-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Biochemistry
p-ISSN: 2163-3010 e-ISSN: 2163-3029
2013; 3(2): 34-39
doi:10.5923/j.ajb.20130302.03
Partial Purification and Characterization of Extracellular Proteases of Klebsiella oxytoca and Its Inhibition by the Volatile Oil of Eugenia uniflora
Adeola Segun. A1, Alli-balogun G. O1, Adeyinka O. G.1, Kasali A. A.2, Eshilokun O. A.2
1Department of Biochemistry, Lagos State University, PMB 0001, LASU post office, Ojo, Lagos, Nigeria
2Department of Chemistry, Lagos state University, PMB 0001, LASU post office, Ojo Lagos, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Alli-balogun G. O, Department of Biochemistry, Lagos State University, PMB 0001, LASU post office, Ojo, Lagos, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The low vulnerability of pathogenic microbes to antibiotics and other conventional drugs has led to the need for the discovery of alternative therapy against such organisms. In this study, the antibacterial activity of the volatile oil of Eugeniauniflorawas evaluated using the extracellular protease (ECP) of Klebsiellaoxytoca as a potential drug target. The volatile oil of E.uniflorainhibited the growth of Klebsiellaoxytocawith MIC and MBC values of ≤ 0.8%v/v and ≥ 0.95%v/v respectively. The optimum pH of the extracellular protease was 6.5, while the optimum temperature was 45℃. The activity of K.oxytocaextracellular protease was found to be reduced in the presence of zinc and mercury while relatively higher activities were observed in the presence of Potassium, Calcium, magnesium and manganese. The extracellular protease was observed to have an unaltered Vmax of 1.0 × 103µmol/min while the Km was determined as 1.140mg/ml and 0.685mg/ml in presence and absence of the volatile oil as an inhibitor respectively. This suggests that the mode of inhibition by the volatile oil on the extracellular protease from K.oxytocais competitive. The findings from this study suggest that the volatile oil derived from E.uniflora is a potential therapeutic agent against K.oxytoca.
Keywords: KeywordsKlebsiellaoxytoca,Eugenia uniflora, Extracellular Proteases, Volatile Oil
Cite this paper: Adeola Segun. A, Alli-balogun G. O, Adeyinka O. G., Kasali A. A., Eshilokun O. A., Partial Purification and Characterization of Extracellular Proteases of Klebsiella oxytoca and Its Inhibition by the Volatile Oil of Eugenia uniflora, American Journal of Biochemistry, Vol. 3 No. 2, 2013, pp. 34-39. doi: 10.5923/j.ajb.20130302.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Eugenia uniflora is a small tropical tree growing to 25 ft. (7.5 m) high. It is widely distributed in South America while it is cultivated as an ornamental hedge and for its edible fruits in tropical and subtropical Africa[1]. The fresh and dried leaves are utilized in ethnomedicine for the treatment of inflammation, stomach diseases, fever and hypertension[2]. The leaf extract has also been used as an inhibitor of DNA polymerase, maltase, sucrose and α-glucosidase[3]. In addition to this, the plant is an important source of essential oils with biological activities which range from antibacterial, antifungal and anti-inflammatory activities some of which have been applied in cosmetics[4]. Antimicrobial activities have been reported for the essential oils of this plant in various bacterial isolates[5, 6, 7]. In one study, the essential oil from the leaves of E.uniflora was shown to inhibit the yeast phase of Paracoccoides brasiliensis[8].Klebsiella species represent the second most frequent cause of gram negative bacteraemia[9]. Klebsiella oxytoca has been recognised as being clinically significant since the early 1980s[10]. It is typically associated with hospital acquired infections usually involving immunocompromised patients or those in need of intensive care[11]. The production of an extended spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL) by K.oxytoca confers bacterial resistance to β-Lactam antibiotics thereby obscuring therapy[12]. Proteases play an important role in several pathological processes some of which include arthritis, tumour invasion, metastasis, infections as well as antibiotic resistance. Jones[13] proposed that microbial proteases can serve as virulence factors in a variety of disease conditions associated with microorganisms. It is however pertinent to identify and characterize microbial proteases prior to an understanding of their specific role in the pathogenesis of diseases and also to serve as potential drug targets in antimicrobial therapy.Some works have been carried out to investigate the antimicrobial effects of volatile oils against K.oxytoca. However, this is about the only study designed to evaluate the kinetics of inhibition of K.oxytoca ECP by the volatile oil of E.uniflora. Therefore, the aim of this study is to partially purify, characterize and evaluate the kinetics of K.oxytoca ECP using the volatile oil of E.uniflora as a potent inhibitor.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
- Fresh mature leaves of Eugenia uniflora were collected from Ogbomosho and authenticated at the Forest Research Institute of Nigeria (FRIN), Ibadan. The leaves were then shade dried for five days prior to extraction of volatile oils.
2.2. Microorganism
- The microorganism used in this study; Klebsiella oxytoca was obtained from the Nigerian Institute of Medical Research (NIMR), Yaba, Lagos and was obtained on Mueller Hinton (MH) agar petri dishes at 4℃.
2.3. Extraction of Volatile Oil
- This was done using the hydro distillation procedure described by Lawrence and Reynolds[14]. 300g of the leaves of E.uniflora were loaded into a 5 litres flask and 3 litres of distilled water was added. The extractor was switched on and the temperature was adjusted at regular intervals. About 3.5ml of hexane was added almost immediately to trap the volatile oil. The resulting extract was run through the tap and refrigerated in an air tight sample container.
2.4. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration and Minimum Bactericidal Concentration
- The MIC and MBC of the volatile oil of Eugenia uniflora were determined using microbroth dilution method described by Janssen et al[15]. A colony of the organism was added to 200 μL of susceptiblity test broth containing two-fold serial dilution of the volatile oil using Tween 80 (≤0.5%v/v) as a diluent in the microtitre plate. The plate was incubated at 37℃ for 18-24 hours. Each of the microwells on the plate was inoculated on a freshly prepared Muller Hinton agar where MIC and MBC were determined. The MIC is described as the lowest concentration of the volatile oil that prevents visible growth of the microorganisms in the required medium. It is also referred to as the Minimum Lethal Concentration (MLC). The MBC is described as the lowest concentration of the oil that yields no colonial growth of the sub-cultured microorganisms in the required medium under favourable conditions.
2.5. Extraction of Crude Enzyme
- This was done according to the method of Makino et al.[16]. Klebsiella oxytoca was inoculated on the MH broth in a McCartney bottle for about 18-24 hours at 37℃ after which it was then centrifuged at 9000rpm for 10 min at room temperature. The supernatant was decanted and stored in a sample bottle at 4℃.
2.6. Determination of Total Protein and Enzyme Activity
- The total protein of the crude enzyme extract was determined using the method described by Lowry et al[17] while ECP activity was assayed using the method of Folin&Ciocalteu[18] with casein serving as the substrate. Specific activity of crude protease was defined as the amount of L-tyrosine released from casein per milligram protein of crude enzyme extract. L-tyrosine concentration was determined from a standard curve prepared by making a serial dilution of a 0.2 mg/ml solution of L-tyrosine.
2.7. Determination of Optimum pH
- This was also done according to a procedure described by Makino et al.[16] with subtle modification. Protease activity was assayed using 0.6% casein solution in 0.05 M Tris buffer solution (pH 6.0-8.5) at 37℃.
2.8. Determination of Optimum Temperature
- Protease activity was assayed under varying temperatures ranging from 30-60℃ using 0.6% casein solution in 0.05 M Tris buffer at pH 8.0[16].
2.9. Effects of Metallic Salts on Enzyme Activity
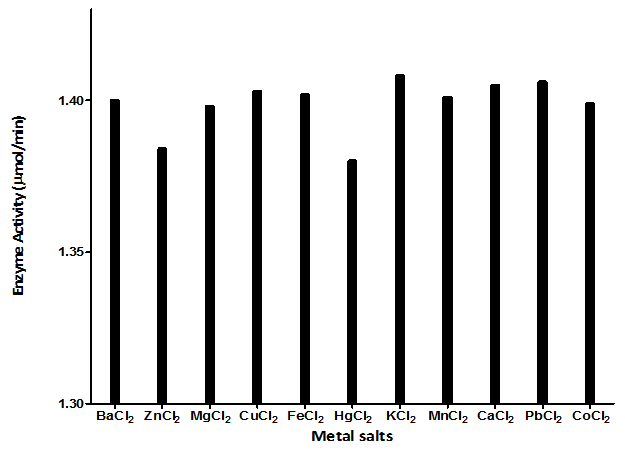
- 0.1ml of the crude enzyme extract was pipetted into 11 test tubes and 0.9ml of distilled water was added to each tube. Various solutions of metal salts were prepared and 0.1ml of salt solution was pipetted into test tubes. 5.0ml of casein was added to each and the tubes were incubated for 10 minutes at 37℃, 5.0ml of stop solution was added to terminate the reaction and solutions were then filtered. Enzyme activity was then determined in the filtrates.
2.10. Enzyme Inhibition Assay
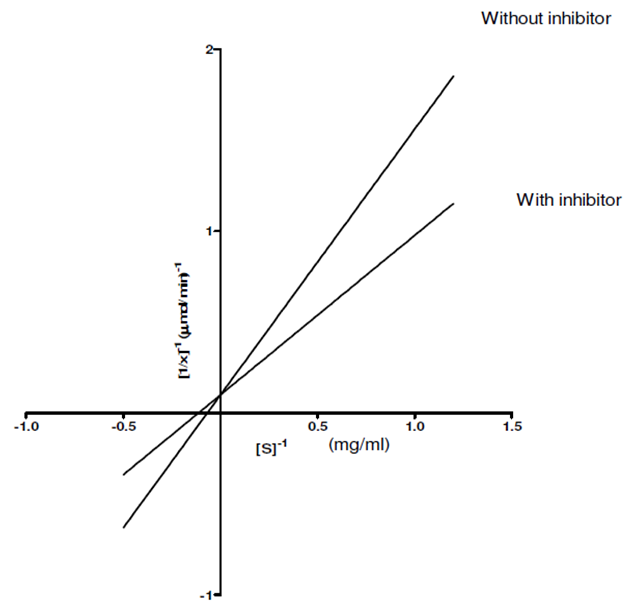
- This was carried out by adding 0.1mL of the crude enzyme extract and 0.1mL of 3.5% v/v volatile oil (inhibitor) in 0.5% v/v tween 80 solution to different concentrations of casein ranging from 0.2-1.0% w/v solutions in Tris- buffer (0.05M, pH 8.0). Enzyme activity was determined in the absence of inhibitor at 37℃ incubation for 10 minutes. The procedure was then repeated in the absence of the volatile oil to serve as the enzyme reaction in the absence of the inhibitor.
2.11. Dialysis
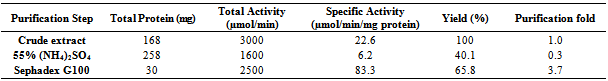
- 0.55g of Ammonium sulphate was added to 1ml of the crude enzyme extract in a dialysis bag submerged for 48 hours in a tris-buffer. The solution was then centrifuged at 9000 rpm for 10 minutes. The pellet was collected and assayed for total protein and enzyme activity. 0.5g of ammonium sulphate was further added to the pellet, dissolved in 1ml of tris-buffer and dialyzed for another 48 hours. The resultant was centrifuged and the enzyme activity and total protein of the supernatant (supernatant-1) and pellet was determined.
2.12. Gel-Filtration
- 3g of Sephadex G- 100 was soaked for 72 hours in water. It was poured gently into columns and packed to a length of about 20cm. A small amount of sodium azide was added to the column to prevent contamination. The resulting flow rate was about 3ml/Hour. The packed gel was equilibrated with the elution buffer. A buffer reservoir was connected to the top of the column and adjusted to a convenient hydrostatic pressure that measured up with the flow rate. 1ml of supernatant-1 in the dialysis step was added to the gel and was allowed to run through the column. 50 elution samples were collected and in each, protein and enzyme activity were assayed.
3. Results
- 300g of dried E.uniflora leaves produced approximately 2.0 ml of the volatile oil. The antimicrobial activity of this volatile oil was evaluated by examining its effects against a partially purified ECP from Klebsiella oxytoca. The MIC and MBC of the volatile oil against K.oxytoca were ≤0.8% and ≥0.95% v/v respectively.Figures 1 and 2 depict the effects of pH and temperature on the activity of K.oxytoca ECP. Optimum protease activity was observed at pH 6.5 and 40℃. The effects of various metallic salts on the activity of the protease were also determined (figure 3). Highest enzyme activity was observed in the presence of potassium chloride (1.406 µmol/min) while the lowest activities were observed in the presence of zinc and mercury salts (1.384 µmol/min and 1.36 µmol/min respectively). Kinetics of the ECP is shown in figure 4. There was an increase in KM from 0.685mg/ml to 1.140mg/ml in the presence of the volatile oil respectively. This suggests that the mode of inhibition of the volatile oil on K.oxytoca ECP is competitive.K.oxytoca extracellular protease was partially purified using dialysis and gel size exclusion chromatography. As shown in table 1 and figure 5, a purification fold of 3.7 and enzyme activity of 83.3 compared with the crude enzyme extract was observed.
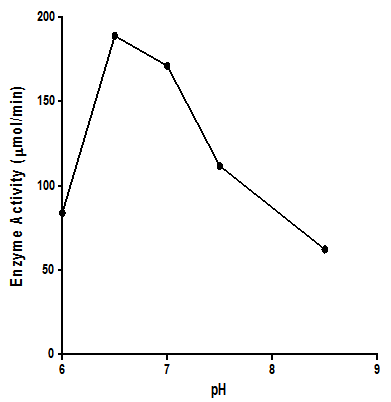 | Figure 1. Effects of pH on activity of K.oxytoca ECP. Enzyme activity was maximal at a mildly acidic pH |
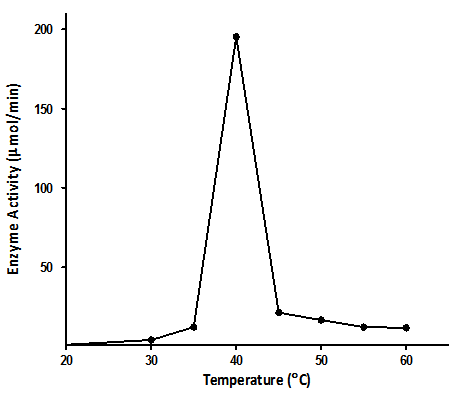 | Figure 2. Effects of temperature on K.oxytoca extracellular protease. Enzyme activity was found to be maximal at 40℃ |
|
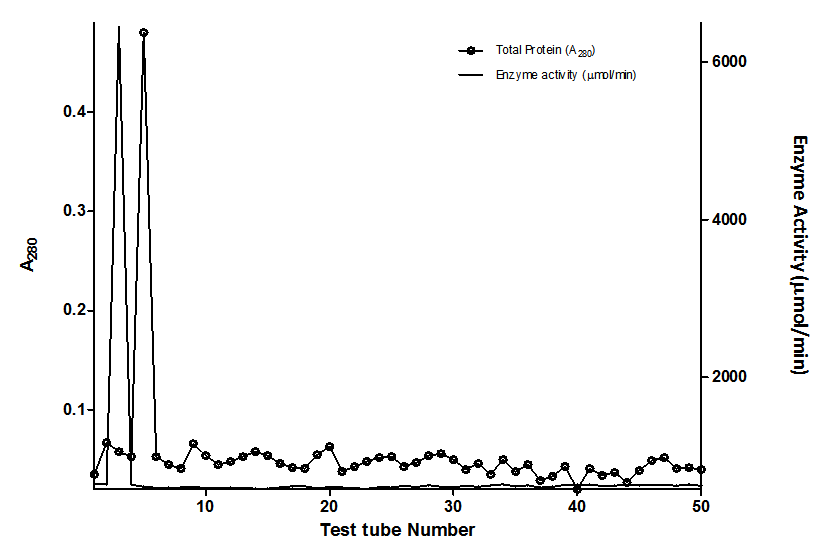 | Figure 5. Elution profile of Sephadex-G100 purification of the Extracellular protease of Klebsiella oxytoca |
4. Discussion
- The antimicrobial effects of volatile oils on a myriad of microorganisms which are pathogenic to humans have been investigated in various studies. In this study, the effects of the volatile oil extracted from Eugenia uniflora on the extracellular protease of Klebsiella oxytoca were determined. The MIC of the volatile oil of E.uniflora against. Oxytoca was ≤0.8%v/v and the MBC was ≥0.95%v/v. These values suggest that the bacterium is relatively sensitive to very low concentrations of the volatile oil. K.oxytoca ECP was observed to have an optimum activity of 188.9µmol/min at a pH of 6.5 suggesting that the microorganism thrives in a mildly acidic environment. The organism is usually found in the colon whose pH varies between 5.5-7 and thus, the extracellular protease may be regarded as a virulence factor for pathogenicity[19]. In addition, the enzyme exhibited optimum activity of 195.5µmol/min at 40℃. This might explain the relative thermostability of enteric pathogens. Similar results were observed in the study by Tondo et al.[20] in which optimal activity was observed at pH 5-7 and 37℃.Earlier reports have shown that metallic compounds such as copper and mercury can be used as inhibitors against pathogenic microorganisms[21]. In this study, Zinc and mercuric chlorides resulted in diminished enzyme activity when compared with other metallic salts. This might explain the susceptibility of the microorganism to these metals and thus substantiate the role of the extracellular protease in the virulence.Lineweaver Burke analysis was used to assess the type of inhibition elicited by the extracellular protease by the volatile oil. The oil exhibited a competitive mode of inhibition against the activity of the extracellular protease of K.oxytoca with Km increasing from 0.65 mg/ml to 1.40 mg/ml in the presence of the volatile oil. This mode of inhibition shows that the active components of the volatile oil reduced catalytic activity of the extracellular protease by occupying the substrate binding site.Purification with sephadex G-100 size exclusion chromatography revealed a purification fold of 3.7 from the initial culture (crude) with a percentage yield of 65.8%. The specific activity of the G-100 purified enzyme was 83.3 µmol/min/mg protein while the elution chromatogram revealed one peak each for total enzyme activity and total protein.
5. Conclusions
- The findings from this study suggest that the extracellular protease is a virulence factor and the volatile oil of E.uniflora is a potent therapeutic agent. It is however pertinent to subject the ECP to further purification and characterization. Further investigation into the active components of the volatile oil is required, using more sophisticated techniques; it would be possible to identify the agent responsible for enzyme inhibition.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML