-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Biochemistry
p-ISSN: 2163-3010 e-ISSN: 2163-3029
2017; 7(2): 23-26
doi:10.5923/j.ajb.20170702.02

Biochemical Effects of Dichlorvos Pesticide on the Liver of Poultry Birds (Gallus domestica)
Ethelbert U. Ezeji1, Ikechukwu N. E. Onwurah2
1Department of Biotechnology, Federal University of Technology, Owerri, Nigeria
2Pollution Control and Biotechnology Unit, Department of Biochemistry, University of Nigeria Nsukka, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Ethelbert U. Ezeji, Department of Biotechnology, Federal University of Technology, Owerri, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Continuous use of pesticides can pose severe health hazards to humans and animals. Dichlorvos (DDVP) is widely used as an insecticide to control household pests, in public health, protecting stored product from insects and control of parasites in livestock. The objective of this study is to determine the effect of dichlorvos on biochemical parameters of the liver of poultry birds. Seven weeks old poultry birds (pullets) were fed on commercial poultry feed contaminated with 0.01, 0.02 and 0.04% dichlorvos (w/v). The control group has no pesticide added to their feed. The birds were sacrificed after 10 weeks of exposure and the liver removed. Analysis of the liver homogenates revealed a significant (p<0.05) reduction in total protein as well as cytoplasmic and membrane bound cholesterol. There were no significant differences (p > 0.05) in the levels of triglyceride in the cytoplasm of the liver between the control and the birds exposed to pesticide. However, there was a significant reduction (p < 0.05) in the concentration of membrane bound triglyceride from 4.65 ± 0.023 mg/g tissue to 2.81 ± 0.015 mg/g tissue in the birds exposed to 0.04% pesticide. There was a significant increase in serum protein and lipid peroxidation; significant reduction (p<0.05) in serum glutathione and glutathione s-transferase activity at 0.04% pesticide contamination as against the control. The above results show that biochemical parameters can be used as indicators of pesticide exposure in poultry birds.
Keywords: Dichlorvos, Pesticide exposure, Non-target organisms, Biochemical effects, Poultry birds
Cite this paper: Ethelbert U. Ezeji, Ikechukwu N. E. Onwurah, Biochemical Effects of Dichlorvos Pesticide on the Liver of Poultry Birds (Gallus domestica), American Journal of Biochemistry, Vol. 7 No. 2, 2017, pp. 23-26. doi: 10.5923/j.ajb.20170702.02.
1. Introduction
- The use of insecticides has become very important because of the increasing menace of insects, especially in the tropics, posing a threat to health or competition for food or other materials with man [1]. Frequent uses of pesticides for various industrial, agricultural and domestic purposes are veritable sources of introduction into the environment [2]. Widespread use of pesticides in agriculture and domestic pest control has contributed to the pollution of the environment [3]. In addition to their intended effect, pesticides are sometimes found to affect non-target organisms including humans [4, 5]. Dichlorvos is widely used as an insecticide to control household pests, in public health, protecting stored product from insects and control of parasites in livestock. Like all organophosphate pesticides, dichlorvos works through the inhibition of the activity of the enzyme acetylcholesterase [6]. Exposure to an organophosphate could be lethal resulting in death due to respiratory failure [7]. This study examines the toxicological effects of dichlorvos on poultry birds using some biochemical biomarkers.
2. Materials and Methods
- Test SampleDichlorvos (2, 2 – dichlorovinyldimethyl phosphate) –DDVP, was purchased from an agrochemical shop in Owerri, Nigeria.Formulation of contaminated dietThe feeds were contaminated by weighing out a definite amount of the feed and then mixing with dichlorvos pesticide to give 0.01, 0.02 and 0.04% (w/v) contaminations respectively. The feed for the control group contained no pesticide.Experimental AnimalsSeven weeks old pullet chicks with an average weight of 557.5 ± 9.5 g were divided into four groups containing 10 birds each and housed in poultry pens at the livestock unit of the Department of Animal Science and Technology, Federal University of Technology, Owerri, Nigeria. All animals were humanely treated in accordance to the WHO guidelines for animal care, and the study resign was approved by the School of Biological Sciences, Federal University of Technology, Owerri Research Ethics Committee. Three out of the four groups were fed on commercially available poultry feeds contaminated with concentration range (0.01 - 0.04%, w/v) of dichlorvos (DDVP). The control group has no pesticide added to the feed. Preparation of Liver HomogenatesAfter ten weeks of exposure, two birds each were taken from each group and sacrificed by decapitation and the liver extirpated. The hepatic tissues were homogenized in KCl - phosphate buffer [10 mM] with ethylene-diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA; pH 7.4) and centrifuged at 12,000rpm for 60 min. The soluble (cytoplasmic) protein was estimated in the supernatant of the liver homogenate. The supernatant was separated and pellet dissolved in PBS and shaken with known volume of 1% solution of the detergent SDS for 1 hr at 37°C. The solution was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 30 minutes, pellet discarded and supernatant used for estimation of membrane bound proteins and lipids. Determination of Lipid profileQualitative determination of total lipid was carried out following the sulfo-phospho-vanillin calorimetric method described by [8]. Total cholesterol was determined using a cholesterol enzymatic colorimetric test [9]. Triglyceride concentration was determined using a triglyceride enzymatic colorimetric test method [10] while high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol was determined according to the method of Burstein and Co-workers [11]. Determination of Total ProteinTotal proteins were estimated using the Buiret method [12].Determination of Lipid PeroxidationLipid peroxidation was determined spectrophotometrically by assessing the concentration of Thiobarbituric acid reacting substances (TBARS) expressed in the quantity of malodialdehyde (MDA) formed [13].Statistical AnalysisThe results were analyzed statistically using a one way analysis of variance (ANOVA). The results were expressed as mean ± SEM. The means were separated using Turkey’s test and considered different at p<0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
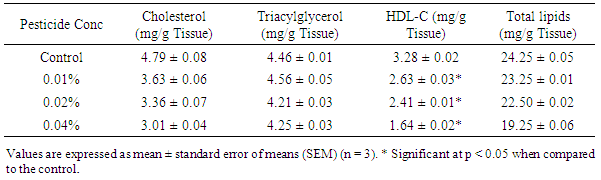
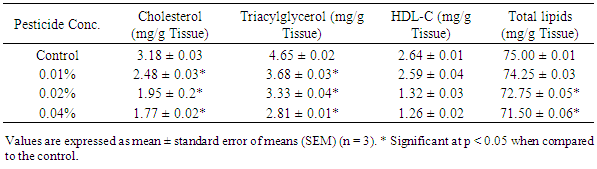
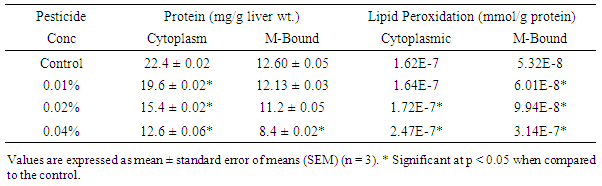
- Results of the lipid profile (Tables 1 & 2) show significant reductions (p<0.05) in cytoplasmic and membrane bound cholesterol in the liver homogenates of poultry birds exposed to dichlorvos compared with the control. Kaur and Dhanju [14] reported a reduction in cholesterol in rats exposed to some organophosphate pesticides. There were no significant differences (p > 0.05) in the levels of triglyceride in the cytoplasm of the liver between the control and the birds exposed to pesticide. However, there was a significant reduction (p < 0.05) in the concentration of membrane bound triglyceride from 4.65 ± 0.023 mg/g tissue to 2.81 ± 0.015 mg/g tissue in the birds exposed to 0.04% pesticide. Zama et al. [15] reported a significant reduction in serum cholesterol and triglyceride in rats exposed to some pesticides. The level of high density lipoprotein cholesterol reduced significantly in both the cytoplasm and membrane with increase in pesticide concentration. High density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) is regarded as a ‘good cholesterol’. The higher the HDL-C level, the lower the risk of corolary artery disease. This result suggests that prolonged exposure to dichlorvos may lead to corolary heart disease.The concentration of cytoplasmic and membrane bound proteins deceased significantly (p<0.05) in the livers of poultry birds exposed to dichlorvos when compared with the control (Table 3). The decrease in protein is an indication of degerative changes in the liver of the birds fed on pesticide contaminated diet. Similar changes have been reported in other organophosphates pesticides [16-18].Significant increases (p<0.05) in lipid peroxidation (MDA) were recorded in both the cytoplasm and membrane of the liver homogenates of the poultry birds exposed to dichlorvos compared with the control (Table 3). Serum MDA level is considered as an index of the general peroxidative damage to different tissues [19]. The increased lipid peroxidation observed in this study is an indication that there is oxidative stress occasioned by exposure to pesticide.
|
|
|
4. Conclusions
- The result of this study shows that dichlorvos affects some hepatic biochemical parameters in poultry birds and these parameters can serve as useful biomarkers in evaluating the ecological effect of exposure to pesticides.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML