-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Biochemistry
p-ISSN: 2163-3010 e-ISSN: 2163-3029
2012; 2(3): 29-35
doi: 10.5923/j.ajb.20120203.03
Activity Inhibition of Sulfate Reducing Bacteria Using Some Cationic Thiol Surfactants and Their Nanostructures
Azzam E. M. S. 1, Sami R. M. 1, Kandile N. G. 2
1Applied Surfactants Laboratory, Petrochemicals Department, Egyptian petroleum research institute, Nasr City, Cairo, 11727, Egypt
2Chemistry Department, Faculty of Girls, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt
Correspondence to: Azzam E. M. S. , Applied Surfactants Laboratory, Petrochemicals Department, Egyptian petroleum research institute, Nasr City, Cairo, 11727, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
In the present work the application of some the synthesized cationic thiol surfactants and their nanostructures as potential biocides for the Sulfate Reducing Bacteria (SRB) was investigated. The nanostructures of the synthesized surfactants as nanopowders and with silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) were prepared and characterized using Transmission electron microscope (TEM). The antimicrobial activity of the synthesized surfactants and their nanostructures was measured against sulfate reducing bacteria (SRB) by the inhibition zone method. If the bacteria are susceptible to a particular antibiotic, an area of clearing surrounds the wafer where bacteria are not capable of growing (called a zone of inhibition). This along with the rate of antibiotic diffusion is used to estimate the bacteria's sensitivity to that particular antibiotic. In general, larger zones correlate with smaller minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antibiotic for those bacteria. This information can be used to choose appropriate antibiotics to combat a particular infection. The antibacterial results showed the improvement in the antibacterial activity of the synthesized surfactants using their nanostructures as nanopowder forms and with the AgNPs.
Keywords: Cationic Thiol Surfactants, Nanostructure, Antimicrobial Activity, Sulfate Reducing Bacteria (SRB)
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Sulfate reducing bacteria (SRB) comprise several groups of bacteria that use sulfate as an oxidizing agent, reducing it to sulfide. SRB have been implicated in the corrosion of cast iron and steel, ferrite stainless steels, 300 series stainless steels (also very highly alloyed stainless steels), copper nickel alloys, and high nickel molybdenum alloys. They are almost always present at corrosion sites because they are in soils, surface water streams and waterside deposits in general. Their mere presence, however, does not mean they are causing corrosion. The key symptom that usually indicates their involvement in the corrosion process of ferrous alloys is localized corrosion filled with black sulfide corrosion products. The sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) form a specialized group of microbes that use sulfate as terminal electron acceptor for their respiration and generate H2S as terminal product. The ubiquity of these bacteria leads to a variety of impressive industrial, economic and ecological effects because of their proneness to generate large quantities of H2S. Many corrosions of industrial equipment have been ascribed to microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC)[1, 2]. SRB are the main reason to cause the MIC by accelerating corrosion rate, inducing stress corrosion and pitting corrosion[3-5]. Previous studies show that the living of SRB accelerate corrosion rate and induce stress corrosion and pitting corrosion of metals[4, 5, 6] , and put influences on the environment parameters[7], which are possible factors inducing the metal corrosion. No report studies the relativities among SRB, seawater condition and corrosion behavior of metals, but the understanding of relativities among them might be helpful on getting a better insight of the corrosion mechanism induced by SRB. A wide variety of bacteria have been isolated or detected in these environments by molecular techniques, but because of their detrimental effects, sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) have been the most commonly studied group. The SRB presence in oil environments was rapidly recognized as responsible for the production of hydrogen sulfide, which is a toxic and corrosive gas responsible for a variety of environmental and economic problems including reservoir souring, contamination of natural gas and oil, corrosion of metal surfaces, and the plugging of reservoirs due to the precipitation of metal sulfides and the consequent reduction in oil recovery[8, 9]. The SRB are most probably a subject of preoccupation in the oil industry not only because of sulfide production, but also due to their ability, for some of them, to (i) oxidize hydrogen, (ii) use O2 and Fe3+[10], (iii) their capacity for aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons utilization[11], (iv) their capacity to connect sulfate reduction to the magnetite intracellular production[12] and (v) their aptitude to compete with nitrate-reducing/sulfur-oxidizing bacteria (NRB–SOB) since they may have a nitrite reducing activity[13]. Cationic surfactants have applicability as biocides against bacteria[14], fungi and yeast[15]. Studies of the cationic surfactants as biocides showed a strong relationship between their surface and biological activity. Increasing the surface activity was accompanied in several studies by a strong biocidal activity, and vice versa. That was referred to action mode of these compounds as biocides towards the different microorganisms. Several works described the action mode of the cationic surfactants as biocides[16]. Several applications utilizing silver nanoparticles as an antimicrobial agent have been in use for a number of years. There is also continuing research being performed towards the improvement of current applications as well as the development of new nano-silver-containing products. This section briefly mentions a wide variety of silver nanoparticle applications in both the medical and consumer products industries. Selected research case studies are then discussed in detail, followed by a discussion of potential future applications. It has been known that silver ions exhibit strong inhibitory effects towards a broad spectrum of bacterial strains. Studies have also demonstrated antiviral activities towards human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) by various metal nanoparticles[17]. However, the exact mechanism by which silver inhibits microbial growth is not entirely understood. Several investigations have suggested possible mechanisms involving the interaction of silver ions. Generally, it is believed that heavy metals release with biological macromolecules. Ions which react with the thiol groups (-SH) of surface proteins. Such proteins protrude through the bacterial cell membrane, allowing the transport of nutrients through the cell wall were the first to discover the accumulation of granules on the membrane surface[18]. The reaction of mono valent silver with sulfhydryl groups produces a much more stable –S-Ag group only on the bacterial cell surface. In our previous publication[19], we investigated the improvement in the surface activity of the synthesized cationic thiol surfactants using their nanostructures as nanopowder forms and with silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs). Here in we investigate the application of the synthesized surfactants and their nanostructures as potential biocides for the Sulfate Reducing Bacteria (SRB).
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Synthesis of the cationic thiol surfactants (C10, C12 and C16)
- A mixture of 2-mercapto pyridine and decyl, dodecyl, cetyl Bromide respectively at molar ratio 1:1 were dissolved 50 ml acetone and added in 100 ml conical flask. The reaction mixture was refluxed and stirred for 5 hr. The reaction mixture was concentrated to evaporate acetone. The obtained precipitate was crystallized using benzene and petroleum ether 60-80 %., to give yellow crystals of 2-Mercapto-N-decylpyridinium Bromide (C10) (M .P = 910C), 2-Mercapto-N-dodecylpyridinium Bromide (C12) (M .P = 970C) and2-Mercapto-N-cetylpyridinium Bromide (C16) (M .P = 94 0C) surfactants respectively. The chemical structure of the cationic thiol surfactants as shown in scheme 1 was confirmed via the FTIR and 1HNMR spectra[19].
2.1.2. Preparation of the colloidal silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) solution
- In typical experiment 50 ml of 1x10-3 M AgNO3 was heated to boiling. To this solution 5 ml of 1 % trisodium citrate was added drop by drop. During the process solution was mixed vigorously. Solution was heated until color’s change is evident (pale yellow). Then it was removed from the heating element and stirred until cooled to room temperature [19].
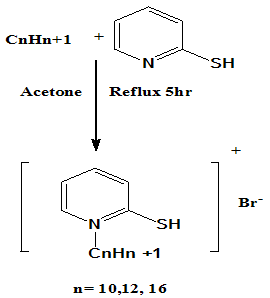 | Scheme 1. The chemical structure of the synthesized cationic thiol surfactants (Azzam et al 2011)[19] |
2.1.3. Preparation of the cationic thiol surfactants-coated silver nanoparticles
- A 20 mL volume of citrate-capped silver nanoparticles solution was mixed with 5 mL saturated surfactant solution in deionized water and stirred effectively. Stirring was continued for 24 h until the yellow faded[19].
2.2. Preparation of Nanopowder Forms for the Synthesized Cationic Thiol Surfactants
- The nanopowder forms of the synthesized cationic thiol surfactants were prepared using RETSCH Planetary Ball Mills Type PM 400. The surfactant sample was milled using the Ball mill at speed 150 rpm for 6-8 h[19].
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Ball milling technique
- The nanopowder forms of the synthesized cationic thiol surfactants were prepared using RETSCH Planetary Ball Mills Type PM 400.At[19]. Transmission electron microscope (TEM) measurementsA convenient way to produce good TEM samples is to use copper grids. A copper grid pre-covered with a very thin amorphous carbon film. To investigate the prepared colloidal AgNPs, the coating of the synthesized thiol surfactants with the AgNPs and the nanopowder forms of these surfactants using TEM, a small droplet of the liquid was placed on the carbon-coated grid. A photographic plate of the transmission electron microscopy (Type JEOL JEM-1230 operating at 120 kV attached to a CCD camera) employed on the present work to investigate the nanostructure of the prepared samples[19].
2.3.2. Antimicrobial Activity
- The antimicrobial activity of aqueous solution of the synthesized surfactants and their nanostructures as nanopowders and with the prepared AgNPs was measured against sulfate reducing bacteria (SRB) by the inhibition zone method, Kirby-Baure disc diffusion method[20 Bauer et al 1966]. Standard discs of tetracycline (antibacterial agent) served as positive controls for antibacterial activity but filter disc impregnated with 10 Ul of solvent (distilled water, chloroform, DMSO) were used as negative control. The mean value obtained for three individual replicates was used to calculate the zone of growth inhibition of each sample.
3. Results
3.1. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) of the Nanopowder Forms of the Synthesized Surfactants
- The size and morphology of the nanopowder forms for the synthesized surfactants were investigated using TEM (transmission electron microscope). The TEM images of the nanostructures of the prepared surfactants (C10, C12, and C16) as nanopowder forms are represented in Figures. 1-3.
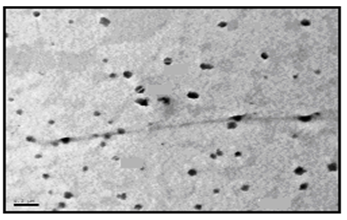 | Figure 1. TEM image of C10 nanopowder (Azzam etal 2011)[19] |
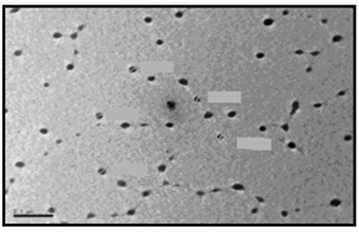 | Figure 2. TEM image of C12 nanopowder (Azzam etal 2011)[19] |
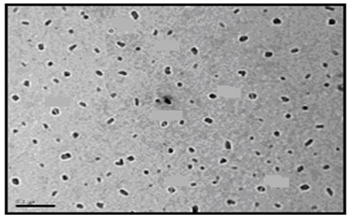 | Figure 3. TEM image of C16 nanopowder (Azzam etal 2011)[19] |
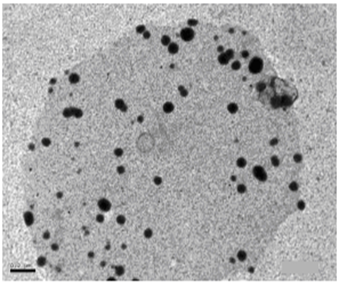 | Figure 4. TEM image of AgNPs (Azzam etal 2011)[19] |
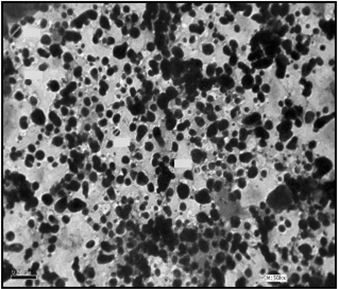 | Figure 5. TEM image of C10 coated AgNPs (Azzam etal 2011)[19] |
 | Figure 6. TEM image of C12 coated AgNPs (Azzam etal 2011)[19] |
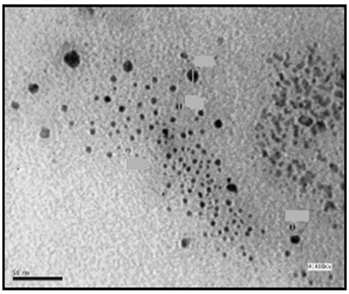 | Figure 7. TEM image of C16 coated AgNPs (Azzam etal 2011)[19] |
3.2. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) of the Synthesized Surfactants Assembled on Silver Nanoparticles
- The self assembling of the synthesized surfactants (C10, C12 and C16) on the prepared silver nanoparticles was also studied using the TEM technique as shown in Figures. 5-7. The size and morphology of silver nanoparticles were investigated by the TEM image in Figure. 4.
3.3. Antibacterial Activity
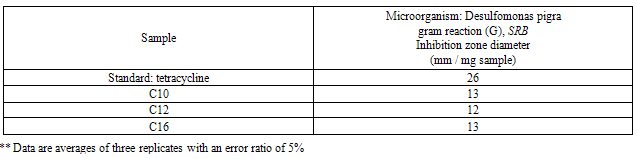
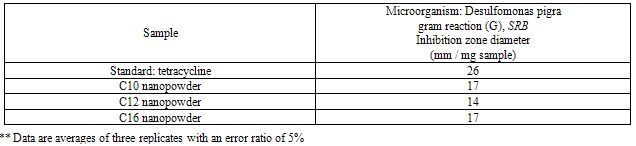
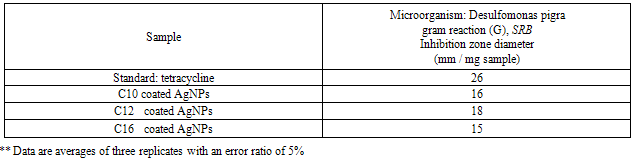
- The results of the antibacterial activity for the synthesized surfactants and their nanostructures as (nanopowder forms and with the silver nanoparticles) against the sulfate reducing bacteria (SRB) are listed in Tables 2-4.
|
|
|
4. Discussion
- The TEM images revealed that the nanopowder forms of these surfactants are appear as very small particles with different sizes. The sizes of these particles are different according to the different in alkyl chain length of the synthesized surfactants and the small particles size (15-41 nm) was found with the 2- mercapto-N-cetyl pyridinium bromide (C16) as shown in Figure 3[19]. The TEM image in Figure 4 indicates that the silver particles are spherical shape and polycrystalline structure. Figures 5-7 show the nanoshells formed between the spherical silver nanoparticles and the surfactant molecules, which related to the self- assembling of the surfactant molecules on the silver nanoparticles. The TEM images further revealed the stabilization of the silver nanoparticles due to the interaction of these nanoparticles with the surfactant molecules. It was noticed from the TEM images in Figures 5-7 the effect of the alkyl chain of the synthesized surfactants on the stabilization of the AgNPs, as the alkyl chain increase from C10 to C16 the aggregation of the AgNPs decrease and cause more stabilization of these particles as shown from the average size of the particles in Table 1. The adsorption of surfactant-like molecules to nucleated nanocrystals lowers the free energy of the surface and, therefore, the reactivity of the particles. The ratio of surfactant to metal precursor can control the size distribution of the nanoparticles. The mechanism by which this ratio controls the nucleation events and limits the growth of the particles is understood in general qualitative terms. The steric bulk of the surfactants due to the presence of the alkyl chain in the hydrophobic part provide a physical barrier that prevents the metal surfaces from contacting each other directly. They can also change the surface charge of a cluster and thus change its stability toward aggregation. The combination of the energetic stabilization of the metal surface by the surfactant, the consequences of charge-charge interactions, and the steric repulsion between particles prevents the system from forming aggregates[19]. The data in Table 2 represented the inhibition zone diameter of the SRB sample against the synthesized surfactants (C10, C12 and C16) samples. The data in Table 1 show that the inhibition zone diameter of the SRB increase as the alkyl chain length in the hydrophobic moiety of the synthesized surfactants increase from C12 to C16 (from 12 to 13 mm / mg) surfactant. The difference in activity depends on the length of hydrophobic chains and the interfacial properties of the synthesized surfactants. Increasing the hydrophobic chain length increase the antibacterial activity[21]. In addition, the biological activity of the synthesized surfactants is also related to the presence of quaternary group as a hydrophilic moiety in the pyridinium ring of the synthesized surfactants which influence the adsorption of the synthesized surfactants on the surface of the bacteria and act by disrupting the cell membrane. The results in Table 3 show the antibacterial activity of the nanopowder forms of the synthesized surfactants. The antibacterial activity of the nanopowder forms (17, 14 and 17 mm / mg) is higher than that of the individual surfactants (13, 12, 13 mm / mg) as shown from Tables 2-3. This is may be related to that the nanopowder forms have a very small particle size which improve the permeability of this nanopowder forms of the synthesized surfactants through the cell membrane and influence the inhibition of the bacteria more than with the individual surfactants. The antibacterial activity of the nanostructures of the synthesized surfactants with the prepared AgNPs is shown in Table 4. It is clear form the data in Table 3 that the nanostructures of the synthesized surfactants have higher inhibition zone diameter values (16, 18 and 15 mm / mg) than that of the individual surfactants (13, 12, 13 mm / mg) in Table 2. This is due the presence of the silver nanoparticles which react with the sulfhydryl or thiol (SH) groups on the protein surface and form stable S-Ag group by replace the hydrogen cation of sulfhydryl or thiol groups inactivating the protein decreasing membrane permeability and eventually causing cellular death. The results in Tables 2-4 indicate that the nanostructure of the synthesized surfactant 2- mercapto-N-dodecyl pyridinium (C12) with AgNPs has the higher antibacterial the activity. It can be conclude form Tables 2-4 that the antibacterial activity of the synthesized surfactants against the SRB bacteria was improved using the nanostructures as nanopowder forms and with the AgNPs.
5. Conclusions
- From the obtained results we can conclude the following points:The synthesized cationic thiol surfactants have antibacterial activity against the sulfate reducing bacteria (SRB) with clear effect of the alkyl chain on this activity.The nanopowder forms of the synthesized cationic thiol surfactants under investigation have more antibacterial activity against the (SRB) than the individual surfactants.The presence of silver nanoparticles improved the antibacterial activity of the synthesized cationic thiol surfactants against the SRB.
References
| [1] | A. , ‘’Sulphate-Reducing Bacteria and Anaerobic Corrosion’’, Annu. Rev. Microbiol. vol. 39, pp 195-217, 1985 |
| [2] | Washington A. Hamilton, ‘’Bioenergetics ofsulphate-reducing bacteria in relation to their environmental impact. Biodegradation’’, vol. 9, pp 201-212, 1998. |
| [3] | Michel Magot, Gilles Ravot, Xavier Campaignolle, Brenard Ollivier,, Bharat K. C. Patel , Michel L. Fardeau, Philip Thomas, Jean-Louis Crolet, Jean-Louis Garcia,Dethiosulfovibrio peptidovorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a new anaerobic, slightly halophilic, thiosulfate-reducing bacterium from corroding offshore oil wells. Int J. Syst Bacterio, vol. 47, pp 818–824, 1997b. |
| [4] | Sadegh Sh. Abedi, Ail .Abdolmaleki, N. Adibi, Failure analysis of SCC and SRB induced cracking of a transmission oil products pipeline. Engineering Failure Analysis, vol. 14, pp 250-261, 2007. |
| [5] | Reza Javaherdashti, Singh R.K. Raman, Chris. Panter, Elena V. Pereloma, Microbiologically assisted stress corrosion cracking of carbon steel in mixed and pure cultures of sulfate reducing bacteria. Biodegrad., vol. 58:, pp 27-35, 2006. |
| [6] | Jean-Louis Crolet, Michel Magot, Non-SRB sulfidogenic bacteria in oilfield production facilities. Mater. Perform vol. 3, pp 60-64, 1996. |
| [7] | Benedetto, J.S.; Almeida, S.K.; Gomes, H.A.; Vazoller, R.F.; (2005), Monitoring of sulfate-reducing bacteria in acid water from uranium mines. Miner. 18: 1341-1343. |
| [8] | Michel Magot, Brenard Ollivier, Bharat K. C. Patel, Microbiology of petroleum reservoirs. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, vol. 77, pp 103–116, 2000. |
| [9] | I. Davidova, M.S. Hicks, phillip M. Fedorak, J.M.. Suflita, The influence of microbial processes occurring in oil industry production waters. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. vol. 27, pp 80-86, 2001. |
| [10] | Hang T. Dinh, Jan Kuever, Marc Mu mann, Achim W. Hassel, Martin Stratmann, Friedrich Widdel, Iron corrosion by novel anaerobic microorganisms. Nature, vol. 427, pp 829-832, 2004. mann, Achim W. Hassel, Martin Stratmann, Friedrich Widdel, Iron corrosion by novel anaerobic microorganisms. Nature, vol. 427, pp 829-832, 2004. |
| [11] | Petra Rueter, Ralf Rabus, Heinz Wilkest, Frank Aeckersberg, Freda Rainey, Holger W. Jannasch, Friedrich Widdel, Anaerobic oxidation of hydrocarbons in crude oil by new types of sulphate-reducing bacteria. Nature, vol. 372, pp 455-458, 1994. |
| [12] | Toshifumi Sakaguchi, Atsushi Arakaki, Tadashi Matsunaga , Desulfovibrio magneticus sp. nov., a novel sulfate-reducing bacterium that produces intracellular single-domain-sized magnetite particles. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. vol. 52, pp 215-221, 2002. |
| [13] | E. A. Greene,. C. Hubert, M. Nemati, G.E., Jenneman, G. Voordouw, Nitrite reductase activity of sulphate-reducing bacteria prevents their inhibition by nitrate-reducing, sulphide-oxidizing bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. vol 5, pp 607-617, 2003. |
| [14] | Nabile A. Negm, Moshira F. Zaki, Mohamed A. I. Salem, Cationic Schiff base amphiphiles and their metal complexes: surface and biocidal activities against bacteria and fungi. Colloids Surf B. vol. 77, pp 96–103, 2010. |
| [15] | Nabile A. Negm, Souad A. Mohamed, Synthesis,characterization and biological activity of sugar-based Gemini cationic amphiphiles. J. Surf Deterg. 11, pp 215–221, 2008. |
| [16] | Nabile A. Negm, Salwa M. Morsy, S. M., Mohamed M, Said, Biocidal activity of some mannich base cationic derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. vol 13, pp 5921–5926, 2005. |
| [17] | J. Q. Cheng, S. W. YAO, Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles by sonoelectrode-position, Rare Metals. vol. 24, pp 376-378, 2005. |
| [18] | L Nover, K. D. Scharf, D. Neumann, Formation of cytoplasmic heat shock granules in tomato cell cultures and leaves. Mol Cell Biol. vol 13, pp 1648–1655, 1983. |
| [19] | Eid M. S. Azzam, Nadia G. Kandile,, Abd elfatah M. Badawi, Radwa M. Sami, Influence in the Surface Activity for Some Cationic Thiol Surfactants Using Their Nanostructures, J. Disp. Sci. and Tech. vol. 32, pp 1325-1331, 2011. |
| [20] | A. W. Bauer, W. M. Kirby, J. C. Sherris, M. Turck, Am. J. Clin. Pathol. vol. 45, pp 493-496, 1966. |
| [21] | Milton J. Rosen, F. Li, Stephen W. Morrall, D. J. Versteeg, Environ. Sci. Technol. vol. 35, 954-959, 2001. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML