalues of the characteristic equation should be of the form λi = ui +ivi, and du/dh2≠0, i=1, 2, 3. After substituting the values, the condition C = A1A2-A3 becomes
); β2 determines the stability of bifurcating periodic solutions. and T2 determines the period of the bifurcating periodic solutions, the period increases (decreases) if T2 > 0 (T2 < 0).Similarly if we take h2 as the bifurcation parameter. The necessary and sufficient conditions for the existence of the Hopf-bifurcation for h2 = h2*, if it exist are (i)Ai(h2* ) > 0, i=1, 2, 3 (ii) A1(h2*)A2(h2*)-A3(h2*) = 0 and (iii) the eigenvalues of the characteristic equation should be of the form λi = ui +ivi, and du/dh2≠0, i=1, 2, 3. After substituting the values, the condition C = A1A2-A3 becomes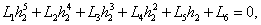 | (23) |
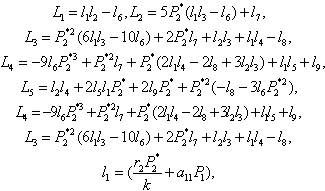
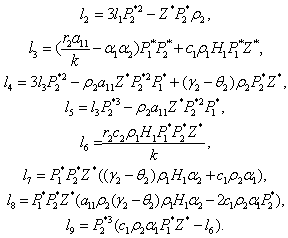 The Equation (23) has at least one positive root say h2 = h2* .Therefore, one pair of eigenvalues of the characteristic Equation (8) at h2 = h2* are of the form λ 1, 2 = ±iv, where v is positive real number and also
The Equation (23) has at least one positive root say h2 = h2* .Therefore, one pair of eigenvalues of the characteristic Equation (8) at h2 = h2* are of the form λ 1, 2 = ±iv, where v is positive real number and also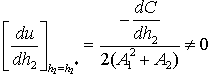 This ensures that the above system has a Hopf-bifurcation around the positive interior equilibrium E*.As above, similarly we have computed C1(0), μ2, β2 and T2 for studying the direction and stability of Hopf-bifurcating solution for the parameter h2 and obtain,
This ensures that the above system has a Hopf-bifurcation around the positive interior equilibrium E*.As above, similarly we have computed C1(0), μ2, β2 and T2 for studying the direction and stability of Hopf-bifurcating solution for the parameter h2 and obtain,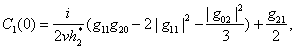
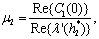 | (24) |
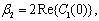
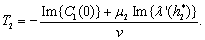 Theorem 3.4. μ2 determines the direction of the Hopf bifurcation: if μ2>0 (μ2<0), then the Hopf bifurcation is supercritical (subcritical) and the bifurcating periodic solutions exist for h2 >
Theorem 3.4. μ2 determines the direction of the Hopf bifurcation: if μ2>0 (μ2<0), then the Hopf bifurcation is supercritical (subcritical) and the bifurcating periodic solutions exist for h2 > 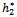 (h2 <
(h2 <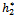 ); β2 determines the stability of bifurcating periodic solutions. and T2 determines the period of the bifurcating periodic solutions, the period increases (decreases) if T2 > 0 (T2 < 0).
); β2 determines the stability of bifurcating periodic solutions. and T2 determines the period of the bifurcating periodic solutions, the period increases (decreases) if T2 > 0 (T2 < 0).4. Stability of the Interior Equilibrium and Local Hopf Bifurcations of the Model with Time Delay
- From the previous analysis we know that this system has seven equilibriums with certain conditions. In this section, we shall study the stability of the interior equilibrium and the existence of local Hopf bifurcations because the remaining six equilibria do not show the effects of delay in the analysis process.The characteristic equation of system of Equations (1)-(3) at the equilibrium E* is
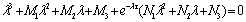 | (25) |
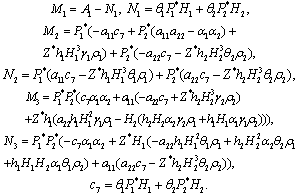 For stability of E*, all the eigenvalues of the characteristic Equation (25) should have negative real part. It is difficult to analyze the condition under which Equation (25) has all roots with negative real part. However, for zero time delay, Equation (25) becomes
For stability of E*, all the eigenvalues of the characteristic Equation (25) should have negative real part. It is difficult to analyze the condition under which Equation (25) has all roots with negative real part. However, for zero time delay, Equation (25) becomes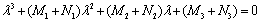 | (26) |
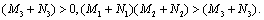 then all roots of Equation (26) have negative real parts. Obviously, iw(τ )(w > 0)is a root of Equation (26) if and only if
then all roots of Equation (26) have negative real parts. Obviously, iw(τ )(w > 0)is a root of Equation (26) if and only if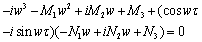 | (27) |
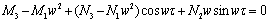 | (28) |
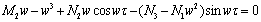 | (29) |
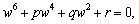 | (30) |
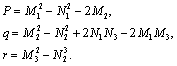 Let x = w2, then Equation (30) becomes
Let x = w2, then Equation (30) becomes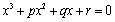 | (31) |
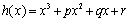 Lemma 4.1. For the polynomial Equation (31), we have the following results.(1) If r < 0, then Equation (31) has at least one positive root.(2) If r≥0 and
Lemma 4.1. For the polynomial Equation (31), we have the following results.(1) If r < 0, then Equation (31) has at least one positive root.(2) If r≥0 and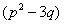 ≤ 0, then Equation (31) has no positive roots.(3) If r≥0 and ∆>0, then Equation (31) has positive roots if and only if
≤ 0, then Equation (31) has no positive roots.(3) If r≥0 and ∆>0, then Equation (31) has positive roots if and only if 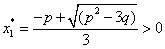 and
and 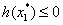 The proof of Lemma 4.1 is similar to that in the proof of Lemma 2.1 in[7], we therefore omit it here.From Equation (28) and Equation (29), we obtain,
The proof of Lemma 4.1 is similar to that in the proof of Lemma 2.1 in[7], we therefore omit it here.From Equation (28) and Equation (29), we obtain,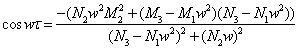 | (32) |
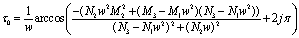 | (33) |
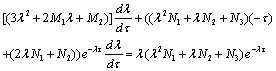 Thus
Thus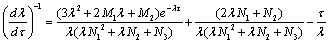 From (28)-(30), we have
From (28)-(30), we have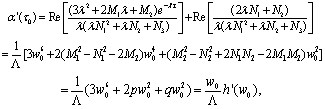 where
where 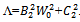 . Notice that Λ > 0 and w0 > 0, we conclude that sign
. Notice that Λ > 0 and w0 > 0, we conclude that sign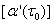 =sign
=sign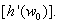 This proves the lemma.Theorem 5.1 Suppose that (H1) is satisfied(i) If r≥0 and ∆≤0, all roots of Equation (25) have negative real parts for all τ ≥0, and hence the equilibrium E* of system of Equations (1)-(3) is asymptotically stable for all τ ≥0.(ii) If either r < 0 or r≥0 and ∆> 0, x1* > 0 and h(x1*)≤0 holds then the equilibrium E* of system of Equations (1)-(3) is asymptotically stable for all τ ε[0; τ 0).(iii) If all conditions as stated in (ii) and h’(x0) ≠0 hold, then system of Equation (1)-(3) undergoes a Hopf bifurcation at the equilibrium E*, when τ =τj, j = 0,1,2,…….
This proves the lemma.Theorem 5.1 Suppose that (H1) is satisfied(i) If r≥0 and ∆≤0, all roots of Equation (25) have negative real parts for all τ ≥0, and hence the equilibrium E* of system of Equations (1)-(3) is asymptotically stable for all τ ≥0.(ii) If either r < 0 or r≥0 and ∆> 0, x1* > 0 and h(x1*)≤0 holds then the equilibrium E* of system of Equations (1)-(3) is asymptotically stable for all τ ε[0; τ 0).(iii) If all conditions as stated in (ii) and h’(x0) ≠0 hold, then system of Equation (1)-(3) undergoes a Hopf bifurcation at the equilibrium E*, when τ =τj, j = 0,1,2,…….5. Numerical Results
- In this section we used MATLAB to perform some numerical simulation on system with delay and without delay. Firstly in the absence of time delay, we took some parameter values as r1 = 2.5; r2 = 2.55, k = 20, α1= 0.01; ρ1 = 0.66; α2= 0.02; ρ2 =0.55; γ1 = 0.43; γ2 = 0.21; d = 0.1; h1 = 12; h2 = 10.8;
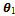 = 0.09;
= 0.09; 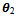 = 0.06. For this set of parameter values we observed that the positive interior equilibrium is E*(0.9127, 11.0817, 44.5116) which is asymptotically stable (see Fig. 1).
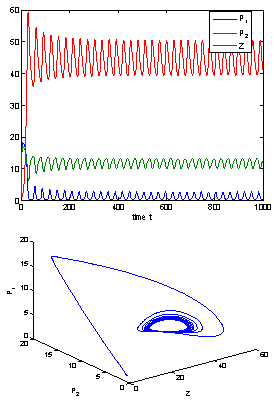
= 0.06. For this set of parameter values we observed that the positive interior equilibrium is E*(0.9127, 11.0817, 44.5116) which is asymptotically stable (see Fig. 1).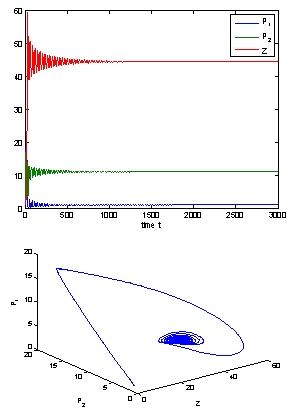 | Figure 1. The positive interior equilibrium point E*(0.9127, 11.0817, 44.5116) of system without delay is asymptotically stable |
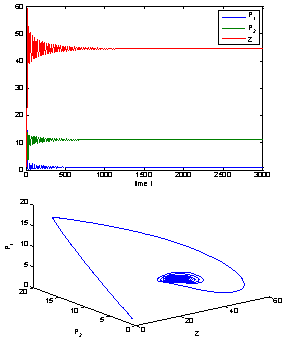 | Figure 2. The positive interior equilibrium point E* of system without delay is asymptotically stable when 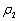 = 0.55 > = 0.55 >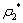 = 0.531 = 0.531 |
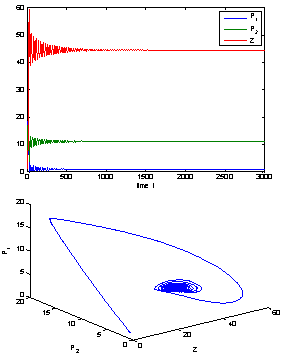 | Figure 4. The positive interior equilibrium point E* of system without delay is asymptotically stable when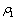 = 0.66 < = 0.66 <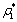 = 0.683535 = 0.683535 |
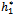 = 11:7554. Further, from the above process, we can determine the stability and direction of periodic solutions bifurcating from the positive equilibrium at the critical point
= 11:7554. Further, from the above process, we can determine the stability and direction of periodic solutions bifurcating from the positive equilibrium at the critical point 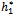 . For instance, when h1 =
. For instance, when h1 = 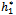 = 11:7554, C1(0) =-0.00002467-0.0001229i, Re{λ’(
= 11:7554, C1(0) =-0.00002467-0.0001229i, Re{λ’(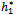 )}= -0.0124335. It follows from (22) that μ2 < 0 and β2 < 0. Therefore, the bifurcation takes place when h1 crosse
)}= -0.0124335. It follows from (22) that μ2 < 0 and β2 < 0. Therefore, the bifurcation takes place when h1 crosse 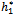 s to the left (h1 <
s to the left (h1 <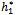 ), and the corresponding periodic orbits are orbitally asymptotically stable, as depicted in Fig. 6 and Fig. 7.If we take ρ1=0.66< ρ1*=0.683535, ρ2=0.55> ρ2*=0.53106 and h1 =12>
), and the corresponding periodic orbits are orbitally asymptotically stable, as depicted in Fig. 6 and Fig. 7.If we take ρ1=0.66< ρ1*=0.683535, ρ2=0.55> ρ2*=0.53106 and h1 =12> 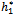 =11.7554, taking h2 as the bifurcation parameter, the transversality condition hold with these parameter when h2 =
=11.7554, taking h2 as the bifurcation parameter, the transversality condition hold with these parameter when h2 = 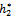 =11.2643. Further, from the above process, we can determine the stability and direction of periodic solutions bifurcating from the positive equilibrium at the critical point
=11.2643. Further, from the above process, we can determine the stability and direction of periodic solutions bifurcating from the positive equilibrium at the critical point 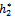 . For instance, when h2 =
. For instance, when h2 = 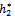 = 11:2643, C1(0) =-0.0000283042-0.000129115i, Re{λ (
= 11:2643, C1(0) =-0.0000283042-0.000129115i, Re{λ (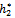 )}= = 0.00253856. It follows from (24) that μ2 > 0 and β2 < 0. Therefore, the bifurcation takes place when h2 crosses
)}= = 0.00253856. It follows from (24) that μ2 > 0 and β2 < 0. Therefore, the bifurcation takes place when h2 crosses 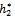 to the right (h2 >
to the right (h2 > 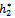 ), and the corresponding periodic orbits are orbitally asymptotically stable, as depicted in Fig. 8 and Fig. 9.
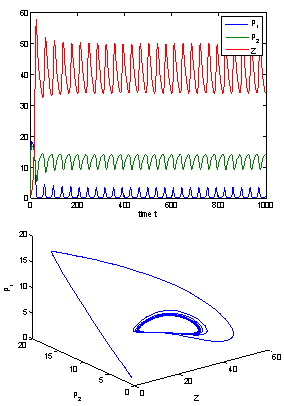
), and the corresponding periodic orbits are orbitally asymptotically stable, as depicted in Fig. 8 and Fig. 9.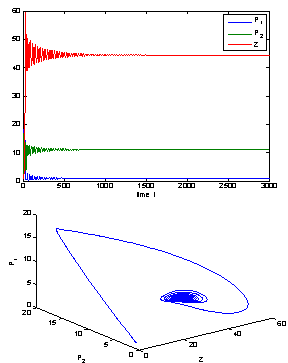 | Figure 6. The positive interior equilibrium point E* of system (1) is asymptotically stable when h1 = 12 >h1 * = 11:7554 |
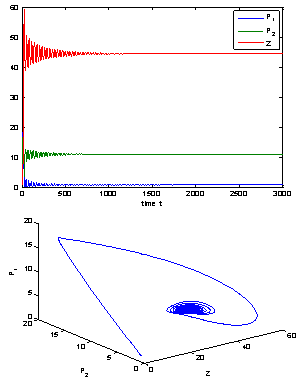 | Figure 8. The positive interior equilibrium point E* of system (1) is asymptotically stable when h2 = 10:8 > h2* =11.2643 |
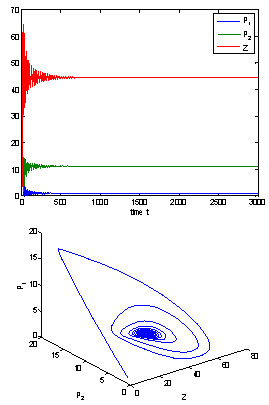 | Figure 10. The positive interior equilibrium point E *of system (1) is asymptotically stable when 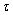 = 9 < = 9 <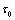 = 9.40825 = 9.40825 |
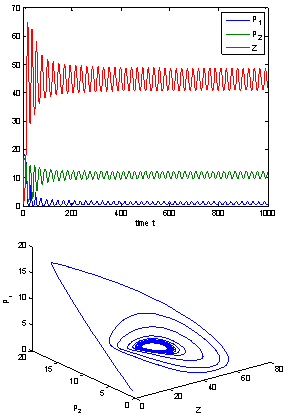 | Figure 11. When 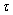 = 9.8 > = 9.8 > 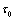 = 9.40825, the positive interior equilibrium point E* of system (1) loses its stability and a Hopf-bifurcation occurs = 9.40825, the positive interior equilibrium point E* of system (1) loses its stability and a Hopf-bifurcation occurs |
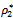 = 0.53106, h1 = 12 >
= 0.53106, h1 = 12 > 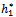 = 11.7554, and h2 = 10.8 <
= 11.7554, and h2 = 10.8 < 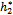 = 11.2643 the interior equilibrium point of the system becomes stable then we will study the role of time lag in the system. So we take delay as a bifurcation parameter and find out the critical value of delay parameter τ = τ0 = 9.40825, the interior equilibrium point loses its its stability and Hopf-bifurcation occurs, as depicted in Fig. 10 and Fig. 11.
= 11.2643 the interior equilibrium point of the system becomes stable then we will study the role of time lag in the system. So we take delay as a bifurcation parameter and find out the critical value of delay parameter τ = τ0 = 9.40825, the interior equilibrium point loses its its stability and Hopf-bifurcation occurs, as depicted in Fig. 10 and Fig. 11.6. Discussion
- In the previous studies, researchers have established with the help of experimental results and mathematical modeling that toxin-producing phytoplankton may be used as a controlling agent for the termination of planktonic bloom. But those studies do not contain the presence of two harmful phytoplankton in such situation. Moreover, the effect of time lags due to liberation of toxic substances and role of Holling-type II functional response cannot be ignored in this context. In this paper we have proposed and analyzed a three component model consisting of two competing harmful phytoplankton and a zooplankton. We have studied the stability behavior of the system around the feasible steady states. Our theoretical as well as numerical results show that for a certain threshold of the system parameters, the system possesses asymptotic stability around the positive interior equilibrium depicting the co-existence of all the three species. From qualitative and numerical analysis we find that ρ1 and ρ2 are bifurcating parameters for which the interior equilibrium point shows stable bifurcating solution when ρ1 is greater than the threshold value
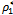 and ρ2 is less than the threshold value
and ρ2 is less than the threshold value 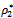 respectively. Similarly, we also find that h1 and h2 are bifurcating parameters for which the interior equilibrium point shows stable bifurcating solution when h1 is less than the threshold value
respectively. Similarly, we also find that h1 and h2 are bifurcating parameters for which the interior equilibrium point shows stable bifurcating solution when h1 is less than the threshold value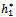 and h2 is greater than the threshold value
and h2 is greater than the threshold value 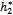 respectively. However, it is interesting to note that the dynamical nature of the bifurcating solution depends upon the parameters ρ1, ρ2, h1 and h2. When the time-lag is considered in the system, it is observed that the stable interior equilibrium point again exhibits Hopf-bifurcation for certain critical value of delay parameter.
respectively. However, it is interesting to note that the dynamical nature of the bifurcating solution depends upon the parameters ρ1, ρ2, h1 and h2. When the time-lag is considered in the system, it is observed that the stable interior equilibrium point again exhibits Hopf-bifurcation for certain critical value of delay parameter.ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- Appreciation is extended toward the C. S. I. R., New Delhi, India, for their financial support, without which this research effort would not have been possible.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML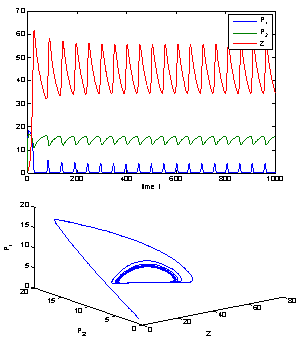
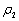 = 0.4 <
= 0.4 < 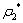 = 0.531, the positive interior equilibrium point E* of system without delay loses its stability and a Hopf-bifurcation occurs. Further, the bifurcating periodic solution is orbitally, asymptotically stable.
= 0.531, the positive interior equilibrium point E* of system without delay loses its stability and a Hopf-bifurcation occurs. Further, the bifurcating periodic solution is orbitally, asymptotically stable.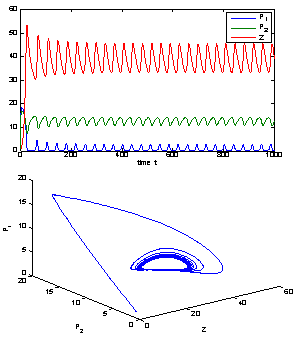
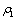 = 0.75 >
= 0.75 >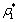 = 0.683535, the positive interior equilibrium point E * of system (1) loses its stability and a Hopf-bifurcation occurs. Further, the bifurcating periodic solution is orbitally, asymptotically stable
= 0.683535, the positive interior equilibrium point E * of system (1) loses its stability and a Hopf-bifurcation occurs. Further, the bifurcating periodic solution is orbitally, asymptotically stable