-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Biomedical Engineering
p-ISSN: 2163-1050 e-ISSN: 2163-1077
2013; 3(6): 148-168
doi:10.5923/j.ajbe.20130306.04
Nanometre Scale Hydroxyapatite Ceramics for Bone Tissue Engineering
Gérrard Eddy Jai Poinern, Ravi Krishna Brundavanam, Derek Fawcett
Murdoch Applied Nanotechnology Research Group, Department of Physics, Energy Studies and Nanotechnology School of Engineering and Energy, Murdoch University, Murdoch, Western Australia 6150, Australia
Correspondence to: Gérrard Eddy Jai Poinern, Murdoch Applied Nanotechnology Research Group, Department of Physics, Energy Studies and Nanotechnology School of Engineering and Energy, Murdoch University, Murdoch, Western Australia 6150, Australia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The consequences of bone traumatisation, loss or damage, resulting from injury or disease can dramatically reduce the quality of life for a patient at a significant socioeconomic cost.The aim of bone tissue engineering is not only to repair, but also to initiate natural bone regeneration. The ultimate goal is to develop a synthetic tissue scaffold that uses biocompatible materials to produce an effective functional replacement for damaged bone tissue. Thus, avoiding all the problems associated with current bone transplantation procedures. However, repairing and regenerating damaged bone tissue is still a challenging task. Since the skeletal tissues are complex and the presence of foreign materials used to construct a tissue scaffold within the body’s environment will initiate an inflammatory response, which ultimately leads to failure of the repair procedure. This review discusses a number of materials currently being used or has the potential to be used in bone tissue engineering applications. In particular, the advantages and limitations of hydroxyapatite are discussed at length, since its desirable properties such as biocompatibility, bioactivity, osteoconductivity and osteoinductivity make it an ideal starting material for bone tissue engineering applications.
Keywords: Bone Tissue Engineering, Biomaterials, Tissue Scaffolds, Hydroxyapatite
Cite this paper: Gérrard Eddy Jai Poinern, Ravi Krishna Brundavanam, Derek Fawcett, Nanometre Scale Hydroxyapatite Ceramics for Bone Tissue Engineering, American Journal of Biomedical Engineering, Vol. 3 No. 6, 2013, pp. 148-168. doi: 10.5923/j.ajbe.20130306.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Today, there is a high demand for advanced biosynthetic bone-like materials for the development of biomedical devices and implants for use in tissue engineering applications. For example, tissue loss as a result of injury and diseases in an increasingly aging population reduces the quality of life for many at a significant socioeconomic cost. This is compounded by the fact that many conventional implants fail due to non-integration with the surrounding normal tissue. This leads to complications that require revision surgery to remove or repair the implant device. Furthermore, problems also exist for biomedical devices implanted within the body for the controlled release of drugs and similar clinical applications. Hence there is an all round interest to develop novel tissue engineering applications that incorporate “living” constructional materials that are similar to natural bone tissue and posses the potential to integrate with the surrounding native tissue for a faster healing outcome.Conventional medical procedures such as autograft (patient’s own bone) and allograft, (sourced from another donor) treatments for the replacement of bone loss resulting from damage or disease have met with varying degrees of success to date. Both procedures have significant risks associated with them. In the case of an autograft, donor site morbidity is a frequent outcome[1, 2], while disease transmission is potentially a serious side effect of an allograft procedure[3]. Furthermore, both procedures suffer from the limited supply of viable bone tissue. An attractive alternative to nature bone grafts is the use of tissue engineering techniques to create synthetic scaffolds that can effectively replicate the various physical, chemical and mechanical properties found in natural bone tissue.There has been considerable development over the past few decades in multidisciplinary field of tissue engineering, which has being able to produced engineered implantable human tissues such as bone, cartilage and skin[4, 5]. The research to date has clearly demonstrated that a major function of tissue engineering is to create an environment that can promote productive and efficient cellular activity for regenerative purposes. Therefore, it is very important that any potential tissue scaffold be capable of replicating the extracellular matrix (ECM) and solicits favourable cell responses. From the cellular perspective, the interaction between the cell and nanometre scale structures is crucial for controlling a variety of cell functions such as adhesion and proliferation[6].The operational demands placed on an engineered biomedical device or tissue scaffold are numerous and presents many challenges that must be overcome to achieve a successful clinical outcome. For example, the biological compatibility of the device or scaffold material is crucial in preventing any cytotoxicity, immunological reactions, and inflammation responses from the body[7–9]. The presence of any foreign material within the body environment will initiate an immediate inflammatory response at the site. As a consequence, a complex biochemical cascade of events takes place in which cells arrive and start producing chemokines, cytokines and growth factors to initiate the repair of damaged tissues surrounding the foreign material. When a scaffold is implanted into the body environment, the presence of these cells on the surface of the scaffold can initiate a foreign body reaction to the biomaterial used to manufacture the scaffold. These cells produce oxygen radicals and enzymes that have the potential to degrade the scaffold, which can ultimately lead to the failure of the scaffold[10]. Historically, a variety of different metals, ceramics and polymers have been used to repair or replace damaged bone tissue with varying degrees of success. Despite having a wide selection of biomaterials and surgical implants, no single material to date can exactly match the composition, structure, chemical and physical properties of any particular body part. This is especially true of bone tissue, with its very complex hierarchical structure and its associated biological functions such as providing a natural reservoir of healing cells and mineral ions that play an important part in maintaining the biochemical balance within the body[11, 12].Since the first total hip replacement in 1970 by Hamadouche et al, based on ceramic alumina, the use of hip and knee replacements has steadily increased worldwide[13]. Recently, the Australian Orthopaedic Association’s National Joint Replacement Registry noted that there are more than 75,000 hip and knee replacements being carried out annually. The register also indicated that there was an increasing trend of around 8% per annum in surgical procedures involving implant replacements. This trend was also reflected in the aging population statistics and also in the increasing number of implants and biomedical devices being used in younger patients[14]. This health issue is not unique to Australia, but in fact is a major global health problem facing the world today. And due to its global importance, the United Nations, the World Health Organization and 37 countries declared the period from 2000 to 2010 as the Bone and Joint Decade[15].For the last 40 years, several approaches have been employed to develop biosynthetic bone grafting substitutes for the reconstruction of osseous defects[16, 17]. These procedures offer patients restored mobility and long-term pain relief. However, it should be mentioned that the biomaterials used to manufacture the biomedical device or implant will have to operate in an environment that is both chemically hostile and at the same time very sensitive to the presence of foreign materials. Conventional metallic materials (316 stainless steel, cobalt chromium and titanium alloys) used for hip and knee replacements, unfortunately can fail due to an incompatibility between the modulus of elasticity of the orthopaedic implant and the surrounding bone tissue (stress shielding)[18]. They also fail due to low wear, corrosion resistance and lack of biocompatibility. There are currently considerable clinical concerns regarding the known toxicities associated with elements in metal implants and known pathologies such as particle induced inflammation (particles coming from wear debris) and hypersensitivity associated with metal implants degradation. The body tissues are extremely sensitive to the presence foreign particles and materials, which solicit an immune response that ultimately result’s in the rejection of the foreign particles[19]. Despite a new generation of Ti implants and a closer elastic modulus to that of natural bone, the resulting wear resistance under normal loading conditions is still poor[20].Alternative materials such as polymers and ceramics have also been investigated for possible use in a wide range of tissue engineering applications. Polymers are large molecules composed of smaller repeating structural units called monomers. These high purity monomers are usually attached by covalent chemical bonds, with cross-linking taking place along the length of the macromolecule. It is the amount of cross-linking that gives the polymer its physiochemical properties. There are many methods of producing polymer materials, but electro-spinning is one of the most effective processes used for producing nanometre sized fibres which can then be woven into a variety of components[21]. Polymers have been used in a variety of applications ranging from bone and dental cements, bone grafting materials, plates and fixation devices to load bearing applications in orthopaedics[22]. In addition to polymers, several other biosynthetic ceramic based bone substitutes have been developed[23-27]; however, to be acceptable, the material should have a high porosity and exhibit good mechanical properties, otherwise osteoconductivity and resorption at the implant site will be affected by the body’s immunological responses[28]. There has also been considerable research work into combining materials with desirable properties, while at the same time trying to avoid some of their less attractive properties. The combination of two or more materials for their favourable properties creates a new composite material with a set of unique properties that each individual components or phases do not possess. For example, bone is a natural two phase organic-inorganic ceramic composite composed of collagen fibrils forming one phase, with a well embedded array of inorganic nano-crystalline components forming the second phase[29]. Recently, a biosynthetic bone grafting composite material based on nanometre sized hydroxyapatite (nano-HAP) and silica were evaluated by Gerike et al and Gotz et al, and shown to exhibit good osteoinductivity[30, 31]. However, the biosynthetic bone graft granules had agglomerated HAP crystals attached to their surface. To fully benefit from the intrinsic physiochemical properties of nano-HAP that originates from its large surface area, it is necessary that the nano-HAP crystals are completely dispersed and are individually anchored to the underlying matrix of the composite. This problem highlights the need for careful preparation and efficient manufacture of the composite to take full advantage of the respective phases when forming the new composite biomaterial potential tissue engineering applications.
2. Bone
- The skeletal system of the human body is important for two main reasons; the first is the structural support of the organs and other related tissues, the second is related to the attachment of muscle groups that permits the motion of the body. The skeleton is constructed of a hard natural tissue called bone and cartilaginous materials. The adult human skeleton consists of some 206 bones[32]; some of these provide protection to the internal organs of the body from external forces, while others do specialized functions such as the inner ear bones that transmit sound vibrations for the sense of hearing. The bone matrix also provides a natural reservoir of healing cells and mineral ions that play an important part in maintaining the biochemical balance within the body. For example, the calcium level in the body is closely monitored and regulated (in a process called homeostasis) since calcium is an important element involved in muscular action and nerve conduction[11].
2.1. Bone Formation
- Bone formation (osteogenesis) commences as early as the foetal stage and continues throughout adulthood. During this period the softer bones of the infant slowly increase in hardness during childhood, eventually becoming quite hard by the adult stage. This hardening process or ossification is the result of the initial hyaline cartilage being transformed into bone. There are two methods in which ossification can take place, the first is by intramembranous and the second is endochondral. Both methods produce bone tissue by replacing existing cartilage; however the mechanism that is used in each case is quite different[33]. Intramembranous ossification occurs during the formation of the craniofacial bones in which mesenchymal cells instead of cartilage are transformed directly into osteoblasts. In the remainder of the body endochondral ossification takes place and begins in the embryonic stage with mesenchymal cells forming a cartilage matrix. In the following stage, osteoblasts and osetoclasts attach themselves to the cartilage matrix. During this stage the osteoclasts generate an acidic microenvironment that degrades the cartilage, while the osteoblasts build a bone matrix onto the cartilage, which now forms a scaffold structure[12, 34].
2.2. Bone: Its Hierarchical Structure and Mechanical Properties
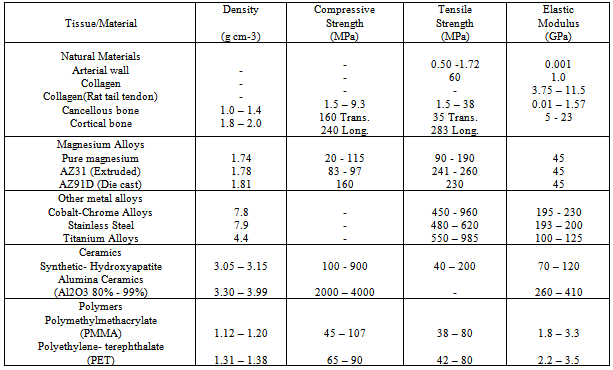
- The structural architecture of bone is hierarchical and complex[35]. It is an irregular composite material with various combinations, arrangements and orientations of its component materials at various scales that gives bone its heterogeneous and anisotropic nature[36]. The overall structure of bone makes it a remarkable biomaterial with unique physical and mechanical properties. For example, the toughness of bone is achieved by the interplay of the organic collagen scaffold that supports the inorganic mineral phase[37, 38].The hierarchical structural of bone consists of five size scales as shown in Figure 1. The first scale is the largest and is called the macrostructure, which consists of cortical and cancellous bone; the second is the microstructure, which ranges in size from 10 to 500 µm and consists of single trabeculae or osteons[35]. The oseteon or Haversian system consists of cylindrical structures composed of concentric layers or lamellae surrounding a central duct called the Haversian canal. This canal delivers the blood supply and provides connection for the nerves in surrounding bone tissue[39]. The next step down in size brings us to the sub-microstructure scale, which ranges from 1 to10 µm and contains the lamellae which are thin plate like structures that form the basic structural unit of the bone in the sub-microstructure. The fourth scale is the nanostructure, which ranges in size from around 500 nm up to 1µm and contains collagen fibre assemblies composed predominantly of collagen fibrils with implanted minerals[40]. The final and smallest scale is the sub-nanostructure, which covers the range from 500 nm and below. This size range covers the molecular structure of the individual elements, such as collagen molecules, bone mineral crystals and the non-collagen organic proteins[41].Bone is a natural two phase organic-inorganic ceramic composite consisting of collagen fibrils with embedded well-ordered inorganic nano-crystalline component. The primary organic phase of the bone matrix is Type I collagen and is secreted by osteoblast cells, which in turn forms self-assembled collagen fibrils. The fibrils are bundled together and predominately self orientate themselves parallel to the load-bearing axis of the bone. During the self assembly process the collagen fibrils, which are typically 300 nm long, develop a 67 nm periodic pattern in which a 40 nm gap or hole is formed between the ends of the fibrils while a 27 nm overlap results from the bundle behind[43]. This pattern creates discrete and discontinuous sites for the deposition of plate-like hydroxyapatite (HAP) crystals of bone, which form the second phase of the matrix. HAP is a mineral composed of calcium phosphate which has the general chemical formula of[Ca10(OH)2 (PO4)6]. It is the main inorganic component of natural bone, accounting for up to about 65% by weight of cortical bone and in teeth it accounts for 97 % by weight of dental enamel in mammalian hard tissue[44]. The discontinuous discrete sites limit the growth of the crystals and force the crystals to grow with a specific crystalline orientation, which is parallel to the load-bearing axis of the bone and collagen fibrils. The crystal plates typically have a length of 50 nm, a width of around 25 nm and on average a thickness of 3 nm[45-48]. The hydroxyapatite has also trace amounts of potassium, manganese, sodium, chlorine, hydrogen phosphate, citrate and carbonate[49]. The final component of the bone composite consists of the non-collagen organic proteins such as the phosphoprotein group, which are believed to regulate the formation of the inorganic crystal phase by influencing the size, orientation and the depositional environment within the spaces between the collagen fibrils. This organic phase is also believed to be a source of calcium and phosphate ions, which are later used in the formation of the mineral phase[50].The combination of the organic and inorganic phases of the composite bone structure perform together to give bone its unique mechanical properties. Properties such as elastic modulus, toughness, strength, stiffness, and fracture properties of this complex composite structure gives bone and the skeletal system in general its remarkable ability to withstand the various mechanical and structural loads encountered during normal and extreme physical activity[51]. Typical mechanical and physical properties of bone are presented in Table 1 along with other biocompatible materials that are currently being used or under investigation. When an implant is used within the skeletal structure for load bearing applications, its mechanical properties should be as close as possible to those of natural bone, since both will be exposed to the same external loads. If there are significant differences in the mechanical properties, with the implant having the greater loading bearing capacity, the resulting mechanical mismatch produces a much lower stress distribution in the surrounding bone. The lower stress or stress shielding, results in necrosis of the surrounding bone tissue, which ultimately leads to implant failure[52, 53]. This is why it is very important that the biomaterial used for the implant should have sufficient strength to withstand the stress created by the load, have sufficient stiffness to resist the effects of deformation without failure and have its mechanical properties match the surrounding bone tissue[54]. The type of stress the implant will experience is dependent on the application of the load. The loads that can be encountered singularly or in combinations are tensile, compressive, shearing, and tensional.
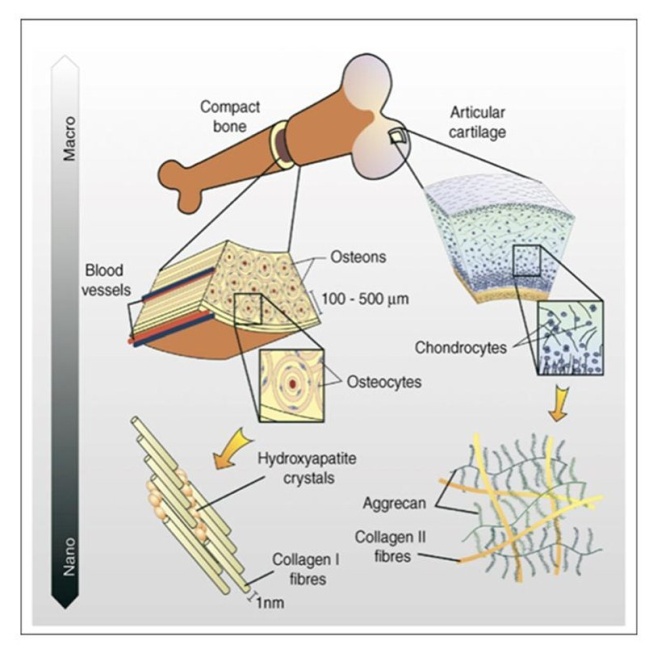 | Figure 1. Hierarchical structure of bone represented by different levels of organization from Bonzani et al.,[42] |
|
2.3. Bone Replacement Therapies
- Since the dawn of humanity, the organs and bones of the body have been subjected to a variety of medical complications such as damage, wear, disease or just the normal aging process. Unfortunately, there are times when the natural healing processes of the human body are unable to effectively repair and heal the damage or disease to the organs and bones. It is under these circumstances that medical intervention is required to correct or alleviate the problem with a suitable procedure that returns functionality and removes the pain associated with damage. Historically, the demand for biomaterials started with the Egyptians over 4000 years ago with the use of elephant’s tusks to manufacture artificial legs and teeth. Since then many civilizations such as the ancient Chinese, Indians, Greeks, Romans and Aztec’s have used gold for dentistry, gold wires for repairing fractures, glass for artificial eyes and wood for artificial legs and teeth[55-57]. Today, medicine has been able to extend the average life expectancy in many countries and in turn has increased the average lifespan of the population. One significant problem that has arisen from the aging population is the need for suitable bone replacement therapies. These bone replacement procedures can range from bone grafts needed to fill bone cavities resulting from infections and tumours resulting from disease, reconstructive surgery to repair bone damage resulting from accidents or total joint replacements to restore a patient’s mobility after their own joint has failed due to disease, injury or wear.
2.3.1. Bone Transplantation
- Apart from blood, bone is the most frequently transplanted tissue. Historically the preferred bone replacement procedure involved the use of autologous bone tissue (autograft), since it displays both excellent biocompatibility and osteogenic properties. The use of autograft’s is well established with good clinical results, which makes this procedure the gold standard for bone transplantation. There are basically two types of bone transplant procedure carried out; the first is small fragment, in which the fragments are used to induce osteogenesis. The second uses larger bone fragments, which are used to compensate for the large bone loss produced by the removal of tumours, bone cysts and traumas[65]. Every year, hundreds of thousands of people worldwide require a bone transplant[66, 67]. But problems such as donor site morbidity and limited supply sources have led researchers to investigate alternative sources of bone material. Bone tissue can be sourced from a suitable donor of the same species, which is called an allograft or it can be sourced from another species, xenograft. Medical procedures that uses xenogenic and allogenic bone grafts generally result in a significant response from the body’s immune system. In addition, there are also problems associated with the possible transmission of pathogens to the donor from the graft that needs to be addressed. In addition, obtaining bone tissue for an allograft and/or a xenograft is complicated, (medically, ethically and legally) and the grafts are expensive to process for human use. Because of these concerns there has been a great deal of interest in using man-made materials commonly called biomaterials for use in bone tissue engineering applications.
3. Biomaterials as Bone Substitutes
- An alternative to using natural bone grafts is to use a biocompatible synthetic material that possesses unique properties that can affectively replace bone tissue.To do this the material needs be biologically compatible, i.e. it should be nontoxic to the body tissues, non-immunogenic and should be chemically stable at body temperature and pH[68]. Other important properties include a high surface area for maximum cell coverage; the surface chemistry should maximize cell and tissue adhesion, support the transfer of body fluids and promote vascular activity, the material should be cable of being sterilized to remove any contamination. And finally the material should also be mechanical strong enough to withstand normal physical loading encountered in vivo[69, 70]. Biomaterials can be classified into four main groups; metals, polymers, ceramics and composites. A short discussion of each is presented below for completeness, before a detailed discussion of nanometre sized hydroxyapatite (nano-HAP) in section 5, which is the focus of this research.
3.1. Metals and Metal Alloys
- Metallic materials such as stainless steel, cobalt-chromium based alloys (Co-Cr), titanium (Ti) and its alloys have been widely used for decades to replace failed hard tissues. The high elastic modulus and yield strength, coupled with good ductility and fracture toughness makes metallic materials the ideal choice for high load bearing applications[71]. Because of these superior mechanical properties metal alloys have been used to manufacture total hip joints, bone plates, dental components, pins, screws and a variety of load bearing implants. Unfortunately, the elastic modulus and strength of metallic implants is much higher than that of natural bone tissue. Depending on the metal alloy used the elastic modulus maybe as much as 10 times greater than that of bone in the case of Co-Cr alloys and as much as 5 times for Ti alloys[72]. The mismatch between the mechanical properties of the implant and the surrounding bone tissue results in stress shielding, which in turn produces bone resorption and implant failure. In addition, because metallic materials are bio-inert, they do not biologically or chemically interact with the surrounding tissues and as a result there is very little interfacial bonding or osteointegration taking place[73]. One technique currently being used to improve the osteointegration of metallic implants is to coat it with a bioactive material such as HAP.The main disadvantages of metallic implants are; they are difficult to manufacture, are heavier than bone and they tend to suffer the effects of corrosion induced by the chemical environment of the body fluids. Furthermore, the corrosion bi-products of the metallic implants are toxic and induce an immune response. This is why the current generation of metallic implants are being manufactured from Ti alloys; they have a low elastic modulus and have a higher resistance to corrosion than conventional stainless steel and Co-Cr alloys[74]. In addition, Ti can be anodized to produce a porous oxide layer that can be used directly to improve integration with the surrounding tissues or be used as an anchoring structure for a coating of bioactive material that can integrate with the surrounding tissues[75, 76].
3.2. Polymers
- The application of biomaterials in tissue engineering for tissue repair and regeneration has generally favoured bio-inert materials for permanent bio-implants such as hip-replacements. And in the case of scaffolding materials, both natural and synthetic polymers have been investigated. Polymers are long chain molecules composed of repeated small simple chemical monomer units. Polymers have low densities, are flexible, resilient and are surface modifiable which makes them suitable for a variety of applications[77]. Typical applications of polymers are tissue scaffolds, skin augmentation, breast implants, denture bases, hip joints, blood vessels, cartilage replacement, sutures, bone screws, pins, plates and drug delivery devices[78].The operational demands placed on polymeric materials used in tissue scaffolds or implants are numerous and there are many challenges to overcome to achieve successful clinical outcome. For example, biocompatibility is crucial in preventing any cytotoxicity, immunological reactions and inflammation responses from the body[79-81]. In addition, the scaffolding material must be able to cope with the mechanical stresses resulting from the growth stages as well as prevent any rapid bulk degradation crating voids. The material must also be easily sterilised prior to application without any significant changes to its surface chemistry[82-84]. At the molecular level, this is extremely important as the surface’s topography and chemistry are key factors in gaining the correct response from the cells, which will in return promote cell adhesion and proliferation [85-88]. The findings of Andersson et al suggests that in the case of epithelial cell attachment to surfaces of similar chemistry, the morphology and cytokine production are strongly dependent on the underlying nanometre sized topography[89].Polymeric materials can be manufactured from many natural sources or from synthetic materials. Natural biodegradable materials have been extensively investigated for use in tissue engineering since the body’s natural pathways can easily handle the breakdown of their metabolic by-products. Natural polymers such as polysaccharides[90-94], chitosan[95-99], hyaluronic based derivatives[100-103] and protein-based materials such as fibrin gel[104, 105] and collagen[106, 107], have shown favourable outcomes. On the other hand, synthetic biodegradable polymers have been fabricated under controlled conditions to produce scaffolds with tuneable, predictable mechanical and physical properties. And being based on simple high purity constituent monomers, these biopolymers have lower toxicity reactions with the body and their degradation rate can easily be controlled. Examples of bulk biodegradable polymers include Poly (lactic acid), PLA[108-113], Poly (L-lactic acid), PLLA [114-117], Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid), PLGA[118-121], Poly-caprolactone PCL[122-125] and Poly (glycolic acid), PGA[126-129]. These are generally poly-α-hydrox esters that de-esterifies in the body as the polymer degrades to simple metabolites[130]. Currently available biodegradable sutures in clinical use are made from PLA and PGA. These synthetic polymers can also be made into different shapes and structures, such as pellets, disks, films and fibres as required for the specific application.Due to the fact that the extracellular matrix (ECM) has a fibrous nature and has features at the nanometre scale or sub micron level, engineering materials mimicking the ECM is the ultimate goal of many research teams worldwide. Two recent developments in nanotechnology, has been the refinement of electro-spinning and phase separation techniques to produce polymeric nanoscaffolds[131-134]. Initially developed by the textile industry, electro-spinning has been used for the past 100 years. Refinements in the past decade have seen this technique being used increasingly in the manufacture of nanometre sized fibrous polymer scaffolds. Membranes of PLA and PLGA, fibroin and collagen have been made using this technique. As shown by Agarwal et al[135], this technique is favourable and conducive for cells attaching and proliferating onto this material. This nano-fibrous electro-spun material can be further bioengineered to resemble the ECM at the nanometre scale level by coating the material with collagen macromolecules. This technique is still evolving and there are still challenges ahead. Other nano-polymeric substrates have been manufactured using phase separation techniques that produce a film of the desired polymer. Recent developments to this technique have produced nanometre-sized features over its surface to enhance the value of this material[136-138]. The studies by Ma have shown that nano-polymers by this technique have an advantage in terms of surface area and enhanced 3D connectivity for tissue engineering[139]. Furthermore, polymeric materials are effective biocompatible materials that have also been extensively investigated for the controlled delivery of drugs to specific organs within the body[140-142].Although polymers have been effectively used in a number of tissue engineering applications, polymers have a lower mechanical strength compared to metals and ceramics, so they are generally used predominantly in low load bearing applications such as soft tissue engineering. In addition there are still issues to be resolved like local inflammation resulting from the degradation products and the uneven bio scaffold degradation, which can disrupt the gradual integration of the surrounding tissues. Because of this, alternate scaffold and implant materials are currently under investigation. For example, recent studies using bioactive glass as a scaffold; revealed that when the glass was seeded with osteoblasts, a positive effect could be seen in cell proliferation[143].
3.3. Biological Ceramics
- Ceramics are non-metallic and inorganic materials that are used in hard tissue engineering applications where they are collectively termed as biological ceramics or bioceramics. The advantages of using bioceramics are; they are physically strong, both chemically and thermally stable, provide good wear resistance and are durable[144]. In addition, these materials are readily available, can be shaped to suit the application, they are also biocompatible, hemocompatible, nontoxic, non-immunogenic and can be easily sterilised[145]. The only disadvantages of using bioceramics are, they tend to be brittle, have low fracture toughness and are not resilient. But they have found application in hip joints, coatings on implants, maxillofacial reconstruction, bone tissue engineering and drug delivery devices.Bioceramics can be categorized into four types, which are dependent upon the tissue response they solicit. The first type is bio-inert ceramics, (i.e. alumina and zirconia) which are generally used in dental implants and orthopaedics[146,147]. These materials do not biologically or chemically interact with the surrounding tissues; hence they don’t solicit a noticeable response from the tissues. The second category is bioactive (i.e. bioactive glasses, hydroxyapatite and glass ceramics), these materials interact with the surrounding tissues and induce a strong osteointegrative response[148]. A typical application of these materials is the coating of titanium alloy implants to improve their osteointegration with the surrounding tissues[149]. The third type is resorbable ceramics, (i.e. tricalcium phosphate (TCP)) in this case the TCP forms a scaffold structure for new bone cells to adhere to and proliferate[150,151]. During this process the new bone tissues continue to grow and replace the scaffold structure as it is slowly resorbed[152]. And the final type is porous; this type of bioceramic permits the surrounding host tissues to penetrate into the pores of the implant (HAP coated metal and alumina implants). Because of the attractive features and properties of bioceramics there has been a significant effort into researching and developing new synthetic biomaterials such as porous coralline, calcium sulphates, and calcium phosphates, i.e. HAP[153-155]. The importance of calcium phosphates as bioceramics is discussed in detail in section 4 and particular attention is paid to HAP in section 5, a member of the calcium phosphate family and the focus of this review.
3.4. Composites
- A composite material consists of two or more distinct parts or phases[156]. The major advantage of using composite biomaterials stems from the fact a single phase material may not have all the required properties for a particular application[157]. However, by combining this phase with one or more other phases with differing physical and chemical properties it is possible to create a composite material with superior properties to those of the individual components. A good example is bone, which is a composite of Type 1 collagen and HAP, and an example of a manmade composite is coating a titanium implant with a bioactive material such as HAP or bioactive glass to promote bone attachment[158]. Similar composites have been developed to produce biomaterials for hard tissue engineering applications that have used a 2 phase HAP-polymer mixture to produce a composite with a modulus of elasticity close to natural bone[159].
4. Calcium Phosphates Ceramics
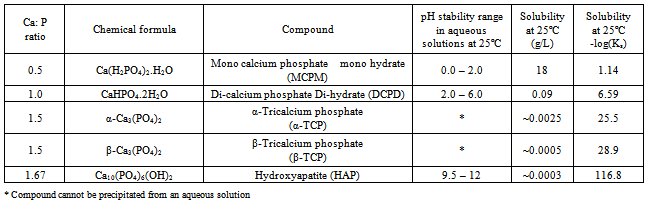
- The inorganic phase of bone is composed of a calcium phosphate (CaP) compound, namely, HAP which forms crystal platelets, a description of which was presented in section 2.2. (Bone: Its hierarchical structure). CaP compounds exist in several phases which can be discriminated by the stoichiometric ratio of calcium to phosphate (Ca:P) which is important for crystallinity, solubility and strength[160]. There are numerous Ca:P compounds, each with their own unique crystalline structure and Ca:P ratio, which means that they have different properties and form under different conditions[161]. For example, the stability of CaP compounds is influenced by controlling the Ca:P ratio, water present, formation temperature and pH[162]. The Ca:P ratio varies from 0.5 to 2.0, see Table 2, however, for ratios below 1, the solubility rates and the acidity are both high making these CaP compounds unsuitable for biomedical applications. Several members of CaP family have been used in a variety of tissue engineering applications to date. In addition, CaP compounds have been combined with collagen, to form composite biomaterials that display some similarity to natural bone tissue[163].Amorphous calcium phosphate (ACP) is the least stable solid phase of the CaP family formed in solution[164]. It is usually the first phase formed by precipitation in solutions containing high concentrations of calcium and phosphate. ACP has a Ca:P ratio of around 1.5, generally has spherical morphology and lacks any internal crystalline structure normally associated with CaP compounds[165]. It is usually considered the precursor crystalline CaP compounds, since heating can convert ACP to poorly crystalline apatite at 600℃, tri-calcium phosphate (TCP) at 800℃ and HAP around 800℃ respectively[166]. ACP has been used in mineral releasing composites for dental fillings, bone cements and for non-load bearing implants in bone tissue engineering[167].However, the two most prominent calcium phosphate bioceramics currently being used in a variety of medical procedures are TCP and HAP. Both materials are biocompatible, osteconductive and directly bond with natural bone[168, 169]. TCP is a polymorph material with two distinct phases (α-TCP and β-TCP) each phase is formed by varying the humidity and the sintering temperature. The α phase is formed in dry heat with temperatures above 1300℃ then quenching in water, while the β phase is produced in a humid atmosphere during the sintering process[166]. There are also significant differences in the properties, for example β-TCP is less soluble and less reactive than α-TCP which is unstable in water and reacts to produce HAP. A major advantage of using β-TCP in vivo is that its solubility, dissolution and re-precipitation results in a gradual phase change into carbonated apatite. The resorption of the carbonated apatite by the macrophages, giant cells and osteclasts allows the β-TCP to be gradually replaced by natural mineralized bone tissue. Both α-TCP and β-TCP have been used in bone tissue engineering applications; α-TCP is mainly used in some CaP cements while β-TCP has been used in bone cements and fillers, low load bearing implants, used to provide a degradable coating on metallic implants to induce a favourable biological response and increase oseointegration of the implant[170, 171].
|
5. Hydroxyapatite and Nanometre Scale Hydroxyapatite
5.1. Hydroxyapatite
- Due to the close chemical similarity of synthetic HAP to the natural inorganic bone matrix component, there has been an extensive research effort to employ synthetic HAP as a bone substitute or replacement in several clinical procedures[174, 175]. There are four main of advantages of using synthetic HAP; firstly, it has good biocompatibility to surrounding body tissues, secondly its biodegradability in situ is slow, thirdly it provides good osteoconductivity and finally it has good osteoinductivity capabilities[176-179]. An investigation by Taniguchi et al[180] revealed that sintered HAP provided a good biocompatible response to soft tissues such as skin, muscle and gums. It is this favourable tissue response that makes synthetic HAP an ideal candidate for orthopaedic and dental implants. This is the reason why synthetic HAP has been widely used for a variety of hard tissues applications such as; bone repair, bone augmentation, the coating of metal implants and used as a filling material in both bone and teeth[181,182].Despite its many advantages, pure HAP has unfortunately very poor mechanical strength. As a result, pure HAP ceramics are restricted to low load-bearing applications. However in some cases, combining HAP with other materials such as polymers and/or glass to form a composite material can alleviate these inherently low mechanical properties. For example materials such as high-density polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene have been successfully used to improve the load bearing capabilities of HAP[183, 184]. Another significant advantage of using HAP as a component of a composite material is that its complex structure provides a good absorption matrix for other molecules. The absorption properties of HAP have been exploited for a number of in situ applications, such as HAP-antibiotic and HAP-drug composites for slow release[186-188]. These composites have also proved to be effective in the treatment of diseases such as osteomyelitis, where the slow drug release has resulted in a successful recovery from the disease[189].
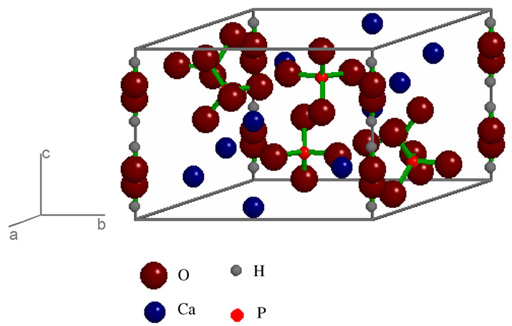 | Figure 2. The unit cell of hydroxyapatite in P63/m space group[185] |
5.2. Nanometre Scale Hydroxyapatite
- Research to date in both nanoscience and nanotechnology has highlighted the need to investigate the formation of HAP in the nanometre size range and to clearly define the properties of HAP at this scale. This is very important in nanotechnology because different forms of a material at the nanometre scale can result in significant differences in its physicochemical properties[190-193]. Parameters such as the structure of the HAP and how it is processed can influence the properties. For example when the parameters are adjusted it is possible to change the particle shape of the HAP being produced. This means that it is possible to produce rods, tubes, plates and spheres[46, 194-196]. Major improvements in the properties of HAP can be achieved when the material is synthesised in the nanometre scale[197-200].The improved properties of the HAP can also have a significant effect in interacting with surrounding body tissues[201, 202]. For example, in a HAP particle study conducted by Sun et al[197], the influence of particle size on in vivo osteoblast cells found that the inflammatory response was inhibited when smaller particles sizes (0.5 – 3.0 μm) were used. Furthermore, Hu et al was able to demonstrate that nano-HAP particles used in their study displayed a strong anti-tumour effect, and in particular the nano-HAP particles were able to inhibit the growth of hepatic tumour cells[203]. In a similar study, Li et al were able to demonstrate the beneficial effect of a nano-composite material composed of HAP and chitosan on human gastric cancer cells[204]. Similar studies have also looked using nano-HAP as a delivery platform for the slow release of drugs and gene therapies for the treatment of tumours[205, 206]. In a comparable study using nano-HAP impregnated with an antibacterial or antifungal material, it was possible to effectively inhibit the growth and proliferation of infectious microorganisms[207].Bioceramics composed of nano-HAP are currently being researched and in some cases used in a variety of medical procedures other than drug delivery. For example, nano-HAP has been extensively used in a range of bone cements and fillers which are used to provide a scaffold structure that encourages the growth of natural bone forming tissue and form an effective alternative to bone grafts in a number of procedures[208]. Currently many orthopaedic implants are based on metallic materials such as stainless steel and titanium alloys[209]; unfortunately these materials are bio-inert and do not interact or form direct bonds with the surrounding bone tissue. The use of nano-HAP has opened new opportunities in designing biocompatible coatings for metallic implants. For example, the use of plasma spraying techniques to create thin coatings that can deliver controlled thicknesses of nano-HAP that can create an effective environment for osteoconduction, protein adhesion and bone in growth[210]. Another interesting feature of using nano-HAP as a scaffold is that it can be pre-treated to produce micrometer sized cracks to simulate the cracks naturally found in bone tissue that results from repetitive stress injuries such as running or repeated lifting of heavy loads. As in the case of natural bone, the cracks in the nano-HAP can promote bone re-growth[211].The advantage of using nano-HAP lies in its ability to integrate with bone tissue, promote and support bone in growth. In fact, one interesting property of nano-HAP is that when it bonds with bone, it forms an indistinguishable union with the surrounding bone tissue. Unfortunately, there are some disadvantages of using nano-HAP; they range from the initial synthesis process, where the composition of the final product can be greatly affected by even small changes in the initial reaction conditions such as pH and formation temperature. Furthermore, nano-HAP cannot be used in bulk form to a make a load bearing orthopaedic implant because the HAP has low mechanical properties such as strength and fracture toughness. Also the solubility and bioactivity of nano-HAP is influenced by its phase purity, ionic purity and its crystalline structure. To overcome the disadvantages in the properties of pure nano-HAP, in particular its mechanical strength, composite materials composed primarily of nano-HAP combined with a variety of other materials with desirable properties have been investigated. For example, organic materials such as collagen, gelatine, chitosan and poly (lactic acid) (PLA) have been used to reinforce the nano-HAP matrix, in a similar way collagen does in the natural bone matrix, and significantly improve the mechanical properties[212-216]. Also adding nano-HAP into a polymer matrix has been found to turn a non-bioactive polymer into a bone bonding composite with improved mechanical properties such as elastic modulus and hardness[215]. The possibility of making a nano-HAP composite as strong as cortical bone with good biocompatibility, slow biodegradability in situ, and osteoconductivity and osteoinductivity capabilities by adding an extra reinforcing phase or phases makes the composite a very attractive alternative[213].
5.3. Synthesis of Nanometre Size Hydroxyapatite
- Traditionally, several procedures have been developed and used to produce HAP and calcium phosphate ceramics. These diverse procedures include homogeneous precipitation[217, 218], sol-gel[219, 220], spray dry method[221], plasma spray[222], hydrothermal[223, 224], reverse micelle[225] and ultrasonic spray freeze drying processes[226]. Of these the sol-gel is the most appealing method since it is based on a wet chemical technique that has a simple and straight forward procedure that can economically produce HAP without relying on expensive specialised equipment. Furthermore, this technique can be scaled up to meet high demands. However; the main problem in using this technique is being able to effectively fine-tune, within a small parameter range, the size and morphology of the nano-particles produced. This fine-tuning of the size and morphology is crucial in determining the properties of the resulting ultrafine nano-HAP powders.Crystalline materials can be produced from solutions, using wet chemical techniques, but a subsequent thermal treatment at elevated temperatures is required to produce the specific crystalline phases. Both the particle size and morphology of HAP produced using this technique can be efficiently controlled by varying the experimental parameters that regulate the nucleation, the aging process and the growth kinetics of the forming particles. The parameters that control the production of mono phase HAP are the initial reactants, the preparation temperature and the pH value. Both Khopade et.al[227] and An et.al[228]; using a wet chemical method were able to produced HAP particles that with a plate like structure or morphology. This structure is in complete contrast to the spherical-shaped HAP particles that are normally synthesized when ultrasonic irradiation is used during the processing stage.The most commonly used wet chemical technique is the precipitation method and it can be used to produce homogeneous or inhomogeneous calcium phosphate ceramics[229]. It is important to note that variables such as Ca:P ratios, structural defects, crystal size, temperature and the preparation procedures can have a significant impact on the electronic properties of the manufactured HAP[230]. A number of chemical routes have been used to manufacture HAP; each producing a significant variation from the normal HAP phase, and this clearly demonstrates that the HAP produced is procedure dependent[231]. Furthermore, different HAP phases can be produced by the influence of other molecules present in the manufacturing process. Wang et al successfully studied the influence of other molecules as molecular templates, for producing nanometre sized HAP rods[232]. Guo and Xiao studied the properties of nano-crystalline HAP produced during a hydrothermal process and their investigation revealed that the particle size decreased when the thermal treatment temperature increased[233]. In a similar investigation by Meissner et al. found that both size and morphology of the produced HAP could be controlled, both particle size and morphology were dependent on the precipitation temperature and the ultrasonic power used[234]. The particle size and temperature relationship has also been investigated by Laquerriere et al who were able to demonstrate that increasing thermal treatment temperatures produced a decreasing particle size[235]. In addition, Li-Yun et al confirmed the dependence of the particle’s size and morphology under ultrasonic irradiation, as they prepared a mono-phase nano-HAP material using a 300W ultrasonic transducer[236].An important procedure carried out during sample preparation is wet milling. Ultrasonic irradiation is used during the wet milling procedure as an efficient means of dispersing and de-agglomerating the sample particles during the grinding process. The sonochemical effect, which produces acoustic cavitations, also promotes both chemical reactions and physical effects that directly influence the particle morphology during the growth phase. There are a number of advantages in using ultrasonic irradiation during the manufacture of superfine particle slurries. The first is the increased reaction speed, secondly there is a significant reduction in processing time and thirdly there is an overall improvement in the efficient use of energy during the process operation[237, 238]. Preliminary work in this thesis research used a number of chemical precipitation techniques, during which several reactants were investigated. The subsequent results found that each reactant had varying degrees of success in controlling the particle size and morphology. Out of this work a new chemical route was developed that used calcium nitrate tetra hydrate[Ca (NO3)2.4H2O] and potassium dihydrogen phosphate[KH2PO4] as the main reactant materials. These reactants greatly improved the control of both particle size and morphology. The pH was regulated during the synthesis process by the addition of ammonium hydroxide [NH4OH][239]. Once the nano-HAP powder had been manufactured and dried, it was then used in its present form for advanced characterization or alternatively compacted in a hydraulic press to produce a variety of coupon sizes and shapes. The coupons were then sintered in a furnace at temperatures below the melting point, to fuse the crystals into a ceramic structure.
5.4. Properties of Porous Nano Hydroxyapatite Ceramics
5.4.1. Porosity and Permeability
- The porosity, or storage capacity, of porous HAP can be defined as the percentage of space in a material not occupied by the ceramic matrix, usually called the volumetric porosity. In the case of cortical bone the pore size ranges from 1 to 100 µm with typical volumetric porosities ranging from 5 to 10%[240]. HAP ceramics with low volumetric viscosities generally have high mechanical properties but provide only limited opportunities for cell and tissue in growth. Porous HAP ceramics have the potential to provide a good biological environment to promote cell adhesion, cellular interactions, proliferation, and migration. The downside to the increase in porosity is the decrease in mechanical properties, such as strength, stiffness and elastic modulus. Both the cellular response and the mechanical properties are dependent upon the pore size, porosity, interconnecting porosity and pore distribution. The American Society for Testing Materials (ASTM) has defined porous materials into three classifications, interconnecting (open pores), non-connecting (closed pores), or a combination of both[241]. The interconnecting porosity within the matrix scaffold is a very important property since it permits fluid flow through the porous ceramic material. The effectiveness of the fluid flow through this natural plumbing system is called the permeability.Pore sizes smaller than 10 µm define a micro-porous structure in the ceramic. The size of these micro-pores usually prevents the influx of cells into the pore structure, but fluids are still able to penetrate into and flow through the scaffold structure. When the pore size is greater than 10 µm they are classified as macro-pores and are large enough for both cells and fluids to enter the pore structure. The macro-pores have a large pore surface area to bulk volume ratio which actively promotes cell adhesion, cellular interactions, proliferation, and migration. Using techniques that can assist in forming a porous structure within the ceramic has many advantages, since the architecture of the porous structure can be controlled efficiently. The ability to select the pore size, pore geometry and the interconnecting porosity allows cell and tissue growth throughout the porous scaffold structure. For example bone forming cells grow far more efficiently when they are attached to a substrate rather than being suspended in a culture medium. In fact the ability of bone to bond with HAP is a major reason why many researchers have studied and continue to investigate this ceramic for biomedical applications[242]. When the pores are large and open, the HAP matrix is usually formed into a strut like structure, which forms the pore walls. The resulting interconnecting open face pore structure produces a network of struts that form flow channels throughout the matrix. The pore channels are conducive for cell and tissue colonisation. In addition the pore channels provide high permeability flows for the cells to be supplied with nutrients and for the removal of metabolic waste products from natural cell’s activity[243]. This type of pore structure is ideal for cells and tissue growth, but it has poor mechanical properties. On the other hand, if the pores are closed, the HAP matrix forms a network of interconnecting plate like structures that produce a high-density solid. This configuration prevents the passage of fluids or cells to neighbouring pores or the rest of the scaffold. Since the architecture of the scaffold requires a significant amount of porosity to accommodate fluid transfer and tissue in growth, an effective balance between porosity and the mechanical properties must be achieved. It simply comes down to the fact that when the porosity increases, the mechanical properties of the scaffold decrease rapidly. Furthermore, as the porosity increases, there is an increase in matrix surface area, which is exposed to the environmental effects of erosion, changing surface chemistry and cellular activity. For example, bioactive materials like HAP, exhibit surface modification with time when exposed to bodily fluids and cellular activity. So the application of high porosity, low strength biomaterials is restricted to non-load bearing applications. In this particular application, where the initial function of the scaffold is not load-bearing, then the porous scaffold can provide an effective functional implant or biomedical device.
5.4.2. Mechanical Properties
- The architecture of a scaffold for bone tissue engineering requires a significant amount of porosity to accommodate fluid transfer and tissue in growth. In addition, the mechanical properties of the scaffold must also be closely matched with those of natural bone. Therefore, an effective balance between porosity and the mechanical properties such as strength must be achieved. The fact is that when the porosity increases, the strength, along with other mechanical properties rapidly decreases. Because strength is an important property of a load-bearing scaffold, the internal architecture of the scaffold structure must be carefully considered since it strongly influences the ability of the scaffold to resist applied loads and perform successfully[244]. Therefore, by adjusting the porosity, it is possible to fine-tune the strength of a scaffold for a site-specific application[245]. The strength of a bio-ceramic composed of nanometre sized HAP powders is dependent on grain size, grain distribution, porosity, compression pressure, sintering temperature and micro-structural defects resulting from the manufacturing process. Hardness testing is frequently used to characterise mechanical properties, such as strength, of bulk solid samples and thin films. The hardness technique involves pressing a hard indenter of well-defined geometry into the surface of the sample under a predetermined load[246]. Indentation is considered an attractive method for assessing the mechanical properties of materials since it is basically a non-destructive in contrast to other techniques such as bending, compression and extension of samples[247]. Some typical mechanical properties of a synthetic HAP are presented in Table 1 along with other biocompatible materials for comparative purposes. Unfortunately, due to its low mechanical strength and brittle nature, pure HAP based ceramics are restricted to low load bearing clinical applications[248]. Current and probable future directions of research in this field will focus on efficiently combining nanometre scale HAP with other biocompatible materials to produce a composite that alleviates the lower mechanical properties of pure HAP. This is currently an active area of study with materials such as high-density polymers[183, 184], metals and bioactive glasses being investigated[249, 250].
6. Conclusions
- The consequences of bone traumatisation, loss or damage, resulting from injury or disease can dramatically reduce the quality of life for a patient at a significant socioeconomic cost. This is further complicated by the non-integration of current conventional implants and biomedical devices with the surrounding normal tissues. And as a result, revision surgery is often required to remove or repair the implant device. The aim of bone tissue engineering is not only to repair, but also initiate natural bone regeneration. The ultimate goal is to develop a synthetic tissue scaffold that uses biocompatible materials to produce an effective functional replacement for damaged bone tissue. Thus, avoiding all the problems associated with current bone transplantation procedures. From a materials point of view, the intrinsic properties of HAP offer many significant advantages to the development of a hard tissue scaffold. These favourable properties include good biocompatibility and bioactivity, slow in situ biodegradability and good which can osteoconductivity and osteoinductivity capabilities complement bone remodelling.Despite substantial progress in the manufacture of HAP and HAP based ceramics, there are still significant challenges to overcome. For example, fine tuning of the ceramics mechanical properties to match those of natural bone will permit uniform distribution of stresses in situ and prevent stress shielding. Future research into improving the mechanical performance of HAP ceramics lies in investigating potential composites composed of HAP and suitable additives that could significantly enhance the composites performance and stability in situ. The development of these new improved HAP based composites would require that their structure and mechanical properties be optimized to effectively mimic bone. The challenge will be to find suitable biocompatible additives with desirable properties that can be incorporated with the HAP to form a composite with superior mechanical properties without soliciting any unfavourable inflammatory responses. Recent studies of HAP based composites composed with blended natural polymers such as chitin; chitosan and collagen have shown both improved biocompatibility and mechanical properties[251, 252]. For example, Rivera-Munzoz has demonstrated that the inclusion of small concentrations of gelatine, (typically around 10%) can produce dramatic improvements in the compressive strength[253]. While studies by Balani et al. have shown the inclusion of carbon nano-tubes (CNT) and Al2O3 into the matrix could significantly improve the mechanical properties of the HAP composite[254]. And recently, Venkatesan et al. has investigated the properties of a CNT-chitosan-HAP composite for potential tissue engineering applications[255]. The construction of these new HAP based composites could also initiate further investigations into the effects of scale on the chemical-physical properties at both the nanometre and micrometre scales. In addition, surface functionalization of the HAP material could also be used to incorporate slow release biological active molecules, which could promote both cellular activity and bone integration. Future studies in bone tissue engineering using a combination of the above mentioned techniques have the potential to create a more efficient regeneration of traumatised, lost or damage skeletal tissue and result in a more successful clinical outcome.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This work was partly supported by the Western Australian Nanochemistry Research Institute (WANRI). Dr Derek Fawcett would like to thank the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation for their research fellowship. The authors would like to thank Mrs. Sridevi Brundavanam for her assistance in the preparation of this review article.
Disclosure
- The authors report no conflict of interest in this work.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML