-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Biochemistry
p-ISSN: 2163-3010 e-ISSN: 2163-3029
2023; 13(1): 14-24
doi:10.5923/j.ajb.20231301.03
Received: Nov. 16, 2023; Accepted: Dec. 13, 2023; Published: Dec. 23, 2023

Phytochemical Analysis, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Vitex doniana Sweet Leaves and Fruits Extracts
Durand Dah-Nouvlessounon1, Adjoavi Esse Agossou2, Ismaël M. S. Hoteyi3, Djihal Koda1, Christine N’tcha1, Martial Nounagnon1, Oscar Didagbé1, Haziz Sina1, Adolphe Adjanohoun4, Lamine Baba-Moussa1
1Laboratoire de Biologie et de Typage Moléculaire en Microbiologie, FAST, Université d’Abomey Calavi, Cotonou, Bénin
2Laboratory of Pharmacology and Improved Traditional Medicines, FAST, Department of Animal Physiology, University of Abomey-Calavi, Cotonou, Benin
3Centre Béninois de la Recherche Scientifique et de l’Innovation (CBRSI), Cotonou, Benin
4Centre de Recherches Agricoles Sud, Institut National des Recherches Agricoles du Bénin, Attogon, Cotonou, Bénin
Correspondence to: Durand Dah-Nouvlessounon, Laboratoire de Biologie et de Typage Moléculaire en Microbiologie, FAST, Université d’Abomey Calavi, Cotonou, Bénin.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Vitex doniana belong to Verbernaceae family, has medicinal importance in West Africa. Based on its folkloric medicinal use in Benin, this study aimed to search for phytochemical constituents and evaluated antimicrobial and antioxydant activity of V.doniana plant extracts. Disc diffusion method was used to evaluate the antibacterial activity using 10 references strains and 9 meat isolated Staphylococcus. The antifungal activity was evaluate with 03 fungal strains (Penicillium citrinum, Aspergillus tamarii and Fusarium verticilloides) and the antioxidant activity was determined by both DPPH and ABTS methods. 31% of the secondary metabolites sought were found in the leaves compared to 30% in the fruits. Besides, polyphenols are more concentrated in the fruits ethanol extract (356.12 ±28.10 µgEAG/g) than those of leaves (86.76±19.93 µgEAG/g). For antibacterial activity, the inhibition zones diameters of the active extracts vary depending on the strains (p= 0.001) for the fruits ethanol extracts (p= 0.01) and leaves ethanol extracts (p< 0.05) respectively. The fruits ethanolic extract inhibited 80% of the reference strains while the leaves ethanolic extract inhibited 60% of the strains. The inhibition diameters of the fruits ethanolic extract vary from 12.75±0.35 mm (M. luteus) after 24 hours to 4.00±0.00 mm obtained with the E. coli strain after 48 hours. Furthermore, the inhibition diameters of the leaves ethanolic extract vary from 12.5±0.00 mm (S. epidermidis) after 24 hours to 6.5±0.00 mm obtained with the E. coli strain after 24 hours. The lowest MIC (0.312 mg/mL) was obtained with the leaves ethyl acetate extract with the S. equorum strain while the highest MIC (20 mg/mL) was obtained with the fruits ethanolic extracts (S. xylosus and S. saprophyticcus), fruits ethyl acetate (S. aureus). The leaves ethyl acetate extract also showed the lowest MBC of 0.625 mg/mL on the S. equorum strain with a bactericidal effect. The bactericidal effect was also observed with the S. lentus and S. haemolyticcus strains. The comparative effect of the susceptibility of the fungal strains to the extracts shows that F. verticilliodes strain is the most sensitive while A. tamarii is the most resistant. Furthermore, the two extracts of V. doniana fruits showed weak antioxidant activities with IC50 ranging from 3375.00±189.93 µg/µL (fruits ethyl acetate extract) to 3800.0±70.71 µg/µL (fruits ethanol extract). The leaves and fruits extracts displays the good antibacterial, antifungal and antioxidant activities. These results partialy justify the traditional use of V. doniana extracts.
Keywords: Plant extract, Polyphenols and flavonoids content, Biological activity, Benin
Cite this paper: Durand Dah-Nouvlessounon, Adjoavi Esse Agossou, Ismaël M. S. Hoteyi, Djihal Koda, Christine N’tcha, Martial Nounagnon, Oscar Didagbé, Haziz Sina, Adolphe Adjanohoun, Lamine Baba-Moussa, Phytochemical Analysis, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Vitex doniana Sweet Leaves and Fruits Extracts, American Journal of Biochemistry, Vol. 13 No. 1, 2023, pp. 14-24. doi: 10.5923/j.ajb.20231301.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Plants have long played an important role for humanity, because they can synthesize a large number of complex organic molecules, often with biological activities. Throughout the world, medicinal plants are mostly used in the preventive or curative treatment of several diseases [1]. Medicinal plants can be defined as any plant with one or more of its organs containing a substance that can be used for therapeutic purposes or that can be used as a synthetic antimicrobial precursor [2]. In the past, these resources were used in their crude form, then over time, the preparation of concentrated extracts made it possible to intensify their medical effect [3]. However, the crude form remains widely used in Africa by traditional medicine. Indeed, traditional African medicine includes all the knowledge and practices, explainable or not, to which traditional practitioners use to diagnose, prevent or eliminate a physical, mental or social imbalance by relying exclusively on lived experience and the observation transmitted from generation to generation [4,5]. Nowadays, despite the progress of modern medicine, which for the most part uses synthetic products and the latest generation techniques, there is an alarming evolution of several chronic diseases including microbial, parasitic, viral infections, cancers, oxidative stress and many more [6].For the infectious diseases, certain groups of bacteria secrete toxins and possess virulence genes which are very dangerous for health [7]. Apart from bacterial toxins, mycotoxins are fungal secondary metabolites that can contaminate animal and human nutrition at all stages of the food chain [8]. Resistance of microbes has led to failures and stern complications in the treatment of bacterial fungal infections, escalating morbidity and mortality around the world [9]. It therefore seems important to explore other alternative for fighting infectious diseases. In addition uncontrolled reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) production are known to cause redox imbalances and cellular oxidative stress. The effects of these ROS and RNS are harmful and have been reported to be critical in a variety of diseases such as neurodegenerative disorders, cancer, and autoimmune diseases [10]. The search for agents that can control both bacterial infections and the harmful effect of free radicals is an important challenge to resolve public health problems.Numerous studies have been undertaken in order to find antimicrobial agents from plants against organisms ranging from viruses to protozoa [11]. Vitex doniana Sweet (West African plum or black plum) is a flowering plant, of the family Verbernaceae, and is one such medicinal plant of importance [10]. V. doniana has a lot of useful applications it serves as a source of food and medicine and provides timber for furniture [12]. Based on folkloric medicinal used of V. doniana in Benin, this study aimed to search for phytochemical constituents and evaluated antimicrobial and antioxydant activity of V. doniana plant extracts.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
- Vitex doniana Sweet leaves and fruits, were collected in Adjohoun, department of Oueme, southern Benin. The specimens were then deposited for official certification at the National Herbarium of Benin, located at the University of Abomey-Calavi in Cotonou, under the supervision of Herbarium conservator Prof. Hounnankpon Yedomonhan. The certification was recorded under voucher No. YH258/HNB. The plants materials were air dried at 25°C - 30°C for two weeks, grinded and sieved into a bark powder. The smooth powder was stored in airtight glassware and kept in darkness at -20°C until use.
2.2. Phytochemical Profiling
- The phytochemical profiling of Vitex doniana Sweet leaves and fruits powders to determine the major constituents (nitrogenous, polyphenolic and terpenic compound, and glycosides) was done according to Houghton and Raman [13].
2.3. Preparation of Plant Extracts
- The protocol described by Chokki et al. [6] was used. Three solvents (Ethanol, ethyl acetate and dichloromethane) were used for V. doniana leaves and fruits crud extract preparation. For each solvent, 1 g of powder in 100 mL of solvent was subjected to ultrasonication (35 Hz) at room temperature for 2 hours. Each mixture was filtered through Whatman N° 1 paper (125 mm ø, Cat No. 1001 125) and concentrated under reduced pressure using a rotary evaporator before oven dried at 40°C. The extraction yields were determined by the ratio between the mass of powder and extract obtained.
2.4. Microplate Determination of Total Polyphenol Content
- The total polyphenol content was determined by applying the Folin–Ciocalteu method descrieb by Dicko et al. [14] using a 96-well plate analysis. First, 25 µL of Folin–Ciocalteu reagent was added to 10 µL of each extract. After 5 min of incubation, 25 µL of a 20% aqueous sodium carbonate solution and ultrapure water was added until the final volume reached 200 µL. Blanks were also prepared for each sample by replacing the Folin–Ciocalteu reagent with ultrapure water. A freshly prepared gallic acid solution (0.97 - 500 µg/mL) was used as a standard reference, and the results presented as µg equivalents of gallic acid per mg of sample. After 30 min, the absorbance values of the samples at 760 nm were recorded using a multiwell plate reader (Tecan Pro 200, Tecan Trading AG, Männedorf, Switzerland).
2.5. Microplate Determination of Total Flavonoids Content
- V. doniana leaves and fruits total flavonoid content was quantified by a 96-well plate analysis using aluminum chloride described by Dah-Nouvlessounon et al. [15]. First, 100 µL of an aqueous 2% aluminum chloride solution was added to 100 µL of each extract sample. After 15 min of incubation, the sample absorbance values at 415 nm were read using the Tecan Pro 200 multiwell plate reader. Quercetin was used as a reference standard (0.078 - 40 µg/mL), and the results are presented as µg equivalents of quercetin per mg of sample.
2.6. Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity
2.6.1. Microorganisms
- The antimicrobial activity of Vitex doniana extracts was evaluated on: Ten (10) reference strains including Gram+ bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213, Staphylococcus epidermidis T22695, Micrococcus luteus ATCC 10240, Streptococcus oralis, Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212), Gram- bacteria (Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Proteus mirabilis A24974, Proteus vulgaris A25015, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853) and yeast (Candida albicans MHMR). In addition to the reference strains, we used three (03) fungal strains (Penicillium citrinum, Aspergillus tamarii and Fusarium verticilloides) isolated from Beninese traditional cheese wagashi by Sessou et al. [16] and nine (09) strains of staphylococcus (Staphylococcus sciuri, Staphylococcus simulans, Staphylococcus lentus, Staphylococcu saureus, Staphylococcus equorum, Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Staphylococcus xylosus, Staphylococcus cohnii, Staphylococcus saprophyticus) isolated from meat products by Attein et al. [17].
2.6.2. Microorganisms Growth Conditions
- Overnight (18h) cultures were prepared by inoculating 1 mL Muller Hinton broth with 1-2 young colonies of each organism obtained from 24 h-old Muller Hinton Agar cultures. Broths were incubated overnight at 37°C with shaking. Inocula were prepared by diluting overnight cultures in saline to approximately 108 cfu mL−1 for bacteria and 107 cfu mL−1 for C. albicans. These suspensions were further diluted with sterile saline as required.
2.6.3. Sensitivity of Bacterial and Yeast Strains
- The agar perforation method inspired of those described by Bauer et al. [18] was used to screen the antimicrobial activity. Briefly, four to five perforations were performed under aseptic conditions, on Mueller Hinton agar petri dish previously flooded of the appropriate bacterial culture (adjusted to 0.5 McFarland standard). Twenty five microliter of extract solution (20 mg/mL) were aseptically lodged in the hole. These dishes were kept for 15-30 min at room temperature before incubation at 37°C for 24 and 48 h. After the incubation period, the dishes were examined for inhibitory zones. Each sample was used in triplicate for the determination of antibacterial and antifungal activity.
2.6.4. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory/Bactericidal Concentrations (MIC and MBC/CMF)
- The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration were determined by microdilution method using iodonitrotetrazolium (INT) as an indicator of bacterial viability with 96-well plates [19].The extracts concentrations range from 10 to 0.039 mg/mL were tested on the microbial strains. In fact, 150 µL of distilled water was distributed in all the wells (from well 2 to 10) of the plate. Then 150 µL of each extract at 20 mg/mL were introduced into wells 1 and 2 of the plate. Successive half dilutions were then carried out from well 2 to well 10 and 150 μL from the last well was discarded. Also 150µL of bacterial inoculum (106 CFU/ml) was added to all wells from 1 to 10. The plate was then covered and incubated at 37°C for approximately 18 hours. After incubation, 10 µL of p-iodonitrotetrazolium chloride (INT, Sigma Aldrich, Gillingham, UK) solution was added followed by incubation at 37°C for 30 min. The MIC corresponds to the first well in which red/pink coloring is not observed starting from the last well. The MBC of the extracts was also determined by subculturing 2 μL aliquots of the MIC assay preparations in 100 μL MHB and incubating for 24 h at 37°C. The MBC was defined as the lowest concentration of each sample that did not exhibit a color change after the addition of INT, as described above [19].
2.6.5. Antifungal Activity
- The in vitro antifungal activity of V. doniana extracts was evaluated according to the method previously described by Dohou et al. [20]. The assay was performed on the Potato-Dextrose Agar medium. Briefly, the extracts (20 mg/mL) use for the antifungal activity was dissolved with sterilize distillated water or if necessary with a water-ethanol mixture (60:40). One ml of the dissolved extract (20 mg/mL) was thoroughly mixed with 10 mL of the sterilized Potato-Dextrose Agar medium (PDA) before it transferred to sterile petri dishes for solidification. After the medium solidification, a sterile 6 mm disc treated with fungal strain was placed in each Petri plate. Each treatment was replicated twice. Plates were incubated at 25 ± 1°C for 5 days. Fungal radial growth was measured by averaging the two diameters taken from each colony. Percentage growth inhibition of the fungal colonies was calculated using the formula:
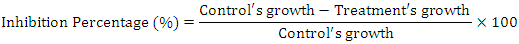
2.7. Antioxidant Activity Determinations
- The antioxidant activity was measured using both DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) and ABTS [2,2’-azinobis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid)] methods. The ABTS assay was conducted according to the method described by Re et al. [21]. The working solution of ABTS+ (10 mg of ABTS, 2.6 ml of deionized water and 1.72 mg of potassium persulphate) was left to stand at room temperature for 12 h in the dark before use. This solution was diluted with ethanol until obtaining an absorbance of 0.70 ± 0.02 at 734 nm. Twenty µl of each extract sample (1 mg/ml) was diluted with a fresh prepared ABTS solution to a total volume of 1 ml. All the assays were performed in triplicates, the absorbance was read after 15 min in dark at 734 nm and the reference molecule was ascorbic acid. The concentration of compounds with a capability to reduce ABTS+ radical cation is expressed as µmol equivalent Ascorbic Acid (µmol EqAA) per gram of dry extract using the following formula used by Guenne et al. [22].The DPPH method was conducted by adaptation as described by Scherer and Godoy [23]. Equal volumes (100 µl) of DPPH (50 μM) and plant extracts (200 μg/ml) were mixed in a 96 well microplate and allowed to stand in darkness for 20-30 min at room temperature. Then, the absorbance was read at 517 nm and the blank was a mixture of methanol and DPPH (v:v). The inhibitory percentage of DPPH radical indicating the antioxidant activity of extracts and BHA, gallic acid was obtain using the formula establish by Schmeda-Hirschmann et al. [24]. The Concentration providing 50% inhibition (IC50) was determined graphically using a calibration curve in the linear range by plotting the extract concentration and the corresponding scavenging effect. Antioxidant activity index (AAI) was calculated according to the formula used by Scherer and Godoy [23].
2.8. Statistical Analysis
- All experiment was done in triplicate and data thus obtained reported as a mean ± standard deviation (SD). The data were analyzed using Graph Pad Prism 5 software for quantitative analysis. Differences of p < 0.05 were considered significant.
3. Results
3.1. Extraction Yield
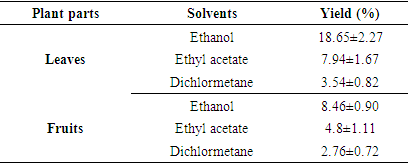
- The extraction yield varies depending on the V. doniana organs and the extraction solvent (Table 1). With V. doniana leaves, the highest yield (18.65±2.27%) was obtained with the ethanolic extract while the lowest (3.54±0.82%) was obtained with the dichloromethane. The same trend was obtained with V. doniana fruits where the ethanolic extract showed the highest yield (8.46±0.90%) compared to 2.76±0.72% obtained with dichloromethane solvent. For both organs, ethyl acetate showed intermediate yields of 4.8±1.11% for fruits and 7.94±1.67% for leaves. By comparing the two organs, we see that the leaves gave better yields whatever the extraction solvent.
|
3.2. Phytochemical Screening
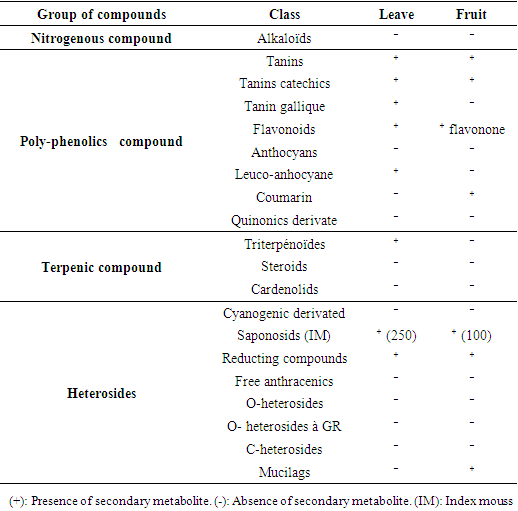
- Various secondary metabolites were found in the leaves and fruits of V. doniana (Table 2). Indeed, 31% of the secondary metabolites sought were found in the leaves compared to 30% in the fruits. Catechic tannins, flavonoids, saponosides and reducing compounds were found simultaneously in the leaves and fruits of V. doniana. On the other hand, tanin gallic, leucoanthocyans and triterpenoids were found only in the leaves while coumarins and mucilages were found only in the fruits.
|
3.3. Polyphenol and Flavonoids Content of V. doniana Extracts
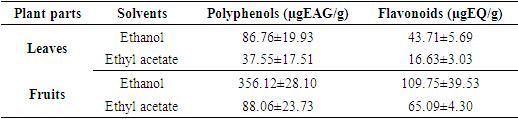
- Total Polyphenol and total flavonoids content of V. doniana the leaves and fruits were presented in Table 3. Contrary to the remark made during the extraction yield, the total polyphenols are more concentrated in the fruits ethanolic extract (356.12 ±28.10 µgEAG/g) than those of leaves (86.76±19.93 µgEAG/g). The contents obtained with the ethyl acetate extract are respectively 88.06±23.73 µgEAG/g with fruits and 37.55±17.51 µgEAG/g for the leaves. Considering the total flavonoid composition, the same observation was made. Indeed, the fruits ethanolic extract showed the highest content of flavonoids (109.75±39.53 µgEQ/g) compared to 43.71±5.69 µgEQ/g obtained with the same leaf extract. Likewise, flavonoids are more concentrated in the fruits ethyl acetate extract (65.09±4.30 µgEQ/g) than those of leaves with a content of 16.63±3.03 µgEQ/g.
|
3.4. Antimicrobial Activity of V. doniana Leaves and Fruits Extracts with Reference Starins
- The susceptibility of reference strains to V. doniana fruit and leaf extracts varies depending on the extracts and over time for certain strains (Figure 1). The dichloromethane extracts of the two organs not showed activity on the reference strains. The inhibition zones diameters of the active extracts vary depending on the strains (p=0.001) and over time (between 24h and 48h) for the fruits ethanolic extracts (p=0.01) and leaves ethanolic extracts (p<0.05) respectively with the P. vulgaris and E. coli strains. The fruits ethanolic extract inhibited 80% of the strains while the leaves ethanolic extract inhibited 60% of the strains. The inhibition diameters of the fruits ethanolic extract vary from 12.75±0.35 mm (M. luteus) after 24 hours to 4.00±0.00 mm obtained with the E. coli strain after 48 hours. Furthermore, the inhibition diameters of the leaves ethanolic extract vary from 12.5±0.00 mm (S. epidermidis) after 24 hours to 6.5±0.00 mm obtained with the E. coli strain after 24 hours. This observation shows that of all the sensitive strains to fruits and leaves ethanolic extracts, E. coli is the one which recorded the lowest inhibition diameters. Regarding the ethyl acetate extracts of the two organs of V. doniana, the largest diameters were obtained with P. mirabilis strains (11.75±0.35mm) and C. albicans (12.00±0.00 mm obtained after 24 hours) respectively for the fruits and leaves ethyl acetate extracts.
 | Figure 1. Medium inhibitory diameter zone of V. doniana leaves and fruits extracts on reference strains |
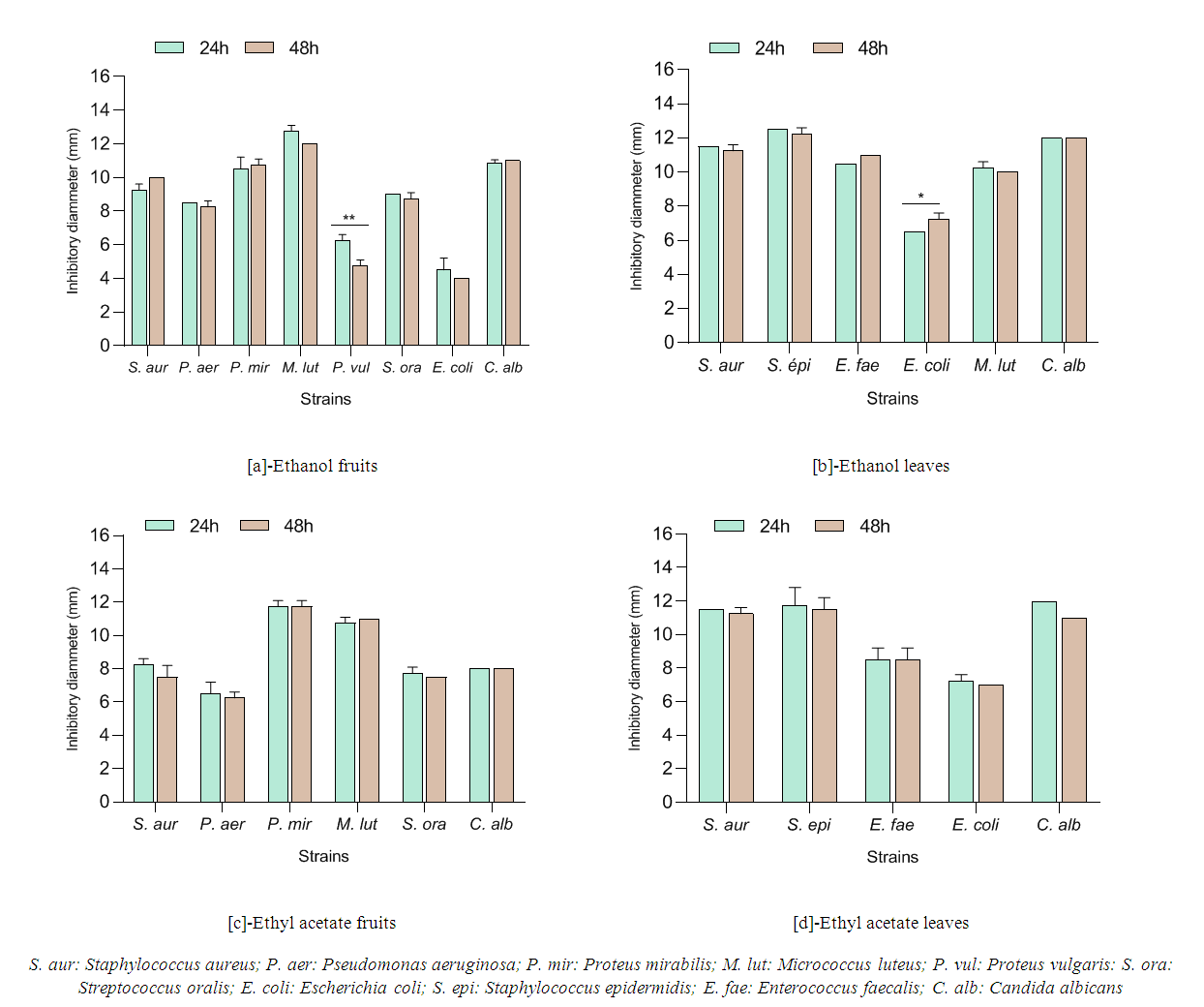
 | Table 4. Minimum Inhibitory (MIC) and Bactericidal/Fungicidal Concentration (MBC/MFC) of V. doniana leaves and fruits extracts with reference starins |
3.5. Antimicrobial Activity of V. doniana Leaves and Fruits Extracts with Meat Isolated Starins
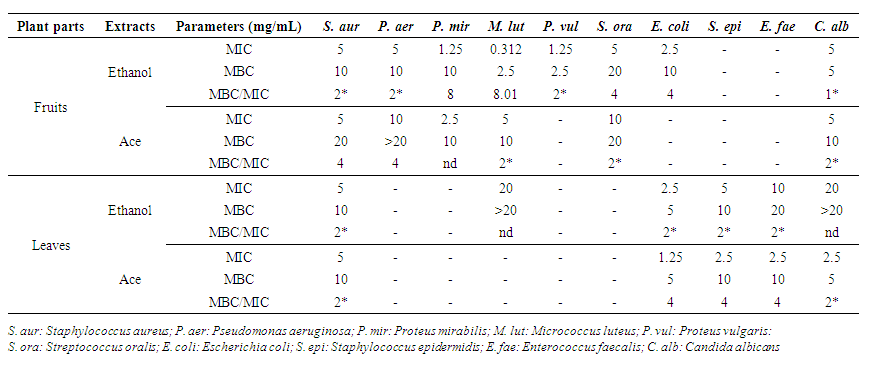
- The susceptibility of meat isolated strains to V. doniana extracts is presented in Figure 2.The inhibition zones diameters of meat isolated strains vary depending on the strains and extracts (p=0.001). There was no variation (p>0.05) in inhibitory diameters between 24h and 48h. The action spectrum of the extracts shows that the fruits ethanolic extract inhibits 100% of meat isolated strains while those of the leaves inhibits 80% of strains. Furthermore, the fruits ethyl acetate extract inhibits 55.55% of the strains compared to 44.44% for those of the leaves. The S. lentus strain is the most sensitive to fruits ethanolic extracts and leaves with respective inhibition diameters of 17.75±0.35 mm and 16.00±0.00 mm. On the other hand, for the ethyl acetate extract of the two organs, the largest diameter (13.5±0.70 mm) was recorded with the S. equorum strain (fruits ethyl acetate extract) and S. cohnii strain (12.75±0.35 mm) with leaf extract (Figure 2).
 | Figure 2. Medium inhibitory diameter zone of V. doniana leaves and fruits extracts on meat isolated strains |
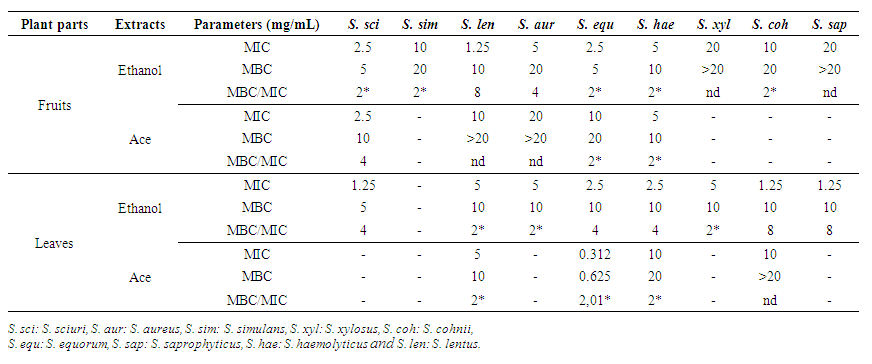 | Table 5. Minimum Inhibitory (MIC) and Bactericidal/Fungicidal Concentration (MBC/MFC) of V. doniana leaves and fruits extracts with meat isolated starins |
3.6. Antifungal Activity
- The antifungal potency of the extracts is presented in Figure 3. The four types of extract inhibited F. verticilliodes and P. citrinium at various proportions while the fruits ethyl acetate extracts and the leaves ethanolic extracts had no potency on the growth of A. tamarii strain. Considering the F. verticilliodes strain, the leaves ethanol extract showed the highest inhibition percentage (49.24±1.04%) while the leaves ethyl acetate extract inhibited the strain less (p<0.05) at a rate of 40.63±4.42%. The same trend was observed for the P. citrinium strain where the fruits ethanolic extract showed the highest inhibition rate (34.92±2.24%) while the leaves ethyl acetate extract showed the lowest fungal growth inhibition rate (12.70±2.24%). We note a significant difference (p<0.0001) between the action of these two extracts with P. citrinium. Likewise, a difference (p=0.002) was observed between the inhibitory power of the fruits ethanolic extracts and the extracts (fruits ethyl acetate and leaves ethanolic). No variation (p>0.05) in the inhibition power was observed with the fruits ethyl acetate extracts and the leaves ethanolic extracts (Figure 3). On the other hand, these two extracts had inhibition rates (22.50±3.54%) higher (p<0.05) than that of the leaves ethyl acetate extract which showed the low inhibition of the P. citrinium strain (12.70±2.24%). Regarding the A. tamarii strain, it turns out to be the most resistant to extracts. Contrary to what was observed with the two other strains, the leaves ethyl acetate extract which showed a low inhibition rate with the previous strains showed here the highest growth inhibition rate (45.90±2.32%) of A. tamarii while the fruits ethanolic extract recorded the lowest (18.33±2.36%) with a large difference (p<0.0001). The comparative effect of the susceptibility of the strains to the extracts shows that F. verticilliodes strain is the most sensitive while A. tamarii is the most resistant.
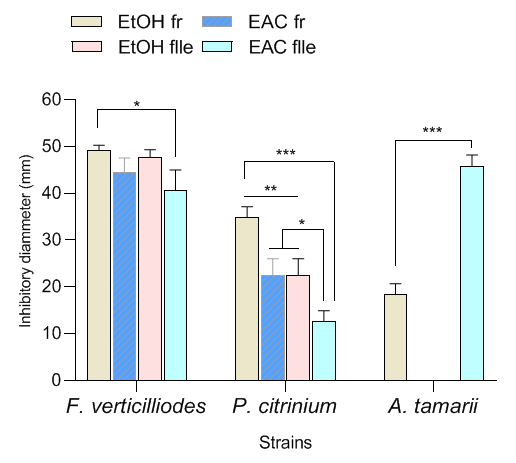 | Figure 3. Inhibition rate of V. doniana extracts in the fungal growth |
3.7. Antioxidant Activity
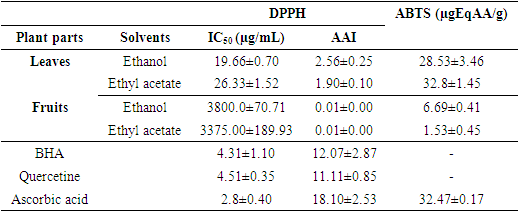
- The four extracts showed varied antioxidant activities through the DPPH and ABTS methods (Table 6). Considering the scavenging activity of DPPH radical, the leaves ethanolic extract showed the strong antioxidant capacity with an IC50 of 19.66±0.70 µg/µL followed by the leaves ethyl acetate extract (IC50=26.33±1.52 µg/µL). Furthermore, the two extracts of V. doniana fruits showed weak antioxidant activities with IC50 ranging from 3375.00±189.93 µg/µL (ethyl fruits acetate extract) to 3800.0±70.71 µg/µL (fruits ethanolic extract). In terms of plant organ, the same observation was made with the ABTS method where leaf extracts showed the best powers of reducing ABTS+ radical cation. However, it should be noted that the leaves ethyl acetate extract showed the highest activity (32.8±1.45 µgEqAA/g) followed by the leaves ethanolic extract (28.53±3.46 µgEqAA/g). The antioxidant activity index (AAI) and the IC50 of reference molecules such as BHA (IC50=4.31±1.10µg/µL; AAI=12.07±2.87), quecetin (IC50=4.51±0.35µg/µL; AAI=11.11±0.85) and ascorbic acid (IC50=2.8±0.40 µg/µL; AAI=18.10±2.53) show that the extracts have low activities compared to the reference molecules. The same observation was made with the ABTS method where ascorbic acid showed stronger activity (32.47±0.17 µgEqAA/g) than that of the extracts (Table 6).
|
4. Discussion
- V. doniana Sweet, commonly called Black plum, belongs to the Verbernaceae family is part of Benin pharmacopeae. The leaf and fruits of this plants were used widely for their pharmacological property. This study aimed to search for phytochemical constituents and evaluated antimicrobial and antioxydant activity of V. doniana plant extracts. Extraction is an important step in the itinerary of phytochemical processing for the discovery of bioactive constituents from plant materials [25]. Selection of a suitable extraction technique is also important for the standardization of herbal products as it is utilized in the removal of desirable soluble constituents, leaving out those not required with the aid of the solvents [26]. In this study, we used three solvents such as ethanol, ethyl acetate and dichloromethane. The extraction yield obtained varies depending on the V. doniana part and the extraction solvent (Table 1). The same observation with made by Barry et al. [27] with various extraction solbents. In this study, with V. doniana leaves, the highest yield (18.65±2.27%) was obtained with the ethanolic extract while the lowest (3.54±0.82%) was obtained with the dichloromethane. The solubility of a drug in a given solvent is mainly a function of the polarity of the solvent [28]. Many factors influence extraction yields from biomass, and some of these factors can even influence one another in interdependent ways. Following are a few of the most influential factors when it comes to botanical extraction yields, we can have: Factors within the plant itself, Environmental influences, Harvest practices, Post-harvest storage and processing, Extraction method [29].Contrary to the remark made during the extraction yield, the total polyphenols are more concentrated in the fruits ethanolic extract (356.12±28.10 µgEAG/g) than those of leaves (86.76±19.93 µgEAG/g). The same observation was made considering the total flavonoid composition. The results obtained in this study is lower than those of Memi et al. [30] who obtained 39.63±0.97 mgGAE/g and 6.65±1.05 mgQE/g respectively for polyphenols and flavonoids content in leaves ethyl acetate extracts. This variation can be linked to several factors such as the place and the harvest period because the quality of the soil and the environmental conditions influence the formation and expression of metabolites in a plant.The susceptibility of tests strains to V. doniana fruit and leaf extracts varies depending on the extracts and over time for certain strains. The inhibition zones diameters of the active extracts vary depending on the strains (p=0.001) and over time (between 24h and 48h) for the fruits ethanolic extracts (p=0.01) and leaves ethanolic extracts (p<0.05) respectively with the P. vulgaris and E. coli strains. The MIC and CMB obtained with the active extracts vary (p=0.001) also depending on the strains. Egharevba et al. [31] through their studies also showed that the acetate, methanolic and hexanic extract of V. doniana leaves inhibited the proliferation of certain microorganisms (S. aureus, P. vulgaris, P. mirabilis, C. albicans, P. aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae) at a concentration of 10mg/mL. Odoom et al. [10] repported that the Gram-positive bacteria, such as E. faecalis and S. aureus were the organisms most susceptible to the antimicrobial action of the fruit essential oils. Others authors [10,12,32,33] have also shown the antibacterial and antifungal activity of V. doniana extracts on reference strains and those isolated from various matrices. This antimicrobial power of V. doniana extracts would be linked to its chemical composition. Bunu et al. [12] isolated saponin from V. doniana extracts and authors of antimicrobial studies on the species attribute antibacterial effects to them. Because saponin-enriched extracts have demonstrated non-discriminate activity against Gram-positive [34] and Gram-negative [35] bacteria, then it is likely that saponins are important in these antimicrobial outcomes. Outside antimicrobial activity, V. doniana fruits extracts showed weak antioxidant activities with IC50 ranging from 3375.00±189.93 µg/µL (ethyl fruits acetate extract) to 3800.0±70.71 µg/µL (fruits ethanolic extract). In terms of plant organ, the same observation was made with the ABTS method where leaf extracts showed the best powers of reducing ABTS+ radical cation. Antioxydant activity of these extracts would also be linked to its chemical composition. Traore et al. [36] identified some phenolics acids like: Gallic acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, chlorogenic acid, cinnamic acid, p-coumaric acid, o-coumaric acid and syringic acid in V. doniana extract. Ajiboye [37] also identified some phytochemical constituents in V. doniana fruits extract such as: Campesterol, Apigenin, saikosaponin, galangin and catechol. These compounds are known for their antioxidant activities. For exemple, Natella et al. [38] reported that cinnamic acids had the highest antioxidant activity compared to their benzoic equivalents, resulting in a strong ability to neutralise peroxyl radicals. Phenolic acids possess much higher in vitro antioxidant activity than well-known antioxidant vitamins [39]. Hydroxycinnamic acids, derived from cinnamic acid, present in foods often as simple esters with quinic acid or glucose. The most abundant soluble bound hydroxycinnamic acid present is chlorogenic acid (a combined from form of caffeic and quinic acids). The four most common hydroxycinnamic acids are ferulic, caffeic, p-coumaric, and sinapic acids. On the other hand, hydroxybenzoic acids possess a common structure of C6-C1 and derived from benzoic acid [40]. These compounds are reported by several authors for the strong antioxidant activity [41-43].
5. Conclusions
- V. doniana organs use in this study display the good biological activity. Qualitative phytochemical analysis revelate various secondary metabolites in the leaves and fruits of V. doniana. Indeed, catechic tannins, flavonoids, saponosides and reducing compounds were found simultaneously in the leaves and fruits. On the other hand, total polyphenols are more concentrated in the fruits ethanolic extract than those of leaves. Considering the total flavonoid composition, the same observation was made. The leaves and fruits extracts displays the good antibacterial, antifungal and antioxidant activities. These results partialy justify the traditional use of V. doniana extracts.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- The authors thank the Laboratory of Biochemistry, enzymology, Industrial Biotechnology and Bioinformatic, UFR/SVT University of Ouagadougou, Burkina-Faso.
Conflict of Interests
- The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML