-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Biochemistry
p-ISSN: 2163-3010 e-ISSN: 2163-3029
2016; 6(5): 130-135
doi:10.5923/j.ajb.20160605.03

Effects of Aqueous Stem Bark Extract of Jatropha curcas on Some Biochemical Indices of Mice Infected with Plasmodium berghei
S. Sarkiyayi, H. A. Zailani, Simon J. G.
Department of Biochemistry School of Pure and Applied Sciences, Modibbo Adama University of Technology, Yola, Nigeria
Correspondence to: S. Sarkiyayi, Department of Biochemistry School of Pure and Applied Sciences, Modibbo Adama University of Technology, Yola, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

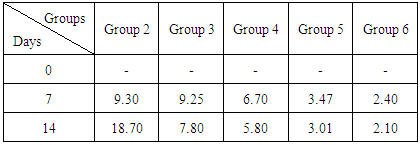
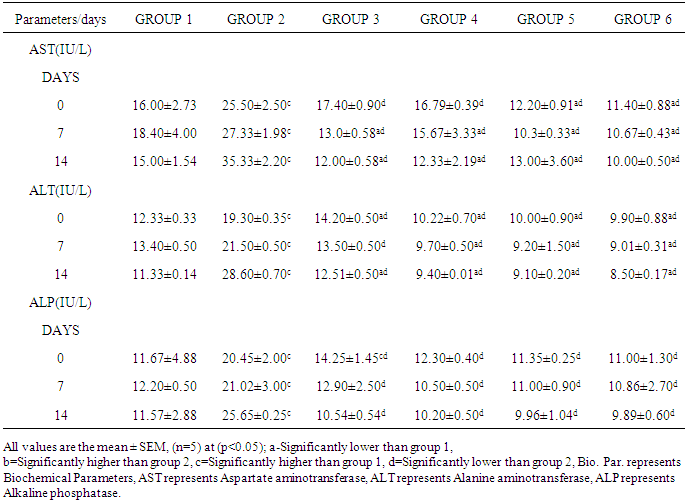
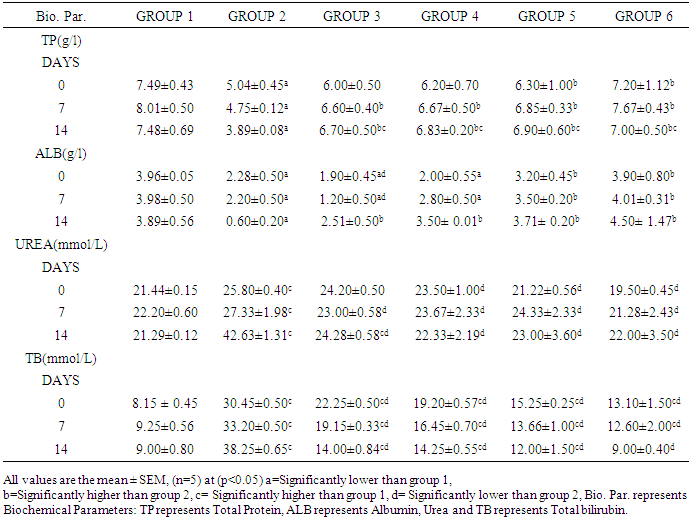
The aim of this research work was to investigate the effect of Jatrophacurcasplant in Mice infected with Plasmodium berghei in order to ascertain the efficacy of the plant stem bark extract in the treatment of malaria as claimed by traditional practitioners in Nigeria. The LD50 of the plant extract was determined. Six groups of fifteen mice each were used for the research. Group 1 was uninfected and untreated, group 2 was infected, but untreated, Groups 3, 4 and 5 were infected and treated with 250mg/kg, 500mg/kg, and 750mg/kg of aqueous stem bark extract of Jatrophacurcas respectively. While Group 6 was infected and treated with Arthemether (20mg/kg). Treatment commenced on the third day and lasted for a period of 12 days. Then, the animals were sacrificed, blood was collected and used for biochemical investigations. Our findings shows that infection caused a significant (p< 0.05) increase in the activities of AST, ALT, ALP and the concentration of total bilirubin and urea when compared to control. However, treatment with the plant extract and arthemether significantly decreased (p<0.05) the activities of liver enzymes and the concentration of total bilirubin and urea compared untreated control. The total protein in infected extract-treated and Arthemether treated animals were found to increase (p<0.05) significantly when compared with the infected untreated mice. Our findings revealed that the decrease in values for AST, ALT, and ALP activity by the plant extract may suggest that the extract has some inhibitory effect on malaria parasite, since the there were no physiological disturbances in the biochemical parameters investigated. Our research had revealed the LD50 was greater than 5000mg/kg, suggesting that the plant extract was relatively safe for oral medication. The percentage parasitemia has decreased from 9.25 to 7.80 for the treated group, where as the infected and untreated has the parasitemia increased from 9.30% to 18.70%. Suggesting that the plant extract possess some anti-malarial properties. Our findings support the possibility of using Jatrophacurcas plant leaf as anti bacterial agent.
Keywords: Plasmodium berghei, Jatrophacurcas, Biochemical indices, Parasitemia Malaria parasite
Cite this paper: S. Sarkiyayi, H. A. Zailani, Simon J. G., Effects of Aqueous Stem Bark Extract of Jatropha curcas on Some Biochemical Indices of Mice Infected with Plasmodium berghei, American Journal of Biochemistry, Vol. 6 No. 5, 2016, pp. 130-135. doi: 10.5923/j.ajb.20160605.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Malaria remains one of the major killers of humans worldwide, threatening the lives of more than one-third of the world’s population. It thrives in the tropical areas of Asia, Africa, and Central and South America, where it affects millions of people. Each year 350 to 500 million cases of malaria occur worldwide. Sadly, more than 1 million of its victims, mostly young children, die yearly [1]. Although malaria has been virtually eradicated in the United States and other regions with temperate climates, it continues to affect hundreds of people in Nigeria every year. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimated 1,200 cases of malaria are diagnosed each year in the United States.Plants have been recognized for their several life saving and therapeutic properties. Several herbs are parts of socio-cultural and socio-economic heritage. Even in the present times rural populations turn to herbal medicine as the most preferred therapeutic source. Jatropha curcas is a drought resistant large shrub or small tree, belonging to the genus Euphorbiaceae, producing oil containing seeds [2]. Jatropha curcas is the commonest specie found in Nigeria, but many species exist in different parts of the world. Traditionally, Jatropha curcas is used for the treatment of fever, mouth infections, jaundice, guinea worm, sores and joint rheumatism [3, 4]. Previous studies also reveals the presence of antibacterial agents in different parts of Jatropha curcas [5]. For developing herbal treatment for malaria from various parts of Jatropha curcas which part will be more effective against Plasmodium berghei. The present study aims to investigate the antiplasmodial potential of the stem bark of Jatropha curcas using the aqueous extract on Plasmodium berghei. The people of Jada local government area and its inhabitants widely use Jatropha curcas stem bark for the treatment of many ailments including malaria. However, there are no scientific bases for this treatment. Therefore, this research is designed to provide the scientific evidence for the use of the aqueous stem bark extract of Jatropha curcas in the treatment of malaria and its safety in the medication.
2. Materials and Methods
- Collection of Plant Material Fresh Jatropha curcas Linn plantwas collected from the Staff quarters of Government Secondary School, Jada Local Government Area of Adamawa State, Nigeria and was taxonomically identified and authenticated in the Plant Science Department of Modibbo Adama University of Technology, Yola. Chemicals and ReagentsAssay kits for enzymes (ALT, AST and ALP) and liver function indices (Albumin, Total and direct Bilirubin and total protein) were obtained from Randox Laboratories Ltd, UK while those of creatinine and urea were obtained from Agappe Diagnostics, Switzerland. All other reagents and solvents used were of analytical grade.Experimental Animals Ninety mice weighing between18-22g were obtained from Animal Facility Centre, National Veterinary Research Institute Vom, Jos, Nigeria. The mice were housed in polypropylene cages, and given standard laboratory diet and water and maintained under standard laboratory conditions.Malaria Parasite The malaria parasite (Plasmodium berghei NK-65) was obtained from National Institute for Medical Research (NIMR), Lagos, Nigeria. Extract Preparation The stem bark was carefully removed from the Jatropha curcas plant and washed thoroughly with tap water then rinsed twice with distilled water and allowed to sun dry. The dried stem bark was crushed to powder with pestle and mortar and two hundred grams of the powder was cold macerated in 1000ml of distilled water for 24 hours with constant shaking and filtered using Whitman’s filter paper No. 1. It was then concentrated to dryness on water bath at 40°C and the crude extract was kept in desiccator and dried. Acute Toxicity Test The LD50 of the aqueous extract of the stem bark was tested using [6] method in order to determine its safety. The aqueous extract of the stem bark of Jatropha curcas was administered in doses of 1000, 3000 and 5000 mg/kg body weight to four groups of mice (n = 3). The mice were kept under same conditions and observed for toxic signs and mortality for 24hs.Parasite Inoculation The inoculation of the parasite was carried out by determining both the percentage parasitemia and erythrocytes count of the donor mouse using a haemocytometer and appropriate dilutions of the infected blood with isotonic saline were made. Each mouse was inoculated intraperitoneally with 0.2 ml of infected blood containing about 1 x 107 Plasmodium berghei parasitized red blood cells. After 72 hours the mice were treated for malaria conditions for twelve days. Experimental Design Ninety Swiss albino mice were divided into six groups of fifteen [15] mice each. Groups 2-6 were inoculated with the rodent malaria parasite Plasmodium berghei from the same donor mouse. Groups 3, 4 and 5 were treated with 250, 500 and 750 mg/Kg body weight of the aqueous leaf stem bark extract of Jatrophacurcas respectively. Group 6 was treated with 20 mg/Kg body weight of arthemether. Groups 1 and 2 served as normal and untreated controls respectively.Determination of Biochemical ParametersTest for liver function indicesBilirubin was determined by the method of Walter and Gerard [7]. Total protein was determined by the Method of Tietz [8] while albumin was determined as described by Doumas et al [9].Test for kidney function indicesSerum urea concentration was determined according to the method described by Fawcett and Scott [10] while Creatinine was determined as described by Bartels et al [11].Enzyme assaysAlkaline phosphatase activity of serum was determined as described by Wright et al [12]. Alanine and aspartate aminotransferase activities were assayed by the method of Reitman and Frankel [13].Statistical Analysis Results were expressed as mean ± SEM. Student t-test was used to analyse the data between groups at p values(p<0.05) was considered significant in all cases (SPSS version 21 was used).
3. Results and Discussion
- Acute Toxicity Tests Our findings had shown that there was no mortality recorded in the mice at a dose of 5000 mg/kgbody weight of the aqueous extract of the stem bark of Jatropha curcas, suggesting that the plant extract was not toxic and relatively safe for oral consumption.The antimalarial properties observed in this study could be attributed to bioactive constituents in the extract. Guido et al [14] reported that antimalarial activity could be attributed to alkaloids in plants extract. Our findings in table 1 had shown that the aqueous stem bark extract of Jatropha curcas produced some antiplasmodial effects on the parasitemic levels when compared to the standard anti malarial drug. in a related development Abiodun et al [15] reported that ethyl acetate extract of leaves of Ocimum gratissimum Linn. (Labiatae) and hexane extract of stem bark of Trema orientalis (L.) Blume (Ulmaceae) showed the highest antiplasmodial activity against P. falciparum K1 strain but elicited low cytotoxicity. Thus the percentage of parastitemia has decreased from 9.25 to 7.80 for the treated group, where as the infected and untreated has the parisetemia increased from 9.30 to 18.70. However, it was observed that at higher dose of the extract was able to exhibit a considerable effect comparable to the standard drug. Hence use of standard drug has percentage parastitemia decreased from 9.30 to 2.10, suggesting that aqueous extract of the stem bark of Jatropha curcas posessess some anti malaria activities. A review conducted by Sabandar et al [16] had shown that, the genus Jatropha (Euphorbiaceae) comprises of about 170 species of woody trees, shrubs, sub shrubs or herbs are used in medicinal folklore to cure various diseases of 80% of the human population in Africa, Asia and Latin America. Species from this genus have been popular to cure stomachache, toothache, swelling and inflammation.
|
|
|
4. Conclusions
- The aqueous stem bark extract of Jatropha curcas possess some antimalarial properties. The extract showed protective effect on liver tissues and kidney indices. This suggest the possibility of using Jatropha curcas extract in the treatment of malaria and perhaps a promising future for this new class of anti bacterial agent could be actualized.
5. Recommendations
- Further studies should be carried out other parts of Jatropha curcas as a source of antimalarial remedy and isolation and characterization of the active components responsible for the antimalarial property should be investigated.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML