| [1] | Kew M. C. “Hepatocellular cancer. A century of progress.’’ Clin Liver Dis. 2000; 4:257–268. |
| [2] | Lai CL, Lau JY, Wu PC, Hui WM, Lai EC, Fan ST, et al. “Subclinical hepatocellular carcinoma in Hong Kong Chinese.’’ Oncology 1992; 49:347–353. |
| [3] | Sell. S.’’ Cellular origin of hepatocellular carcinoma.’’ Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2002; 13(6):419-24. |
| [4] | Esraa. M. H, Mai S. M. “A study of Support Vector Machine Algorithm for Liver Disease Diagnosis.’’ American Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2014, 4(1): 9-14. |
| [5] | Saigo, K., Yoshida, K., Ikeda, R., Sakamoto, Y., Murakami, Y., Urashima, et al. “Integration of hepatitis B virus DNA into the myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia (MLL4) gene and rearrangements of MLL4 in human hepatocellular carcinoma.’’ Hum Mutat, 2008; 29 (5): 703–708. |
| [6] | Groeger J, Flaxman AD, Wiersma ST. “Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection: New estimates of age-specific antibody to hepatitis C virus sero prevalence.’’, Hepatology. 2013; 57(4):1333-42. |
| [7] | Nobuo O, Masahiro Y, Takanobu Y, Michihiro S, Noriyuki M, Kenichi T, et al. “Evaluation of the prognosis for small hepatocellular carcinoma based on tumor volume doubling time.’’ A preliminary report.cancer 1989; 63(11): 2207-2210. |
| [8] | Mai. S.M, Esraa. M. H, Amr. Sh. “Statistical Approaches for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) Biomarker Discovery’’. American Journal of Bioinformatics Research. 1012; 2 (6): 102: 109. |
| [9] | Anant N.B, Rohit M, Abdullah F, Amit V. “Cancer biomarkers - Current perspectives.’’, Indian J Med Res 132, 2010; 132:129-149. |
| [10] | Gupta S, Bent S, Kohlwes J, “Test characteristics of alpha-fetoprotein for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C. A systematic review and critical analysis.’’, Ann. Intern. Med., 2003 Jul 1; 139(1):46-50. |
| [11] | Howard A. L, Barbara C. F, Myron J. T, Rita A. B, Kwang-J. L, Shou. D. L.B. “Des-gamma-carboxy (abnormal) prothrombin as a serum marker of primary hepatocellular carcinoma.’’, .N. Engl. J. Med, 1984; 310: 1427–1431. |
| [12] | Network CGAR, “Comprehensive Genomic Characterization Defines Human Glioblastoma Genes and Core Pathways.’’, Nature.2008; 455(7216):1061-1068. |
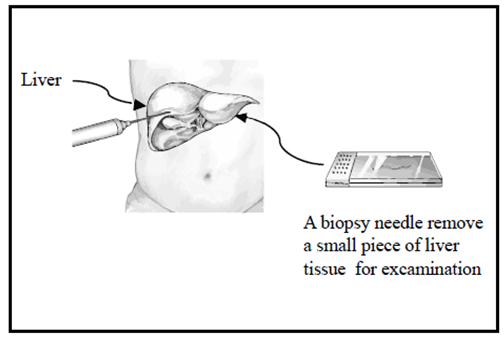
| [13] | Rockey D.C, Caldwell S.H, Goodman Z.D, Nelson R.C, Smith A.D. “Liver biopsy’’. Hepatology, 2009 Mar; 49(3):1017-44. |
| [14] | Geoffery M.D. “Diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma, In: Di Bisceglie AM, moderator. Hepatocellular carcinoma’’. Ann Intern Med.1988; 108:395-7390. |
| [15] | Alpert M.E, Uriel .J, Nechand, d. “Alpha-1 fetoglobulin in the diagnosis of human hepatoma.’’, N EngI J Med.1968; 278: 984: 986. |
| [16] | Okuda. K, Kotoda. K., Obata. H, Hayashi. N, Hisamitsu. T. “Clinical observation during a relatively early stage of hepatocellular carcinoma, with special reference to serum alpha fetoprotein levels.’’, Gastroenterology, 1975 Jul; 69(1): 226-34. |
| [17] | Khien, V. V, Mao H. V, Chinh T. T. et al. “Clinical evaluation of lentil lectinreactive alpha-fetoprotein-L3 in histology-proven hepatocellular carcinoma’’, International Journal of Biological Markers, 2001; 16(2): 105-111. |
| [18] | Tchelepi H, Ralls P.W, Radin. R, E. Grant, “Sonography of Diffuse Liver Disease.’’, Ultrasound Med, 2002; 21: 1023–1032. |
| [19] | Bennett G.L, Krinsky G.A, Abitbol R.J, Kim, S.Y, Theise N.D, Teperman LW, “Sonographic detection of hepatocellular carcinoma and dysplastic nodules in cirrhosis. Correlation of pretransplantation sonography and liver explant pathology in 200 patients.’’, AJR, 2002; 179: 75–80. |
| [20] | Yuen. M.F & Lai. C.L. “Screening for hepatocellular carcinoma: survival benefit and cost-effectiveness.’’, Annals of Oncology. 2003; 14:1463–1467. |
| [21] | Eldad. S.B & Adrian. M. DI “Diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.’’, HPB, 2005; 7: 26–34. |
| [22] | B. Josephn. B. L. “Recent Developments in the First Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.’’, Clin Biochem Rev, 2005; 26:65-79. |
| [23] | Medline plus update date 11/9/2012. |
| [24] | Chalasani N, Horlander JC Sr, Said A, Hoen H, Kopecky KK, Stockberger SM Jr, et al. “Screening for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with advanced cirrhosis.’’, Am J Gastroenterol 1999; 94(10):2988-93. |
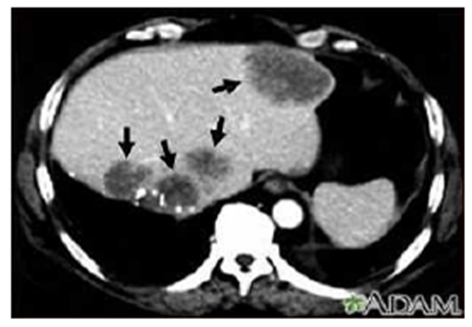
| [25] | Lim .J.H, Kim .C.K, Lee W.J, Park .C.K, K.C .Koh, Paik S.W, Joh J.W, “Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma and dysplastic nodules in cirrhotic livers. Accuracy of helical CT in transplant patients.’’, AJR, 2000 Sep; 175(3):693-8. |
| [26] | Lawrence. P, MS IV, “Common CT Findings Secondary to Liver’’, Tumors. New Jersey Medical School, 2006. |
| [27] | Janet. C.M, Susanna I.L, “Screening for Hepatocellular Cancer in Cirrhotic Patients.’’, Radiology Rounds, 2005; 3. |
| [28] | Arguedas .M.R, “Screening for hepatocellular carcinoma: why, when, how?.’’ , Curr Gastroenterol Rep, 2003; 5:57-62. |
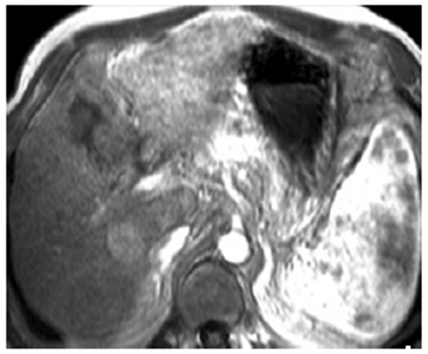
| [29] | Semelka. R.C, Martin. D.R, Balci. C, Lance T, “Focal hepatic lesions: comparison of dual phase CT and multisequence multiplanar MR imaging including dynamic gadolinium enhancement.’’, J Magn Reson Imaging, 2001 Mar; 13(3):397-401. |
| [30] | Yamshita .Y, Mitsuzaki. Yi T, Ogata I, Nishiharu T, Urata J, Takahashi M. “Small hepatocellular carcinoma in patient with chronic liver damage: prospective comparison of detection with dynamic MR imaging and helical CT of the whole liver.’’, Radiology, 1996 Jul;200(1):79-84. |
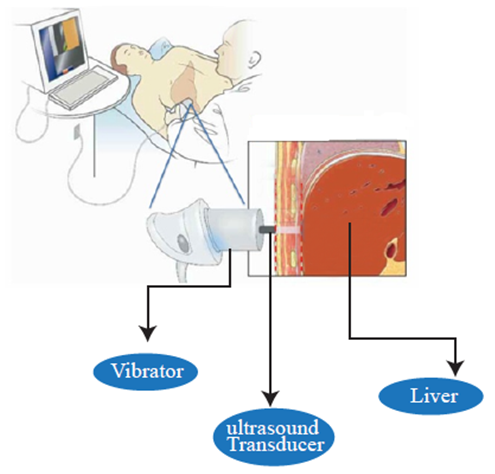
| [31] | Gheorghe. L, Iacob. S, Gheorghe C. “Real-time sonoelastography – a new application in the field of liver disease.’’ J Gastrointestin Liver Dis, 2008; 17:469-474. |
| [32] | Nezam. H A, “Fibroscan (Transient Elastography) for the Measurement of Liver Fibrosis’’, Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 2012; 8(9): 605:607. |
| [33] | Liana. G, Speranta. I, Razvan. I, Mona. D, Gabriel. B, Vlad .H, “Real Time Elastography – a Non-invasive Diagnostic Method of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhosis.’’, J Gastrointestin Liver Dis, 2009; 18:439-446. |
| [34] | Sameer. P, Davied. H, “Hepatocellular Cancer: A Guide for the Internist,’’, The American Journal of Medicine, 2007; 120:194:202. |
| [35] | Bruix, J., Sherman, M., Llovet, J.M., Beaugrand, M., Lencioni, R., Burroughs, A.K.et al, “EASL Panel of Experts on HCC. Clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma.’’ Conclusions of the Barcelona-2000 EASL conference. European Association for the Study of the Liver. J Hepatol. 2001; 35:421–430. |
| [36] | Alok. M, Mukesh. V, “Cancer Biomarkers: Are We Ready for the Prime Time?”, Cancers, 2010; 2: 190–208. |
| [37] | Ju. S. L, “Genomic Profiling of Liver Cancer’’, Genomics and informatics, 2013; 11:180-185. |
| [38] | MMarion. M & Zdenk. H, “From hepatitis to hepatocellular carcinoma: a proposed model for cross-talk between inflammation and epigenetic mechanisms.’’, genome medicine, 2012; 4(1):4-8. |
| [39] | Wentao. G, Yutaka. K, Lanlan. Sh, Yasuhiro. Sh, Tsuyoshi. S, Kenji. Y. et al, “Variable DNA methylation patterns associated with progression of disease in hepatocellular carcinomas’’, Carcinogenesis, 2008; 29:1901–1910. |
| [40] | Seon. H. Y and Yeun. J. Ch, “an Overview of Biomarkers and Molecular Signatures in HCC’’, Cancers, 2010; 2:809-823. |
| [41] | Ming. L, Lingxi. J, Xin. Y. G, “the genetic and epigenetic alterations in human hepatocellular carcinoma: a recent update’’, Protein Cell, 2014; 5:673-691. |
| [42] | Ynfei. P, Ting. Z, Victor. Re, Xuegong. Z, “An overview of hepatocellular carcinoma study by omics-based methods’’, Acta Biochin Biophys Sin, 2009;41:1-15. |
| [43] | Jin. W. K and Xin. W. W, “Gene expression profiling of preneoplastic liver disease and liver cancer: a new era for improved early detection and treatment of these deadly diseases?’’, Carcinogenesis, 2003;24(3) :363–369. |
| [44] | Chuma. M, Sakamoto. M, Yamazaki. K, Ohta. T, Ohki. M, Asaka. M, et al, “Expression profiling in multistage hepatocarcinogenesis: identification of HSP70 as a molecular marker of early hepatocellular carcinoma’’, Hepatology, 2003; 37: 198–207. |
| [45] | Luda. D, Yun. F. L, Aaron. P. C. Alex. C, Fauzia. M, et al, “Suppression subtractive hybridization: a method for generating differentially regulated or tissue-specific cDNA probes and libraries, Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA,1996; 93:6025–6030. |
| [46] | Kondoh N, Shuda M, Tanaka K, Wakatsuki T, et al., “Enhanced expression of S8, L12, L23a, L27 and L30 ribosomal protein mRNAs in human hepatocellular carcinoma’’, Anticancer Res., 2001, 21:2429-2433. |
| [47] | Kanetaka. K, Sakamoto. M, Yamamoto. Y, Yamasaki,. S, Lanza. F, Kanematsu. T. et al, “Overexpression of tetraspanin CO- 029 in hepatocellular carcinoma’’, J. Hepatol, 2001; 35: 637–642. |
| [48] | Frédérique. C, Martine H, Odile G, Marie G,. Arnaud F, Michel S, “Novel serum markers of fibrosis progression for the follow-up of hepatitis C virus-infected patients’’, Am J Pathol, 2009;175:46-53. |
| [49] | Balad. A. V, Ji Y, Talluri R, Nieto-Barajas LE, Morris JS., “Bayesian Random Segmentation Models to Identify Shared Copy Number Aberrations for Array CGH Data’’, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, 2010; 105(492): 13581375. |
| [50] | Beckmann. JS., Estivill. X, Antonarakis S.E, “Copy number variants and genetic traits: closer to the resolution of phenotypic to genotypic variability’’, Nature Reviews Genetics, 2007; 8: 639-646. |
| [51] | Korbel. J.O, Urban AE, Affourtit JP, Godwin B, Grubert F, Simons JF et al, “Paired-end mapping reveals extensive structural variation in the human genome’’, Science, 2007; 318: 420 -426. |
| [52] | Mills, R.E. et al, “Mapping copy number variation by population-scale genome sequencing’’, Nature, 2011; 470: 59–65. |
| [53] | Scherer SW, Lee C, Birney E, Altshuler DM, Eichler EE, Carter NP, Hurles ME, Feuk L,’’ Challenges and standards in integrating surveys of structural variation’’, Nat. Genet,2007; 39:.7-15. |
| [54] | Mai. S. M, Esraa. M. H, Amr. Sh, “Discrete Stationary Wavelet Transform of Array CGH Data for Biomarkers Identification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma’’, 2012; 1 (2): 148-154. |
| [55] | Subharup. G, Yi. L, and Donna. N, “Bayesian Hidden Markov Modeling of Array CGH Data’’. American Statistical Association, 2008 Jun 1; 103(482): 485–497. |
| [56] | Rudkin .G.T, Stollar. B.D, “High resolution detection of DNA-RNA hybrids in situ by indirect immunofluorescence’’, Nature, 1977; 265:472–473. |
| [57] | Lichter. P, Cremer .T, Borden. J, et al, “ Delineation of individual human chromosomes in metaphase and interphase cells by in situ suppression hybridization using recombinant DNA libraries’’, Hum. Genet, 1988; 80:224–234. |
| [58] | Jeremy. S, Eliane. F. M, Karen .L. Ch, Nigel. A. M, Ara. G. H, et al. “Localization of the human interferon-induced, “ds-RNA activated p68 kinase gene (PRKR) to chromosome 2p21-p22’’, Genomics, 1933; 16(3):768–770. |
| [59] | Gregory. E. H, Jane. B, Rosanna. W, Barbara. B, Ajay. P.et al, “Mapping of the gene encoding the integrin-linked kinase, ILK, to human chromosome 11p15.5-p15.4’’, Genomics, 1997; 42:177–179. |
| [60] | Ludwig. W, Peer. F, Micheal. G, Joerg. B, Christof. T, et al, “Induction of aneuploidy by increasing chromosomal instability during dedifferentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma’’, PNAS, 2004;101(5): 1309–1314. |
| [61] | Lichter. P. M, FISHing, “what’s the catch?’’ Trends Genet, 1997; 13:475–9. |
| [62] | Weiss. M M, Hermsen, M A, Meijer. G. A, Grieken. N. C, Baak. J. P, et al, “Comparative genomic hybridization.’’, Mol Pathol; 1999; 52(5):243-251. |
| [63] | Kusano .N, Okita. K, Shirahashi H, Harada. T, Shiraishi .K, Oga. A, Kawauchi, S. et al, “Chromosomal imbalances detected by comparative genomic hybridization are associated with outcome of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.’’ Cancer, 2002 Feb 1; 94(3): 746-51. |
| [64] | Jane. B, Jeremy. A. S, “Application and interpretation of FISH in biomarker studies’’, Cancer Letters, 2007; 249: 97–109. |
| [65] | Kallioniemi. A, Kallioniemi. O.P, Sudar. D, Rutovitz. D, Gray. J.W, Waldman. F, and Pinkel. D, “Comparative Genomic Hybridization for Molecular Cytogenetic Analysis of Solid Tumors’’, Science, 1992; 258:818–821. |
| [66] | Albertson. D.G, and Pinkel. D, “Genomic microarrays in human genetic disease and cancer’’, Hum Mol Genet, 2003; 12: 145–152. |
| [67] | Antoine. M.S, Norma. N, Richard. S, Stephanie. B, N ils. B, J ils. C, et al. “Assembly of microarrays for genome-wide measurement of DNA copy number.’’ Nat. Genet, 2001; 29:263– 264. |
| [68] | Pinkel. D, Seagraves .R, Sudar. D, Clark. S, et al. “High resolution analysis of DNA copy number variation using competitive genomic hybridization to microarrays’’, Nat Gen, 1998; 20:207–11. |
| [69] | Forozan. F, Karhu. R, Kononen. J, Kallioniemi. A and Kallioniemi. OP. “Genome screening by comparative genomic hybridization.’’, Trends Genet, 1997 Oct; 13(10): 405-9. |
| [70] | Kim .B.Y, Lee. J.G, Park. S, Ahn. J.Y, Ju. Y.J, Chung. J.H, Han. C.J, et al, “Feature genes of hepatitis B virus-positive hepatocellular carcinoma, established by its molecular discrimination approach using prediction analysis of microarray’’, Biochim Biophys Acta, 2004; 739:50-61. |
| [71] | Mantripragada. K.K, Buckley. P.G, de stahl. T.D and. Dumanski. J.P, “Genomic microarrays in the spotlight’’, TRENDS in Genomic, 2004; 20: 87-94. |
| [72] | Cheng. C, Kimmel. R, Neiman. P, and Zhao. L.P, “Array ranks order regression analysis for the detection of gene copy-number changes in human cancer.’’, Genomics, 2003; 82:122-129. |
| [73] | Kees. J, Elena. M, Aad. V, Bauke. Y, Gerrit. M, “Chromosomal Breakpoint Detection in Human Cancer, in Applications of Evolutionary Computing: Evolutionary Computation and Bioinformatics’’, New York: Springer-Verlag, 2003; 2611: 54–65. |
| [74] | Pollack. J.R, Sorlie. T, Perou. C, Rees.C, Jerey. S, Lonning. P, Tibshirani. R, Botstein. D, et al, “Microarray analysis reveals a major direct role of DNA copy number alteration in the transcriptional program of human breast tumors’’, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA ,2002;99: 12963-12968. |
| [75] | OLingjaerde. O.C, Baumbusch. L.O, Liestol. K, Glad. I.K, and Borresen. A.L, “CGH–Explorer: A Program for Analysis of Array-CGH Data’’, Bioinformatics, 2005; 21:821–822. |
| [76] | Esraa. M.H, Mai. S. M, Amr. Sh, “Circular Binary Segmentation Modeling of Array CGH Data on Hepatocellular carcinoma.’’, Radio Science Conference (NRSC), 29th National, 2012: 667 – 674. |
| [77] | Hreinn. S, Dan. R, et al., “Large recurrent microdeletions associated with schizophrenia’’, Nature, 2008; 455: 232–236. |
| [78] | Campbell .P. J. et al., “Identification of somatically acquired rearrangements in cancer using genome-wide massively parallel paired-end sequencing’’, Nat. Genet, 2008; 40: 722–729. |
| [79] | Ross .J.S, Cronin. M, “Whole Cancer Genome Sequencing by Next-Generation Methods”, Am J Clin Pathol, 2011; 36:527-539. |
| [80] | Metzker. M.L, “sequencing technologies - the next generation’’. Nat Rev Genet, 2010; 11:31-46. |
| [81] | Jens. U. M and Jesper. B. A, “Next-Generation Sequencing: Application in Liver Cancer—Past, Present and Future?’’, Biology (Basel), 2013; 1: 383–394. |
| [82] | Totoki. Y, Tatsuno. K, Yamamoto. S, Arai. Y, Hosoda. F, Ishikawa. S et al, “Highresolution characterization of a hepatocellular carcinoma genome’’. Nat Genet, 2011; 43: 464–469. |
| [83] | Olena. M, Marco A. M, “Applications of next-generation sequencing technologies in functional genomics’’, Genomics, 2008; 92: 255–264. |
| [84] | Zhengyan. K, Hancheng. Z, Xiano. L, Shuyu. L, Thomas. D. et al, “Whole-genome sequencing identifies recurrent mutations in hepatocellular carcinoma.’’, Genome Res, 2013; 23:1422-1433. |
| [85] | Kai. Z, Zhi. D, and Jian .Z, “Biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma: progression in early diagnosis, prognosis, and personalized therapy’’, Biomarker Research, 2013, 1:10. |

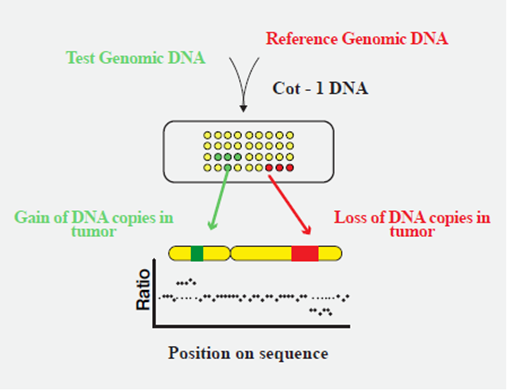
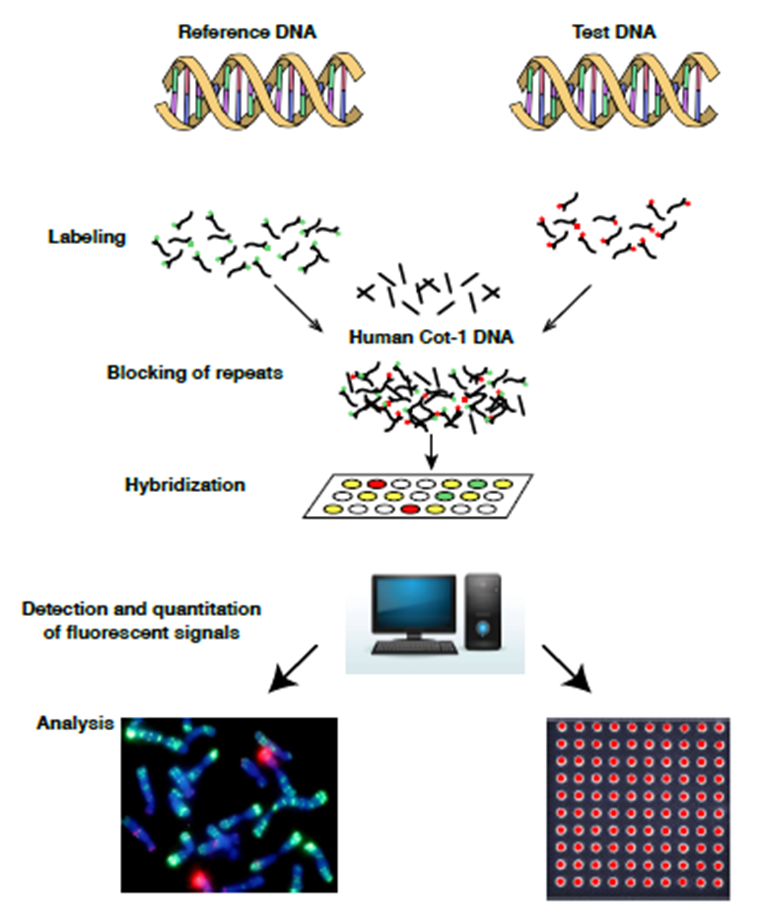
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML