-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Biochemistry
p-ISSN: 2163-3010 e-ISSN: 2163-3029
2015; 5(5): 99-112
doi:10.5923/j.ajb.20150505.03

Antiurolithic and Antioxidant Influence of Pleurotus ostreatus and Agaricus bisporus Aqueous Extracts and Carvedilol in Male Rats
Osama M. Ahmed 1, Mohammed B. Ahmed 2, Mahmoud R. Mohammed 3
1Physiology Division, Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, Egypt
2Biochemistry Division, Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, Egypt
3Biochemistry Laboratory, Department of Laboratories, Sohag General Hospital, Sohag, Egypt
Correspondence to: Osama M. Ahmed , Physiology Division, Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Urolithiasis, a urinary tract stone formation, is the major clinical result of hyperoxaluria. Hyperoxaluria was induced in Wistar rats by receiving 0.75% ethylene glycol (EG) (v/v) in drinking tap water for 9 weeks. Hyperoxaluric rats were treated with Pleurotus ostreatus (P. ostreatus) and Agaricus bisporus (A. bisporus) infusions (100 mg/kg b. w.) and carvedilol (30 mg/kg b. w.) daily during the last 7 weeks. The study revealed that P. ostreatus and A. bisporus aqueous extracts and carvedilol could successfully inhibit EG-induced reduction of body weight gain (BWG) and urine magnesium, increase of relative kidney weight (RKW) and elevation of serum, urine and kidney oxalate, urine calcium, urine sodium and urine phosphorus. In addition, serum concentrations of potassium and sodium were not significantly altered. The tested agents markedly reduced the decrease in levels of kidney alkaline phosphatase (ALP), kidney alanine aminotransferase (ALT), kidney aspartate aminotransferase (AST), kidney glutathione (GSH) and activities of kidney glutathione-S-transferase (GST), kidney superoxide dismutase (SOD), kidney glutathione peroxidase (GPX) and kidney catalase. It also caused decreases in the elevated kidney and serum nitric oxide (NO) and kidney lipid peroxidation (LPO). According to these results, it can be concluded that aqueous extracts of P. ostreatus and A. bisporus as well as carvedilol might have a preventive effect against urolithiasis induced by EG, and that effect might be performed through stimulation of the antioxidant defense system.
Keywords: Urolithiasis, Hyperoxaluria, Ethylene glycol, Pleurotus ostreatus, Agaricus bisporus, Carvedilol, Antioxidant
Cite this paper: Osama M. Ahmed , Mohammed B. Ahmed , Mahmoud R. Mohammed , Antiurolithic and Antioxidant Influence of Pleurotus ostreatus and Agaricus bisporus Aqueous Extracts and Carvedilol in Male Rats, American Journal of Biochemistry, Vol. 5 No. 5, 2015, pp. 99-112. doi: 10.5923/j.ajb.20150505.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Urolithiasis is a multifaceted process, progressing from supersaturation of urine to the formation of complete kidney stone [1]. It was revealed that urolithiasis is a common urinary ailment, with increasing incidence allover the world [2]. It was also speculated that urolithiasis is a widespread illness in developed countries with current prevalence rates above 5% [3]. In 50% of cases, urolithiasis is a recurrent disease, which can lead to the loss of a kidney function if not correctly treated [4]. Consumption of diets with high oxalate content is a major risk agent for stone formation [5]. In another site, it was suggested that the damaged epithelium of the kidney, due to an increment of oxidative stress (OS) and with decreased anti-adherent glycosaminoglycan layer, might play a nidus for stone formation [6]. EG instigates hyperphosphaturia, hypercalciuria and hyperoxaluria leading to urolithiasis [7].Hyperoxaluria is the urinary excretion of more than 40 mg/day and it is a serious risk factor for stones and present in around 20 to 40% of stone formers [8, 9]. Calcium oxalate (CaOx) is the main constituent of about 75% of all urinary calculi [10]. Male rats were chosen to induce urolithiasis because the urinary system of male rats looks like that of humans and previous investigations demonstrated that the quantity of stone deposition in female rats was significantly less [11]. Hyperoxaluria model induced by EG was used to evaluate the antilithiatic activity in albino rats [12].Oxalate caused increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation that reduces the activity of aminophospholipid translocase which has a role in hyperoxaluria promoted CaOx urolithiasis by facilitating the redistribution of phosphatidylserine in epithelial cells of the kidney [13]. Besides, it was noticed that oxalate promotes OS which is considerably retarded by antioxidants and if antioxidants fail then it resulted in urolithiasis [14, 15]. Renal cell damage is associated with lipid peroxide production indicating cell injury due to production of free radicals; the damage seems due primarily to hyperoxaluria and is augmented by crystal deposition in the kidney tubules [16]. Thus, the injury of the kidney tubular cells and fixed crystal particles could be involved in the pathogenesis of urolithiasis [17].The antioxidant provided a beneficial effect and showed superior renal protection on preventing and treating the deposition of calculi in the kidney of rat [18]. It was also postulated that phytochemicals with antioxidant activity are proposed as an alternative therapy for nephrolithiasis control [19, 20, 21]. It was concluded that fungi have developed as antioxidants novel sources in the form of their secondary metabolites [22, 23]. Some wild mushrooms might be promising dietary sources of antimicrobial factors and natural antioxidants [24]. P. ostreatus, along with other species of mushroom, has been confirmed to have medicinal value. The biological effects of these mushrooms range from antioxidative and immuno-stimulating to anti-carcinogenic, antihypercholesterolaemic, antiviral and the ability to regulate glucose levels and blood lipid [25, 26, 27, 28]. Like this, the button mushroom A. bisporus which is cultivated almost in all world sites [29], could substantially be utilized in part of well-balanced diets and as a source of antioxidant constituents [30].Carvedilol (1-(carbazolyl-(4)-oxy)–3-(2-methoxyphenoxyethyl) amino–propanol - (2)) is an antihypertensive drug with powerful antioxidant capacity [31]. Moreover, it was concluded by previous publications that carvedilol has a potent antioxidant activity and a significant characteristic not found in other drugs of the same pharmacological group [31, 32]. In addition, carvedilol has anti-inflammatory [33] and antioxidant [34] properties.Thus, this study aimed to assess the treatment effects of P. ostreatus and A. bisporus aqueous extracts as natural agents and carvedilol as a synthetic drug on kidney function and integrity in ethylene glycol-induced urolithic rats.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Housing
- Male albino rats 12-13 weeks old, weighting 115-140 g, were used in the experiment. Animals were obtained from the National Research Center (NRC), Dokki, Giza, Egypt. They were kept under observation for 10 days before the onset of the experiment to exclude any intercurrent infections. The animals were housed in stainless steel cages at room temperature (20-25 °C) and natural 12 hours light/dark cycle, given enough food (balanced standard diet), and were allowed free access to water. The rats were weighted at the onset and the end of the experiment and body weight gain was calculated. All animal procedures are in accordance with the recommendations of the Canadian Committee for care and use of animals [35]. All efforts were done to reduce the number and suffering of animals.
2.2. Mushrooms
- Mushrooms (P. ostreatus and A. bisporus) were purchased from Agriculture Research Center, Giza, Egypt. They were authenticated by Dr. Fathy Ragab Houssan, Associate Professor of Food Science and Technology, Food Technology Research Institute, Agriculture Research Center, Giza, Egypt. Fruiting bodies were dried with air shade.
2.3. Preparation of P. ostreatus and A. bisporus Aqueous Extracts
- The air shade dried fruiting bodies of P. ostreatus and A. bisporus were roughly cut and powdered with an electric grinder. Mushroom aqueous extracts in the form of infusions were prepared by adding certain volume of boiling distilled water to certain weight of the powdered mushroom (2% w/v, each 100 mg was infused in 5 ml boiling distilled water) and was left for 15 minutes then filtrated. The resulting filtrated infusion was orally given to the rats at dose level of 100 mg/kg b.w. daily for 7 weeks. The doses of P. ostreatus and A. bisporus were used according to El Bohi et al. [36] and Yamac et al. [37], respectively.
2.4. Preparation of Carvedilol Dose
- Carvedilol dose was prepared by dissolving 6 tablets of carvedilol (25 mg) in 25 ml distilled water (30 mg/5 ml) and was orally given to the rats at dose level of 30 mg (dissolved in 5 ml distilled water)/kg b.w. [38] every day for 7 weeks. Carvedilol was purchased from Acapy Pharmaceutical Company, Egypt.
2.5. Induction of Hyperoxaluria
- Hyperoxaluria was induced in albino rats by adding 0.75% EG (v/v) in drinking water for 9 weeks. A 0.75% EG (v/v) in drinking water for 28 days is one of the standard models to induce hyperoxaluria [39, 40]. EG was purchased from Sd fine- chem. limited-Mumbai-India.
2.6. Animal Grouping
- Experimental animals were divided into five groups each group containing six animals as follow:Group 1 (normal control) was given tap water (without EG) as a drinking water for 9 weeks and was orally given the equivalent volume of the vehicle (distilled water) 5 ml/kg b. w. every day during the last 7 weeks.Group 2 (EG group) was given 0.75% EG (v/v) in drinking tap water for 9 weeks and was orally given the equivalent volume of the vehicle (distilled water) 5 ml/kg b. w. every day during the last 7 weeks.Group 3 (EG and aqueous extract of P. ostreatus group) was given 0.75% EG (v/v) in drinking tap water for 9 weeks and was orally given the P. ostreatus aqueous extract at dose level of 100 mg (infused in 5 ml boiling distilled water)/kg b. w. every day during the last 7 weeks.Group 4 (EG and aqueous extract of A. bisporus group) was given 0.75% EG (v/v) in drinking tap water for 9 weeks and was orally given the A. bisporus aqueous extract at dose level of 100 mg (infused in 5 ml boiling distilled water)/kg b. w. every day during the last 7 weeks.Group 5 (EG and carvedilol group) was given 0.75% EG (v/v) in drinking tap water for 9 weeks and was orally given the carvedilol at dose level of 30 mg (dissolved in 5 ml distilled water)/kg b.w. during the last 7 weeks.Group 1 was considered as a control group for group 2. Group 2 was considered as a control group for groups 3, 4 and 5.
2.7. Blood and Tissue Sampling
- At the end of the experimental period, animals were weighed and sacrificed under diethyl ether anesthesia after 12 hours of food and water deprivation. Blood samples from jugular vein and urine samples from urinary bladder were collected. The blood was left to coagulate at room temperature then centrifuged at 3000 r.p.m. for 30 minutes. The clear nonhaemolysed supernatant sera were quickly removed for analysis of various biochemical parameters related to kidney functions. The obtained serum and urine samples were kept at -30 °C until used. Kidneys of each animal were excised and weighed. A 0.5 g from kidney of each animal was homogenized in 5 ml 0.9% NaCl (10%w/v) using Teflon homogenizer (Glas-Col, Terre Haute, USA). The obtained homogenate was kept in deep freezer at -30 °C to be used later for measurements of oxalate level, OS markers and various enzyme activities. The homogenate supernatant for kidney samples were obtained by centrifuging the homogenate at 3000 r.p.m. for 5 minutes.
2.8. Determination of Body Weight Gain and Relative Kidney Weight
- Body weight gain and relative kidney weight were calculated from formulas: Body weight gain (BWG) = body weight at end of the experiment-body weight at onset of the experiment.Relative kidney weight (RKW) % = [kidney weight/ body weight at end of the experiment] x 100.
2.9. Biochemical Analysis
- Serum, urine and kidney oxalate levels were detected according to method of Young [41] by using kits obtained from Ben-Biochemical Enterprise (Italy). Serum potassium was measured by using kits developed by Spectrum Diagnostics (Egypt) according to Tietz [42]. Serum and urine sodium levels were determined by using kits purchased from Spectrum Diagnostics (Egypt) according to Trinder [43]. By using kits obtained from Biodiagnostic (Egypt), urine concentrations of calcium and phosphorus were detected according to Gindler and King [44] and El-Merzabani et al. [45], respectively. Urine concentration of magnesium was determined by using kits purchased from Spectrum Diagnostics (Egypt) according to Mann and Yoe [46]. Kidney ALP activity was measured by using kits developed by Biodiagnostic (Egypt) according to Belfield and Goldberg [47]. According to the methods of Murray [48, 49] and by using kits purchased from Diamond Diagnostics (Egypt), kidney ALT and AST activities were respectively detected. NO level in serum and kidney was determined by using kits obtained from Ben-Biochemical Enterprise (Italy) according to method of Montgomery and Dymock [50]. Kidney LPO, GSH content were determined according to the methods of Preuss et al. [51] and Beutler et al. [52]. GST, SOD, GPX and catalase activities were estimated according to the methods of Mannervik and Gutenberg [53], Marklund and Marklund [54], Matkovics et al. [55] and Cohen et al. [56], respectively.
2.10. Statistical Analysis
- The data were analyzed using the one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) [57] followed by LSD analysis to compare various groups with each other. Results were expressed as mean ± standard error (SE). F-probability obtained from one-way ANOVA, expresses the general effect between groups.
3. Results
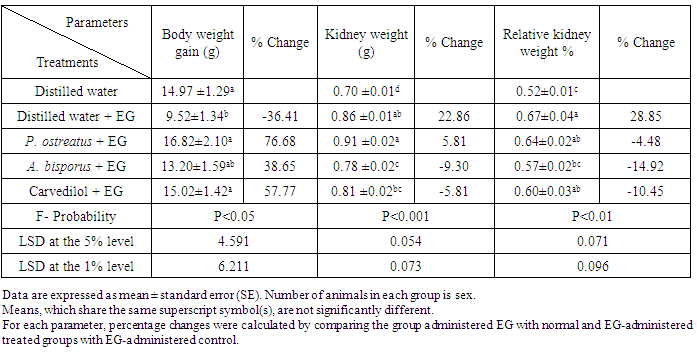
3.1. Effect on BWG, Kidney Weight and RKW
- The data showing the effect of P. ostreatus aqueous extract, A. bisporus aqueous extract, and carvedilol on BWG, kidney weight and RKW of EG-administered rats were represented in table 1. The administration of EG to albino rats produced a profound decrease in BWG and a marked increase in kidney weight and RKW recording percentage changes of -36.41, 22.86 and 28.85%, respectively as compared with normal control. While treatment of EG-administered rats with the aqueous extracts and carvedilol led to a noticeable increase of BWG, they induced a detectable decrease of RKW. The treatment with P. ostreatus aqueous extract and carvedilol caused a highly significant and a significant improvement of BWG, respectively whereas the treatment with A. bisporus aqueous extract induced a highly significant decrease of the elevated RKW. On the other hand, while kidney weight was non-significantly changed (P>0.05; LSD) as a result of treatment with P. ostreatus and carvedilol, it was highly significantly decreased as a result of treatment with A. bisporus (P<0.01; -9.30%).
|
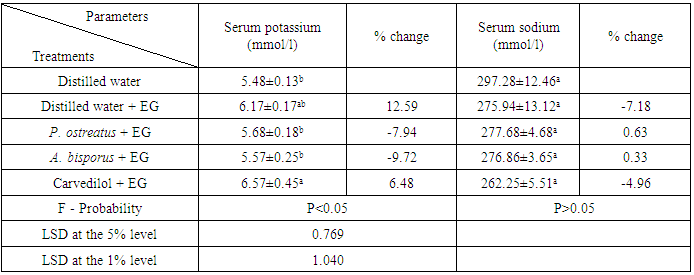
3.2. Effect on Serum Potassium and Sodium
- Administration of EG to albino rats caused an increase of serum potassium recording percentage change of 12.59% and decrease of serum sodium level recording percentage change of -7.18% as compared with normal control. Treatment with the examined agents resulted in non-significant change (P>0.05; LSD) of serum potassium and sodium (table 2).
|
3.3. Effect on Levels of Various Urine Ions
- Urine calcium, oxalate, sodium and phosphorus levels were increased recording percentage changes of 2.92, 5446.93, 65.36 and 369.47%, respectively after administration of EG while the urine magnesium level, was decreased recording percentage change of -12.16%. The effect on urine calcium and magnesium levels was non-significant (P>0.05; LSD) and significant (P<0.05; LSD), respectively, while it was highly significant (P<0.01; LSD) on oxalate, sodium and phosphorus levels as compared with normal control. Treatment with P. ostreatus led to highly significant decrease of calcium, oxalate, sodium and phosphorus levels (P<0.01; LSD) and significant increase of magnesium level (P<0.05; LSD). Magnesium and oxalate concentrations were highly significantly changed (P<0.01; LSD) and sodium concentration was non-significantly decreased (P>0.05; LSD) as a result of treatment with A. bisporus and carvedilol. While the treatment with A. bisporus led to a non-significant change (P>0.05; LSD) of urine calcium level, it induced a highly significant effect on urine phosphorus level (P<0.01; -43.98%). In contrast, carvedilol treatment produced a highly significant change of urine calcium level and a non-significant effect on urine phosphorus level (table 3).
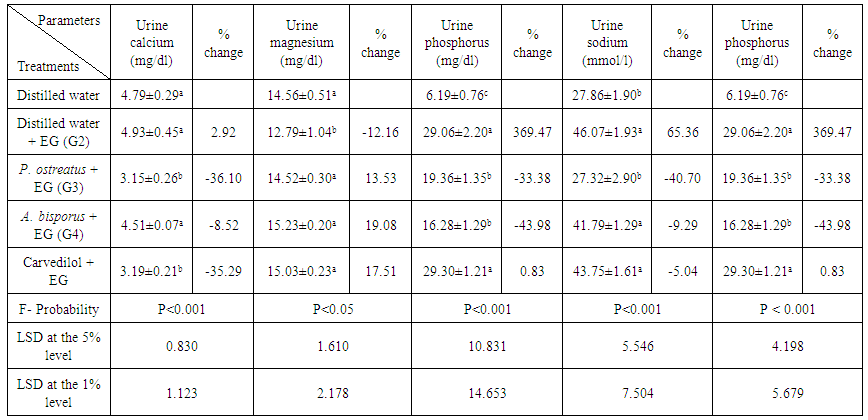 | Table 3. Effect of P. ostreatus and A. bisporus aqueous extracts and carvedilol on levels of some urine ions in EG-administered rats |
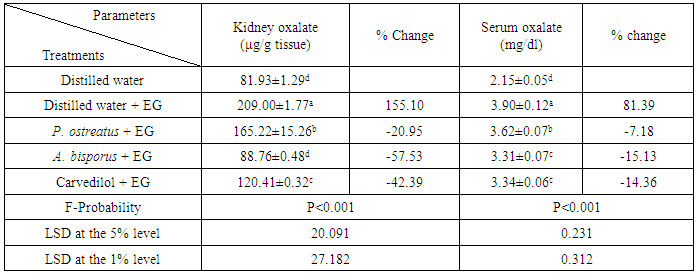
3.4. Effect on Kidney and Serum Oxalate
- The decrease of kidney and serum oxalate level was highly significant as a result of administration of EG to albino rats recording percentage changes of 155.10 and 81.30%, respectively as compared with normal control. Kidney oxalate was highly significantly decreased (P<0.01; LSD) by treatment with all tested agents. On the other hand, serum oxalate was significantly decreased by treatment with P. ostreatus aqueous extract (P<0.05; -7.18%) and highly significantly decreased by treatment with A. bisporus and carvedilol recording percentage changes of -15.13 and -14.36%, respectively as compared with EG control group (table 4).
|
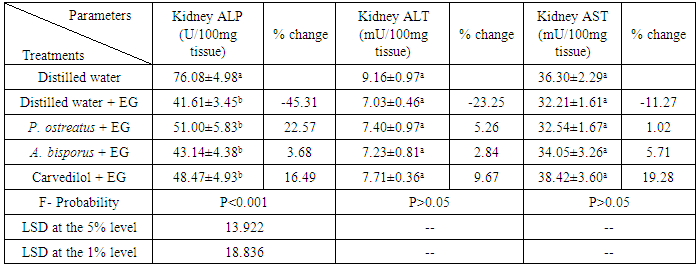
3.5. Effect on Some Kidney Enzymes
- A highly significant decrease (P<0.01; LSD) of ALP activity and a non-significant decrease (P>0.05; LSD) of ALT and AST activities were resulted after EG administration. P. ostreatus, A. bisporus and carvedilol treatments induced a non-significant increase (P>0.05; LSD) of all above parameters (table 5).
|
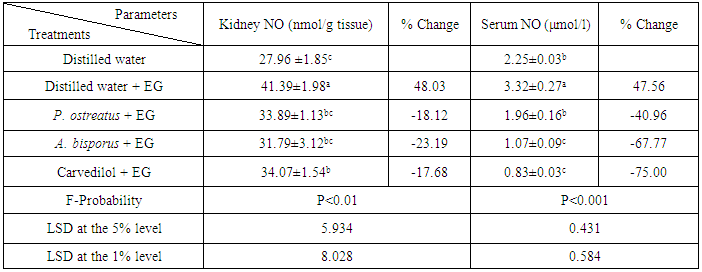
3.6. Effect on Kidney and Serum NO Levels
- Hyperoxaluric rats exhibited a highly significant increase of kidney and serum NO levels recording percentage changes of 48.03 and 47.56%, respectively as compared with normal control. Kidney NO level was significantly decreased (P<0.05; LSD) by treatment with P. ostreatus and carvedilol and highly significantly decreased by treatment with A. bisporus (P<0.01; -23.19%). In the other site, serum NO level was highly significantly decreased (P<0.01; LSD) by using of all above treatments (table 6). A. bisporus and carvedilol seemed to be the most potent in decreasing the kidney and the serum NO level, respectively.
|
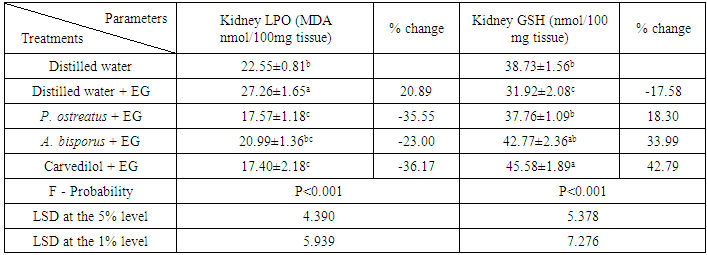
3.7. Effect on Kidney LPO and GSH
- Changes of kidney LPO level and GSH content as a result of treatments of EG-administered rats with P. ostreatus, A. bisporus and carvedilol were illustrated in table 7. EG-administration to albino rats induced a significant increase (P<0.05; LSD) of LPO level and a significant decrease (P<0.05; LSD) of GSH content. The treatment with P. ostreatus caused a highly significant decrease (P<0.01; -35.55%) of LPO level and a significant increase (P<0.05; 18.30%) of GSH content. On the other hand, LPO level and GSH content were highly significantly altered (P<0.01; LSD) as a result of treatment with A. bisporus and carvedilol.
|
3.8. Effect on Various Kidney Antioxidant Enzymes
- EG administration to albino rats induced a decrease of kidney GST, SOD, GPX and catalase activities, but while the decrease was non-significant (P>0.05; -10.80%) in SOD activity and significant (P<0.05; -25.98%) in GPX activity, it was highly significant (P<0.01; LSD) in GST and catalase activities as compared with normal control. Kidney GST and SOD activities were highly significantly (P<0.01; 59.24%) and non-significantly (P>0.05; 16.27%) increased, respectively by treatment with P. ostreatus. In contrast, Kidney GST and SOD activities were non-significantly (P>0.05; LSD) and highly significantly (P<0.01; LSD) increased, respectively by treatment with A. bisporus. The treatment with carvedilol led to non-significant (P>0.05; 17.11%) and significant (P<0.05; 29.18%) increase of GST and SOD activities, respectively. A highly significant (P<0.01; LSD) and a non-significant (P>0.05; LSD) increase of GPX and catalase activities, respectively was induced treatment of EG-administered rats with all tested agents (table 8).
 | Table 8. Effect of P. ostreatus and A. bisporus aqueous extracts and carvedilol on various kidney antioxidant enzymes activities in EG-administered rats |
4. Discussion
- The present study was conducted to evaluate the antiurolithic and antioxidant effects of P. ostreatus and A. bisporus aqueous extracts as natural agents and carvedilol as a synthetic drug on EG-induced urolithiasis.The present study showed that the BWG was significantly decreased in the EG-administered control rats. The administration of aqueous extracts of P. ostreatus and A. bisporus as well as carvedilol to EG-administered rats profoundly decreased the lowering in the BWG. Body weight loss is considered by some researchers to be good reliable toxicity marker [58, 59, 60]. The decrease in BWG, in the present study, by EG may represent the first preliminary marker of its toxicity. The prevention of body weight loss in EG-administered rats by P. ostreatus, A. bisporus and carvedilol may be due to their ability to antagonize the biochemical deteriorations of EG. The improvement of the biochemical perturbations by these tested agents may lead to an improvement of general health and feeding talent and that generally reflects their ameliorative influences. On the other hand, kidney weight and RKW in the EG-administered rats exhibit a significant increase compared with the normal control and that increase may be due to accumulation of fluid and inflammation as a result of EG administration [61]. Cellular hypertrophy is a resultant indicator for oxidative damage to epithelial cells of kidney tubules which induced by oxalate through the activation of NADPH (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen) oxidase via cytokine TGF-β (Transforming growth factor-beta) induction [62]. A valuable role in the accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins and TGF-β induction in experimental hyperoxalosis is induced by reactive oxygen intermediates and protein kinase C [63]. The changes in body weight and kidney weight may reflect the beginning of tissue damage as a result of OS of oxalate. The treatment of EG-administered rats with P. ostreatus, A. bisporus and carvedilol reduced the increase of RKW which reaffirms their reformed features. These results go along with Wang et al. [64], Gupta et al. [65], Jagannath et al. [66], Khan et al. [67], Saeidi et al. [68], Aggarwal et al. [69] and Shukla et al. [70] who found that the body weight was significantly reduced both in hyperoxaluric and lithogenic rats when compared with normal control rats, while kidney weight and RKW showed a significant increase. In contrast, it was found that kidney weight and RKW were decreased in EG-administered control rats as compared with normal control rats [71].Concerning serum, urine and kidney levels of minerals and solutes, while levels of serum sodium and urine magnesium were decreased as a result of EG-administration, the levels of serum oxalate, serum potassium, urine calcium, urine oxalate, urine sodium, urine phosphorus and kidney oxalate were markedly increased. These findings go parallel with several researchers [72, 73, 74, 75, 76]. In that regard, it was found that the administration of EG caused increase of serum potassium [77]. It was reported that renal toxicity with glycerol resulted in increment of serum level of potassium and reduction of serum level of sodium [78], and escalation of the excretion of sodium [79]. Moreover, it was demonstrated that hyponatremia can happen only when some conditions hinder usual free water excretion [80]. It was also noticed that a low level of citrate and magnesium is also encountered in stone-forming rats as well as in human stone formers [81]. In normal conditions, urine is a supersaturated solution and only some individuals are prone to this disease. One reason for this is the presence of inhibitors of lithogenesis in urine, including magnesium, citrate and macromolecules [82]. Thus, an imbalance between the promoters such as phosphate, oxalate, uric acid, calcium, low urine volume and inhibitors may represent a prospect agent in lithogenesis [83]. The increased level of urine calcium in the present study may be due to kidney injuries which cause loss of calcium in urine. This attribution was supported by Arneson and Brickell [84] who explained that membrane damage in hyperoxaluria mainly results in renal leakage of calcium and increases the grade of excretion of calcium. Increased calcium in urine is an agent favoring the nucleation and precipitation of CaOx or apatite (calcium phosphate) from urine and subsequent crystal growth [85, 86]. On the other hand, it was elucidated that formation of stones in EG-administered animals is caused by hyperoxaluria, which leads to elevation of kidney excretion and retention of oxalate [11]. In that manner, it was showed that the crystals of CaOx and high oxalate concentrations in nephrons damages epithelial cells, inducing nucleation of heterogeneous crystal and causing crystals aggregation [87, 88]. Hyperoxaluria is a more important risk agent in the pathogenesis of kidney stones than hypercalciuria or the elevation of concentrations of other minerals [89]. In addition, it was concluded that the increased levels of oxalate and calcium in the kidney tissue of EG-administered rats were noticed as a result of precipitation of crystalline material as CaOx [83]. Relative to urine phosphorus, it was reported that EG causes hyperphosphaturia, hypercalciuria and hyperoxaluria leading to urolithiasis [7]. Also, it was found that phosphorus excretion has been increased in stone formers [85]. Increased excretion of urinary phosphate along with oxalate stress provides a condition suitable for stone formation by forming calcium phosphate crystals, which induces deposition of CaOx [11, 90]. These calcium phosphate crystals appeared to be the origin of future CaOx stones development, which formed by the attachment of additional matrix molecules and CaOx from the urine to the plaque [91]. The previous results are in contrasting with Khan et al. [92] who found a decrease in the levels of urine calcium and urine sodium and an increase in the level of urine magnesium after administration of EG to rats and with Pawar et al. [93] who noticed a reduction of urine calcium.Treatments of EG-administered rats with the tested mushroom infusions and carvedilol resulted in decrease the risk factors and increase the inhibitory factors of stone formation. Urinary supersaturation with stone forming minerals is primary requisition for crystal precipitation and a major risk factor for the stone development [94]. In that way, P. ostreatus and A. bisporus infusions and carvedilol treatments led to increase in the urine magnesium concentration and decrease levels of urine calcium, urine sodium and urine phosphorus. Magnesium binds to oxalate to form a soluble complex, subsequently reducing the concentration available for calcium oxalate precipitation [95]. In another site, the complexion between oxalate and magnesium enhances the CaOx solubility product [96]. These results are in harmony with numerous researchers. Saha and Verma [97] found that urine calcium and phosphate were decreased while serum sodium was increased as a result of treatment of EG-administered rats with hydroalcholic Dolichos biflorus seed extract. Also, urine calcium, oxalate and phosphate were decreased, while urine magnesium was increased as a result of treatment of EG-administered rats with hydroalcholic Copaifera langsdorffii leaves extract [98]. Further, it was obtained by Ingale et al. [99] and Patel et al. [83] that the levels of calcium and oxalate in kidney were decreased as a result of treatment of EG-administered rats with methanolic extract of aerial parts of Hygrophila spinosa and the saponin rich fraction of Solanum xanthocarpum fruits, respectively. On the other hand, it was postulated that carvedilol has protective effects against biochemical, behavioral and mitochondrial dysfunction induced by D-galactose in mice [100]. In dissimilarity with our findings, it was obtained an increment of urine calcium in the group of EG-administered rats after treatment with hydroalcholic Rubia cordifolia roots extract [90].Regarding kidney enzymes, abnormal decrease of ALP, ALT and AST activities of kidney homogenate in EG control group may be an indicator of tubular dysfunction. An earlier study [101] showed a correlation between enzyme leakage and cell damage. It was also speculated that the enzyme ALP, located in the cytoplasm, is also released to the circulation after cellular damage leading to its decrease in kidney tissue [102, 103]. Decreased tissue AST and ALT activities and proteinuria are solid indicators of cellular, tubulointerstitial injury and inflammation [104]. Calcium oxalate crystals are known to damage proximal tubular epithelium and are generally associated with shedding of the brush border membrane and leakage of enzymes in urine [105]. ALP, AST and ALT which present in the brush border of the kidney are implicated in the calcification process and so, decrease the level of these kidney enzymes in EG control group might be due to the leakage of them in general circulation or in filtrate within the lumens of renal tubules. The treatments of EG-administered rats with the tested mushroom infusions and carvedilol in the present study reduce the decrease of the above kidney enzymes levels, and this may indicate the protective effects of these agents against destructive effects of hyperoxaluria. These changes coincide also with those obtained by Sathya et al. [106] who found that kidney ALP, ALT and AST levels were increased after treatment of EG-administered rats with ethanolic extract of Acalypha indica.In view of OS and antioxidant defense system, administration of EG which caused hyperoxaluria, resulted in elevation of kidney and serum NO levels and kidney LPO as well as reduction of kidney GSH content and kidney GST, SOD, GPX and catalase activities. These data go parallel with many publications. Pan et al. [107] and Chen et al. [108] found an increase in inducible-nitric oxide synthase expression and NO level in lithogenic rats. Increased NO level can interact with oxygen radicals and lead finally to acute renal failure deterioration [109, 110]. In another site, it was concluded that the subacute EG administration promotes LPO, raises enzymes of tissue damage serum marker and result in fluctuation in the antioxidative systems in different rats tissues [111]. The decrease of GSH in our study is in accordance with abundant studies which showed deficiency in GSH content in the hyperoxaluric rats [83, 112]. GSH depletion by itself could share in the uremia development because it has been demonstrated that depletion of GSH in rats caused acute renal failure [113]. Various antioxidant enzymes levels have been decreased in chronic kidney disease patients [114, 115, 116]. Further, SOD and catalase activities were declined in hyperoxaluric patients [117] and kidney SOD, GPX and catalase activities were decreased in EG-administered rats [118]. In the same way, it was obtained little values of kidney GST, SOD, GPX and catalase activities of EG-administered rats as compared to normal control group [103]. In addition, it was reported that antioxidants retard the ROS production induced by oxalate and if antioxidants fail, urolithiasis will be occurred [14, 15]. The decreased level of GSH in the current study may be due to the reduction in GSH synthesizing enzymes activities, glutathione reductase (GR) and glucose 6- phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD). Modification of thiol groups of G6PD during OS causes loss of its activity which ultimately resulted in reduction of level of NADPH [119]. So, the decrease of the production of NADPH is due principally to the inhibition of G6PD, and hence GSH production decreased [6]. The decreased activity of catalase might be due to direct inhibition of catalase by oxalate and decreased catalase regeneration from its inactive form, because falling of NADPH availability [120]. With regard mode of action, it was suggested that GPX contain critical sulfhydryl group in its active site for effective functioning of the enzyme; free radicals attack on that sulfhydryl group might have reduced its activity [121]. The depletion of GSH could influence GSH-dependent enzymes such as GST, GPX and G6PD, leading to additional oxidative challenge [122]. The decrease in activities of the antioxidant enzymes in our study might be also due to increase the level of free radicals during hyperoxaluria. The free radicals when present in high levels are able to interacting with the enzymes and inhibiting them [121]. Our results are in disagreement with Bijarnia et al. [123] who obtained high activities of kidney SOD and catalase with compared to normal rats.Treatment of EG-administered rats with P. ostreatus, A. bisporus and carvedilol led to decrease of serum NO as well as kidney NO and LPO, while kidney GSH, GST, SOD, GPX and catalase were increased for different extents. These results are in accordance with many authors. Kosanić et al. [124] suggested that mushroom may be utilized as good sources of natural antioxidants and for pharmaceutical objectives in treatment of different diseases. A number of medicinal and edible mushrooms have been demonstrated to have strong antioxidant activities and prospected applications as natural antioxidants [125, 126, 127, 128, 129, 130]. In addition, it was postulated that Pleurotus tuberregium, which has high nutritive value, could protect the kidneys and liver from oxidative damage caused by toxicants and drugs [131]. In that way, it was concluded that P. ostreatus extract can protect the major organs of Wistar rats from age-related oxidative damage through enhancement of the antioxidant enzymes [132]. Furthermore, it was revealed that P. ostreatus shows perfect in vivo antioxidant activity by decreasing LPO level and by enhancing the levels of non-enzymatic and the activities of enzymatic antioxidants [133]. On the other hand, it was found that consuming of A. bisporus, which is the most widely investigated edible mushroom, has been demonstrated to retard the free radicals progression [134]. It was speculated that A. bisporus ethanolic extract had strong antioxidant activity and could be explored as a novel natural antioxidant [135]. Some polyphenols and flavonoids (which naturally occurring in P. ostreatus and A. bisporus) are reported to have the potential effect of enhancing the activities of antioxidant enzymes such as SOD, catalase and GPX [136, 137]. In concurrence with the present study, it was postulated that carvedilol caused decline in the NO concentration in injured rat kidney [138]. It was also speculated that carvedilol has renoprotective potential against nephrotoxicity induced by cyclosporine A and suggest a considerable contribution of its antilipoperoxidative feature in this beneficial influence [139]. Equally, it was elucidated that ROS play a causal function in ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal injury and carvedilol exerts renoprotective effects possibly by the antioxidant activities and radical scavenging [140]. Moreover, it was found that carvedilol is a novel β-adrenoreceptor blocker, with antioxidant potencies inhibiting LPO and preventing the endogenous antioxidants depletion [141]. Carvedilol also blocks renal cell death and mitochondrial dysfunction through the protection against cisplatin induced-ROS production and redox state unbalance [142]. Finally, it was concluded that carvedilol has antifibrotic effects that can be explained by restoration of antioxidant enzyme activities, GSH replenishment and decreasing of lipid peroxides [143].
5. Conclusions
- The present study demonstrated that the aqueous extract of edible mushrooms P. ostreatus and A. bisporus as well as carvedilol exhibited preventive effects against elevation of kidney function markers induced by EG. These agents may prevent urolithiasis mainly through decreasing hyperoxaluria-induced oxidative stress which lead to cell injury and so prevent calcium oxalate crystals from attachment with renal tubular epithelial cells and subsequent stone development. However, further clinical studies are required to assess the efficacy and safety of P. ostreatus, A. bisporus and carvedilol in human beings.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML