-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Biochemistry
p-ISSN: 2163-3010 e-ISSN: 2163-3029
2015; 5(5): 92-98
doi:10.5923/j.ajb.20150505.02

Evaluation of Osteoprotegerin Levels in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
Nareman Y. Mohamed1, Hasnaa S. Mustafa1, Wafaa Abd-Elaziz1, Abd-El Rahman Ibrahim2
1Department of Clinical Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine (for girls), Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
2Department of Cardiology, Faculty of Medicine (for boys), Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
Correspondence to: Nareman Y. Mohamed, Department of Clinical Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine (for girls), Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Background: Osteoprotegerin (OPG) is classed as an osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor plays an important regulatory role in the skeletal, immune, and vascular systems.OPG acts as a soluble decoy receptor for receptor activator of nuclear factor-kabba Bligand (RANKL) and TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). OPG has been identified as a survival factor for endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC). Atherosclerosis is the most frequent underlying cause of coronary artery disease (CAD), carotid artery disease and peripheral artery disease. It appears that OPG is able to prevent, but not reverse, the process of vascular calcification. The aimof this study to determine the possible association of OPG with coronary artery disease and to detect early subclinical arthrosclerosis. Subjects and methods: the study was conducted on seventy subjects, suffering from chest pain and underwent diagnostic coronary angiography. On the basis of coronary angiography the present study was conducted on seventy subjects are arranged into 4 groups:20patients with one stenotic vessel (group II). 15 patients with two stenotic vessels (group III). 20 patients with three stenotic vessels (group IV) as well as fifty apparently healthy control (gruop I). All subjects included in this study were subjected to the following: Full history taking, clinical examination, laboratory investigations including fasting blood glucose levels and lipid profile (LDL, HDL, total cholesterol and triglycerides). in addition, specific investigations which include serum ostoprotegerinlevel by ELISA technique and serum CRP by latex serology testwere done.Results: it was found that all patients have significantly higher serum OPG level (p≤ 0.05) . The higher serum OPG levels were observedin the group with three stenotic vesselcompared with the groups with one-stenotic vessel, towstenotic vessel and conrol. Significant positive correlation was found between serum OPG and age. Conclusion: present study revealed an association between OPG and the number of stenotic vessels. This means that, OPG level might a marker for coronary artery disease severtyalso, it is a simple adjuvant to other noninvasive diagnosticmodalities of coronary atery disease.
Keywords: Osteoprotegerin, Coronary Artery Disease
Cite this paper: Nareman Y. Mohamed, Hasnaa S. Mustafa, Wafaa Abd-Elaziz, Abd-El Rahman Ibrahim, Evaluation of Osteoprotegerin Levels in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease, American Journal of Biochemistry, Vol. 5 No. 5, 2015, pp. 92-98. doi: 10.5923/j.ajb.20150505.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Osteoprotegerinis a soluble tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily receptor that inhibits the actions of the cytokines receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANKL) and TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) by preventing their binding to signaling receptors in the cell membrane [1]. OPG is a soluble glycoprotein widely expressed in most human tissues including the bone (osteoblasts) and the vasculature (endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells, VSMC) [2]. OPG, RANK and RANKL network regulates the differentiation and activation of osteoclasts and hence balance between bone formation (osteoblasts) and bone resorption (osteoclasts). RANKL expressed on osteoblastic, stromal and T cells binds to RANK on the surface of osteoclasts, monocytic and dendritic cells [3]. By acting as a soluble decoy receptor competing RANK, OPG prevents RANK-RANKL interactions and thus osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. Besides RANKL, OPG is also able to bind and neutralize the pro-apoptotic actions of (TRAIL) expressed by VSMC and T cells [4] Biochemically, OPG is a basic secretory glycoprotein composed of 401 amino acid residues with 7 distinct structural domains. It exists as either a monomer of 60 kDa or a disulfide bond linked homodimer of 120 kDa. The homodimeric form of OPG is biologically more active than the monomeric form.The human OPG gene is a single copy gene found on chromosome 8q which consists of five exons and spans a region of 29 kb [5]. OPG-deficient mice display vascular calcification while [6]. Atherosclerosis is a disease of large and medium-sized arteries [7] (Hansson, 2005). Atherosclerosis is the most frequent underlying cause of coronary artery disease, carotid artery disease and peripheral artery disease. Age, total cholesterol and LDL concentrations are risk markers for future cardiovascular events [8] A common feature of atherosclerosis is the dysfunction and death of vascular cells [9]. Therefore, the ability of OPG to promote vascular cell survival suggests that, itcan potentially protect against this process [10].
2. Subjects and Methods
- The present study was carried out in at medical Biochemistery department, in collaboration with cardiology Department, Al-azhar f aculty of medicine for Girls and Al-Hussien university hospital and written informed consent was obtained from all participants.The present study was carried on 70 subjects categorized into four groups: Group 1: included 15 healthy subjects showing no signs or symptoms of cardiac ischemia were selected and assigned as a control group, and confirmed by electrocardiography (ECG).Group II: included 20 patients with one stenotic vessel (1-SV)Group III: included 15 patients with two stenotic vessels (2-SV). Group IV: included 20 patients with three stenotic vessels (3-SV). Patients proved malignancy; Serum creatinine > 2 mg/dL and treatment with corticosteroids were excluded from the study. All included cases and controls were submitted to full history taking, clinical examination, ECG, lipid profile (total cholesterol, triacylglycerides, LDL and HDL), serum creatinine and serum C-reactive protein.
3. Special Investigations
- 1- Estimation of serum OPG marker level By Enzyme Linked Immuno- Sorbent Assay technique (ELISA) 2- Coronary angiography was done to all subjects for detection of the number of diseased vessels.Sampling: five ml venous blood was withdrawn aseptically from each subject after 12 hours fasting. Samples allowed to clot, centrifuged. Sera were separated and aliquoted. All biochemical parameters were freshly measured. Part of serum was stored at -80°C for measurement of osteoprotegerin.
4. Analytical Methods
- Blood glucose was measured by enzymatic colorimetric assay using glucose oxidase method by Roche / Hitachi 912 (Roche Diagnostic, Indianapolis, USA) [11]. Serum total cholesterol was assayed by enzymatic colorimetric assay using cholesterol esterase method [12]. Determination of serum triglyceride was done by an enzymatic colorimetric assay using lipoprotein lipase enzyme [1]. reby magnesium chloride / dextran sulfate reagent [14].LDL was calculated according to Friedwald Equation to the Friedewald Formula (LDL = total cholesterol –
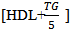 [15].Determination of CRP was done by Latex agglutination serology test (Qualitative method) [16]. Determination of serum creatinine was done by colorimetric assay [17].OPG was estimated by Enzyme Linked Immuno- Sorbent Assay technique (ELISA), using kit produced by BioVendeor-Laboratories medicína A. S.) [18]It is an enzyme ljnked immunosorbent assay sandwich technique in which diluted standards, quality controls and samples were added to microplate wells coatedwith capture monoclonal antiosteoprotogerin antibody. After incubation and washing steps, biotin – labeled polyconal antihuman osteoprotegerin antibody solution was added for a further incubation step. after a final step, hydrogen peroxide tetramethylbenzidine was incubated into the wells resulting in a coloured product.After the addition of stope solution, the colour was measured at 450 nm. The absorbance and colour intensity were considered proportional to the concentration of OPG in the sample. A standared curve was constructed and the consternation of OPG in the sample was determind.
[15].Determination of CRP was done by Latex agglutination serology test (Qualitative method) [16]. Determination of serum creatinine was done by colorimetric assay [17].OPG was estimated by Enzyme Linked Immuno- Sorbent Assay technique (ELISA), using kit produced by BioVendeor-Laboratories medicína A. S.) [18]It is an enzyme ljnked immunosorbent assay sandwich technique in which diluted standards, quality controls and samples were added to microplate wells coatedwith capture monoclonal antiosteoprotogerin antibody. After incubation and washing steps, biotin – labeled polyconal antihuman osteoprotegerin antibody solution was added for a further incubation step. after a final step, hydrogen peroxide tetramethylbenzidine was incubated into the wells resulting in a coloured product.After the addition of stope solution, the colour was measured at 450 nm. The absorbance and colour intensity were considered proportional to the concentration of OPG in the sample. A standared curve was constructed and the consternation of OPG in the sample was determind.5. Statistical Analysis of Data
- The collected data was organized, tabulated and statistically analyzed using SPSS software (statistical package for social sciences) version 17. For quantitative data, the mean and standard deviation were calculated. The difference between two means was statistically analyzed using the student (t) test. Analysis of variance was used to compare quantitative data between more than two groups. For non-parametric data, the median and range were calculated and Mann-Whitney test was used as a test of significance. For qualitative data, the number and percent distribution were calculated. Chi square (χ2) or Fisher Exact test was used as a test of significance, to compare qualitaive parameters pearson’s correlation coefficient was used.Significance was adopted at P < 0.05 for interpretation of results of significance tests [19].
6. Results
- Results of the present study are shown in tables (1, 2, 3) and figures (1).
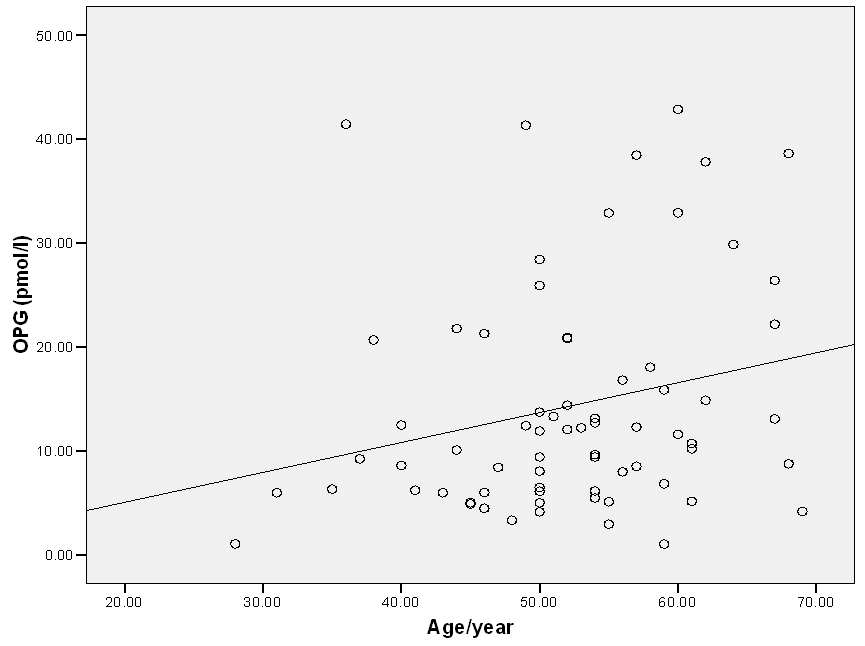 | Figure (1). Correlation between OPG and age within all cases |
|
|
|
7. Discussion
- Osteoprotegerin,a key factor in bone remodeling, a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family, and a decoy receptor for the receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand and tumour necrosis factor–related apoptosis-inducing ligand [20]. OPG also named osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor (OCI) [21]. Expression of OPG has been observed in the heart, arteries and veins [22]. OPG is expressed in both endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells (SMCs). SMCs has recently been suggested to be the main source of circulating OPG. In endothelial cells, OPG expression is stimulated by TNFα, IL-1α, IL-1β, and activated integrin [23]. In vascular SMCs TNFα, IL-1β, basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), platelet derived growth factor (PDGF) and angiotensin II are reported to increase the expression of OPG [24].Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death globally; Atherosclerosis is the mostfrequent underlying cause of coronary artery disease, carotid artery disease and peripheral artery disease.various risk factors are known to contribute to the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis, such as diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidaemia and chronic vascular inflammation [25]. The early detection of atherosclerotic complications is important in reducing mortality and morbidity from cardiovascular disease. Endothelial dysfunction is an early process in atherosclerosis and a predictor of cardiovascular lesions. [26]Osteoprotegerin (OPG) is a soluble member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily, produced by osteoblasts, vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. It has an anti-osteoclastic effect being a soluble decoy receptor for the osteoclast activator (receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand). Moreover, it appears to be an important regulator of vascular calcification [27]. It may inhibit the active calcification process through downregulation of alkaline phosphatase enzyme (ALP) activity. Moreover, OPG blocks the actions of RANKL which increased in diseased and calcified vessels [28] and can invitroinduce ALP activity and calcification in vascular cells [29]. The aim of this study was to evaluate the possible association of serum OPG as a biomarker with the presence of CAD and its severity in patients with chest pain. This study used the number of stenotic coronary arteries as a marker of coronary atery disease severity.In the present study serum osteoprotegerin significantly increasedin patients with three stenotic vessels,more than groups with two stenotic vessels or one stenotic vessel and they were higher than those of the control group (P=0.001). So there was association between level of OPG and the severity of CAD. This results in agreement with the results of Pedersen et al., (2012) [29] who reported that serum level of OPG was significantly higher among CAD patients compared to the control group they suggested that High serum OPG levels may lead to vascular calcification, formation of atherosclerotic plaques, increasing blood pressure, and cardiovascular diseases.Our results go hand on hand with Reinhard et al., (2011) [30] who showed that increased OPG level was a predictor of significant CAD. One proposed mechanism for this increased rate of plaque instability and poor cardiovascular outcome is up-regulated expression of OPG in endothelial cells, in the presence of proinflammatory cytokines, which in turn increases the expression of endothelial cell adhesion molecules upregulation of the inflammatory cells and increased activity of matrix metalloproteinase which leads to degradation of the extracellular matrixand reduced thickness of the fibrous cap, the erosion of which causes thrombus formation (Venuraju et al., 2010) [6]. As regard CRP which is an acute-phase protein produced predominantly by hepatocytes under the influence of cytokines. This study found that there was statistical significant difference on comparing the four groups (P= 0.04). This agree) with Gupta et al, (2012) [31] who foundan association between serum CRP level and multiple measures of athrosclosis. Their results demonstrates that CRP seems to provide an assessment of atherosclerotic plaque activity. In the current study, lipid profile showed that there was statistically significant differences regardingthe mean serum levels of toal cholesterolbetween the studied groups (p=0.001). This disagrees with the results obtained by Ghaffari et al., (2013) [32] who reported that there wasno significant difference in cholesterol levelbetween subjects with CAD and subjects without CAD. This agrees with Ohmori et al., (2003) [33] who found high OPG level in hypercholesterolemic subjects.In this study there is no significant difference in serum HDL-c and LDL between the three patients groups and control group. This agree with [32] Ghaffari et al., (2013) who reported that there was no significant difference in LDL and HDL level between subjects with CAD and subjects without CAD groups (P=0.363). this is disagree with Myrna et al., (2008) [34] who found in a cohort of elderly men, a favorable association between OPG, triglycerides and HDL cholesterol, a finding that isconcordant with the fact that elevated serum cholesterol and triglycerides largly contribute to the incidence of CAD. Lack of such difference in this study is possibly due to limitations of the study.In the present study there was statistical significant differences between studied groups regarding to age (p=0.03) and sex (p=0.1) similarlyVanderl et al; (2003) [35] were found that the mean age and the percentage of males were significantly higher in the groups of coronary heart disease patients than control A finding that is concordant with the fact that age and sex are one ofmajor established factors of coronary heart disease.Onthe other hand Ghazauani et al; (2010) [36] found no significant difference in the mean age and sex between the groups of CAD and that of control subjects.This study showed that there was significant positive correlation between serum OPG levels and age (P = 0.04), while there were no correlation between OPG levels and other variables (FBG, Creatinin, TG, Total Cholesterol, HDL and LDL). Similarly Yang et al., (2011) [37] found positivecorrelation between serum OPG level and age (P = 0.039), but no correlation were found between serum OPG level and hypertension, TC, HDL, LDL and TG.On the other hand Schoppet et al., (2003) [11] found that OPG serum levels were negatively correlated with triglyceride but were not correlated with total Cholesterol, HDL, LDL or Creatinin.
8. Conclusions
- This study showed that serum OPG level may be involved in the progression of CAD, predict cardiovascular events and it is a simple adjuvant to other noninvasive diagnosticmodalities of CAD. Further studies including larger numbers of patients are recommended for further detection of relevance of OPG to other diagnostic factors. Further studies are needed to evaluate the predictive and diagnostic value of serum OPG levels for clinical use as well as the pathogenic importance of this mediator in the process of atherosclerosis and plaque rupture.We recommend assessing OPG serum levels in age-matched groups, because OPG serum levels increase with aging.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML