-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Biochemistry
p-ISSN: 2163-3010 e-ISSN: 2163-3029
2014; 4(1): 6-13
doi:10.5923/j.ajb.20140401.02
Effect of NutriSim© and the Interactive Response of Pro-inflammatory and Anti-inflammatory Cytokines in a Model of Septic Shock Induced by E coli Serotype 0111:B4
Irma E. Velázquez-Brizuela1, Fermín P. Pacheco-Moisés2, Rolando Romero-Dávalos3, Luís A. Romero-Tirado3, José J. Hernández-Andalón3, L. Javier Flores-Alvarado4, Oscar K. Bitzer-Quintero1, Erika D. González-Renovato1, 4, Moisés A. Alatorre-Jiménez1, 4, Angélica L. Sánchez-Lopez1, 4, Deha G. Nuño-Penilla1, 4, Genaro Gabriel Ortiz1, 4
1Laboratorio de Mitocondria, Estrés Oxidativo & Patología, División de Neurociencias. Centro de Investigación Biomédica de Occidente, Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social. Guadalajara, Jalisco. México
2Departamento de Química, Centro Universitario de Ciencias Exactas e Ingenierías. Universidad de Guadalajara. Guadalajara, Jalisco. México
3Laboratorios BioSim©; Área de Desarrollo e Investigación Científica. México D.F.
4Centro Universitario de Ciencias de la Salud, Guadalajara, Jalisco. México
Correspondence to: Genaro Gabriel Ortiz, Laboratorio de Mitocondria, Estrés Oxidativo & Patología, División de Neurociencias. Centro de Investigación Biomédica de Occidente, Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social. Guadalajara, Jalisco. México.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The biological effects and possible mode of actions of anti and pro-inflammatory cytokines on the evolution of sepsis and of its most severe complication, the septic shock, were exposed. These data were analyzed in order to clarify the complex pathogenic mechanisms taking place in animal models of sepsis and human sepsis. This study makes possible the development of new drugs and other effective and safe therapeutically procedures for the treatment of a severe disease causing a high morbidity and mortality worldwide. The complex interactions occurring among the diverse pro-inflammatory cytokines were stressed, as well as the interactions with other mediators of the so-called systemic inflammatory response. The dual behavior of the actions of some cytokines, occasionally carriers of opposed effects, as well as their actions depending on the period of time in which they were administered, were emphasized. Another significant characteristic was that they frequently varied, and that there was no correspondence between the results of the effects of the cytokines in humans and those obtained in experimental animal models of sepsis or endotoxic shock. The effect of NutriSim©, a nutritional supplement, on serum anti and pro-inflammatory cytokines levels using an experimental model of endotoxic shock were studied. The results exhibited that a single dose of NutriSim© prior the endotoxic insult diminishes significantly the production of serum TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IL-4 and IL-10 cytokines.
Keywords: NutriSim©, TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IL-10, IL-4, Septic Shock, Lipopolysaccharide
Cite this paper: Irma E. Velázquez-Brizuela, Fermín P. Pacheco-Moisés, Rolando Romero-Dávalos, Luís A. Romero-Tirado, José J. Hernández-Andalón, L. Javier Flores-Alvarado, Oscar K. Bitzer-Quintero, Erika D. González-Renovato, Moisés A. Alatorre-Jiménez, Angélica L. Sánchez-Lopez, Deha G. Nuño-Penilla, Genaro Gabriel Ortiz, Effect of NutriSim© and the Interactive Response of Pro-inflammatory and Anti-inflammatory Cytokines in a Model of Septic Shock Induced by E coli Serotype 0111:B4, American Journal of Biochemistry, Vol. 4 No. 1, 2014, pp. 6-13. doi: 10.5923/j.ajb.20140401.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Septic ShockSepsis and septic shock are responsible for a high morbidity, are also the most common cause of death in intensive care units. Historically, the mortality associated with sepsis was maintained between approximately 50 and 75% in the patients, but with the advent of antibiotic therapy was reduced to a range of 30 to 50%. Despite this progress, recent estimates indicate the existence of 750 000 cases of severe sepsis per year in the U.S.[1]. But the number is gradually increasing in 9.5% of the reported cases and the mortality rate remains high. Given its importance, the role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of septic shock will be addressed, because the modulation of these mediators is the most important and promising strategy being investigated as a therapeutic option to reduce morbidity and characterizing high mortality in septic shock[2].It is known that sepsis syndrome occurs due to bacteria and other microorganisms that cause infectious focus (pneumonia, abscesses, etc.) Or bacterial exotoxins constituents released in the local or systemic host environment. These constituents include bacterial cell wall components such as endotoxins in Gram-negative bacteria, teichoic acid and other antigens in Gram-positive bacteria and bacterial DNA[3]. These products stimulate the generation of pro-inflammatory cytokines both locally and systemically, which exert multiple effects, such as stimulating the production and release of other pro-inflammatory mediators. Among them, the most important pro-inflammatory cytokines known that exert with both synergistic effects by stimulating the cascade of inflammatory mediators are: tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin 1beta (IL- 1beta), triggering the so-called systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) due to an infection[4]. The next phase in the cytokine response to infection is an opposite response to inflammatory activity, which is exerted by inhibitors such as receptor antagonist of (IL-1) and TNF receptor inhibitor and some anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-9, IL-10 , IL-11 and IL-13, which produces the compensatory anti-inflammatory response syndrome (CARS). It is precisely the balance between these cytokines in different periods of time, which determines the clinical manifestations (figure 1) and the successful or fatal outcome in sepsis and septic shock[5].Gram negative bacteria release LPS to the bloodstream, inducing a local and systemic effect. LPS is known to stimulate immune response thus the release of pro-inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor Alfa (TNF-α) and interleukin 1-beta (IL-1β), leading to a systemic inflammatory response syndrome due to infection. The next phase produces the compensatory syndrome, where the balance between anti and pro inflammatory mediators will determine the clinical manifestations of sepsis.
2. Pro-inflammatory Cytokines
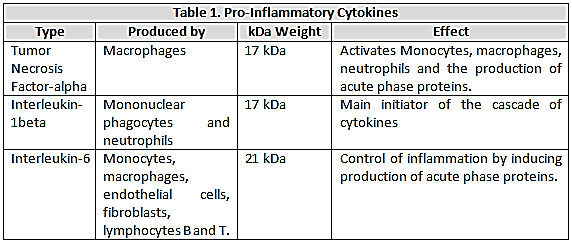
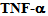 This molecule was first identified in the pathogenesis of septic shock; from a structural point of view is a 17kDa protein produced predominantly by macrophages and has the ability to activate monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils and induce the production of acute phase proteins through the IL- 6 pathway[6].Two different cell surface receptors have been described for the
This molecule was first identified in the pathogenesis of septic shock; from a structural point of view is a 17kDa protein produced predominantly by macrophages and has the ability to activate monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils and induce the production of acute phase proteins through the IL- 6 pathway[6].Two different cell surface receptors have been described for the 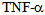 ; the type I having a molecular weight of 55 kDa and type II with a molecular weight of 75 kDa. The stimulation of these receptors leads to cytotoxicity, activation of factor nuclear kappa B (NF-kB) as well as the expression of adhesion molecules on endothelial cells[7]. Both receptors are also present in soluble form and retain their affinity for
; the type I having a molecular weight of 55 kDa and type II with a molecular weight of 75 kDa. The stimulation of these receptors leads to cytotoxicity, activation of factor nuclear kappa B (NF-kB) as well as the expression of adhesion molecules on endothelial cells[7]. Both receptors are also present in soluble form and retain their affinity for 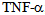 . Soluble receptors competing with cell surface receptors for binding to free
. Soluble receptors competing with cell surface receptors for binding to free 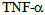 , because it is inactivated when bound or soluble binds receptor, the generation of these receptors actually represents an anti-inflammatory response mechanism[8]. Numerous studies have demonstrated the presence of high levels of
, because it is inactivated when bound or soluble binds receptor, the generation of these receptors actually represents an anti-inflammatory response mechanism[8]. Numerous studies have demonstrated the presence of high levels of 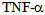 in clinical sepsis and septic shock[9]. (Table 1)
in clinical sepsis and septic shock[9]. (Table 1)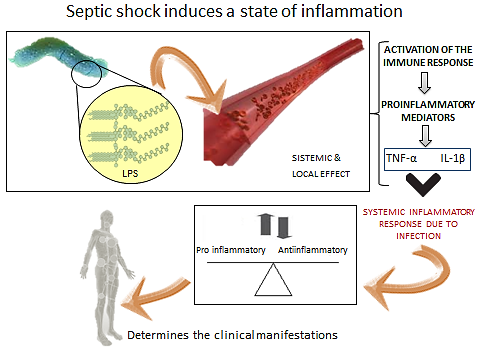 | Figure 1. Septic shock induces a state of inflammation |
|
|
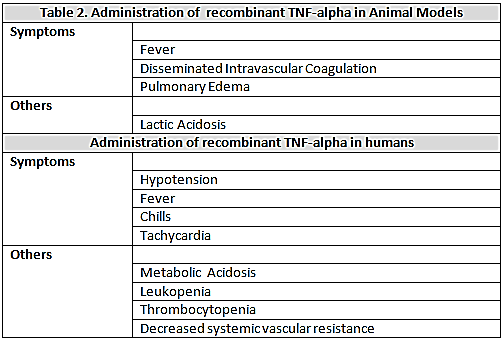
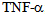 , which is associated with cardiovascular and metabolic disorders, similar to those that occur in sepsis and septic shock in human[10]. Animal models, administration of recombinant
, which is associated with cardiovascular and metabolic disorders, similar to those that occur in sepsis and septic shock in human[10]. Animal models, administration of recombinant 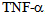 causes fever, lactic acidosis, disseminated intravascular coagulation, pulmonary edema and death[11]. The behavior of the cardiovascular system in these animals is similar to that of septic shock in humans and is characterized by hypotension and decreased of systemic vascular resistance. Administration of
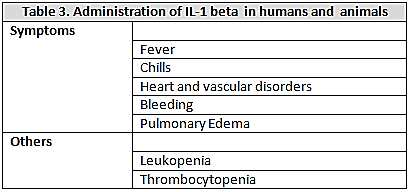
causes fever, lactic acidosis, disseminated intravascular coagulation, pulmonary edema and death[11]. The behavior of the cardiovascular system in these animals is similar to that of septic shock in humans and is characterized by hypotension and decreased of systemic vascular resistance. Administration of 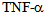 to human induces fever, chills, metabolic acidosis, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, tachycardia and hypotension with decreased peripheral vascular resistance[12]. (Table 2)Interleukin 1-βIs a polypeptide of 17kDa produced by mononuclear phagocytes and neutrophils. Currently they are recognized to be the main mediators present, in addition with the TNF-alpha, in the cascade of cytokines released in sepsis[13]. Most of the biological effects of TNF-alpha induces IL-1beta, which, when injected into animals and humans produces fever chills, heart and vascular disorders with leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, bleeding, and pulmonary edema; the release of IL-1beta is increased in experimental models of sepsis and septic shock in animals (LPS) and humans, and these high levels of both cytokines was also correlated with a high mortality. As the case with endotoxin, administration of TNF-alpha to humans and animals is associated with increased circulating levels of IL-1beta. Detected higher levels of IL-1 beta have been observed in patients with meningococcal sepsis and this has been correlated with the severity of meningococcemia, shock and dead[14]. (table 3)
to human induces fever, chills, metabolic acidosis, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, tachycardia and hypotension with decreased peripheral vascular resistance[12]. (Table 2)Interleukin 1-βIs a polypeptide of 17kDa produced by mononuclear phagocytes and neutrophils. Currently they are recognized to be the main mediators present, in addition with the TNF-alpha, in the cascade of cytokines released in sepsis[13]. Most of the biological effects of TNF-alpha induces IL-1beta, which, when injected into animals and humans produces fever chills, heart and vascular disorders with leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, bleeding, and pulmonary edema; the release of IL-1beta is increased in experimental models of sepsis and septic shock in animals (LPS) and humans, and these high levels of both cytokines was also correlated with a high mortality. As the case with endotoxin, administration of TNF-alpha to humans and animals is associated with increased circulating levels of IL-1beta. Detected higher levels of IL-1 beta have been observed in patients with meningococcal sepsis and this has been correlated with the severity of meningococcemia, shock and dead[14]. (table 3)
|
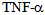 and
and 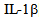 [15]. Most of the activities of IL-6 are associated with the control of inflammation as a result of its potent ability to induce production of acute phase proteins in the liver, which are essentially protecting and limiting the inflammatory process through its anti-protease activity and sequestering capacity[16]. This is confirmed by the fact that injection of IL-6 by LPS protects from death in experimental endotoxic shock[17]. The IL-6 also free receptor antagonist and
[15]. Most of the activities of IL-6 are associated with the control of inflammation as a result of its potent ability to induce production of acute phase proteins in the liver, which are essentially protecting and limiting the inflammatory process through its anti-protease activity and sequestering capacity[16]. This is confirmed by the fact that injection of IL-6 by LPS protects from death in experimental endotoxic shock[17]. The IL-6 also free receptor antagonist and 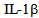 in that context, it is interesting that this has recently been identified as a product of hepatocytes and regulated by pro-inflammatory cytokines, as well as the acute phase proteins (APP) as alfa1antitripsina and alpha1-acid glycoprotein, among others, by which the receptor antagonist of
in that context, it is interesting that this has recently been identified as a product of hepatocytes and regulated by pro-inflammatory cytokines, as well as the acute phase proteins (APP) as alfa1antitripsina and alpha1-acid glycoprotein, among others, by which the receptor antagonist of 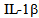 in fact today is regarded also as a APP; they protect-against endotoxin and can even reduce the lethality of
in fact today is regarded also as a APP; they protect-against endotoxin and can even reduce the lethality of 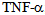 [18]. These results can explain why IL-6 has been shown to have protective activity in infections and septic shock models. However, in contrast to these beneficial effects, IL-6 can cause bone resorption, muscle wasting, anemia and can stimulate the production of neutrophils to platelet activating factor (APP) and the superoxide anion[19-21].IL-6 does not activate endothelial cells but in the presence of its soluble receptor, which is found in the plasma, induced chemokines like monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP- 1) and IL-8 stimulate the recruitment of neutrophils. Also deleterious effects of IL-6 have been detected in vivo in experimental models of ischemia-reperfusion induced in rat[22]. These adverse effects produced by IL-6 may be the explanation why many researchers have pointed out that elevated circulating levels of this cytokine correlate with the severity of sepsis and prognosis of death in patients, many consider the IL -6 cytokine also as a pro-inflammatory (dualism)[23].
[18]. These results can explain why IL-6 has been shown to have protective activity in infections and septic shock models. However, in contrast to these beneficial effects, IL-6 can cause bone resorption, muscle wasting, anemia and can stimulate the production of neutrophils to platelet activating factor (APP) and the superoxide anion[19-21].IL-6 does not activate endothelial cells but in the presence of its soluble receptor, which is found in the plasma, induced chemokines like monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP- 1) and IL-8 stimulate the recruitment of neutrophils. Also deleterious effects of IL-6 have been detected in vivo in experimental models of ischemia-reperfusion induced in rat[22]. These adverse effects produced by IL-6 may be the explanation why many researchers have pointed out that elevated circulating levels of this cytokine correlate with the severity of sepsis and prognosis of death in patients, many consider the IL -6 cytokine also as a pro-inflammatory (dualism)[23].3. Anti-inflammatory Cytokines
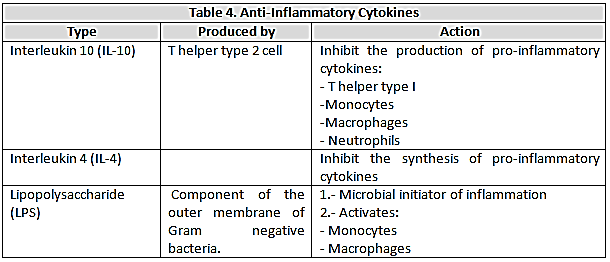
- Currently considered the most importantanti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10, IL-4, IL-6, IL-13, the granulocyte colony stimulating factor-macrophage (GM-CSF), IFN-alpha and transforming growth factor- beta (TGF-β) for the role they play in the pathogenesis of sepsis. It is noteworthy that several cytokines exert a dual role in septic processes and act as pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory in the following influencing factors: a) The amount of cytokines present; b) The nature of the target cells; c) The type of triggering agent that acts on target cells; d) The time period of exposure to target cells; e) The experimental model used[24]. (table 4)
|
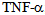 levels, IL-6, IL-8 and the IL-1, when compared with the control group Decreased accumulation was also detected in neutrophils in the lung. However, when treated with IL -10 after administration of endotoxin, the febrile response, the cytokine release, and neutrophil accumulation were not modified[30]. A similar behavior of the IL-10 was observed with relation to hemodynamic parameters (heart rate and pressure) which were not modified by the administration of IL -1 after endotoxin[31].Interleukin-4 (IL-4)This has a potent anti-inflammatory activity and is capable of inhibiting the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines and have been demonstrated the ability of reducing mortality in several models of septic or endotoxic shock, Mice pretreated with IL-4 survive intraperitoneal injection (ip) of live E coli (10 colony forming units and bacteroides fragilis (10CFU), which killed 90% of the mice pretreated with the cytokine. However, it was also demonstrated that pretreatment with IL-4 prior to the induction of sepsis had protective effect, instead when IL-4 is administered during the first infection mortality is increased[32] which argues the importance of selecting the time period and the most suitable of administration to produce the desired effect (in this case, reducing mortality) and also illustrates how this important factor influencing the dual behavior (effectiveness or lack of effect) of each of the different cytokines in the time septic processes[33].Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)Bacterial endotoxin lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a complex glycolipid, is composed of a hydrophilic polysaccharide and a hydrophobic domain known as lipid A. LPS is a major component of the outer membrane of Gram negative bacteria and one of the most potent microbial initiators of inflammation[34]. It has been shown that LPS activates monocytes and macrophages to produce pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-12 also anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10, IL-4 etc. Macrophages also secrete, in response to LPS, a wide variety of other biological response mediators including platelet-activating factor, prostaglandins, enzymes, and free radicals, such as nitric oxide[35]. Production of these inflammatory cytokines and mediators by monocytes/macrophages contributes to the efficient control of growth and dissemination of invading pathogens [36]. However, excessive and uncontrolled production of these inflammatory cytokines and mediators may lead to serious systemic complications including microcirculatory dysfunction, liver and kidney damage[37], and septic shock with a high mortality[38].
levels, IL-6, IL-8 and the IL-1, when compared with the control group Decreased accumulation was also detected in neutrophils in the lung. However, when treated with IL -10 after administration of endotoxin, the febrile response, the cytokine release, and neutrophil accumulation were not modified[30]. A similar behavior of the IL-10 was observed with relation to hemodynamic parameters (heart rate and pressure) which were not modified by the administration of IL -1 after endotoxin[31].Interleukin-4 (IL-4)This has a potent anti-inflammatory activity and is capable of inhibiting the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines and have been demonstrated the ability of reducing mortality in several models of septic or endotoxic shock, Mice pretreated with IL-4 survive intraperitoneal injection (ip) of live E coli (10 colony forming units and bacteroides fragilis (10CFU), which killed 90% of the mice pretreated with the cytokine. However, it was also demonstrated that pretreatment with IL-4 prior to the induction of sepsis had protective effect, instead when IL-4 is administered during the first infection mortality is increased[32] which argues the importance of selecting the time period and the most suitable of administration to produce the desired effect (in this case, reducing mortality) and also illustrates how this important factor influencing the dual behavior (effectiveness or lack of effect) of each of the different cytokines in the time septic processes[33].Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)Bacterial endotoxin lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a complex glycolipid, is composed of a hydrophilic polysaccharide and a hydrophobic domain known as lipid A. LPS is a major component of the outer membrane of Gram negative bacteria and one of the most potent microbial initiators of inflammation[34]. It has been shown that LPS activates monocytes and macrophages to produce pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-12 also anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10, IL-4 etc. Macrophages also secrete, in response to LPS, a wide variety of other biological response mediators including platelet-activating factor, prostaglandins, enzymes, and free radicals, such as nitric oxide[35]. Production of these inflammatory cytokines and mediators by monocytes/macrophages contributes to the efficient control of growth and dissemination of invading pathogens [36]. However, excessive and uncontrolled production of these inflammatory cytokines and mediators may lead to serious systemic complications including microcirculatory dysfunction, liver and kidney damage[37], and septic shock with a high mortality[38]. 4. NutriSim© & Pro-and Anti-inflammatory Cytokines
- Previously we have shown that NutriSim©, a nutritive supplement used empirically in the treatment of several degenerative disorders protects against brain damage induced by ischemia-reperfusion in Mongolian gerbils. These effects are partly attributed to its antioxidant action [39]. Also we demonstrated that administration of NutriSim© 15 min before LPS decrease the level of TNF-α, IL-1 and IL-6 in serum compared to group LPS exhibited a reduction of the levels of secreted TNF-α and IL-6 in serum 30 min after the treatment with LPS. Intraperitoneal administration of lipopolysaccharide stimulates in macrophages cytokines production which conduces to an inflammatory and non-controlled response[40].
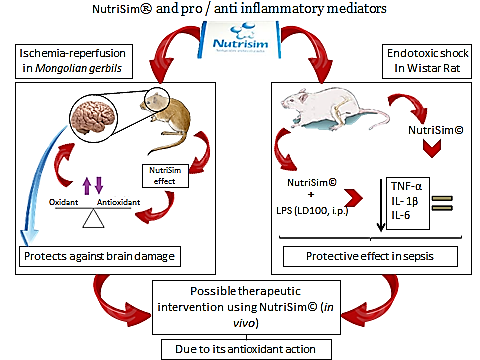 | Figure 2. NutriSim and pro / anti- inflammatory mediators |
5. Conclusions
- It has been already demonstrated that LPS increase the cytokines production in immune cells and it can modulate both pro- and anti-inflammatory response; in this work we state, as demonstrated before by our investigation group, that the use of a nutritional supplement such as NutriSim©, can modulate both pro- and inflammatory response in experimental model of endotoxic shock. Though we can suspect it acts at a cellular level, inducing beneficial changes in the presence of endotoxins. However, the mechanism of action by which this supplement exerts its beneficial effect is still unclear. Whether our findings may be of therapeutic value, it needs to be further investigated.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors wish to thank the veterinary doctor Jose Blanco Fabela (Animal supply, CIBO-IMSS. Guadalajara, Jalisco, Mexico).
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML