| [1] | S.D. Gentry, C.A. Bramblett, The Anatomy and Biology of the Human Skeleton, Texas A&M University Press 1988, p.4. |
| [2] | G.A. Rodan, Bone homeostasis, The National Academy of Sciences, USA Vol. 95, (1998), p. 13361-13362. |
| [3] | M.J. Olszta, X. Cheng, S.S. Jee, R. Kumar, Y.Y. Kim, M.J. Kaufman, E.P. Douglas, L.B. Gower, Bone structure and formation: A new perspective, Materials Science and Engineering, Vol. 58, (2007), p. 77–116. |
| [4] | N. Shepard, Role of proteoglycans in calcification, in: E. Bonucci (Ed.), Calcification in Biological Systems, CRC Press, Boca Raton, (1992), p. 41 |
| [5] | E.P. Katz, E. Wachtel, M. Yamauichi, G.L. Mechanic, The structure of mineralized collagen fibrils, Connective Tissue Research, Vol. 21, No. 1-4, (1989), p. 149-158. |
| [6] | W.J. Landis, M.J. Song, A. Leith, L. McEwen, B.F. McEwen, Mineral and organic matrix interaction in normally calcifying tendon visualized in 3 dimensions by high-voltage electron-microscopic tomography and graphic image-reconstruction, Journal of Structural Biology, Vol. 110, No.1, (1993), p. 39–54. |
| [7] | B. Wopenka, J.D. Pasteris, A mineralogical perspective on the apatite in bone, Materials Science and Engineering C, Vol. 25, No. 2, (2005), p. 131-143. |
| [8] | S. Weiner, H.D. Wagner, The Mineral Bone: Structure– Mechanical function relations, Annual Review of Materials Science Vol. 28, (1998), p. 271-298. |
| [9] | C. Hellmich, F.J. Ulm, Average hydroxyapatite concentration is uniform in the extracollagenous ultrastructures of mineralized tissues: evidence at the 1-10 micron scale, Biomechanics and Modeling in Mechanobiology, Vol. 2, (2003), p. 21-36. |
| [10] | C.F. Nawrot, D.J. Campbell, A Chromatographic Study of the Relative Affinities of Rat Bone and Skin Collagen 1 Chains for Hydroxyapatite, Journal of Dental Research, Vol. 56, No. 8, (1977), p. 1017-1022. |
| [11] | W.F. Neuman, M.W. Neuman, The chemical dynamics of bone mineral, Chicago, The University of Chicago Press, 1958. |
| [12] | R.Z. LeGeros, Properties of osteoconductive biomaterials: calcium phosphates. Clinical Orthopaedics & Related Research, Vol. 395, (2002), p. 81-98. |
| [13] | R.A. Young, Some aspects of crystal structure modelling of biological apatites, In: Colloques Internationeaux C.N.S.R, Paris, No. 230, (1976), p. 21-40. |
| [14] | E.P. Katz, S.T. Li, Structure and function of bone collagen fibrils, Journal of Molecular Biology, Vol. 80, No. 1, (1973), p. 1-15. |
| [15] | C.R.F. Azevedo, Failure analysis of a commercially pure titanium plate for osteosynthesis, Engineering Failure Analysis, Vol. 10, No. 2, (2003), p. 153-164. |
| [16] | Y.C. Fung, Biomechanics: Mechanical properties of living tissue, 2nd ed; Springer-Verlag: New York, USA, (1993), p. 225-229. |
| [17] | J.C. Adams, D.L. Hamblen, Outline of Fractures, 10th ed; Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, (1992), p. 3-18. |
| [18] | K. Wang, The use of titanium for medical applications in the USA, Materials Science and Engineering: A, Vol. 213, No. 1-2, (1996), p. 134–137. |
| [19] | M. Long, H.J. Rack. Titanium alloys in total joint replacement – A materials science perspective, Biomaterials, Vol. 19, No. 18, (1998), p. 1621–1639. |
| [20] | A. Lambotte, L'utilisation du magnesium comme materiel perdu dans l'osteosynthèse, Bulletins et. Mémoires de la Societe Nationale de Chirurgie, Vol. 28, ( 1932), p.1325-1334. |
| [21] | M. P. Staiger, A. M. Pietak, J. Huadmai, G. Dias, Magnesium and its alloys as orthopedic biomaterials: a review, Biomaterials, Vol. 27, No. 9, (2006), 1728-1734. |
| [22] | R. Murugan, S. Ramakrishna, Development of nanocomposites for bone grafting, Composites Science and Technology, Vol. 65, No. 15-16, (2005), p. 2385-2406. |
| [23] | A.M. Rasmir-raven, D.C. Richardson, H.M. Aberman, D.J. Deyong, The response of cancellous and cortical canine bone to hydroxylapatite-coated and uncoated titanium rods, Journal of Applied Biomaterials, Vol.6, No.4, (1995), p. 237-242. |
| [24] | J. Nagels, M. Stokdijk, P.M. Rozing, Stress shielding and bone resorportion in shoulder arthroplasty, Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery, Vol. 12, No. 1, (2003), p. 35-39. |
| [25] | C. Lhotka, T. Szekeres, I. Steffan, K. Zhuber, K. Zweymuller. Four-year study of cobalt and chromium blood levels in patients managed with two different metal-on-metal total hip replacements. Journal of Orthopedic Research, Vol. 21, No. 2, (2003), p. 189-195. |
| [26] | P.A. Dearnly, A brief review of test methodologies for surface-engineered biomedical implant alloys, Surface and Coatings Technology, Vol. 198, No. 1-3, (2005), 483-490. |
| [27] | D.R. Haynes, S.J. Boyle, S.D. Rogers, D.W. Howie, B. Vernon-Robert, Variation in cytokines induced by patients from different prosthetic materials, Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, Vol. 352, (1998), p. 323-230. |
| [28] | N.L. Saris, E. Mervaala, H. Karppanen, J.A. Khawaja, A. Lewenstam, Magnesium. An update on physiological, clinical and analytical aspects, Clinica chimica acta, Vol. 294, (2000), p. 1-26. |
| [29] | S.R. Kim, J.H. Lee, Y.T. Kim, D.H. Riu, S.J. Jung, Y.J. Lee, S.C. Chung, Y.H. Kim, Synthesis of Si, Mg substituted hydroxyapatites and their sintering behaviours, Biomaterials Vol.24, No.8, (2003), p. 1389-1398. |
| [30] | A. D. Robinson, R.W. Griffith, D. Shechtman, R.B. Evans, M.G. Conzemius, In vivo antibacterial properties of magnesium metal against Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus, Acta Biomaterialia, Vol. 6, (2010), p. 1869-1877. |
| [31] | P.E. DeGarmo, Materials and processes in manufacturing, 5th ed. New York, Collin Macmillan, 1979 |
| [32] | M. Razavi, M.H. Fathi, M. Meratian et al. Microstructure, mechanical properties and biocorrosion evaluation of biodegradable AZ91-FA nanocomposites for biomedical applications, Materials Science and Engineering A, Vol. 527, No.26, (2010), p.6938-6944. |
| [33] | A. Feng, Y. Han, The microstructure, mechanical and corrosion properties of calcium phosphate reinforced ZK60A magnesium alloy composites, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, Vol. 504, (2010), p.585-593. |
| [34] | L.C. Li, J.C. Gao, Y. Wang, Evaluation of cyto-toxicity and corrosion behaviour of alkali-heat-treated magnesium in simulated body fluid, Surface and Coatings Technology, Vol. 185, (2004), p. 92-98. |
| [35] | P.S. Mark, M.P. Alexis, H. Jerawala, D. Goerge, Magnesium and its alloys as orthopaedic biomaterials: A review, Biomaterials, Vol. 27, No. 9, (2006), p.1728-1734. |
| [36] | L. Yang, Z. Li-Ming, Chemical structural and chain conformational characterization of some bioactive polysaccharides isolated from natural sources, Carbohydrate polymers, Vol. 76, No.3, (2009), p.349–361. |
| [37] | V.R. Sinha, K. Rachna, Polysaccharides in colon-specific drug delivery, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, Vol. 224, (2001), p. 19–38. |
| [38] | G. Crini, Recent developments in polysaccharide-based materials used as adsorbents in wastewater treatment, Progress in Polymer Science, Vol. 30, No. 1,(2005), p. 38–70. |
| [39] | A. Kanazawa, M. Suzuki, Solid-state poly-condensation of natural aldopentoses and 6-deoxyaldohexoses. Facile preparation of highly branched polysaccharide, Polymer Vol. 47, No.1, (2006), p.176–183. |
| [40] | S. Run Cang, J.M. Fang, A. Goodwin, J.M. Lawther, A.J. Bolton, Fractionation and characterization of polysaccharides from abaca fibre, Carbohydrate Polymers, Vol. 37, No.4, (1998), p.351–359. |
| [41] | M.N.V. Ravi Kumar, A review of chitin and chitosan applications, Journal of Reactive and Functional Polymers, Vol.46, (2000), p.1–27. |
| [42] | X. Wang, Y. Du, J. Luo, B. Lin, J.F. Kennedy, Chitosan/organic rectorite nanocomposite films: Structure, characteristic and drug delivery behavior, Carbohydrate Polymers, Vol. 69, (2007), p. 41–49. |
| [43] | J.M. Dang, K.W. Leong, Natural polymers for gene delivery and tissue engineering, Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, Vol. 58, (2006), p.487– 499. |
| [44] | M.L. Lorenzo-Lamosa, C. Remunan-Lopez, J.L. Vila-Jato, M.J. Alonso, Design of microencapsulated chitosan microspheres for colonic drug delivery, Journal of Controlled Release, Vol. 52, (1998), p.109–118. |
| [45] | M. George, T.E. Abraham, Polyionic hydrocolloids for the intestinal delivery of protein drugs: Alginate and chitosan — a review, Journal of Controlled Release, Vol. 114, (2006), p.1–14. |
| [46] | D. Thacharodi, K. Panduranga Rao, Development and in vitro evaluation of chitosan-based transdermal drug delivery systems for the controlled delivery of propranolol hydrochloride, Biomoterials, Vol.16, No.2, (1995), p.145-148. |
| [47] | M. Halbleib, S. Thomas, L. Claudio de, D. von Heimburgc, H. Hauner, Tissue engineering of white adipose tissue using hyaluronic acid-based scaffolds. I: in vitro differentiation of human adipocyte precursor cells on scaffolds, Biomaterials, Vol. 24, (2003), p. 3125–3132. |
| [48] | J. Jagur-Grodzinski, Biomedical application of functional polymers, Reactive & Functional Polymers, Vol. 39, (1999), p. 99–138. |
| [49] | M. G. Cascone, B. Sim, S. Dowries, Blends of synthetic and natural polymers as drug delivery systems for growth hormone, Biomaterials, Vol.16, (1995), p.569-574. |
| [50] | K. Kafedjiiski, R.K.R. Jetti, F. Florian, H. Hoyer, M. Werle, M. Hoffer, A. Bernkop-Schnurch, Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of thiolated hyaluronic acid for mucoadhesive drug delivery, Internation Journal of Pharmaceutics, Vol.343, No. 1-2, (2007), p.48–58. |
| [51] | S. Jockenhoevel, G. Zund, S.P. Hoerstrup, K. Chalabi, J.S. Sachweh, L. Demircan, B.J. Messmer, M. Turina, Fibrin gel - advantages of a new scaffold in cardiovascular tissue engineering, European Journal of Cardio-thoracic Surgery, Vol.19, (2001), p. 424-430. |
| [52] | E. A. Ryan, L. F. Mockros, A. M. Stern, L. Lorand, Influence of a Natural and a Synthetic Inhibitor of Factor XIIIa on Fibrin Clot Rheology, Biophysical Journal, Vol. 77, (1999), p. 2827–2836. |
| [53] | T.H. Chun, K.B. Hotary, F. Sabeh, A.R. Saltiel, E.D. Allen, S.J. Weiss, A Pericellular Collagenase Directs the 3-Dimensional Development of White Adipose Tissue, Cell, vol. 125, No.3, (2006), p.577–591. |
| [54] | N.T. Dai, M.R. Williamson, N. Khammo, E.F. Adams, A.G.A. Coombes, Composite cell support membranes based on collagen and polycaprolactone for tissue engineering of skin, Biomaterials, Vol. 25, (2004), p. 4263-4271. |
| [55] | T. Sato, G. Chen, T. Ushida, T. Ishii, N. Ochiai, T. Tateishi, J. Tanaka, Evaluation of PLLA–collagen hybrid sponge as a scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering, Materials Science and Engineering C, Vol. 24, No. 3, (2004), p. 365–372. |
| [56] | S. Agarwal, J.H. Wendorff, A. Greiner, Progress in the Field of Electro-spinning for Tissue Engineering Applications, Advanced Materials, Vol. 21, No. 32-33, (2009), p. 3343–3351. |
| [57] | Y. Dong, F. Si-Shen, Methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-poly (lactide) (MPEG-PLA) nanoparticles for controlled delivery of anticancer drugs, Biomaterials, Vol. 25, (2004), p. 2843–2849. |
| [58] | X. Zheng, B. Kan, M. Gou, S. Fu, J. Zhang, K. Men, L. Chen, F. Luo, Y. Zhao, X. Zhao, Y. Wei, Z. Qian, Preparation of MPEG–PLA nanoparticle for honokiol delivery in vitro, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, Vol. 386, No. 1-2, (2010), p. 262–267. |
| [59] | J. Chen, B. Tian, X. Yin, Y. Zhang, D.Hu, Z. Hu, M. Liu, Y. Pan, J. Zhao, H. Li, C. Hou, J. Wang, Y. Zhang, Preparation, characterization and transfection efficiency of cationic PEGylated PLA nanoparticles as gene delivery systems, Journal of Biotechnology, Vol. 130, (2007), p. 107–113. |
| [60] | H. Kranz, R. Bodmeier, Structure formation and characterization of inject able drug loaded biodegradable devices: In situ implants versus in situ micro-particles, European journal of pharmaceutical sciences, Vol.34, No. 2-3, (2008), p.164–172. |
| [61] | J.M. Kanczler, P.J. Ginty, J.J.A. Barry, N.M.P. Clarke, S.M. Howdle, K.M. Shakesheff, R.O.C. Oreffo, The effect of mesenchymal populations and vascular endothelial growth factor delivered from biodegradable polymer scaffolds on bone formation, Biomaterials, Vol. 29, (2008), p.1892-1900. |
| [62] | L. Rimondini, N. Nicoli-Aldini, M. Fini, G. Guzzardella, M. Tschon, R. Giardino, In vivo experimental study on bone regeneration in critical bone defects using an injectable biodegradable PLA/PGA copolymer, Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, Endodontics, Vol. 99, No. 2, (2005), p.148-154. |
| [63] | C. F. Chu, A. Lu, M. Liszkowski, R. Sipehia, Enhanced growth of animal and human endothelial cells on biodegradable polymers, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, Vol. 472, No. 3, (1999), p.479-485. |
| [64] | L. Calandrelli, B. Immirzi, M. Malinconico, M. G. Volpe, A. Oliva, F. Della Ragione, Preparation and characterisation of composites based on biodegradable polymers for in vivo application, Polymer, Vol. 41, (2000), p. 8027-8033. |
| [65] | Z. Wang, S. Wang, Y. Marois, R. Guidoin, Z. Zhang, Evaluation of biodegradable synthetic scaffold coated on arterial prostheses implanted in rat subcutaneous tissue, Biomaterials, Vol. 26, (2005), p.7387–7401. |
| [66] | Z. Ma, C. Gao, Y. Gong, J. Shen, Cartilage tissue engineering PLLA scaffold with surface immobilized collagen and basic fibroblast growth factor. Biomaterials. Vol. 26, No. 11, (2005), p. 1253-1259. |
| [67] | A. Aubert-Pouessel, M.C. Venier-Julienne, A. Clavreul, M. Sergent, C. Jollivet, C.N. Montero-Menei, E. Garcion, D.C. Bibby, P. Menei, J.P. Benoit, In vitro study of GDNF release from biodegradable PLGA microspheres, Journal of Controlled Release, Vol. 95, No. 3, (2004), p. 463–475. |
| [68] | M. Qiao, D. Chen, X. Ma, Y. Liu, Inject able biodegradable temperature-responsive PLGA–PEG–PLGA copolymers: Synthesis and effect of copolymer composition on the drug release from the copolymer-based hydrogels, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, Vol. 294, No. 1-2, (2005), p. 103–112. |
| [69] | J.J. Lee, S.G. Lee, J.C. Park, Y.I. Yang, J.K. Kim, Investigation on biodegradable PLGA scaffold with various pore size structure for skin tissue engineering, Current Applied Physics, Vol. 7S1, (2007), p.e37–e40. |
| [70] | H.S. Yoo, T.G. Park, Biodegradable polymeric micelles composed of doxorubicin conjugated PLGA–PEG block copolymer, Journal of controlled Release, Vol. 70, (2001), p. 63–70. |
| [71] | M. Todo, S.D. Park, T. Takayama, K. Arakawa, Fracture micro-mechanisms of bio-absorbable PLLA/PCL polymer blends, Engineering Fracture Mechanics, Vol. 74, No. 12, (2007), p.1872–1883. |
| [72] | F. Rezgui, M. Swistek, J. M. Hiver, C. G’Sell, T. Sadoun, Deformation and damage upon stretching of degradable polymers (PLA and PCL), Polymer, Vol. 46, No. 18, (2005), p.7370–7385. |
| [73] | L. Calandrelli, B. Immirzi, M. Malinconico, M. G. Volpe, A. Oliva, F. D. Ragione, Preparation and characterization of composites based on biodegradable polymers for “in vivo” application, Polymer, Vol. 41, No. 22, (2000), p. 8027-8033. |
| [74] | B. Li, J. Yu, J. Jung, M. Ree, Amidolysis of some biodegradable polymers, Polymer Degradation and Stability, Vol. 65, No.1, (1999), p.161-163. |
| [75] | Y. Iwasaki, S. Sawada, K. Ishihara, G. Khang, H. B. Lee, Reduction of surface-induced inflammatory reaction on PLGA/MPC polymer blend, Biomaterials, Vol. 23, No. 18, (2002), p.3897–3903. |
| [76] | Y. Li, J. Nothnagel, T. Kissel, Biodegradable brush-like graft polymers from poly(o,L-lactide) or poly(o,L-lactideco- glycolide) and charge-modified, hydrophilic dextrans as backbone-Synthesis, characterization and in vitro degradation properties, Polymer, Vol. 38, (1997), p. 6197-6206. |
| [77] | Y.C. Wang, M.C. Lin, D.M. Wang, H.J. Hsieh, Fabrication of a novel porous PGA-chitosan hybrid matrix for tissue engineering, Biomaterials, Vol.24, (2003), p. 1047–1057. |
| [78] | C.Y. Hsieh, S.P. Tsai, D.M. Wang, Y.N. Chang, H.J. Hsieh, Preparation of g-PGA/chitosan composite tissue engineering matrices, Biomaterials, Vol. 26, (2005), p. 5617–5623. |
| [79] | K. Rezwan, Q.Z. Chen, J.J. Blaker, A.R. Boccaccini, Biodegradable and bioactive porous polymer/inorganic composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering, Biomaterials, Vol. 27, (2006), p. 3413–3431. |
| [80] | C.M. Agrawal, Reconstructing the Human Body Using Biomaterials, Journal of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, Vol. 50, No. 1, (1998), p. 31-35. |
| [81] | S. Ramakrishna, M. Ramalingam, T.S. Sampath, W.O. Soboyejo, Biomaterials: A Nano Approach, CRC Press, Boca Raton, USA, Chap 7 (2010) p.188-196. |
| [82] | L.L. Hench, J. Wilson, An introduction to bioceramics, World Scientific Publishing Co Pt Ltd: Singapore (1993) p.1-24. |
| [83] | L.L. Hench, Bioceramics: From concept to clinic, Journal of the American Ceramic Society, Vol. 74, No.7, (1991), p. 1487-1510. |
| [84] | P.X. Ma, Biomimetric materials for tissue engineering, Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, Vol. 60, No.2, (2008), p. 184-198. |
| [85] | J.B. Park, J.D. Bronzino, Biomaterials principles and applications, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, USA, 2003. |
| [86] | I. Thompson, L.L Hench, Medical applications of composites: In comprehensive composite materials, Edited: A. Kelly, C. Zweben, Amsterdam Elsevier Science: 727 (2000). |
| [87] | Ducheyne P, L.L. Hench, A. Kagan, M. Martens, A. Bursens, J.C. Mulier ,Effect of hydroxyapatite impregnation on skeleton bonding of porous coated implants, Biomedical Materials Research, Vol.14, No.3, (1980), p. 225-237. |
| [88] | S. Itoh, M. Kikuchi, Y. Koyama, N.H. Matumoto, K. Takakuda, K. Shinomiya, J. Tanaka, Development of a novel biomaterial, hydroxyapatite/collagen composite for medical use, Biomedical Materials and Engineering, Vol. 15, No. 1-2, (2005), p.29-41. |
| [89] | C.P. McCord, Chemical gas gangrene from metallic magnesium, Industrial Medicine, Vol. 11, (1942), 71-79. |
| [90] | C.E. Wen, M. Mabuchi, Y. Yamada, K. Shimojima, Y. Chino, T. Asahina, Processing of biocompatible porous Ti and Mg. Scripta Materialia, Vol.45, No.10, (2001), p.1147-1153. |
| [91] | D.Williams, Medical Device Technology, Vol. 17, No. 3, (2006), p. 9-10. |
| [92] | F. Witte, V. Kaese, H. Haferkamp, E. Switzer, A. Meyer-Lindenberg, C.J. Wirth, H. Windhagen, In vivo corrosion of magnesium alloys and the associated bone response, Biomaterials, Vol. 26, No. 17, (2005), p.3557-3563. |
| [93] | E. Ghali, Corrosion resistance of aluminium and magnesium alloys, understanding, performance and testing, Chap 10, Pub: John Wiley (2010), 349. |
| [94] | B.A. Shaw, Corrosion resistance of magnesium alloys. In: Ed: Stephens D. ASM handbook, Vol 13a: corrosion fundamentals, testing and protection. UK: ASM Int.; 2003. |
| [95] | A.M. Fekry, M.A. Ameer, Electrochemistry and impedance studies on titanium and magnesium alloys in Ringer’s solution, International Journal of Electrochemical Science, Vol.6, (2011), p.1342-1354. |
| [96] | G. Song, Control of biodegradation of biocompatible magnesium alloys, Corrosion Science, Vol.49, No. 4, (2007), p.1696-1701. |
| [97] | R.L. Williams, D.F. Williams, Albumin adsorption on metal surfaces, Biomaterials, Vol. 9, No.3, (1998), p.206-212. |
| [98] | K. Endo, Chemical modifications of metallic implant surfaces with bio-functional proteins (Part 2).Corrosion resistance of a chemically modified NiTi alloy, Dental Materials Journals, Vol. 14, (1995), p.199-210. |
| [99] | W.D. Muller, M.L. Nascimento, M. Zeddies, M. Corsico, L.M. Gassa, M.A. Fernandez, L. de Mele, Magnesium and its alloys as degradable biomaterials. Corrosion studies using potentiodynamic and EIS electrochemical techniques, Materials Research, Vol. 10, No.1, (2007), p. 5-10. |
| [100] | R.M.E. Diamant, Applied Chemistry for Engineers, The Pitman Press, Bath, Great Britain, (1972), Chap 5, p. 86-105. |
| [101] | J.J. Jacobs, J.L. Gilbert, R.M. Urban, Corrosion of metal orthopaedic implants, The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, American volume, Vol. 80, (1998), p. 268-82 |
| [102] | R. Zeng, E. Han, W. Ke, Corrosion of artificial aged magnesium alloy AZ80 in 3.5 wt pct NaCl solutions, Journal of Materials Science and Technology, Vol. 23, No. 3, (2007), p. 353-358. |
| [103] | OnlineAvailable:http://corrosionist.com/Pitting_Crevice_Corrosion.htm. |
| [104] | R. Ambat, N.N. Aung, W. Zhou, Evaluation of micro-structural effects on corrosion behaviour of AZ91D magnesium alloy, Corrosion Science,Vol. 42, (2000), p. 1433-1455. |
| [105] | L.J. Liu, M. Schlesinger, Corrosion of magnesium and its alloys. Corrosion Science, Vol. 51, (2009), p. 1733-1737. |
| [106] | R. Zeng, W. Dietzel, F. Witte, N. Hort, C.Blawert, Progress and challenge for magnesium alloys as biomaterials, Advanced Biomaterials, Vol. 35, (2008), p. B3- B14. |
| [107] | M.G. Fontana, N.D. Greene, Corrosion engineering, McGraw-Hill, New York, (1987). |
| [108] | OnlineAvailable: http://corrosion.ksc.nasa.gov/fretcor.htm. |
| [109] | L. J. Korb, ASM handbook- ASM International, Corrosion, Vol. 13, (1987). |
| [110] | A. Neyman, O. Olszewski, Research on fretting wear dependence of hardness ratio and friction coefficient of fretted couple, Wear of materials, International conference No. 9, San Francisco CA, USA, Wear, vol. 162-64, Part B, (1993), pp. 939-943. |
| [111] | P. Shewmon, G. Sundararajan, The erosion of metals, Annual Review of Materials Science, Vol. 13, (1983), p. 301-318. |
| [112] | P. A. Dearnley, Surface and Coating Technology, (2005), p. 198- 483. |
| [113] | K.W. Miller, Material performance and evaluation, ed. R.H. Jones, ASM International, Ohio, (1993), p. 251. |
| [114] | N. Winzer, A. Atrens, G. Song, E. Ghali, W. Dietzel, K.U. Kainer, N. Hort, C. Blawert, Advance Engineering Materials, Vol. 7, (2005), p. 659-693. |
| [115] | S.C. Dexter, Corrosion, Metals Handbook, edited by L. J. Korband, D. L. Olson, ASM International, Materials Park, OH,ASM International, USA, Vol. 13, No. 9, (1987), p. 123-135. |
| [116] | T. Valente, Journal of Materials Science Letters, Vol. 20, (2001), p. 67-69. |
| [117] | N. Winzer, A. Atrens, W. Dietzel, G. Song, K.U. Kainer, Stress corrosion cracking in magnesium alloys: characterisation and prevention, JOM, Vol. 59, No. 8, (2007), p. 49-53. |
| [118] | N. Winzer, A. Atrens, G. Song, E. Ghali, W. Dietzel, K. U. Kainer, N. Hort, C. Blawert, A Critical Review of the Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC) of Magnesium Alloys. Advanced Engineering Materials, Vol. 7, No. 8, (2005), p. 659-693. |
| [119] | R.G. Song, C. Blawert, W. Dietzel, A. Atrens, A study of the stress corrosion cracking and hydrogen embrittlement of AZ31 magnesium alloy. Materials Science and Engineering A - Structural Materials Properties Microstructure And Processing, Vol 399, No. 1-2, (2005), p. 308-317. |
| [120] | E. Ghali, W. Dietzel, K.U. Kainer. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, Vol. 13, No. 1, (2004), p. 7-25. |
| [121] | G. Song, Recent Progress in Corrosion and Protection of Magnesium Alloys, Advanced Engineering Materials, Vol. 7, No. 7, (2005), p. 563-586. |
| [122] | F. Witte, N. Hort, C. Vogt, S. Cohen, K.U. Kainer, R. Willumeit, F. Feyerabend, Degradable biomaterials based on magnesium corrosion, Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science, Vol. 12, (2008), p. 63-72. |
| [123] | S. Song, G.L. Song, W. Shen and M.Liu. Corrosion and electrochemical evaluation of coated magnesium alloys. Corrosion. Vol. 68, No. 1, (2012), p. 015005-1-015005-12. |
| [124] | G.L. Song, A. Andrej, Corrosion mechanisms of magnesium alloys, Advanced Engineering Materials, Vol. 1, (1999), p. 11-33. |
| [125] | F. Zucchi, V. Grassi, A. Frignani, C. Monticelli, G. Trabanelli, Electrochemical behaviour of a magnesium alloy containing rare earth elements, Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, Vol. 36, (2006), p. 195-204. |
| [126] | Z. Li, X. Gu, S. Lou, Y. Zheng. The development of binary Mg-Ca alloys for use as biodegradable materials within bone, Biomaterials, Vol. 29, (2008), p. 1329-1344. |
| [127] | F. Witte, H.A. Crostack, J. Nellesen, F. Beckmann, Characterisation of degradable magnesium alloys as orthopaedic implant materials,synchrotron-radiation-based microtomography, (2001). |
| [128] | F. Witte, H. Ulrich, M. Rudert, E. Willbold, Biodegradable magnesium scaffolds: Part 1: Appropriate inflammatory response, Journal of Biomaterials Research, Vol. 81A, No. 3, (2007), p. 748-756. |
| [129] | F. Witte, H. Ulrich, C. Palm, E. Willbold, Biodegradable magnesium scaffolds: Part II: Peri-implant bone remodeling, Journal of Biomaterials Research, Vol. 81A, No. 3, (2007), p. 757-765. |
| [130] | S.V. Verstraeten, L. Aimo, P.I. Oteiza, Aluminium and lead: molecular mechanisms of brain toxicity, Archives of Toxicolgy, Vol. 82, (2008), p. 789-802. |
| [131] | S.S.A. El-Rahman, Neuropathology of aluminium toxicity in rats: glutamate and GABA impairment, Pharmacological Research, Vol. 47, (2003), p. 189-194. |
| [132] | N. Yumiko, T. Yukari, T. Yasuhide, S. Tadashi, I. Yoshio, Differences in behaviour among the chlorides of seven rare earth elements administered intravenously to rats, Fundamental and Applied Toxicology, Vol. 37, (1997), p. 106-116. |
| [133] | Report of Environmental Health Impacts from Exposure to Metals, Simla, India, WHO, (2005). |
| [134] | Z. Li, X. Gu, S. Lou, Y. Zheng, The development of binary Mg-Ca alloys for use as biodegradable materials within bone, Biomaterials, Vol. 29, (2008), p. 1329-1344. |
| [135] | X. Gu, Y. Zheng, Y. Cheng, S. Zhong, T. Xi, In vitro corrosion and biocompatibility of binary magnesium alloys, Biomaterials, Vol. 30, (2009), p. 484-498. |
| [136] | T.P. Rucdi, W.M. Murphy, AO Principle of Fracture Management, AO Publishing, Dübendorf, Switzerland, (2002), p. 13–14. |
| [137] | G.B. Wei, P.X. Ma, Structures and properties of nano-hydroxyapatite/polymer composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering, Biomaterials, Vol. 25,(2004), p. 4749-4757. |
| [138] | D.M. Brunette, J. Ratkay, B. Chehroudi, The bone–biomaterial interface, Toronto: University of Toronto Press, (1991), p. 49–61. |
| [139] | B. Boyan, T. Hummert, K. Kieswetter, D. Schraub, D. Dean, Z. Schwartz, Effect of Titanium surface characteristics on chondrocytes and osteoblasts in vitro, Cells Materials, Vol. 5, No. 4, (1995), p. 323–335. |
| [140] | M. Jayaraman, U. Meyer, M. Buhner, U. Joos, H.P. Wiesmann, Influence of titanium surfaces on attachment of osteoblast-like cells in vitro, Biomaterials, Vol. 25, No. 4, (2004), p. 625-631. |
| [141] | D. Crotty, C. Stinecker, B. Durkin, Plating Difficult Substrates with Electroless Nickel, Products Finishing, Vol. 60, (1996), p. 44. |
| [142] | J.E. Gray, B. Luan, Protective coatings on magnesium and its alloys – a critical review, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, Vol. 336, No. 1, (2002), p. 88-113. |
| [143] | B. Denkena, D. Boehnke, L. de León, Machining induced residual stress in structural aluminium parts. Production Engineering, Vol. 2, No. 3, (2008), p. 247-253. |
| [144] | M. Salahshoor, Y.B. Guo, Cutting mechanics in high speed dry machining of biomedical magnesium-calcium alloy using internal state variable plasticity model. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 51, (2011), p. 579-590. |
| [145] | B. Denkena, A. Lucas, Biocompatible magnesium alloys as absorbable implant materials-Adjusted surface and subsurface properties by machining processes. Annals of the CIRP, Vol. 56, No. 1, (2007), p. 113-118. |
| [146] | B. Denkena, A. Lucas, F. Thorey, H. Waizy, N. Angrisani, A. Meyer-Lindenberg, Biocompatible magnesium alloys as degradable implant materials-Machining induced surface and subsurface properties and implant performance, Special Issues on Magnesium Alloys, (2011), p. 109-128. |
| [147] | E. Brinksmeier, M. Garbrecht, D. Meyer, J. Dong, Surface hardening by strain induced martensitic transformation, Production Engineering, Vol. 2, No. 2, (2007), p. 109-116. |
| [148] | N.V.D. Hoh, D. Bormann, A. Lucas, B. Denkena, C. Hackenbroich, A. Meyer-Lindenberg, Influence of different surface machining treatments of magnesium-based resorbable implants on the degradation behaviour in rabbits. Advanced Engineering Materials, Vol. 11, No. 5, (2009), p. B47-B54. |
| [149] | G. Reiner, M. Griepentrog, Hard coatings on magnesium alloys by sputter deposition using a pulsed d.c. bias voltage, Surface and Coatings Technology, Vol. 76-77, No. 2, (1995), p. 809-814. |
| [150] | J. Senf, E. Broszeit, Wear and Corrosion Protection of Aluminum and Magnesium Alloys Using Chromium and Chromium Nitride PVD Coatings, Advance Engineering Materials, Vol. 1, No.2, (1999), p. 133-137 |
| [151] | S.B. Dodd, S. Morris, R.W. Gardiner, R.M.D. Brydson, S. Diplas, P. Tsakiropoulos, Priliminary corrosion evaluation of some novel bulk electron beam evaporated magnesium alloys, Corrosion Reviews. Vol. 16, No. 1-2, (1998), p. 159- 174. |
| [152] | T. Mitchell, P. Tsakiropoulos, Microstructure property studies of in situ mechanically worked PVD Mg-Ti alloys, Magnesium Technology 2000, The Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, (2000), p. 169-174. |
| [153] | S. Diplas, P. Tsakiropoulos, R.M.D. Brydson, Journal of Material Science and Technology, Vol. 15, (1999), p. 1349. |
| [154] | R. Jethanandani, The development and application of diamond-like carbon films, JOM, (1997), p. 63-65. |
| [155] | C.L. Liu, Y.C. Xin, X.B. Tian, J. Zhao, P.K. Chu, Corrosion resistance of titanium ion implanted AZ91 magnesium alloy, Journal of Vaccum Science and Technology A, Vol. 25, (2007), p. 334-339. |
| [156] | H.E. Fang, W.Y. Zao, S. Zhou, Y. Huang, Y.L. Wang, Zn ion implantation and corrosion behaviour of new medical Mg-Ca alloys. Metal Science and Heat treatment, Vol. 134, No. 14, (2009), p. 32-37. |
| [157] | Y.Z. Wan, G.Y. Xiong, H.L. Luo, F. He, Y. Huang, Y.L. Wang, Influence of zinc ion implantation on surface nanomechanical performance and corrosion resistance of biomedical magnesium-calcium, Applied Surface Science, Vol. 254, (2008), p. 5514–5516. |
| [158] | E.L. Zhang, L.P. Xu, K. Yang, Formation by ion plating of Ti-coating on pure Mg for biomedical applications, Scripta Materialia, Vol. 53, (2005), p. 523-527. |
| [159] | R.H. Unger, Thermal spray coating, in ASM Handbook: Corrosion, Vol. 13, (1987), p. 458-460. |
| [160] | J. Zhang, Y. Wang, R.C. Zeng, W.J. Huang, Effects of post heat treatment on the interfacial characteristics of aluminium coated AZ91D magnesium alloy, Materials Science Forum, Vol. 529, (2007), p. 546-549. |
| [161] | X. Liu, P.K. Chu, C. Ding, Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications. Materials Science and Engineering: R, Vol. 47, (2004), p. 49-121. |
| [162] | R.C. Zeng, W. Dietzel, J. Chen, W.J. Huang, J. Wang, Corrosion behavior of TiO2 coating on magnesium alloy AM60 in Hank’s solution, Key Engineering Materials, Vol. 373/374, (2008), p. 289-295. |
| [163] | R.C. Zeng, W. Dietzel, F. Witte, N. Hort, C. Blawert, Progress and challenges for magnesium alloys as biomaterials. Advanced Engineering Materials, Vol. 10, (2008), p. B3-B14. |
| [164] | D. Dube, M. Fiset, A. Couture, I. Nakatsugawa, Characterization and performance of laser melted AZ91D and AM60B, Materials Science and Engineering A, Vol. 299, No. 1, (2001), p. 38-45. |
| [165] | R. Galun, A. Weisheit, B.L. Mordike, I. Manna, Improving the surface properties of magnesium by laser alloying, Corrosion Reviews, Vo. 16, No. 1-2, (1998), p. 53-73. |
| [166] | H. Hiraga, T. Inoue, Y. Kojima, S. Kamado, S. Watanabe, Surface modification by dispersion of hard particles on magnesium alloy with laser, Materials Science Forum, Vol. 253, (2000), p. 350-351. |
| [167] | L.A. Dobrzañski, J. Domaga, T. Tañski, A. Klimpel, D. Janicki, Laser surface treatment of cast magnesium alloys, Materials Science and Engineering, Vol. 35, No. 2, (2009), p. 101-106. |
| [168] | S. Hao, B. Gao, A. Wu, J. Zou, Y. Qin, C. Dong, J. An, Q. Guan, Surface modification of steels and magnesium alloy by high current pulsed electron beam, Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, Vol. 240, No. 3, (2005), p. 646-652. |
| [169] | V. Neubert, A. Bakkar, C.A. Huang, Magnesium alloys and their applications, 7th International Conference, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, (2006), p. 842. |
| [170] | J. Yang, F. Cui, I.S. Lee, Surface modifications of magnesium alloys for biomedical applications, Annals of Biomedical Engineering, Vol. 39, No. 7, (2011), p. 1857- 1871. |
| [171] | L.P. Xu, G.N. Yu, E. L. Zhang, F. Pan, K Yang, In vivo corrosion behaviour of Mg-Mn-Zn alloy for bone implant application. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, Vol. 83, No. 3, (2007), p. 703-711. |
| [172] | E.H. Han, W.Q. Zhou, D.Y. Shan, W. Ke, Corrosion and. Protection of magnesium alloy AZ31D by a new conversion coating, Materials Science Forum, Vol. 419, No.4, (2003), p. 879-883. |
| [173] | M.A. Gonzalez-Nunez, C.A. Nunez-Lopez, P. Skeldon, G.E. Thompson, H. Karimzadeh, P. Lyon, T.E. Wilks, A non-chromate conversion coating for magnesium alloys and magnesium-based metal matrix composites, Corrosion Science, Vol. 37, No. 11, (1995), p. 1763-1772. |
| [174] | R.C. Zeng, J. Chen, W. Dietzel, N. Hort, K.U. Kainer, Electrochemical behavior of magnesium alloys in simulated body fluids, Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society China, Vol. 17, (2007), p. s166-s170. |
| [175] | T. Hassel, F.W. Bach, C. Krause, P. Wilk, Corrosion protection and re-passivation after the deformation of magnesium alloys coated with a protective magnesium fluoride layer, Magnesium Technology, 2005 edited by TMS (The Minerals, Metals and Materials Society), (2005), p. 485-490. |
| [176] | F. Witte, J. Fischer, J. Nellesen, C. Vogt, J. Vogt, T. Donath, F. Beckmann, In vivo corrosion and corrosion protection of magnesium alloy LAE442, Acta Biomaterialia, Vol. 6, (2010), p. 1792-1799. |
| [177] | J.C. Gao, Y. Xue, L.Y. Qiao, Y. Wang, Y. Zhang, Surface modification of magnesium with rare earth conversion films for biomedical protection, Materials Science Forum, Vol. 546/549, (2007), p. 601-604. |
| [178] | F. Witte, F. Feyerabend, P. Maier, J. Fischer, M. Stormer, C. Blawert, W. Dietzel, N. Hort, Biodegradable magnesium– hydroxyapatite metal matrix composites, Biomaterials, vol. 28, no. 13, (2007), p. 2163–2174. |
| [179] | D.W. Hutmacher, J.T. Schantz, C.X.F. Lam, K.C. Tan, T.C. Lim, State of the art and future directions of scaffold-based bone engineering from a biomaterials perspective, Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, Vol. 1, (2007), p. 245-260. |
| [180] | W.J.E.M. Habraken, J.G.C. Wolke, J.A. Jansen, Ceramic composites as matrices and scaffolds for drug delivery in tissue engineering, Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, Vol. 59, (2007), p. 234-248. |
| [181] | A. Blom, Which scaffold for which application?, Current Orthopaedics, Vol. 21, No. 4, (2007), p. 280-287. |
| [182] | P. Habibovic, K. De Groot, Osteoinductive biomaterials-properties and relevance in bone repair, Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, Vol.1, (2007), p. 25-32. |
| [183] | S. Hiromoto, T. Shishido, A. Yamamoto, N. Maruyama, H. Somekawa, T. Mukai, Precipitation control of calcium phosphate on pure magnesium by anodization, Corrosion Science, Vol. 50, (2008), p. 2906–2913. |
| [184] | S.J. Kalita, A. Bhardwaj, H.A. Bhatt, Nanocrystalline calcium phosphate ceramics in biomedical engineering, Materials Science and Engineering:C, Vol. 27, No. 3, (2007), p. 441-449. |
| [185] | D.A. Cortes, H.Y. Lopez, D. Mantovani, Spontaneous and biomimetic apatite formation on pure magnesium, Materials Science Forum, (2007), p. 589–594. |
| [186] | Y. Zhang, G. Zhang, M. Wei, Controlling the biodegradation rate of magnesium using biomimetic apatite coating, Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B, Vol. 89, (2008), p. 408–414. |
| [187] | Y. Song, S. Zhang, J. Li, C.Zhao, X. Zhang, Electrodeposition of Ca–P coatings on biodegradable Mg alloy: In vitro biomineralization behaviour, Acta Biomaterialia, Vol. 6, (2010), p. 1736–1742. |
| [188] | C. Zhang, R.C. Zeng, R.S. Chen, C.L. Liu, J.C. Gao, Preparation of calcium phosphate coatings on Mg-1.0Ca alloy, Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, Vol. 20, (2010), p. s655−s659. |
| [189] | M. Tomozawa, S. Hiromoto, Growth mechanism of hydroxyapatite coatings formed on pure magnesium and corrosion behavior of the coated magnesium, Applied Surface Science, Vol. 257, No.19, (2011), p. 8253–8257. |
| [190] | S. Hiromoto, A. Yamamoto, High corrosion resistance of magnesium coated with hydroxyapatite directly synthesized in an aqueous solution, Electrochimica Acta, Vol. 54, (2009), p. 7085–7093. |
| [191] | C. Wen, S. Guan, L. Peng, C. Ren, X. Wang, Z. Hu, Characterization and degradation behaviour of AZ31 alloy surface modified by bone-like hydroxyapatite for implant applications, Applied Surface Science, Vol. 255, (2009), p. 6433–6438. |
| [192] | L. Xu, E. Zhang, K. Yang, Phosphating treatment and corrosion properties of Mg–Mn–Zn alloy for biomedical application, Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, Vol. 20, (2009), p. 859–867. |
| [193] | L. Xu, F. Pan, G. Yu, L. Yang, E. Zhang, K. Yang, In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the surface bioactivity of a calcium phos- phate coated magnesium alloy, Biomaterials, Vol. 30, (2009), p. 1512–1523. |
| [194] | Y. Wang, M. Wei, J. Gao, Improve corrosion resistance of magnesium in simulated body fluid by dicalcium phosphate dihydrate coating, Materials Science and Engineering: C, Vol. 29, (2009), p. 1311-1316. |
| [195] | A. Yanovska, V. Kuznetsov, A. Stanislavov, S. Danilchenko, L. Sukhodub, Calcium phosphate coatings obtained biomimetically on magnesium substrates under low magnetic fields, Applied Surface Science, (2010), doi:10.1016 / j.apsusc.2012.05.052. |
| [196] | R.G. Guan, I. Johnson, T. Cui, T. Zhao, Z.Y. Zhao, X. Li, H. Liu. Electro-deposition of hydroxyapatite coating on Mg-4.0Zn-1.0Ca-o.6Zr alloy and in vitro evaluation degradation, hemolysis and cytotoxicity. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research – Part A, Vol. 100A, No. 4, (2012), p. 999-1015. |
| [197] | L. Li, J. Gao, Y. Wang, Evaluation of cyto-toxicity and corrosion behaviour of alkali-heat-treated magnesium in simulated body fluid, Surface and Coating Technology, Vol. 185, (2004), p. 92-98. |
| [198] | C.L. Liu, Y.C. Xin, G.Y. Tang, P.K. Chua, Influence of heat treatment on degradation behaviour of biodegradable cast AZ63 magnesium alloy in simulated body fluid, Materials Science and Engineering: A, Vol. 456, (2007), p. 350-357. |
| [199] | Y. Mizutani, S.J. Kim, R. Ichino, M. Okido, Anodizing of Mg alloys in alkaline solutions, Surface and Coatings Technology, Vol. 169/170, (2003), p. 143-146. |
| [200] | S. Hiromoto, T. Shishido, A. Yamamoto, N. Maruyama, H. Somekawa, T. Mukai, Precipitation control of calcium phosphate on pure magnesium by anodization, Corrosion Science, Vol. 50, (2008), p. 2906-2913. |
| [201] | H. Kuwahara, Y. Al-Abdullat, N. Mazaki, S. Tsutsumi, T. Aizawa, Precipitation of magnesium apatite on pure magnesium surface during immersing in Hanks’ solution, Materials Transaction, Vol. 42, No. 7, (2001), p. 1317-1321. |
| [202] | J.L. Patel, N. Saka, Microplasmic ceramic coating, Interceram, Vol. 50, No. 5, (2001), p. 398-401. |
| [203] | X.P. Zhang, Z.P. Zhao, F.M. Wu, Y.L. Wang, J.Wu, Corrosion and wear resistance of AZ91D magnesium alloy with and without microarc oxidation coating in Hanks’ solution. Journal of Materials Science, Vol. 42, No. 20, (2007), p. 8523-8528. |
| [204] | H. Hornberger, S. Virtanen, A.R. Boccaccini, Biomedical coatings on magnesium alloys – A review. Acta Biomaterialia, Vol. 8. No. 7, (2012), p. 2442-2455. |
| [205] | G. Song, Control of biodegradation of biocompatible magnesium alloy, Corrosion Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, (2007), p. 1696-1701. |
| [206] | G. Song, S. Song, A possible biodegradable magnesium implant material, Advanced Engineering Materials, Vol. 9, No.4, (2007), p.298-302. |
| [207] | L. Wolgemuth, Assessing the performance and suitability of parylene coatings. Medical device and diagnostic industry, Vol.22, No.8, (2000), p. 42. |
| [208] | J. Jagur-Grodzinski, Polymers for tissue engineering, medical devices, and regenerative medicine.Concise general review of recent studies, Polymers for Advanced Technologies, Vol. 17, No. 6, (2006), p. 395-418. |
| [209] | W. Leventon, New coatings and processes add value to medical devices, Medical device and diagnostic industry, Vol. 23, No. 8, (2001), p. 48. |
| [210] | J.J. Huang, Y.B. Ren, B.C. Zhang, K. Yang, Preparation and property of coating degradable Mg implant, Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, Vol. 17, (2007), p.1465-1469. |
| [211] | M.T.F. Reitman, J. McPeak, Protective coatings for implantable medical devices. Proceedings: Society of Plastic Engineers. ANTEC. (2005), p. 3120-3124. |
| [212] | X.H. Xu, J. Cheng, C.H. Zhang, X.L. Yan, T.B. Zhu, K.D. Yao, L. Cao, Y. Liu, Bio-corrosion and polymer coating modification of magnesium alloys for medicine, Rare Metals Materials and Engineering, Vol. 37, (2008), p. 1225-1228. |
| [213] | X.N. Gu, Y.F. Zheng, A review on magnesium alloys as biodegradable materials, Frontiers of Materials Science in China, Vol. 4, No.2, (2010), p. 111-115. |
| [214] | L. Xu, E. Zhang, D. Yin, S. Zeng, K. Yang, In vitro corrosion behaviour of Mg alloys in a phosphate buffered solution for bone implant application, Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, Vol. 19, No.3, (2008), p. 1017-1025. |
| [215] | H.S. Brar, M.O. Platt, M. Sarntinoranont, P. Martin, M.V. Manual, Magnesium as a biodegradable and bioabsorbable material for medical implants, Journal of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, Vol. 61, No. 9, (2009), p. 31-34. |
| [216] | R.S. Busk, Magnesium products design: Marcel Dekker, New York, USA, (1987), p. 554. |
| [217] | I.J. Polmear: Magnesium alloys and applications. Materials Science and Technology, Vol. 10, No.1, (1994), p. 1-16. |
| [218] | OnlineAvailable:http://www.carbones.at/eng/Products/Magnesium-Mg-Alloys-and-Mg-Granules |
| [219] | P. Auerkari, Mechanical and physical propertries of engineering alumina ceramics. VTT Tiedotteita – Meddelanden–Research Notes 1792.www.vtt.fi/inf/pdf/tiedottect/1996/T1792.pdf |
| [220] | M.P.E. Wenger, L. Bozec, M.A. Horton, P. Mesquida, Mechanical properties of collagen fibrils, Biophysical Journal, Vol. 93, (2007), p. 1255-1263. |
| [221] | J. Black, Hastings GW, Handbook of biomaterials properties. Chapman & Hall. London, Great Britain, (1998). |
| [222] | W.A. Banks, A.J. Kastin, Aluminium-induced neurotoxicity: alterations in membrane function at the blood-brain barrier. Neuroscience Biobehavior Review. Vol. 13, (1989), p. 47-45. |
| [223] | V. Rondeau, H. Jacqmin-Gadda, D. Commenges, C. Helmer, J.F. Dartigues. Aluminium and silica in drinking water and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease or cognitive decline: Findings from 15 year follow-up of the PAQUID cohort. American Journal of Epidemiology. Vol. 169, (2008), p. 489-496. |
| [224] | D. Strausak, J.F. Mercer, H.H. Dieter, W. Stremmel, G. Multhaup, Copper in disorders with neurological symptoms: Alzheimers’s, Menkes and Wilson disease. Brain Research Bulletin. Vol. 55, (2001), p. 175-178. |
| [225] | G.L. Makar, J. Kruger, Corrosion of magnesium Int. Mater. Rev. Vol. 38, No. 3, (1993), p. 138-145 |
| [226] | V.C. Culotta, M. Yang and M. Hall. Manganese transport and trafficking: Lessons learned from Saccharomyces cerecvisiae. Eukaryotic Cell, Vol. 4, (2005), p. 1159-1165. |
| [227] | D. Persaud-Sharma, A. McGordon, Biodegradable magnesium alloys: A review of material development and applications. J. Biomim. Biomater. Tissue Eng. Vol. 12, (2012), p. 25-39. |
| [228] | B. Zberg, P. Uggowitzer, J. Loffler, MgZnCa glasses without clinically observable hydrogen evolution for biodegradable implants. Nature Materials-Letters, Vol. 8, (2009), p. 887-891. |

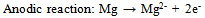
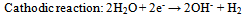
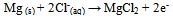
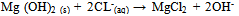
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML