-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Biomedical Engineering
p-ISSN: 2163-1050 e-ISSN: 2163-1077
2013; 3(3): 54-62
doi:10.5923/j.ajbe.20130303.02
Anabolic Steroid Treatment Induces Cardiac Autonomic Dysfunction in Rats: Time-Course of Heart Rate Variability
Moacir Marocolo1, Alex Souto Maior2, Pedro Lourenço Katayama1, Gustavo Ribeiro da Mota1, Octavio Barbosa Neto1, André de Assis Lauria3, Edil Luis Santos4
1Master Program in Physical Education and Sports, Federal University of TrianguloMineiro, Uberaba, MG, Brazil
2Castelo Branco University, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil
3Master Program in Biodynamic of Human Movement – Federal University of Juiz deFora, Juiz de Fora, MG, Brazil
4BiomedicalEngineeringProgram–COPPE/UFRJ Federal Universityof Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil
Correspondence to: Moacir Marocolo, Master Program in Physical Education and Sports, Federal University of TrianguloMineiro, Uberaba, MG, Brazil.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
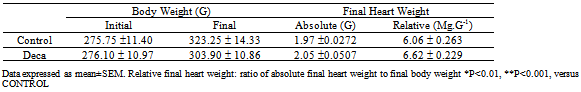
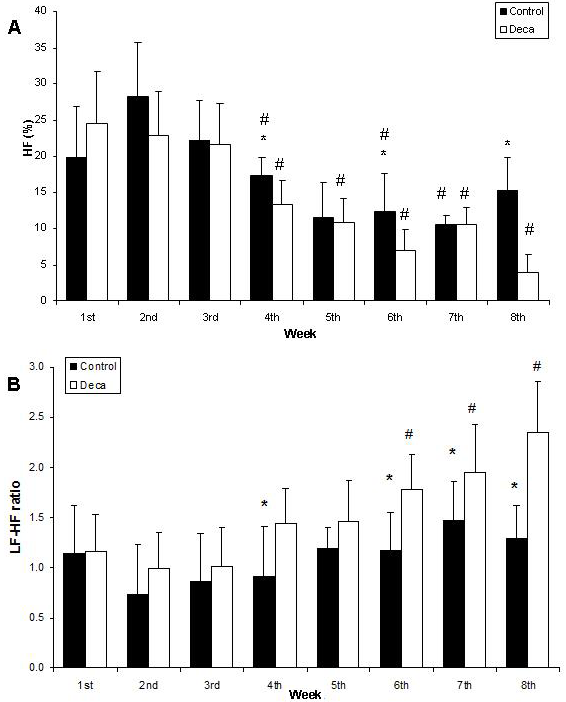
The aim of this study was to investigate time-course of cardiac autonomic activity in rats treated with nandrolonedecanoate (DECA). Twenty male Wistar rats received weekly 10 mg.Kg-1 of DECA (DG) or vehicle (CG) during 8 weeks. To heart rate variability analysis SDNN (standard deviation of RR intervals), RMSSD (square root of the mean squared differences of successive RR intervals), pNN5 (percentage of successive RR interval differences greater than 5ms) and Poincaré analysis was applied in time-domain. Additionally, power spectral was decomposed into high (HF: 0.8-2.5Hz) and low-frequency (LF: 0.2-0.85Hz). For the HF component, differences were found between DG and CG during 4th, 6th and 8th weeks. Progressive increase in the LF-HF ratio was found in DG, resulting in significant differences between groups in 4th, 6th, 7th and 8th weeks. DG showed decreased from 24.5±7.2ms2 to 3.9±2.55ms2 in HF corresponding (83.9% of alteration). Power spectral density function for HF corresponded to 26.3±8.3% and 26.5±4.1% in the 1st and 8th weeks (P=NS) for CG, whereas the DG showed reduced significantly from 26.4±3.6% (1st) to 18.99±2.7% (8th week). Cardiac autonomic dysfunction may constitute an early consequence of DECA administration and an important marker of arrhythmia vulnerability and sudden death identification.
Keywords: Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid, Autonomic Nervous System, Heart Rate Variability, Spectral Analysis, Nandrolonedecanoate, PoincarÉ Analysis
Cite this paper: Moacir Marocolo, Alex Souto Maior, Pedro Lourenço Katayama, Gustavo Ribeiro da Mota, Octavio Barbosa Neto, André de Assis Lauria, Edil Luis Santos, Anabolic Steroid Treatment Induces Cardiac Autonomic Dysfunction in Rats: Time-Course of Heart Rate Variability, American Journal of Biomedical Engineering, Vol. 3 No. 3, 2013, pp. 54-62. doi: 10.5923/j.ajbe.20130303.02.
1. Introduction
- Testosterone is an androgenic-anabolic hormone synthesized in the Leydig cells in men and theca cells in women. Testosterone and other androgenic-anabolic steroids (AAS) stimulate the commitment of pluripotent mesenchymal stem cell toward myogenic lineage rather than adipogenic lineage, hence increase the size of both type I and type II muscle fibers[1, 2] AAS are synthetic derivatives of testosterone, which were developed in order to enhance the anabolic and, otherwise, to attenuate the androgenic effects of testosterone[3]. Given the significant anabolic effect and the associated tissue building properties, Nandrolonedecanoate(DECA) is one of the most often AAS consumed around the world by athletes and non-athletes[4]to improve the physical performance related to muscular mass and strength [5, 6]. The physiological action of AAS may besummarized as a migration of a steroid-receptor complex to the nucleus, where the transcription of genes into mRNA promotes protein synthesis[7, 8]. Nonetheless, the use of high-doses of AAS during the last years has been attributed as the main cause of several cardiovascular disorders, including arterial hypertension[9, 10], lipid profile abnormalities[11], heart failure[12], hypertrophic cardiomyopathy [13], arrhythmia [14], and sudden death [15, 16], generating a serious public health problem [17].Nowadays, the analysis of heart rate variability (HRV) has been widely used as an indirect assessment of cardiac autonomic alterations, associated to immune dysfunction, inflammation, as well as a large range of cardiovascular diseases and sudden death[18-21]. Considering the decreased vagal function as a key factor for all the major risk factors for cardiovascular diseases[21], the HRV analysis may provide a noninvasive method for estimating the sympatho-vagal balance[20, 22], providing independent prognostic information about ventricular arrhythmia [23-25]. Accordingly, both the power spectral [20, 23] and the Poincaré[26] analysis of HRV has been applied to identify cardiac electrical instability. Nevertheless, while marked reductions in the parasympathetic activity was associated to cardiac autonomic impairment after treating with DECA [25], the role of the autonomic nervous system and AAS effects, showing the autonomic early possible effects induced by chronic high doses of AAS remains unknown. Thus, the purposes of this study were: 1 - to investigate “in vivo” the time-course of cardiac autonomic dysfunction in rats treated with DECA, using time- and frequency-domain HRV analysis; and 2 – evaluate a nonlinear method to analyze HRV in this experimental model.
2. Material and Methods
- Experimental AnimalsTwenty male Wistar rats were kept at 25 ±2 °C with free access to rat chow and water ad lib following the guidelines of the institutional animal care and use committee. Animals were randomly allocated into two experimental groups: Control Group (CG, n=10) and DECA Group (DG, n=10). All animals received humane care in compliance with the “Principles of Laboratory Animal Care” formulated by the National Society for Medical Research and the “Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals” published by the National Institutes of Health (NIH publication 85-23, revised 1985).During 8 weeks DG received 10 mg.Kg-1 of intramuscular DECA (DecaDurabolin, Organon®; gluteus medium) weekly and CG received the same volume of vehicle, composed of peanut oil with benzyl alcohol (90:10, V/V) [27, 28].This dose was calculated from thetherapeutic doseof nandrolonedecanoate(about1 mg.Kg-1 each 3weeks). The dose usedin the studypresentsvaluesconsideredsupraphysiological. Reports ofuse byelite athletes had shown do sages between 350-600mg weekly, which corresponds to a rate ofapproximately5-7mg/kg (NATIONAL INSTITUTE ON DRUG ABUSE, 2013).The study was in accordance with the ‘‘Principles of laboratory animal care’’ (NIH publication No. 85-23, revised 1985), and was approved by the Institution’s Animal Care and Use Committee of our University (protocol number 202/2011).Biometric MeasuresBody weights were measured weekly (Marte A-500®). Additionally, at the end of the 8th week animals were anesthetized and sacrificed by cervical dislocation. The hearts were quickly removed and the heart weight was measured (Marte A-500®). Finally, the index of cardiac hypertrophy was expressed as quotient between heart and body weights.Electrocardiogram Acquisition and MeasurementPrior to ECG recordings, animals were conditioned for 7 consecutive days, 20 minutes each day, inside a plexiglass restrainer. All posterior recordings were conducted in a constant environment, during the morning (0700-1100h). After carefully shaving the ventral thoracic region of animals, they were clothed with a custom-made elastic cotton jacket developed to fit the rat’s mean thoracic circumference. Two rectangular pieces of platinum electrodes (7.0 x 3.0 mm) were attached to the jacket’s inner surface. The ECG was acquired in a lead close to DII, maintaining prominent R wave peaks. A conductive ECG gel was applied over each electrode, with care being taken to avoid the establishment of a gel bridge between them. Animals were placed inside a plexiglass restrainer (Figure 1). More details of ECG acquire method see [29]. Electrodes were connected to a differential A/C amplifier (A-M Systems, USA), digitized by a 16 bit A/D interface converter (Digidata 1322-A, Axon Instruments, USA), and sampled at 2 KHz by the software Axoscope 9.0 (Axon Instruments, USA). Data were stored in a PC for off-line processing. The ECG recording started 5 minutes after placing each animal inside the plexiglasrestrainer and was conducted for 12 minutes [29].Illustrates the validated method for electrocardiogram acquisition in conscious rats.Jacket placement on the rat (A).schematic diagram of the inner face of the jacket, illustrating negative and positive electrodes positions. LAL – left anterior limb; RAL – right anterior limb (B). Restrained animal in rest during signal acquisition (C). (Adapted from Annals of the Brazilian Academy of Sciences29)Heart Rate Variability Analysis
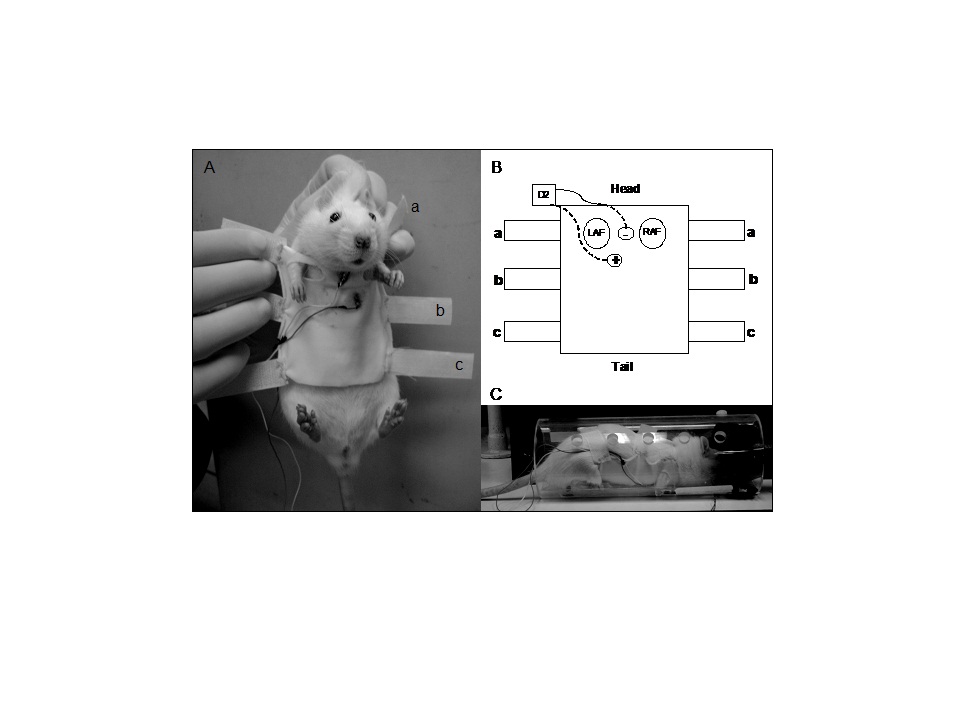 | Figure 1. Electrocardiogram acquisition method |
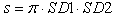 | (1) |
3. Results
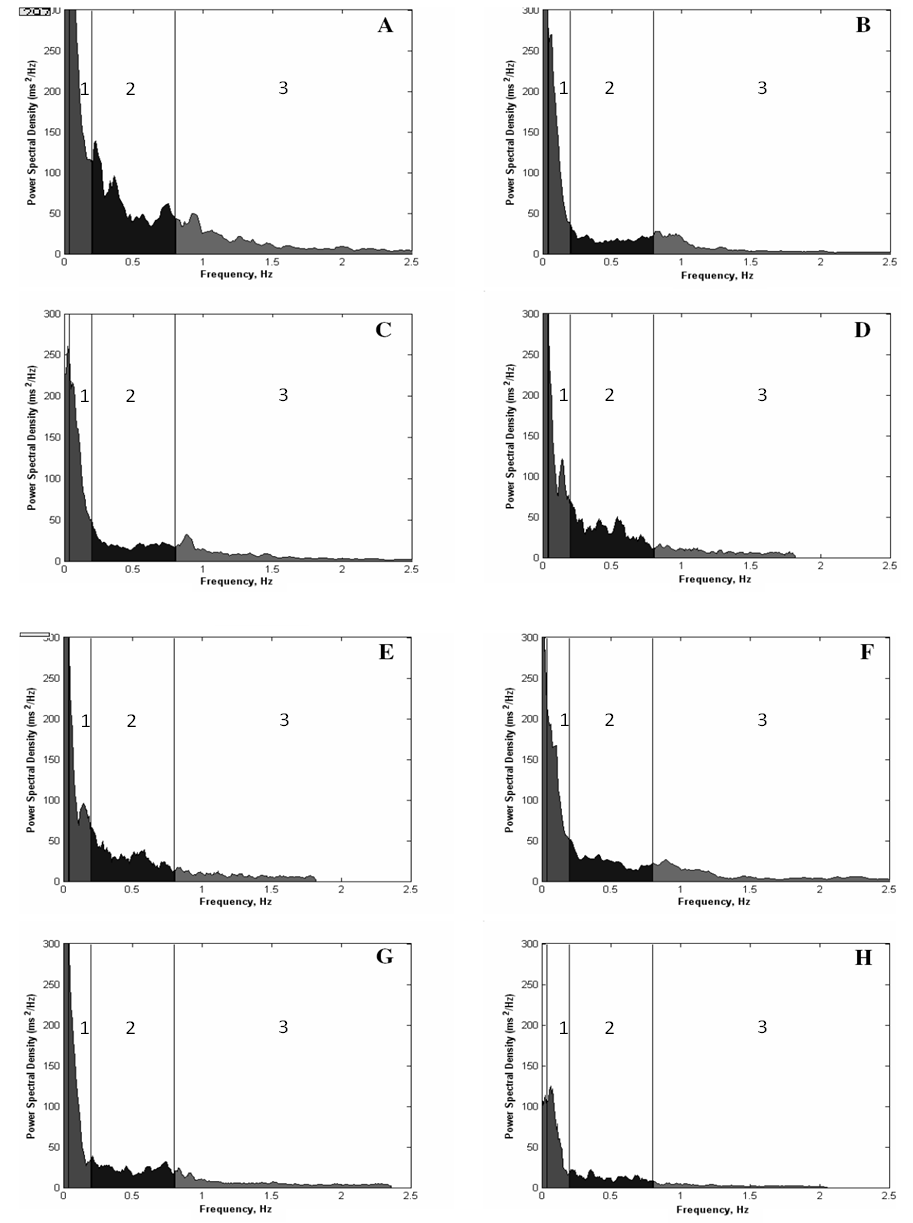
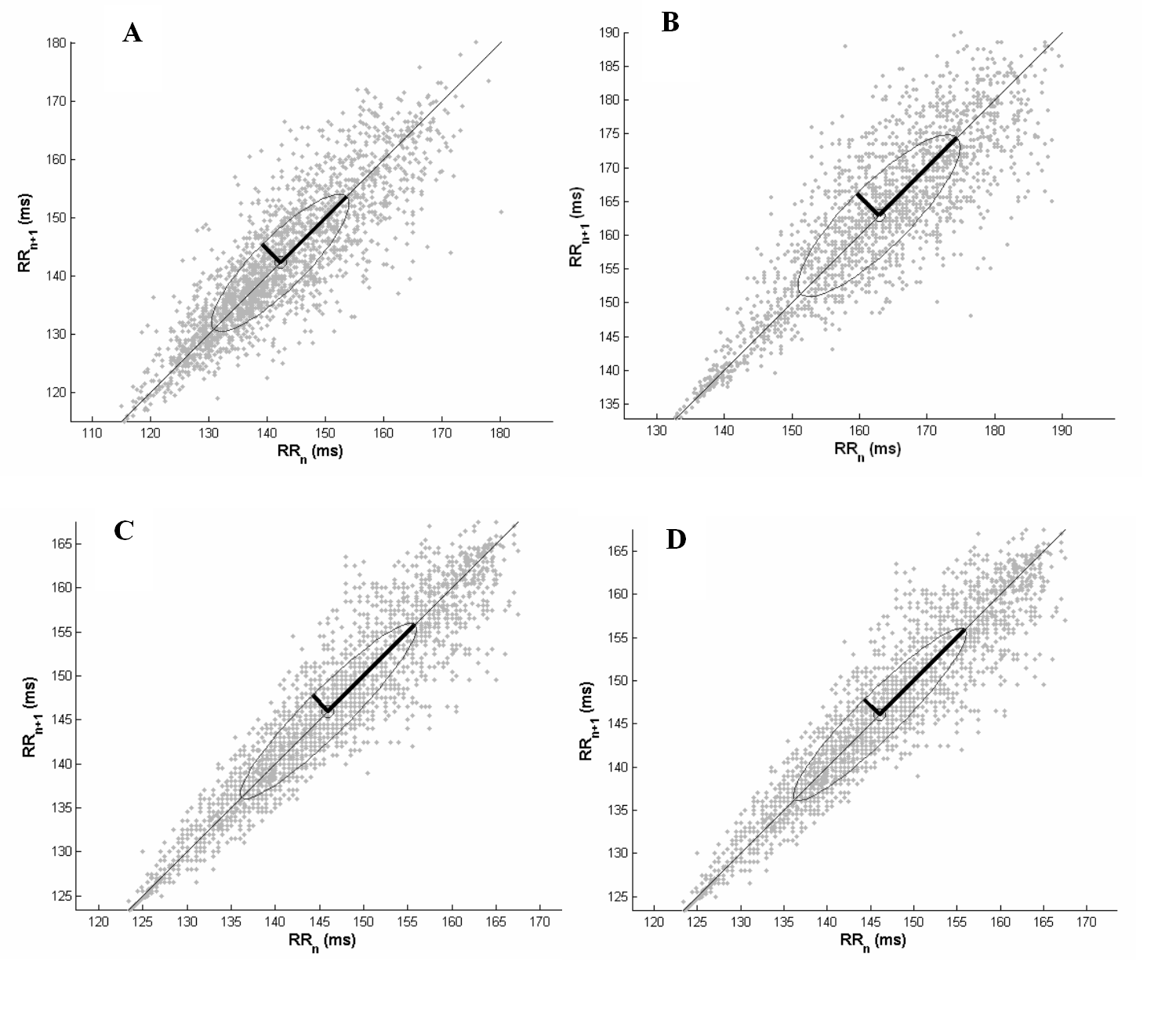
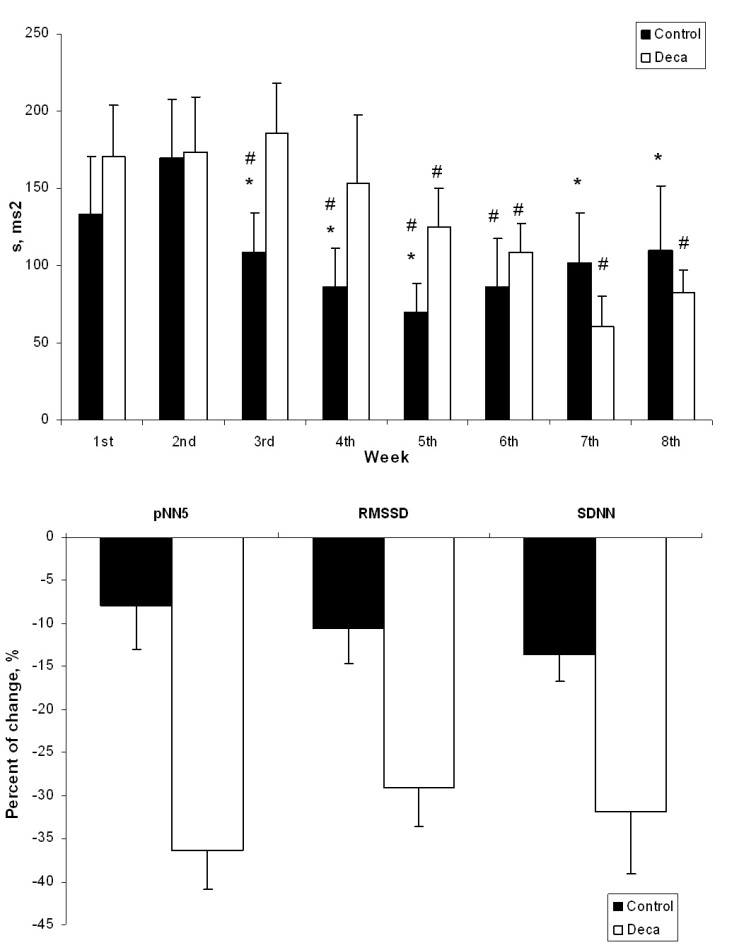
- The effects of AAS treatment on the body weight of rats showed no diferences.The final heart weight was not different between the groups when compared in absolute and relative values (Table 1).Figure 1 illustrates the mean power spectrum in DG throughout the eight weeks of AAS treatment. As depicted by panels A to H, there is a reduction in the PSD total area regarding all the frequency components. During the first week the total PSD averaged 81.9 ± 15.7 ms2, reaching 41.0 ± 6.4 ms2 at the end of the 8th week (P<0.05), while in the vehicle, the total PSD established around 51.8 ± 14.3 ms2.Nonetheless, this characteristic was quite stronger in the high frequency component, and further, is noticeable in Figure 2 (Panel A), where the PSD for the HF component is plotted. Although only significant differences have been found between DG and CG groups during the fourth (P=0.01), sixth (P=0.02) and eighth (P=0.006) weeks, the tendency to reduce the HF component is supported by the differences achieved along time only for the DECA group, from the 4th until the 8th week (P<0.05). Besides the decreasing in the HF PSD% of the vehicle throughout treatment, the DG decreased from 24.5 ± 7.2 to 3.9 ± 2.5 (P<0.01), corresponding to an alteration of 83.9%. Moreover, given that the total PSD diminished in both groups, the relative PSD for HF (Figure 2 A) corresponded to 26.3 ± 8.3% and 26.5 ± 4.1% at the first and eighth weeks (n.s.) for vehicle, whereas the DG reduced significantly from 26.4 ± 3.6% (1st week) to 18.9±2.6% (8th week) (P=0.031). Accordingly, panel B (Figure 2) shows a progressive increasing in the LF-HF ratio quite expressive in the group treated with AAS resulting in significant increasing from the 6th to the 8th week, and similarly differences between groups in the 4th (P=0.03), 6th (P=0.02), 7th (P=0.04) and 8th (P=0.002) weeks. Figure 3 illustrates the Poincaré plot for both groups. The top panels represent the CG (A) and DG (B) in the first week, and the bottom panels are CG (C) and DG (D) in the eighth week. In view of the above considerations, it is possible to distinguish a reduction in the orthogonal dispersion to the identity line, corresponding to a flattening in the ellipsis. This effect can be represented by the SD1 and further corresponds to the short-term variability and likewise the high frequency component of PSD.
|
4. Discussion
- To our knowledge, this is the first report to evaluating the cardiac autonomic control assessed weekly following two different methods based exclusively on the HRV analysis. We showed that the time-course of deleterious effects over the heart function were able to detect early signals of cardiac autonomic dysfunction in rats chronically treated with DECA. Furthermore, the noninvasive method for ECG acquisition was of remarkable use, since it allowed a continuous evaluation of HRV over the 8-week period.Cardiac hypertrophy is often associated to sudden death and arrhythmias in endurance athletes and AAS users [37-39] and further, a number of autonomic dysfunctions may be generated by the cardiac remodeling[40]. In rats, the degree of cardiac hypertrophy has been accessed through the heart weight/body weight ratio [41]. Accordingly, Andrade et al. [42] showed an increase in heart weight and heart weight/body weight ratio after 4-weeks of DECA treatment in rats, confirming the left ventricular hypertrophy by morphometrical and histological analysis. Even though the results achieved here may corroborate the well-known AAS-induced effect on body weight gain of rats, contrarily to previous works [25],in the present study no significant increase in the weight/body weight ratio was recorded. It is possible that this divergence may have occurred due to differences in animal weight at the start of treatment, once Pereira-Jr[25] used animals with ~ 357 g. Different from our previous findings [25] in which older animals were treated with DECA, resulting in significant attenuation of body weight gain, herein no significant differences in the animal body weight were observed between groups. Some investigations showed that recognized disturbances in “core” patterns, indicating progressive destabilization of cardiac rhythm, which would predict the onset of spontaneous sustained ventricular tachyarrhythmias. The possible concomitance of both vagal and sympathetic actions, most likely on a reflex basis, could facilitate arrhythmias by a complex interplay[43]. In fact, the identification of cardiac autonomic dysfunction is frequently used as predictor of sudden death and arrhythmias [20, 24]. Pereira-Junior et al.[25] showed alterations in parasympathetic cardiac autonomic modulation only after 8-week treatment AAS treatment. However, our results demonstrated that cardiac autonomic dysfunction may occur earlier, with significant reduction in the HF PSD and increase in the LF/HF ratio in the DG, starting by the 4th week of treatment. In this regard, it may not entirely discard the hypothesis of the involvement of an acute, non-genomic effect of DECA taking place in the genesis of arrhythmia triggering factors. In fact, Phillis and colleagues[44] recently demonstrated that DECA acutely potentizes the arrhythmogenic effect of cardiac ischemia in rats, decreasing animal survival during an ischemic event. Furthermore, it has been recently shown[45] that Clenbuterol, a beta 2-agonist, which is also misused for increasing muscle mass, may lead to acute arrhythmic events. However, according to Andrade et al. [42] no alterations in the Bezold-Jarisch reflex were found after 4 weeks of treatment with DECA. In face of these findings, we can suggest that the parasympathetic autonomic dysfunction showed in the present work, starting by the fourth week of DECA treatment, may be a possible result of centralabnormalities in cardiovascular autonomic control rather than alterations in cardiac receptor activities. These results suggest that DECA treatment creates a conspicuous substrate to induce electrical disturbances. [27, 28]In addition, it is well established that Poincaré plot analysis allow visual information about heart rate successive fluctuation patterns, constituting a valuable and simple method of evaluating cardiac autonomic control [26]. This method is advantageous in some ways because it constitutes a simple tool that requires low computational cost in order to represent similar information to that extracted from spectral analysis, without a need for stationary and periodic signals for analysis computation. We showed that DG tended to present a significant reduction in s, from 5th week, and the ellipsis area decreased similarly in both groups correlating with the reduction in the total PSD (r2 = 0.83). However, the time-course of s variation was different between groups, with a marked decrease from 5th to 8th week in DG while CG presented preserved pattern of autonomic modulation by the end of treatment.In the present work, the time-domain HRV variables RMSSD and pNN5 were lower in AAS group compared to the control group. The lower values of pNN5 in the AAS group suggest parasympathetic cardiac dysfunction{Maior, 2012 #46}. However, the RMSSD index has better statistical properties for assessing parasympathetic activity than pNN5{, 1996 #52}. The RMSSD has been used as a better index of cardiac parasympathetic control since it is uncontaminated by sympathetically mediated HRV{Berntson, 2005 #56} and suggesting an impairment in the parasympathetic reactivation in rats treated with supraphysiological doses of nandrolonedecanoate. The SDNN value in DECA group was lower compared to the control group. Some studies have associated the decrease of SDNN value with left ventricular dysfunction and development of high blood pressure{Casolo, 1992#58}{Schroeder, 2003 #61}. Thus, supraphysiological doses of AAS seem to induce an autonomic dysfunction that reflects in a reduction of the variability of R-R intervals and in a lower SDNN{Maior, 2012 #46}. The mechanism underlying the cardiac autonomic dysfunction in AAS-abusing remains unknown. However, Previous studies have reported that androgens can cross the blood–brain barrier{Kindlundh, 2004 #62}{Kicman, 2008 #67} and bind to androgen receptors in different brain regions{Sheridan, 1982 #69}{Simerly, 1990 #70}{Penatti, 2009 #72}. Androgens may also be aromatized to estrogens and bind to estrogenreceptors{Penatti, 2009 #72}. AAS affect GABAergic transmission in the hypothalamus and other brain areas by modulation of GABAA receptor function{Henderson, 2006 #76}. Thus, one might speculate that AAS alter the parasympathetic modulation mediated by central GABA and other mechanisms, by binding to androgen receptors in the hypothalamus and brain stem regions that control the tonic and reflex response of cardiovascular system.
5. Conclusions
- In conclusion, we showed that cardiac autonomic dysfunction may constitute an early consequence of the chronic administration of high doses of anabolic steroids. Besides, using a noninvasive approach for assessing heart rate variability in rats and Poincaré analysis method, we have demonstrated that animals treated with nandrolonedecanoate show important reductions in parasympathetic and increases in cardiac sympathetic modulation, which may constitute an important marker of arrhythmia vulnerability and sudden death identification.List of abbreviations AAS, Anabolic androgenic steroids; CG, Control group treated with vehicle; DECA, nandrolonedecanoate; DG, Group treated with nandrolonedecanoate; ECG, Electrocardiogram; FFT, Fast Fourier transform; HF, High frequency component of heart rate variability; HRV, heart rate variability; LF, Low frequency component of heart rate variability; PNN5, Percentage of successive RR interval differences greater than 5 ms; PSD, Power spectral density; RMSSD, Square root of the mean squared differences of successive RR intervals; RR, mean of RR interval of electrocardiogram; SDNN, standard deviations of RR intervals; SD1, standard deviation of projection of the Poincaré plot on the line perpendicular to the line of identity; SD2, the standard deviation of the projection of the Poincaréplot on the line of identity.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML