-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Biochemistry
p-ISSN: 2163-3010 e-ISSN: 2163-3029
2017; 7(3): 47-53
doi:10.5923/j.ajb.20170703.03

Lipoprotein Associated Phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) as an Emerging Cardiovascular Marker
Mirshad P. V.1, Jithesh T. K.2, Jaideep Mahendra3, Prema Gurumurthy1
1Meenakshi Academy of Higher Education and Research, West K. Knagar, Chennai, India
2Department of Biochemistry, MES Medical College, Perinthalmanna, Kerala, India
3Department of Periodontics, Meenakshi Ammal Dental College, Chennai, India
Correspondence to: Jithesh T. K., Department of Biochemistry, MES Medical College, Perinthalmanna, Kerala, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Background: The incidence of cardiovascular diseases (CVD) is on the increase globally. The risk factors like hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, obesity and family history have a strong association with CVD and thus having a predictive value. Biomarkers are important tool used to predict the development of CVD. LpPLA2 is an enzyme specific to arterial inflammation making it a promising biomarker for predicting the development of CVD. This study was undertaken to assess the role of Lipoprotein Associated Phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) as a biomarker to predict CVD in patients with metabolic syndrome (MS) among South Indian population. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted in a tertiary care teaching hospital. Test population comprised of people with any of the three risk factors as per Adult Treatment Panel III (ATP III) guidelines and control population was age and sex-matched healthy individuals. Demographic details, blood pressure and blood samples were collected from each patient. Collected samples were used for analyze the lipid profile, blood glucose level, Apo-A1, Apo-B, hs-CRP and LpPLA2. The values obtained were analysed by using the appropriate statistical tool. Result and Discussion: The result showed that a higher level for Total cholesterol LDL and TG in the test population indicates a higher risk for CVD in test population. The Apo -A1 level was significantly less and Apo-B level was significantly higher in test population compared to control group which is a characteristic feature of cardiovascular risk. The level of hs-CRP found to be elevated in test population showed increased inflammation and cardiovascular risk in test population. The study revealed significantly increased Lp-PLA2 level in test population compare to control group, which confirm the role of Lp-PLA2 as a biomarker in CVD. The outcome of the study is favorable to use Lp-PLA2 as a predictive marker for CVD in south Indian population. Conclusion: The study clearly demonstrates that Lp-PLA2 is a suitable marker to predict CVD. Lp-PLA2 is more specific cardiac marker to predict CVD when compare to conventional markers. The Lp-PLA2 as an independent advanced predictor of CVD needs to be further evaluated by follow-up studies with better sample size in South Indian population.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease, Biomarkers, LpPLA2, South Indian population
Cite this paper: Mirshad P. V., Jithesh T. K., Jaideep Mahendra, Prema Gurumurthy, Lipoprotein Associated Phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) as an Emerging Cardiovascular Marker, American Journal of Biochemistry, Vol. 7 No. 3, 2017, pp. 47-53. doi: 10.5923/j.ajb.20170703.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The incidence of CVD has been increased globally, it has become a leading cause of morbidity and mortality across the globe and it is projected to remain so [1]. The management of CVD is a global burden and it changes the quality of life of the person affected. The incidence of CVDs may increases due to various risk factors; some of them can be controlled, treated or modified such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, obesity, tobacco use, lack of physical activity and diabetes [1]. However, some risk factors like age, genetic factors and family history cannot be modified. The success of preventive measures depends in part on the precise identification of individuals who are at risk for future cardiovascular diseases (risk prediction). Conventionally, risk prediction has relied on assessment of risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, obesity, family history, etc. [1]Biomarkers are considered as an effective tool for early detection of diseases and help to decide treatment accordingly. Conventionally, total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, Lipoprotein (a), Triglycerides etc, are the commonly used biomarkers to assess the cardiovascular risk [2]. The use of new biomarkers to predict cardiovascular risk has attracted substantial attention in the past decade. These interest has been incited by the awareness that traditional risk factors do not identify everyone who will eventually develop CVD [3]. The Adult Treatment Panel III (ATP III) guidelines recognized that CVD risk is not fully exposed by traditional risk factor assessment, adding that “when major risk factors are present, they account for only half of the variability in CVD risk in the various populations” [4]. These findings necessitate the need for more reliable and accurate biomarkers to predict CVD. Evidence has gathered that inflammation plays a crucial role in the triggering and progression of atherosclerosis, proposing that biomarkers of inflammation may help in predicting an individual’s risk for CVD events. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), an acute-phase reactant, has been well documented as a useful inflammatory marker in predicting future CVD events; although hs-CRP was not recommended as a routine measurement in the ATP III guidelines [5].The drawback of hs-CRP as cardiac marker is that it is nonspecific and level may be increased during inflammation due to any reason. Consequently, a considerable group of peer-reviewed studies have substantiated the role of inflammation in atherogenesis as well as the risk predictive value of variety of other inflammatory markers. Among these, Lp-PLA2 has been shown to be a cardiovascular risk marker independent and additive to traditional risk factors [6, 7]. Lp-PLA2 is an enzyme specifically hydrolyzes oxidized phospholipids on oxidized LDL particles within the arterial intima [8]. Since the level of Lp-PLa2 is specific to arterial inflammation, it is considered as a promising biomarker in CVD [6].It has been reported that the incidence of CVD is very higher among South Indian Population and evaluating the role of a new predictive marker with more specificity for CVD in this population is quite useful for the medical fraternity [7]. As far as the author’s knowledge, no similar study which evaluates the role of Lp-PLA2 as a cardiac marker in the south Indian population been conducted. The study was undertaken to evaluate the role of Lp-PLA2 as cardiac biomarker in subjects with MS among South Indian population.
2. Materials and Methods
- A cross-sectional study was conducted in at M.E.S Medical College hospital, Kerala, a tertiary care teaching hospital after obtaining approval from institutional ethics committee (IEC/MES/42/2014). Written informed consent was obtained from all the volunteers recruited to this study. Blood samples were collected from subjects who attended a medical camp conducted in the hospital in three phases. Total 391 cases were enrolled to the study, grouped in to test (n=271), and control (n=120). Subjects with MS, (a cluster of biochemical and physiological abnormalities associated with the development of cardiovascular diseases, stroke, type- 2 diabetes, etc) as per the Adult Treatment Panel III (ATP III) guidelines [4]. were included as test population, age and sex matched healthy subjects who attended the medical camp were included as control population. Subjects with infectious disease, cancer, auto immune disorders and other terminal diseases were excluded from the study. The demographic parameters like age, height, body weight, sex and body mass index (BMI) of both the groups were noted and recorded. Blood pressure (BP) was recorded separately before the blood collection procedure to avoid the BP fluctuations due to apprehension. Blood was collected in fasting state from both control and test group as per CLSI guideleines. A fully automated analyzer (MindrayBS200) had used to analyze the biochemical parameters like random blood sugar, lipid profiles (Total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL, LDL), LpPLA2, hs-CRP, Apo-A1 and Apo-B Statistical Analysis.The demographic data like age, sex, height, and body weight were analyzed by descriptive statistics. Student’s T-test and one way ANOVA was used to analyze the significant difference in parameters between test and control group. The statistical analysis was conducted by using SPSS software (version 17.0).
3. Results
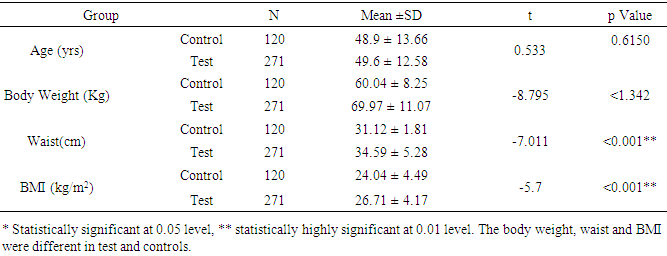
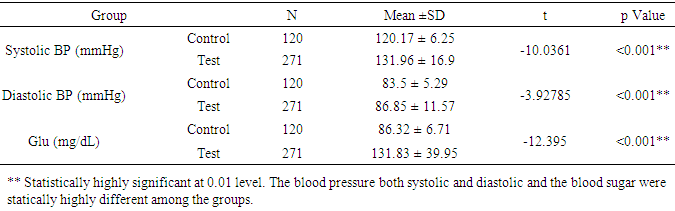
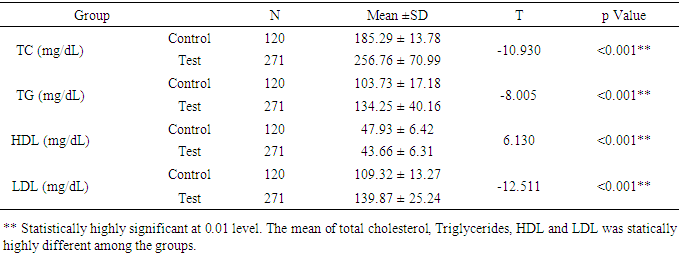
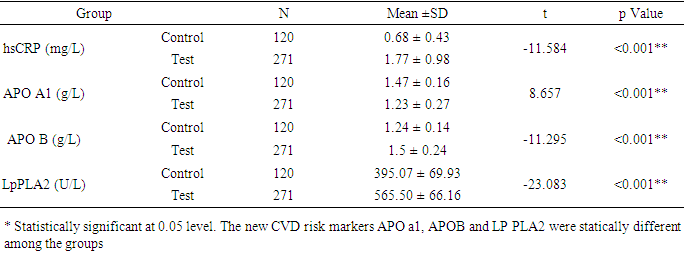
- The study was conducted to assess the role of Lp-PLA2 as a predictive marker in CVD. The result of the study pointed out that average age of control group is 48.9 and that of test group is 49.6 (P=6150). The percentage of females in test group was 59.7% (162 females 109 males) and that of control is 57.5% (69 females, 51 males), there was no statistical difference in both group (p=0.672). The average body weight of control group is 60.04kg and that of test group is 69.97 kg. The average BMI of the test group is higher (26.71) when compare to control group (24.04) (Table 1). The risk factors like BP, random blood sugar, total cholesterol, LDL and TG were significantly higher in the test group when compare to control group (p<0.001). The HDL level was significantly lower in test group (43.66mg/dl) when compare to that of control group (47.93mg/dl) (table 2&3). This showed the presence of risk factors among test population. Further, statistically significant higher value of hs-CRP level in test population (1.77mg/L) indicates higher inflammatory changes among test population (Table 4). A decreased level of Apo-A1 and increased level of Apo-B clearly showed the increased risk for CVD in test group. The mean Lp-PLA2 level in the test group is much higher (565.50 g/L) than that of test group (395.07 g/L). The one way ANOVA between the groups shows a statistically significant difference in the LpPLA2 level (p<0.001).
|
|
|
|
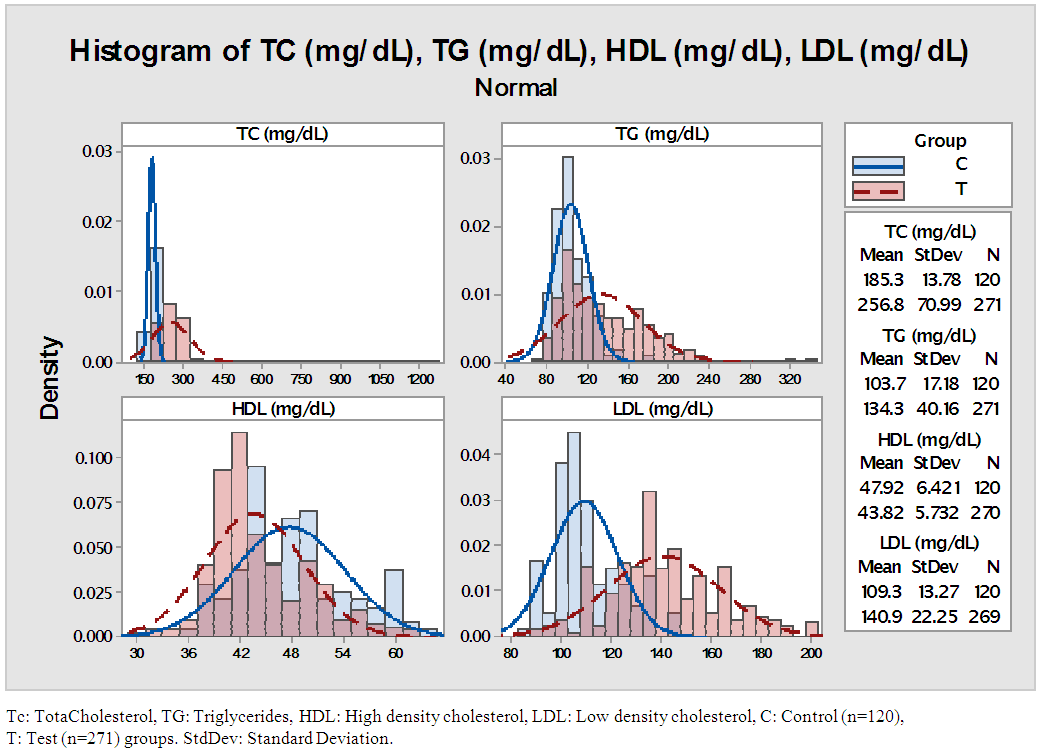 | Figure 1. Distribution of lipid profile parameters in the Test and Control population |
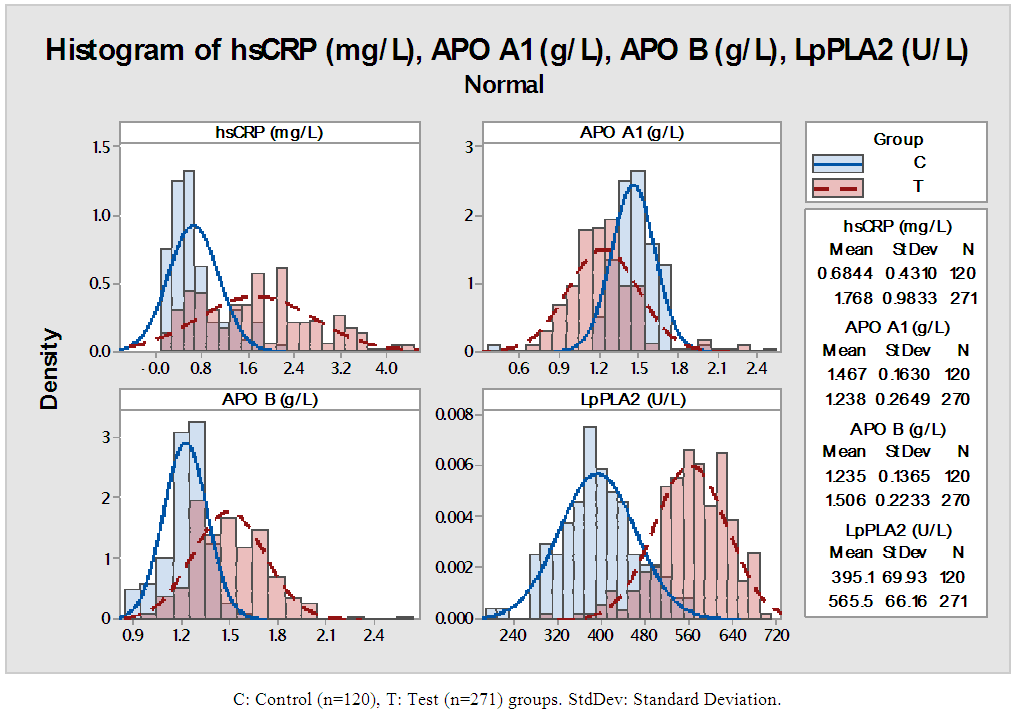 | Figure 2. Distribution of lipid profile parameters in the Test and Control population |
4. Discussion
- CVD is one of the major causes of morbidities and mortalities across the world. The incidence of CVDs can be prevented or minimized to a large extent if the risk factors identified in the early stage. The success of preventive measures depends in part on the precise identification of individuals who are at risk for future cardiovascular events. The lack of a specific biomarker which predicts risk for CVD has fueled intense interest in identifying new biomarkers for early identification of risks for CVD [8]. Various studies suggested that Lp-PLA2 could be a specific biomarker and its level is increased only during the vascular inflammation like atherosclerosis. This study was conducted to identify the role of LpPLA2 as a cardiac risk marker in people with MS. The study population had divided in to two groups, the first group is comprised of subjects with MS (Test) and the other group is comprised of age and sex matched healthy people (Control). The age and sex of the subjects were matched between two groups. The mean value of BMI and waist was higher among the test group. The people with MS usually have a higher BMI; these findings are in accordance with the findings of study conducted by Schnabel RB, et al and Mahmood SS, et al. [9, 10]Our study pointed out that the test population had significantly increased systolic and diastolic blood pressure compare to the control population. According to the Mahmood SS et al, hypertension accounts for about one quarter of CVDs [10]. The findings are in accordance with the findings of the study conducted by Eleni Rapsomaniki, et al and Mahmood SS et al. [10, 11] The study says that blood pressure has a strong association with occurrence of all cardiovascular diseases. The increased glucose level as a result of type2 diabetes is characteristics of MS, the test population in this study had a higher fasting glucose level. The type-2 diabetes is considered as an important risk factor for the cardiovascular risk as per the NCEP- ATP- 3 guidelines and the findings were in agreement with the findings of the study conducted by Staessen JA, et al and Ziaeian B. [12, 13]In the current study, the total cholesterol, LDL- cholesterol and Triglycerides levels were significantly higher in test population. The findings are in accordance with Staessen JA, et al and Anderson, J. L, et al. [13, 14] The Framingham Heart study found that HDL cholesterol, which had an inverse association with the incidence of CVD in either men or women [13]. In our study the HDL level was significantly lower in test group and the finding is similar with the findings of Schnabel RB, et al. [9] It has been noted that the patients with MS may have a low level of HDL cholesterol and a high level of LADL cholesterol.The Apolipoprotein A-1 (ApoA-1) is a lipoprotein present in HDL cholesterol. In our study we found that ApoA-1 level was significantly lower in test group. The decreased level of ApoA-1 in test population is an indication of increased cardiovascular risk in MS. Our findings are similar with the findings of study conducted by Sondermeijer BM, et al, where the ApoA-1 level was significantly less in people with cardiovascular risk [15]. The Apolipoprotein-B (apo-B) an important component of many lipoproteins that are involved in atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. In our study, the elevated level of apo-B in test population indicates the increased incidence of CVD in test population when compared to the control population. These findings are similar to the findings of the study conducted by Jacob J. Clarenbach, et al and Natalie D, et al. [16, 17] According to their study; atherogenic dyslipidemia had been reported in patients with to higher total apo-B levels. In our study, total apo- B, level was higher in the subjects with metabolic syndrome components which are considered as an important risk factor for cardiovascular disease.hs-CRP is an acute-phase reactant and nonspecific marker of inflammation. It has been known for years that inflammation plays a major role in the development of cardiovascular diseases. Assessment of hs-CRP level is often performed to assess the risk of future heart disease. In our study, the level of hs-CRP in the test population was significantly higher when compared to the control population. The elevated hs-CRP level in the test population indicates an increased inflammation and cardiovascular risk in patients with metabolic syndrome. Our findings are in accordance with the findings of Dallmeier D, et al and Goff Jr DC, et al. [18, 19] It has also been suggested that hs-CRP can be used to target therapy and tailor risk modification to prevent CVD [18].Accumulating evidence has suggested that Lp-PLA2 could be a specific biomarker of CVD in future. The recognition that atherosclerosis represents, in part, an inflammatory process has created considerable interest in measurement of Lp-PLA2 as part of cardiovascular disease risk assessment. Our study was undertaken to assess the role of Lp-PLA2 as cardiac marker in patients with MS among south Indian population and compare with the conventional cardiac markers. In the current study, we found that level of Lp-PLA2 is significantly higher in test population compare to the control group. Different studies have proven that the level of LpPLA2 is found to be increased among the population with cardiovascular risk [20-23]. Moreover, the increased level of Lp-PLA2 in test population is correlating with the increased level of other cardiac markers like LDL-C, hs-CRP, etc. The findings are in accordance with the findings of the study conducted by Hatoum IJ, et al, Kardys I, et al and Saremi A, et al. [20-22] Higher plasma levels of Lp-PLA2 may increase the risk for CVD regardless of the presence of MS. The increased level of Lp-PLA2 along with the other markers like Apo-A1, Apo-B, hs-CRP, LDL-C indicates that Lp-PLA2 is a reliable marker in predicting the cardiovascular events in the given population.
5. Conclusions
- This study was undertaken to check the role of Lp-PLA2 as a cardiac biomarker to predict the CVD among South Indian population. The findings from this study pointed that Lp-PLA2 has significant role as a predicative marker like other markers used in CVD. The elevated level of Lp-PLA2 along with other markers like Apo- A1, apo-B, LDL-C and hs-CRP indicates that Lp-PLA2 is a suitable marker to predict cardiovascular risk in given population. The advantage of Lp-PLA2 as an independent advanced predictor of CVD needs to be evaluated by a prospective follow-up study with better sample size.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors are thankful to MES medical college hospital management, Mindray India Pvt Ltd and Diasys India for their technical support.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML