-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Biomedical Engineering
p-ISSN: 2163-1050 e-ISSN: 2163-1077
2014; 4(3): 68-72
doi:10.5923/j.ajbe.20140403.03
Smart Medical Identity Card
Daniyal Rajput1, Ume Kalsoom Rajput2
1Institute of Biomedical Technology, Liaquat University of Medical & Health Science, Jamshoro, Pakistan
2Computer System Engineering, Mehran University Engineering & Technology, Jamshoro, Pakistan
Correspondence to: Daniyal Rajput, Institute of Biomedical Technology, Liaquat University of Medical & Health Science, Jamshoro, Pakistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
As you know that in advanced countries and especially developing countries, storing of medical record of a person is a big problem. Because when a person goes to doctor then doctor doesn’t know past history of disease or treatment of patient. So, it is very helpful for doctor, if a patient has old record of treatment. But it is very difficult for any patient to save old record. Our device “Smart Medical Identity Card” can solve this problem, In which we store all medical record of patient including variety of documentation of patient's history, clinical findings, diagnostic test results, blood type, prescribed drugs, preoperative care, operation notes, post operative care, daily notes of a patient's progress, medications, name diseases, name of last doctor, name of last hospital and about treatment process. It can be kept easily in pocket, purse and etc. Doctor can see all the old record of patient’s treatments and diseases in SMIC. Mainly quick access to patient’s records can be life saving, if an emergency occurs and answers to those questions that are needed during the emergency in decision-making process. It is also very helpful for providing medical records in disaster conditions. Commonly doctors get information about patient’s history by asking patients. Each time a patient visits a new doctor's office; patient fills out forms about his history, including previous surgeries or the drugs patient take on regular basis. If we forget a piece of information or if we don't write it down because it seems unimportant to us then doctors don't have that piece of our medical puzzle to work with. In SMIC, records can easily be shared. It is also helpful for patient when he goes to foreign country for treatment or other purpose. For stored data, we use chip in which data store in 0’s and 1’s form or binary form. We use NAND Flash Memory. In this card, we give particular identity number for each person, CNIC number, name, father name, date of birth, country name and etc. We also use Biometric System for securing data of patients in which we use finger print identification. We use card reader to read, write and sharing data. It is cost effective because it has low price and we don’t need to get medical reports from laboratories repeatedly. For individual patient, access to good care becomes easier and safer by SMIC.
Keywords: SMIC (Smart Medical Identity Card), NAND Flash Memory, Biometric System, Card Reader
Cite this paper: Daniyal Rajput, Ume Kalsoom Rajput, Smart Medical Identity Card, American Journal of Biomedical Engineering, Vol. 4 No. 3, 2014, pp. 68-72. doi: 10.5923/j.ajbe.20140403.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- It is a systematic collection of electronic health information about an individual patient. In developing and undeveloped countries, there are lots of systems for storing patient’s medical record. But these systems are not for Individual person. In most of developing countries, there is no any system for storing medical record. Here, I represent my example. I live at Shahdadpur in Sindh province, Pakistan. [1] Shahdadpur has population of about 2435800 but there is no any medical record saving system. In developing countries, many people live in rural areas and most of them are uneducated. They don’t have previous medical record because they don’t aware about benefits of keeping medical record. [2] In 1990, about 5 million people died worldwide as a result of injury 8.4 million people will die every year from injury, and injuries from road traffic accidents will be the third most common cause of disability worldwide and the second most common cause in the developing world. [3] Over the past decade, about 258 million people have been affected by natural disasters worldwide every year. Every year an average of 10,000 people die because of earthquakes. Floods account for about 46% of disaster-related deaths in the America. [4] The floods in Pakistan began in late July 2010 which affected the Indus River basin. Approximately one-fifth of Pakistan's total land area was underwater. According to Pakistani government data, the floods directly affected about 20 million people, mostly by destruction of property, livelihood and infrastructure, with a death toll of close to 2,000. It is estimated that by the year 2020. When a person gets injured in accident and become unconscious therefore doctor cannot get history. So, treatment is very difficult, in case of natural disaster, all the systems become partially or temporarily fail. People lose their medical record and doctors face difficulties in treatment due to lack of medical record. At that time, SMIC will be the best source for providing medical record and easy to utilize. Moreover, it will also provide medical test report who consume more time. We can save life of many people by using this SMIC because this card will provide history of injured persons without any delay. So, doctor will not need to ask with patient. It is efficient device for treatment. It is secure device by biometric system and also costs low price.
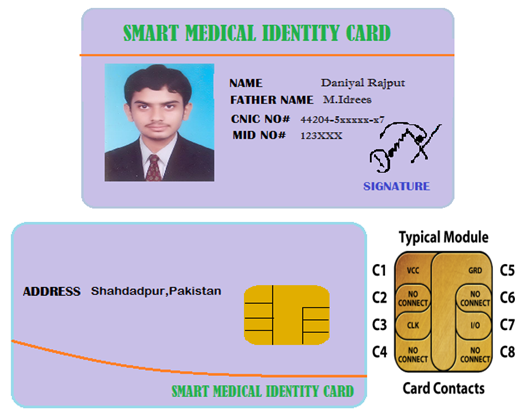 | Figure 1. An example of Smart Medical Identity Card, internal structure of Chip |
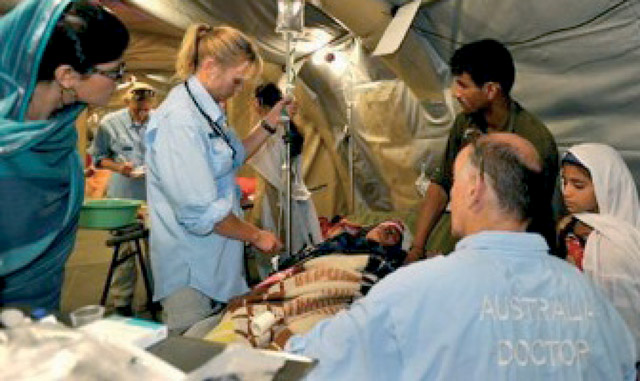 | Figure 2. It shows the treatment process during natural disaster |
2. Method
- 2.1. NAND Flash Memory2.2. Card Reader2.3. Biometric System 2.4. Output2.5. Block Diagram2.6. Flow Chart
2.1. NAND Flash Memory
- NAND Flash memory is Flash Memory. It is an electronic non-volatile computer storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The NAND type is primarily used in main memory, memory cards, USB flash drives, solid-state drives, and similar products, for general storage and transfer of data. [5] Flash memories became very popular in electronic systems. They are used to store program and data information, they allow to update firmware in the field when product is already deployed. They allow storing an immense number of files in a small single chip. The NAND Flash cell is composed of a single FET transistor equipped with extra gate called floating gate which stores the extra charge with information. The set of transistors is connected in a row one by one drain to source building up an AND gate – to read information from the selected page bit line current flows through all transistors. The one from selected page defines actual bit value. At the beginning memory cell stored just single bit of information. However, the charge on the floating gate can be controlled with some level of precision, allowing to store more information than just 0 and 1.
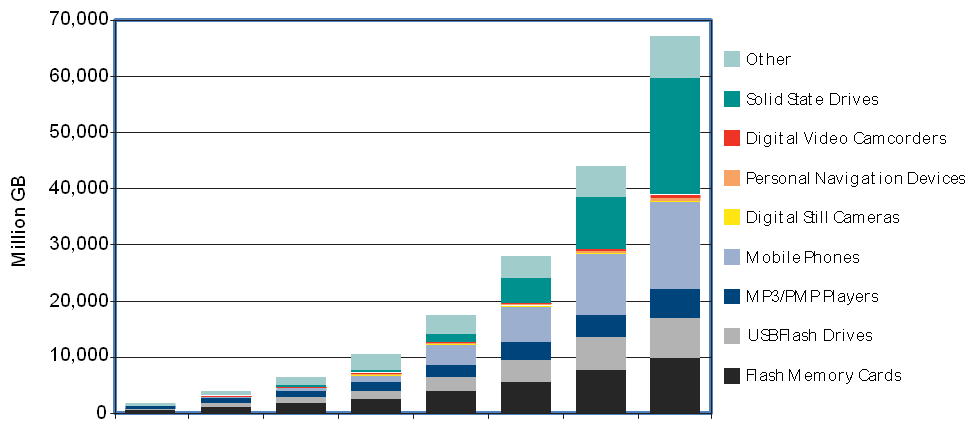 | Figure 3. Major Markets Driving NAND Flash |
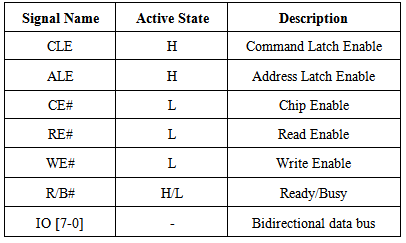
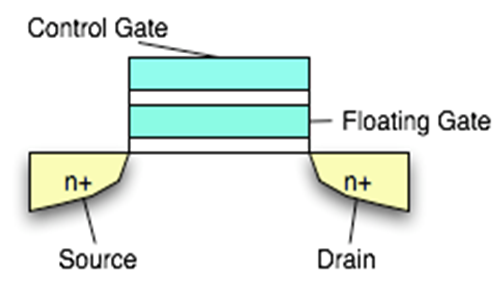
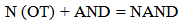 The asynchronous interface is a simple interface composed of separate read and writes signals along with chip select command and address latch. The data bus can be 8 or 16-bit wide. Data transfers are executed using full size of the bus; however, commands and addresses are always transferred in 8-bit fashion. NAND flash memory reads and writes data in units called “pages.
The asynchronous interface is a simple interface composed of separate read and writes signals along with chip select command and address latch. The data bus can be 8 or 16-bit wide. Data transfers are executed using full size of the bus; however, commands and addresses are always transferred in 8-bit fashion. NAND flash memory reads and writes data in units called “pages.
|
 | Figure 4. It shows the structure of Floating gate in FET transistor |
 | Figure 5. Show the different command’s signal along with chip |
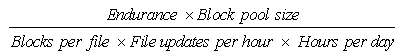 Without wear-leveling only 80 blocks are effectively used. Let’s calculate the lifetime for this case:
Without wear-leveling only 80 blocks are effectively used. Let’s calculate the lifetime for this case: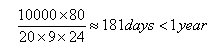 With wear-leveling, the whole memory is used, so 2048 blocks are reused - let’s calculate the lifetime of these 2048 blocks
With wear-leveling, the whole memory is used, so 2048 blocks are reused - let’s calculate the lifetime of these 2048 blocks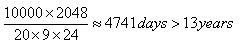
2.2. Card Reader
- A card reader is a data input device that reads data from a card-shaped storage medium. The first were punched card readers, which read the paper or cardboard punched cards that were used during the first several decades of the computer industry to store information and programs for computer systems. Modern card readers are electronic devices that can read plastic cards embedded with either a barcode, magnetic strip, computer chip or another storage medium. It is used to read, write and sharing the medical data.
 | Figure 7. Types of Card Reader which is used for read, write or sharing medical data |
2.3. Biometric System in Card
- [7] Biometric technologies are defined as automated methods of identifying or verifying the identity of a living person based on unique biological (anatomical or physiological) or behavioral characteristics. Biometrics can provide very secure and convenient verification or identification of an individual since they cannot be stolen or forgotten and are very difficult to forge. [8] Fingerprint: Humans have used fingerprints for personal identification for many centuries and the matching accuracy using fingerprints has been shown to be very high [9]. A fingerprint is the pattern of ridges and valleys on the surface of a fingertip, the formation of which is determined during the first seven months of fetal development. [10] it stores the card holder's fingerprint inside the card and is only activated each time the card holder touches a sensor on the surface of the card.
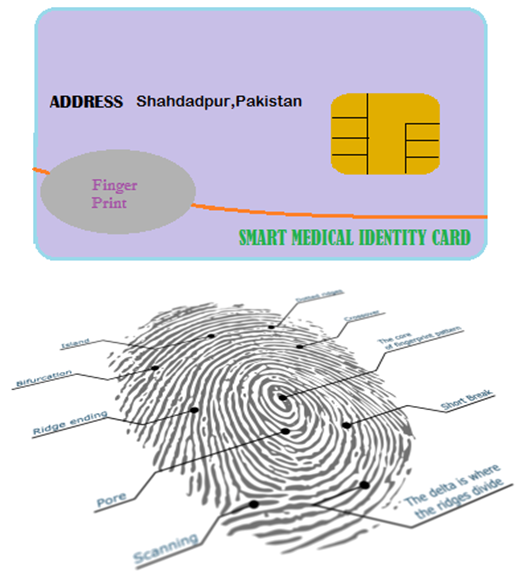 | Figure 8. Biometric technology used in SMI Card and Fingerprint use to identify friction ridge skin impressions |
2.4. Output
- We can use Monitor, Tablets, Mobile or etc for seeing output.
2.5. Block Diagram
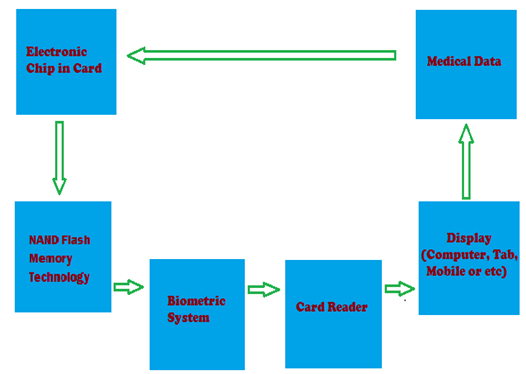
2.6. Flow Chart
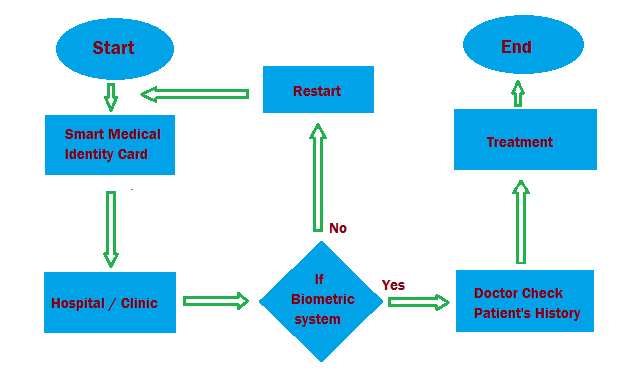
3. Conclusions
- The paper has described that the system and the research mechanism of SMIC which provides an immense help and support to individual person. Medical records help the doctor as well as patient. SMIC not only assists in treatment by providing patient’s history but also provides medical reports immediately in case of emergency because some reports consume more time. It also has some features like ease of data entry, easy to learn, reliability, ease of implementation in EMR, interactivity with other office systems, value for the money, physician satisfaction, staff satisfaction; and patient satisfaction. Allah says that if anyone saved a person, it would be as if he saved the whole humanity. No doubt, the best work is to help humanity.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The deepest gratitude with full of emotions, love and honor to our parents and all of our teachers for their kind support and prays.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML